Infographics
Social Issues
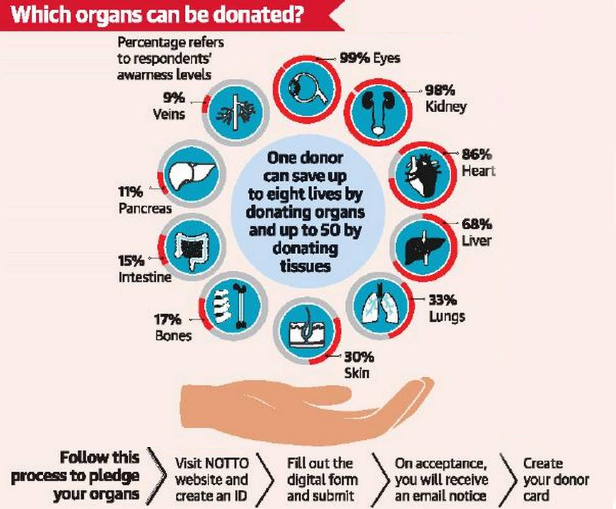
Organ Donation in India
For Prelims: Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994, National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, Organ Donation
For Mains: Need for Promoting Organ Donations
Why in News?
Recently, the critical shortage of organ donations, particularly deceased donations, has led to a dire situation in India, with thousands of patients waiting for transplants and a significant number losing their lives daily.
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has earlier modified National Organ Transplantation Guidelines, allowing those above 65 years of age to receive an organ for transplantation from deceased donors.
- In India, the Transplantation of Human Organs Act, 1994 provides various regulations for the removal of human organs and their storage. It also regulates the transplantation of human organs for therapeutic purposes and for the prevention of commercial dealings in human organs.
What is the Status of Organ Donation in India?
- Growing Demand and Persistent Shortage:
- Over 300,000 patients are on the waiting list for organ donations in India.
- The supply of organ donors has not kept up with the increasing demand.
- Approximately 20 individuals die daily while awaiting organ transplants due to the shortage.
- Slow Growth in Donor Numbers:
- Donor numbers, including both living and deceased, have shown slow growth over the years.
- From 6,916 donors in 2014, the count increased to about 16,041 in 2022, indicating a modest rise.
- The deceased organ donation rate in India has remained consistently below one donor per million population for a decade.
- Deceased Organ Donation Rate:
- Urgent efforts are required to raise the deceased organ donation rate to address the shortage.
- Countries like Spain and the United States have achieved significantly higher donation rates, ranging from 30 to 50 donors per million population.
- Prevalence of Living Donors:
- Living donors constitute the majority, accounting for 85% of all donors in India.
- However, deceased organ donations, especially for kidneys, liver, and heart, remain considerably low.
- Living donors constitute the majority, accounting for 85% of all donors in India.
- Regional Disparities:
- Disparities in organ donation rates exist among different states in India.
- Telangana, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Gujarat, and Maharashtra have reported the highest number of deceased organ donors.
- Delhi-NCR, Tamil Nadu, Kerala, Maharashtra, and West Bengal are prominent regions with a high number of living donors.
- Disparities in organ donation rates exist among different states in India.
- Kidney Transplants:
- Kidney transplantation in India faces a significant disparity between demand and supply.
- Annual demand for 200,000 kidney transplants is met with only around 10,000 transplants each year, creating a substantial gap.
What are the Challenges Regarding Organ Donation?
- Lack of Awareness and Education:
- Limited awareness among the general public about organ donation and its impact.
- Insufficient education among medical professionals to identify potential donors and counsel families effectively.
- Family Consent and Decision-Making:
- Family reluctance to give consent for organ donation, even when the deceased individual had expressed a willingness to donate.
- Emotional and ethical dilemmas that families face when making decisions about organ donation.
- Organ Trafficking and Black Market:
- Illegal organ trafficking and the existence of a black market for organs.
- Criminal activities exploiting the demand for organs and undermining legitimate donation processes.
- Medical Eligibility and Compatibility:
- Matching suitable donors and recipients based on medical compatibility and organ availability.
- Limited availability of compatible organs, leading to prolonged waiting periods for patients.
- Donor Incentives and Compensation:
- Debates over the ethical implications of offering financial incentives or compensation to organ donors.
- Balancing the need for increasing donation rates with ensuring ethical practices.
- Infrastructure and Logistics:
- Inadequate infrastructure and resources for organ retrieval, preservation, and transplantation.
- Challenges in the timely transportation of organs from donors to recipients, especially across different regions.
What are the Highlights of the New National Organ Transplantation Guidelines?
- Removed Age Cap:
- Age limit for organ recipients eliminated due to improved life expectancy.
- NOTTO (National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organization) guidelines previously prohibited end-stage organ failure patients above 65 years from registering for organ transplants.
- No Domicile Requirement:
- Domicile requirement waived for organ recipient registration.
- 'One Nation, One Policy' approach allows patients to register for organ transplants in any state.
- No Registration Fees:
- Removal of registration fees for organ recipient registration.
- States, including Gujarat, Telangana, Maharashtra, and Kerala, no longer charge fees for patient registration.
Note:
- NOTTO is set up under the Directorate General of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, located in New Delhi.
- National Network division of NOTTO functions as the apex centre for all Indian activities for procurement, distribution and registry of organs and tissues donation and transplantation in the country.
Way Forward
- Partner with artists, influencers, and celebrities to create impactful campaigns highlighting organ donation's significance.
- Organize seminars for medical professionals, employing interactive simulations and case studies for donor identification and family counseling.
- Collaborate with educational institutions to raise awareness among students about organ donation through workshops and talks.
- Host community-driven events that showcase the success stories of organ recipients and donors.
- Engage religious leaders to debunk myths and misconceptions about organ donation, emphasizing its compassionate aspect.
- Introduce a program to honour donors and their families, recognizing their selfless contribution through plaques and certificates.
- Foster collaborations between healthcare institutions to optimize organ transplantation processes for efficient outcomes.
- Promote the idea of organ donation as a selfless act of compassion and empathy.
Biodiversity & Environment
Co-Firing Biomass Pellets in Thermal Power Plants
For Prelims: Biomass Co-firing, Revised Biomass Policy, Thermal Power Plants, Central Pollution Control Board, Priority Sector Lending , Government e-Marketplace, Renewable energy.
For Mains: Advantages of Biomass Co-firing, India’s Net Zero Emission Target
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Power and New & Renewable Energy provided valuable insights into the Revised Biomass Policy and 47 Thermal Power Plants that have successfully incorporated the co-firing of coal with biomass pellets derived from agro residues during a written reply in the Rajya Sabha.
- According to Ministry of Power, approximately 1,64,976 Metric Tonnes of agri residues-based biomass has been co-fired in 47 coal based thermal power plants till May 2023
What is the Revised Biomass Policy?
- About:
- The Ministry of Power and Ministry of New & Renewable Energy (MNRE) have taken significant steps towards integrating agro residue-based biomass pellets into the operations of Thermal Power Plants (TPPs).
- This marks a crucial step towards transitioning the energy sector to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly direction.
- Revised Policy:
- On June 16, 2023, the Ministry of Power issued a modification to the biomass policy dated October 8, 2021.
- The revised policy mandates a 5% biomass co-firing in Thermal Power Plants (TPPs) starting from the fiscal year 2024-25.
- The biomass co-firing obligation will further increase to 7% from the fiscal year 2025-26.
- On June 16, 2023, the Ministry of Power issued a modification to the biomass policy dated October 8, 2021.
What are the Government Interventions Related to Biomass Co-firing?
- Financial Assistance:
- The MNRE and Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) have introduced Finance Assistance Schemes to support biomass pellet manufacturing units.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) has approved 'Biomass pellet manufacturing' as an eligible activity under Priority Sector Lending (PSL), fostering financial viability for such endeavors.
- Procurement and Supply Chain:
- A dedicated Procurement Provision of Biomass Category has been established on the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) portal.
- Ministry of Power has introduced a Revised Model Long-Term Contract for Biomass Supply, ensuring a consistent supply chain.
- The provision of Udyam Aadhaar on the National Single Window System streamlines administrative processes for biomass-related projects.
- The Udyam Aadhaar registration process is based on the concept of self-declaration, enabling MSMEs to register themselves for free and obtain the Udyam Aadhaar number.
What is Biomass Co-Firing?
- About:
- Biomass co-firing is a process in which biomass-based fuels are combusted together with traditional fossil fuels (such as coal, oil, or natural gas) in the same power plant or industrial boiler to generate energy.
- Advantages of Co-firing Coal with Biomass Pellets:
- Carbon Emission Reduction: The concept behind biomass co-firing is to reduce the environmental impact of energy generation by substituting a portion of the fossil fuel with biomass, which is considered carbon-neutral over its lifecycle.
- Substituting 5-7 % of coal with biomass in coal-based power plants can save 38 million tonnes of carbon dioxide emissions.
- Renewable Energy Integration: Co-firing helps in integrating renewable energy sources (biomass) with conventional energy sources (coal), aiding in the transition to a cleaner energy mix.
- Economic and Regulatory Benefits: Co-firing can help power plants meet environmental regulations and carbon reduction targets without requiring significant infrastructure changes.
- Utilization of Biomass Waste: Co-firing provides a valuable use for agricultural and forestry residues that might otherwise go to waste.
- Carbon Emission Reduction: The concept behind biomass co-firing is to reduce the environmental impact of energy generation by substituting a portion of the fossil fuel with biomass, which is considered carbon-neutral over its lifecycle.
- Agro Residues for Biomass Pellet Production: The Ministry of Power has identified various surplus agro residues that can be utilized for biomass pellet production. These include:
- Crop Residues:
- Agro-residues from crops such as Paddy, Soya, Arhar, Gwar, Cotton, Gram, Jawar, Bajra, Moong, Mustard, Sesame, Til, Maize, Sunflower, Jute, Coffee, etc.
- Shell Waste:
- Waste products like Groundnut Shell, Coconut Shell, Castor Seed Shell, etc.
- Additional Biomass Sources:
- Bamboo and its by-products, horticulture waste, and other biomass materials like Pine Cone/Needle, Elephant Grass, Sarkanda, etc.
- Crop Residues:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following: (2019)
- Carbon monoxide
- Methane
- Ozone
- Sulphur dioxide
Which of the above are released into atmosphere due to the burning of crop/biomass residue?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (d)
Internal Security
Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill 2023
For Prelims: Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill - 2023, Andaman and Nicobar Command, Commands of Indian Army, Navy, Air Force.
For Mains: Salient Features of Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill - 2023
Why in News?
Lok Sabha recently passed the Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill - 2023 with the aim to bolster the efficiency, discipline, and jointness among the Armed Forces.
What is the Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control & Discipline) Bill 2023?
- Background: :
- Currently, the Armed Forces operate under distinct Service Acts – the Army Act 1950, Navy Act 1957, and Air Force Act 1950.
- However, the diverse nature of these acts has sometimes posed challenges in maintaining uniform discipline, coordination, and expeditious proceedings across the inter-services establishments.
- The Inter-Services Organisation (Command, Control, & Discipline) Bill - 2023, addresses these concerns with its forward-looking provisions.
- ISO Bill 2023 does not propose any alteration to the existing Service Acts, Rules, or Regulations that have stood the test of time and judicial scrutiny over several decades.
- Currently, the Armed Forces operate under distinct Service Acts – the Army Act 1950, Navy Act 1957, and Air Force Act 1950.
- Salient Features:
- Applicability: The bill is applicable to all regular Army, Navy, and Air Force personnel.
- Also, the central government holds the right to designate any force established and maintained within India to which the provisions of the bill will apply.
- Inter-services Organisation: Existing Inter-services Organisations will be deemed to have been constituted under the Bill. These include the Andaman and Nicobar Command, the Defence Space Agency, and the National Defence Academy.
- The central government may constitute an Inter-services Organisation which has personnel belonging to at least two of the three services: the army, the navy, and the air force.
- Applicability: The bill is applicable to all regular Army, Navy, and Air Force personnel.
Note:
- Joint command in Andaman and Nicobar Islands is the first Tri-Service theatre command of the Indian Armed Forces, based at Port Blair in Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India.
- The Indian armed forces currently have 17 commands. There are 7 commands each of the Army and the Air Force. The Navy has 3 commands.
- Each command is headed by a 4-star rank military officer.
- Expanded Command and Control Authority: One of the central tenets of the bill is the extension of command and control authority to the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command of an Inter-services Organisation.
- Unlike the existing structure, where these officers lack disciplinary and administrative powers over personnel from other services, the bill empowers them to exercise full command and control.
- This includes maintaining discipline and ensuring the proper execution of duties by service personnel.
- Commanding Officer: The bill introduces the concept of a Commanding Officer, responsible for overseeing a unit, ship, or establishment.
- This officer, in addition to their unit-specific duties, also carries out tasks assigned by the Commander-in-Chief or Officer-in-Command of the Inter-services Organisation.
- Central Government Authority: The superintendence of an Inter-services Organisation will be vested in the central government.
- The government may also issue directions to such organizations on grounds of national security, general administration, or public interest.
Social Justice
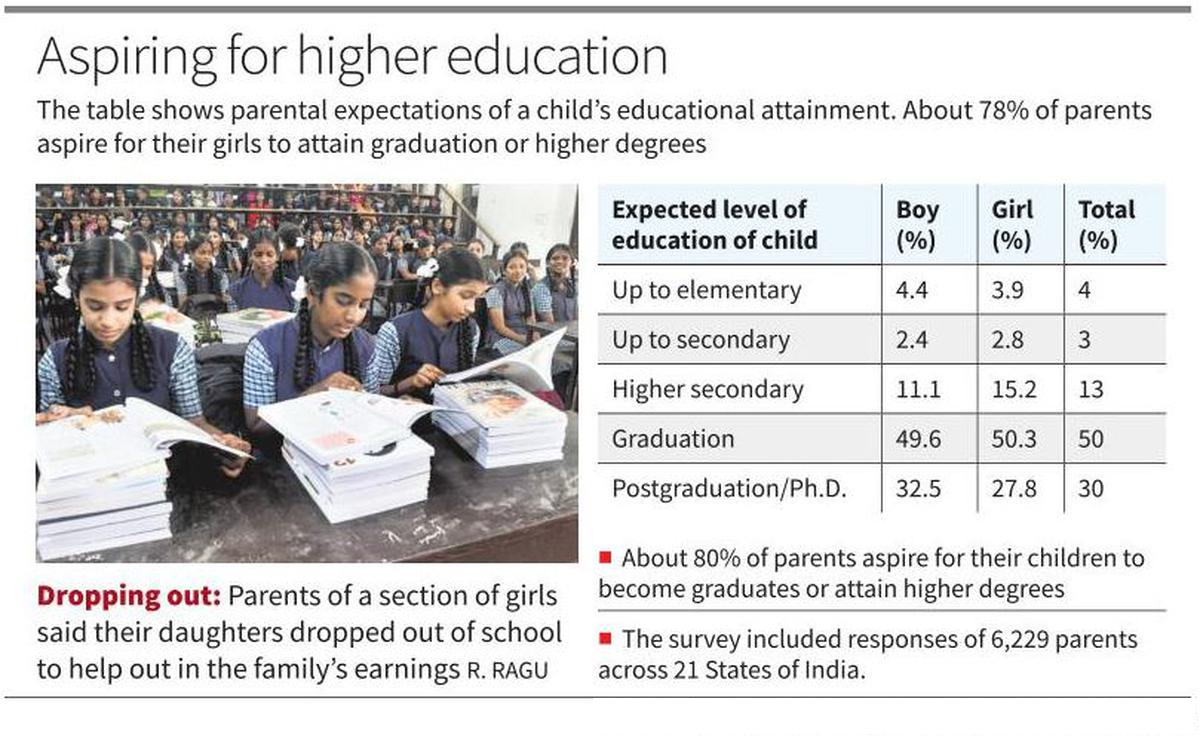
State of Elementary Education in Rural India 2023
For Prelims: State of Elementary Education in Rural India, Prevalence of Smartphone Usage, Entertainment over Educational Activities.
For Mains: State of Elementary Education in Rural India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education has released the State of Elementary Education in Rural India - 2023 report, highlighting the Prevalence of Smartphone Usage among students.
- The report was based on a survey conducted by the Development Intelligence Unit (DIU), a collaboration between NGO Transform Rural India and Sambodhi Research and Communications.
- The survey gathered responses from 6,229 parents of schoolchildren aged 6–16 in rural communities across 21 States.
What are the Key Findings of the Survey?
- Smartphone Usage and Entertainment:
- 49.3% have access to smartphones. 76.7% of parents indicated that their children primarily use smartphones for playing video games, indicating a preference for entertainment over educational activities.
- Additionally, 56.6% of students use smartphones to download and watch movies, while 47.3% use them to download and listen to music.
- In contrast, only 34% of students use smartphones for study-related downloads, and a mere 18% access online learning via tutorials.
- Differential Access Based on Class:
- Smartphone access varies across different class levels. Students in higher classes (Class VIII and above) have greater access to smartphones (58.32%), while even younger students (Classes I–III) show considerable access (42.1%).
- This indicates that smartphone usage for entertainment is prevalent across age groups, potentially impacting their educational engagement.
- Parental Aspirations and Engagement:
- 78% of parents aspire for their children to attain graduation-level education or above, however, there is a gap in parental engagement.
- Only 40% of parents have daily conversations with their children about their school learning, while 32% engage in such conversations a few days a week.
- Reasons for School Dropout:
- For girls, 36.8% of parents mentioned that the need to contribute to family earnings led to their daughters dropping out.
- Meanwhile, 31.6% attributed the dropout to their child's lack of interest in studies, and 21.1% believed household responsibilities played a role.
- For boys, the primary reason for dropping out was a lack of interest in studies, cited by 71.8% of respondents, followed by 48.7% stating the need for boys to contribute to family earnings.
- For girls, 36.8% of parents mentioned that the need to contribute to family earnings led to their daughters dropping out.
- Parent-Teacher Meetings and Learning Environment:
- 84% of parents reported regular attendance. Nonetheless, the two main reasons for non-attendance, are short notice and a lack of willingness.
- Additionally, the availability of age-appropriate reading materials other than textbooks was reported by 40% of parents, highlighting the need for further resources to support children's learning at home.
What are the Recommendations?
- The findings emphasize the need for targeted efforts to enhance the educational environment at home and promote a balanced use of smartphones for both entertainment and learning purposes.
Indian Economy
Medium-Term Expenditure Framework
For Prelims: Medium-Term Expenditure Framework, Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act of 2003, Union Budget, Fiscal Deficit.
For Mains: Medium-Term Expenditure Framework.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Finance has conveyed its inability to release the Medium Term Expenditure Framework (MTEF) statement, mandated by the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act of 2003.
- The ministry had cited “unprecedented global uncertainties that may adversely affect medium-term projections” to justify not placing fiscal projections for 2024-25 and 2025-26 in Parliament at the time of presenting the Union Budget.
Why is the Ministry of Finance Unable to Release MTEF?
- Since the presentation of the Union Budget for FY 2023-24 in February, there has not been any significant and favourable change in global headwinds and associated risks.
- Therefore, amidst aforesaid facts, the medium term projections are not feasible.
- The Finance Ministry emphasized the need for the government to maintain flexibility in fiscal management to effectively manage exogenous shocks and global uncertainties.
- This flexibility is seen as indispensable for the government to retain the necessary fiscal firepower to address unforeseen contingencies that may arise during periods of economic ambiguity.
What is Medium-Term Expenditure Framework (MTEF)?
- About:
- The MTEF statement sets a three-year rolling target for expenditure indicators, along with specifications of underpinning assumptions and risks.
- This statement is presented in Parliament under Section 3 of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003.
- The statement provides an estimate of expenditure for various sectors, including education, health, rural development, energy, subsidies and pension, and so on.
- This statement is presented in the session after the one in which the Budget is presented — usually, that is the monsoon session.
- The MTEF statement sets a three-year rolling target for expenditure indicators, along with specifications of underpinning assumptions and risks.
- Expenditure Commitments:
- Data such as expenditure commitments spread across the various central ministries on salaries and pensions, major programmes, grants-in-aid for creation of capital assets, defence expenditure, interest payment and major subsidies, etc, besides other commitments of the government are considered while formulating this statement.
- Objective:
- The objective of MTEF is to facilitate a closer integration between FRBM statements and the Union Budget.
What is the Fiscal Reduction and Management Act (FRBM)?
- About:
- The FRBM Act is an act of the Parliament which was enacted in 2003 with the aim of ensuring fiscal discipline, transparency and accountability in government spending.
- The act requires the government to ensure that the Fiscal Deficit is reduced over a period of time and to eliminate revenue deficit, which is the excess of government's total expenditure over its total revenue.
- It limited the fiscal deficit to 3% of the GDP.
- Provisions:
- Fiscal Deficit Targets: The act requires the government to reduce its fiscal deficit to a specified target over a period of time. The fiscal deficit would be brought down to below 4.5 per cent by 2025-26.
- Elimination of Revenue Deficit: The act requires the government to eliminate its revenue deficit, which is the excess of government's total expenditure over its total revenue.
- Medium-term Fiscal Strategy: The act requires the government to formulate and implement a medium-term fiscal strategy, which outlines the government's plans for reducing its fiscal deficit over a period of three years.
- Annual Fiscal Reports: The act requires the government to present an annual fiscal responsibility statement to Parliament, which outlines the government's progress in achieving its fiscal consolidation targets.
- Statements:
- Macro-Economic Framework Statement: The Macro-Economic Framework Statement provides a detailed outline of the macroeconomic assumptions that form the basis of the budget estimates.
- It includes key economic indicators and projections that influence revenue and expenditure decisions. These assumptions help in understanding the economic context within which the budget is framed.
- Medium-Term Fiscal Policy Statement: This section outlines the government's medium-term fiscal policy objectives and the strategies to achieve them over a specific period (usually the next three years).
- It highlights the intended direction of fiscal policy, the rationale behind fiscal targets, and how these targets align with broader economic goals.
- Macro-Economic Framework Statement: The Macro-Economic Framework Statement provides a detailed outline of the macroeconomic assumptions that form the basis of the budget estimates.
Conclusion
- As India continues to tread through a complex global landscape, the government's ability to manage its fiscal resources effectively stands as a crucial safeguard against potential economic disruptions.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following statements: (2018)
- The Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Review Committee Report has recommended a debt to GDP ratio of 60% for the general (combined) government by 2023, comprising 40% for the Central Government and 20% for the State Governments.
- The Central Government has domestic liabilities of 21% of GDP as compared to that of 49% of GDP of the State Governments.
- As per the Constitution of India, it is mandatory for a State to take the Central Government’s consent for raising any loan if the former owes any outstanding liabilities to the latter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. Which one of the following was not stipulated in the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003? (2010)
(a) Elimination of revenue deficit by the end of the fiscal year 2007-08
(b) Non-borrowing by the central government from Reserve Bank of India except under certain circumstances
(c) Elimination of primary deficit by the end of the fiscal year 2008-09
(d) Fixing government guarantees in any financial year as a percentage of GDP
Ans: (c)
Q. Along with the Budget, the Finance Minister also places other documents before the Parliament which include ‘The Macro Economic Framework Statement’. The aforesaid document is presented because this is mandated by (2020)
(a) Long standing parliamentary convention
(b) Article 112 and Article 110(1) of the Constitution of India
(c) Article 113 of the Constitution of India
(d) Provisions of the Fiscal Responsibility and Budget Management Act, 2003
Ans: (d)
Mains:
Q. What are the reasons for the introduction of Fiscal responsibility and Budget Management (FRBM) Act, 2003? Discuss critically its salient features and their effectiveness. (2013)
Important Facts For Prelims
Amrit Bharat Stations Scheme
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Prime Minister has laid the foundation stone for the Redevelopment of 508 railway stations across India as a part of Amrit Bharat Stations Scheme, spreading across 27 states and union territories.
- The extensive redevelopment project, estimated to cost more than RS 24,470 crores, aims to transform railway stations into modern, well-equipped hubs.
What is the Amrit Bharat Stations Scheme?
- About:
- The Amrit Bharat Station Scheme aims to redevelop 1309 stations nationwide.
- The redevelopment will provide modern passenger amenities along with ensuring well-designed traffic circulation, inter-modal integration, and signage for the guidance of passengers.
- The Scheme was launched in February 2023 by the Ministry of Railways.
- Station-wise Plans:
- The station buildings' designs will be inspired by local culture, heritage, and architecture.
- For instance, the Jaipur Railway Station will feature elements resembling the Hawa Mahal and Amer Fort from Rajasthan.
- The station buildings' designs will be inspired by local culture, heritage, and architecture.
- Integrated Approach to Urban Development:
- The redevelopment is planned with a holistic approach to urban development, treating the stations as "City Centres."
- This approach aims to integrate both sides of the city and create well-designed traffic circulation, inter-modal connectivity, and clear signage for passengers' guidance.
- Benefits:
- Passenger Amenities: The redeveloped stations will feature modern passenger amenities, including upgraded waiting rooms, improved seating on platforms, and free Wi-Fi connectivity.
- Local Involvement: The redevelopment plans also incorporate the local community's input, aiming to represent the essence of the region in the station's design and amenities.
- Green Energy and Emission Reduction: LED lights will be installed in around 70,000 coaches and the substantial increase in the number of bio-toilets in trains, contributing to environmental sustainability.
- Net Zero Emissions Goal: There is an ambitious goal for India's railway network, aiming for Net-Zero Emissions by 2030. The emphasis on green building standards and energy-efficient practices aligns with the broader vision of environmental sustainability.
What are a Few Key Facts About Indian Railways?
- 169 Years of Heritage:
- The Indian Railways was established on 16th April 1853. The inaugural passenger train covered a 34-kilometer route between Mumbai's Bori Bandar and Thane.
- Unique Mascot:
- The Indian Railways boasts its own mascot, a 'Shubhankar named 'Bholu,' created by the National Institute of Design in 2002. Bholu is an elephant dressed as a railway guard, introduced on the railways' 150th anniversary.
- World's 4th Largest Rail Network:
- The Indian Railways ranks as the world's fourth-largest railway network, encompassing a track length of 67,368 km. Only the US, China, and Russia have larger networks. It's also the world's second-largest network managed under a single administration, spanning 115,000 km.
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites:
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites,
- Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus in Mumbai, Nilgiri Mountain Railway, and Kalka Shimla Railway.
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites,
- Longest Platform:
- Hubli Junction's Platform number 1, also known as Shree Siddharoodha Swamiji Hubballi Junction in Karnataka, holds the record for the world's longest railway platform at 1,505 meters.
- Longest and Shortest Train Rides:
- The longest train ride in India is the Vivek Express, traveling from Kanyakumari to Dibrugarh, covering a distance of 4,189 kilometers with 56 stops in 82 hours and 30 minutes.
- The shortest train ride is just 3 kilometers, running between Nagpur and Ajni.
- World's Highest Rail Bridge:
- India is home to the Chenab Rail Bridge, the world's highest railway bridge, located in Dharot, Jammu, and Kashmir.
- Nagpur's Diamond Crossing:
- Nagpur, Maharashtra, hosts the famous Diamond Crossing, where two railway tracks form a square-like diamond shape, with two lines going North-South and two lines going East-West.
Important Facts For Prelims
Same-Sex Behavior in Rhesus Macaques
Why in News?
A recent study conducted by researchers from Imperial College London, titled "Genetics, Social Environment and Evolution of Male Same-Sex Behavior in Rhesus Macaques," has challenged conventional beliefs about same-sex behaviour (SSB) in animals.
- The engagement of animals in SSB has been considered a ‘Darwinian paradox’: if reproduction is critical to evolution, then SSB – which is non-reproductive – should have ceased to exist.
- This recent study found that male SSB in rhesus macaques is very common and doesn't harm evolution.
What are the Key Findings from the Study?
- Male Same-Sex Behavior (SSB) in Monkeys:
- The study focuses on male same-sex mounting behaviour observed in rhesus macaques, a common monkey model, in Cayo Santiago, an island east of Puerto Rico.
- 72% of observed male rhesus macaques engaged in same-sex mounting.
- Only 46% participated in different-sex mounting.
- It challenges the notion that SSB contradicts principles of evolution due to its non-reproductive nature.
- The study focuses on male same-sex mounting behaviour observed in rhesus macaques, a common monkey model, in Cayo Santiago, an island east of Puerto Rico.
- Role of Non-Genetic Factors:
- The study considers external factors like social interactions and the environment.
- These non-genetic elements contribute to the expression of SSB behaviour in male rhesus macaques.
- SSB-engaging monkeys form coalitions against common enemies.
- Male SSB could serve as a form of emotional communication and regulation.
- No Trade-off with Reproductive Fitness:
- The study disputes the assumption that SSB reduces reproductive opportunities, as sexually active males engage in both SSB and different-sex sexual behaviour (DSB).
- There is no direct correlation between SSB engagement and reduced offspring count in the macaque population.
- Future Research:
- Female SSB and other monkey species require further investigation to broaden understanding.
- The findings cannot be directly extrapolated to humans due to cultural and social influences.
Important Facts For Prelims
Addressing Air Pollution Through Technological Innovations
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of Environment, Forest and Climate Change provided valuable insights into the projects related to deploying various technologies to address Air Pollution in India during a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
What is Air Pollution?
- Air pollution refers to the contamination of the Earth's atmosphere by harmful substances beyond their natural levels, due to human activities and natural processes.
- It originates from sources like industrial emissions, vehicle exhaust, agricultural practices, and natural events, and it can have wide-ranging negative effects on air quality, human well-being, ecosystems, and the overall health of the planet.
- Common air pollutants include: PM2.5, PM10, Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2) and Nitric Oxides (NOx), Sulfur Dioxide (SO2), Carbon Monoxide (CO) etc.
What are Various Technology Based Projects Deployed to Curb Air Pollution?
- Pariyayantra Filtration Units on Buses: A pilot study was initiated where 30 buses were retrofitted with Pariyayantra Filtration units installed on their rooftops.
- These units were designed to effectively capture dust particles (through filters fitted on vehicles) from the surrounding environment, thereby minimizing the contribution of vehicular movement to air pollution levels.
- It does not require any power to operate and is equivalent to the filtration provided by 6 room air filters.
- WAYU Air Purification Units at Traffic Intersections: A total of 54 WAYU Air Purification Units were strategically installed at major traffic intersections in Delhi.
- These units, designed to purify the air in the immediate vicinity, played a crucial role in reducing the impact of vehicular emissions on air quality.
- The WAYU units acted as localized air purifiers, offering a potential solution to combat the adverse effects of traffic-related pollution.
- Ionisation Technology for Ambient Air Pollution Reduction: This technology aimed to neutralize pollutants through ionization processes, thereby enhancing air quality in the target areas.
- The study evaluated the feasibility and impact of ionization technology, potentially opening new avenues for pollution reduction.
- Installation of Medium/Large-Scale Smog Towers: These towers, acting as substantial air purifiers, targeted the reduction of particulate matter and pollutants on a broader scale.
- Retrofitting Emission Control Devices in In-Use Vehicles: Older vehicles, especially those adhering to older emission standards like BS III, contribute substantially to air pollution.
- A pilot project was undertaken to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of retrofitting emission control devices in such vehicles.
- The project aimed to provide recommendations for emission reduction from these vehicles, aligning with broader efforts to improve air quality.
- A pilot project was undertaken to assess the feasibility and effectiveness of retrofitting emission control devices in such vehicles.
- Indigenous Photonic System for Air Quality Monitoring: A project by the Department of Science and Technology (DST) focused on developing an indigenous photonic system for real-time remote monitoring of air quality parameters.
- This initiative aimed to enhance the accuracy and accessibility of air quality data, enabling more informed decision-making in pollution management strategies.
- Advancements in Electric Vehicle (EV) Autonomous Technology: An autonomous navigation foundation focused on EV-based autonomous vehicles was established under the DST National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber Physical Systems (NM-ICPS).
- The integration of autonomous technology in EVs presents an opportunity to optimize driving patterns, reduce traffic congestion, and subsequently lower greenhouse gas emissions.
What are the Other Government Initiatives to Curb Air Pollution?
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)
Important Facts For Prelims
World University Games
Why in News?
Recently, the 31st World University Game was held in Chengdu, China, where India has won a total of 26 medals across 4 disciplines with highest medal count at the World University Games.
- Many of the athletes who won the Medals come from Khelo India Scheme and Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS).
- It had to be held in 2021, the World University Games had to be rescheduled twice due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
What is the World University Game?
- About:
- World University Games," also known as "Universiade," is an international multi-sport event specifically for university athletes.
- It is organized by the International University Sports Federation (FISU).
- FISU is the governing body that oversees and organizes the Universiade events. FISU is responsible for coordinating the host cities and ensuring that the games are conducted in accordance with the organization's principles and regulations.
- The Universiade is held every two years and features a wide range of sports similar to the Olympic Games.
- It includes both summer and winter editions,
- With the summer Universiade typically featuring sports like athletics, swimming, basketball, soccer, and more,
- While the winter Universiade includes sports like skiing, ice hockey, figure skating, and others.
- Previous Edition:
- The previous edition, held in Naples in 2019, saw Japan emerge as the dominant nation, securing the highest position on the medal table.
- Future Events:
- Next Winter World University Games will be held in 2025 in Rhine-Ruhr, Germany.
What is the Khelo India Scheme?
- About:
- Khelo India, which translates to ‘Let’s play India’, was proposed by the government of India in 2017 to revive India’s sporting culture by engaging with children at the grassroots level.
- It is implemented by the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports.
- Under this movement, the Khelo India Youth Games (KIYG), the Khelo India University Games (KIUG) and the Khelo India Winter Games were set up as annual national sports competitions where youngsters, representing their states and universities, respectively, showcased their skills and competed for medals.
- Khelo India, which translates to ‘Let’s play India’, was proposed by the government of India in 2017 to revive India’s sporting culture by engaging with children at the grassroots level.
- Objective:
- The Khelo India scheme is a flagship government-funded program that aims to identify and nurture sporting talent in India.
- The scheme has been very successful in recent years, and the athletes who have been selected for the World University Games are some of the best young talents in the country.
- The Khelo India scheme is a flagship government-funded program that aims to identify and nurture sporting talent in India.
Note: To improve India’s performance at Olympics and Paralympics, the Ministry of Youth Affairs and Sports (MYAS) started the Target Olympic Podium Scheme (TOPS) in September 2014.This was revamped in April 2018 to establish a technical support team for managing the TOPS athletes and providing holistic support.
- The TOPS sponsored athletes gained relative success at the 2016 Rio Olympics and the 2018 Commonwealth Games.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
World Tribal Day 2023
- The International Day of the World's Indigenous Peoples, also known as World Tribal Day, is observed annually on August 9, as per a resolution by the UN General Assembly in December 1994.
- This date commemorates the inaugural meeting of the UN Sub-Commission on the Promotion and Protection of Human Rights Working Group on Indigenous Populations in 1982, highlighting its significance in promoting and safeguarding the rights of indigenous populations worldwide.
- The theme of World Tribal Day in 2023 is "Indigenous Youth as Agents of Change for Self-determination."
- The day is necessary since indigenous peoples are frequently among the most underprivileged racial and ethnic groupings in society.
- The UN estimates that although indigenous people make up less than 5% of the global population, they are responsible for 15% of the world's poorest people.
Read more: World Tribal Day, Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
Quit India Movement Day 2023
- The Quit India Movement, also known as the August Movement or Bharat Chodo Andolan, was a significant civil disobedience movement launched by Mahatma Gandhi and supported by Indian National Congress on 8th August 1942 with the aim to end British colonial rule in India and achieve full independence.
- The year 2023 marks the 81st anniversary of the Quit India movement.
- On this day, August 8th, 1942, Gandhi gave the famous "Do or Die" speech, at the Gowalia Tank Maidan, now popularly known as August Kranti Maidan.
- The slogan ‘Quit India’ was coined by Yusuf Meherally, a socialist and trade unionist who also served as Mayor of Mumbai.
- Meherally had also coined the slogan “Simon Go Back”.
Read more: Quit India Movement, Mahatma Gandhi
Enhanced Transparency in Mahatma Gandhi NREGS through E-Attendance
Recently, the Union Ministry of State for Rural Development provided valuable insights into the E-attendance in Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme during a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
- To bolster transparency in the scheme's execution across various states and union territories, a mandate has been established requiring the use of the National Mobile Monitoring System (NMMS) App.
- This app captures attendance with geo-tagged, two time-stamped photographs of workers engaged in the scheme's activities, except for individual beneficiary works.
- Offline mode enables the capture of morning attendance and photographs, with later uploads when a network connection is available.
- This requirement, effective from January 1, 2023, not only fosters citizen oversight of the program but also expedites payment processing.
- The responsibility of recording attendance and photos lies with worksite supervisors, who employ the NMMS App for this purpose.
Read more: Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme
India's Defence Ministry Adopts 'Maya' OS for Enhanced Cybersecurity
India's Defence Ministry has decided to replace the Microsoft Operating System (OS) on internet-connected computers with a new OS called Maya, developed locally based on open-source Ubuntu.
- The transition to Maya is aimed at bolstering security without disrupting user experience, as it offers an interface and functionality similar to Windows.
- This move comes in response to the escalating incidents of cyberattacks.
- Alongside Maya's implementation, a comprehensive 'end point detection and protection system,' Chakravyuh, is also being introduced to fortify these systems.
Read more: Rising up to Cyber Security Challenges

 2023.png)