Governance
Mission on Advanced and High-Impact Research
For Prelims: Purpose, Objectives and Structure of the mission, E-cooking, Alternatives to Lithium-Ion storage batteries , Green hydrogen
For Mains: Significance of the MAHIR
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Power and the Ministry of New and Renewable Energy have jointly launched a National Mission named “Mission on Advanced and High-Impact Research (MAHIR)”.
- The Mission is planned for an initial period of five years from 2023-24 to 2027-28 and will follow the technology life cycle approach of Idea to Product.
What are the Key Details of the National Mission MAHIR?
- Objectives of the Mission:
- To identify emerging technologies and areas of future relevance for the global power sector and develop them indigenously.
- To provide a platform for collective brainstorming and synergetic technology development among power sector stakeholders.
- To support pilot projects of indigenous technologies developed by Indian start-ups and facilitate their commercialization.
- To leverage foreign alliances and partnerships for research and development of advanced technologies and technology transfer.
- To promote scientific and industrial R&D in the power sector and create an innovative ecosystem.
- To position India among the leading countries in power system-related technologies and applications development.
- Funding:
- It will be funded by pooling resources from the Ministry of Power, Ministry of New & Renewable Energy, and Central Public Sector Enterprises under these ministries.
- Additional funding, if required, will be mobilized from the Government of India's budgetary resources.
- Areas Identified for Research under MAHIR:
- Alternatives to Lithium-Ion storage batteries
- Modifying electric cookers/pans to suit Indian cooking methods
- Green hydrogen for mobility (High Efficiency Fuel Cell)
- Carbon capture
- Geo-thermal energy
- Solid state refrigeration
- Nano technology for EV battery
- Indigenous CRGO technology
What is the Structure of the Mission?
- Two- Tier Structure:
- It has a two-tier structure consisting of a Technical Scoping Committee and an Apex Committee.
- The Apex Committee:
- It deliberates on technology and product development, approves research proposals, and looks into international collaborations.
- The Apex committee will look also into international collaborations. The final approval of all the research proposals / projects shall be given by the Apex Committee.
- It is chaired by the Union Minister for Power & New and Renewable Energy.
- Technical Scoping Committee:
- It identifies research areas, recommends potential technologies, and monitors approved research projects.
- It is chaired by the Chairperson of the Central Electricity Authority.
- The Apex Committee:
- It has a two-tier structure consisting of a Technical Scoping Committee and an Apex Committee.
- Central Power Research Institute (CPRI), Bengaluru will provide all necessary secretarial assistance to the Apex Committee and Technical Scoping Committee.
What is the Scope of the Mission?
- Once research areas are identified and approved, outcome-linked funding proposals will be invited globally.
- Quality cum Cost-Based Selection (QCBS) basis will be used for selecting the proposals.
- Pilot projects of technologies developed by Indian start-ups will be funded, and their commercialization will be facilitated.
- International collaboration and technology transfer will be encouraged.
What is the Significance of the MAHIR?
- Indigenous Development:
- By developing advanced technologies within the country, India can reduce its dependence on imports, enhance self-reliance, and promote domestic innovation and manufacturing capabilities.
- It aligns with the "Make in India" initiative and contributes to the growth of indigenous technology-driven industries.
- Energy Transition and Net Zero Emissions:
- MAHIR can support the adoption of cleaner and greener energy sources, energy storage solutions, and carbon capture techniques.
- This contributes to India's commitment to combating climate change and transitioning towards a sustainable energy future.
- Economic Growth and Manufacturing Hub:
- MAHIR aims to make India a manufacturing hub for advanced power technologies.
By developing and deploying cutting-edge technologies, it can attract investments, foster innovation-driven industries, and create job opportunities.
- MAHIR aims to make India a manufacturing hub for advanced power technologies.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- National Mission for a Green India, also known as Green India Mission (GIM), is one of the eight missions outlined under India’s National Action Plan on Climate Change. It was launched in February 2014.
- Goals of Mission
- To increase forest/tree cover to the extent of 5 million hectares (mha) and improve quality of forest/tree cover on another 5 mha of forest/nonforest lands. Separate sub-targets existing for different forest types and ecosystems (eg.,
- wetland, grassland, dense forest, etc.). Hence, 3 is correct.
- Improvement in quality of forest cover and ecosystem services of forests/non-forests,
- including moderately dense, open forests,
- degraded grassland and wetlands (5 mha).
- Eco-restoration/afforestation of scrub, shifting cultivation areas, cold deserts, mangroves, ravines and abandoned mining areas (1.8 mha) with separate sub–targets for each one of those.
- Improvement in forest and tree cover in urban/peri-urban lands (0.20 mha).
- Improvement in forest and tree cover on marginal agricultural lands/fallows and other non-forest lands under agro-forestry/social forestry (3 mha).
- To improve/enhance eco-system services like carbon sequestration and storage (in forests and other ecosystems), hydrological services and biodiversity; along with provisioning services like fuel, fodder, and timber and non-timber forest produces (minor forest produces or MFPs) etc., which are expected to result from the treatment of 10 mha.
- To increase forest based livelihood income for about 3 million households in and around these forest areas; and enhanced annual CO2sequestration by 50 to 60 million tonnes by the year 2020. Launching 2nd Green Revolution and incorporating green accounting in the Union and State budget are not the objectives of Green India Mission. Hence, 1 and 2 are not correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer


Governance
World Food Safety Day
For Prelims: World Food Safety Day (WFSD), World Health Organization (WHO), Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), International Year of Millets, UN Sustainable Development Goals, Adulteration of food products.
For Mains: Major Challenges Related to Food Safety in India, State Food Safety Index
Why in News?
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) organised a session on June 7th, 2023, to celebrate World Food Safety Day.
- The 5th State Food Safety Index (SFSI) was also unveiled at the event.
What is World Food Safety Day?
- World Food Safety Day is a global campaign that aims to draw attention and inspire action to help prevent, detect and manage foodborne risks.
- It is celebrated on 7 June every year since 2019, following a resolution by the United Nations General Assembly.
- The campaign is led by the World Health Organization (WHO) and the Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO), in collaboration with Member States and other relevant organisations.
- Theme for 2023: Food standards save lives.
What is State Food Safety Index?
- About: FSSAI has developed the State Food Safety Index (first launched in 2018-19) to measure the performance of states on various parameters of Food Safety.
- Parameters: This index is based on performance of State/ UT on five significant parameters, namely, Human Resources and Institutional Data, Compliance, Food Testing – Infrastructure and Surveillance, Training & Capacity Building and Consumer Empowerment.
- The Index is a dynamic quantitative and qualitative benchmarking model that provides an objective framework for evaluating food safety across all States/UTs.
- Recognition of Top Performers: Kerala secured the top rank among larger states, followed by Punjab and Tamil Nadu.
- Goa emerged as the leader among smaller states, with Manipur and Sikkim following suit.
- Jammu and Kashmir, Delhi, and Chandigarh secured the top three ranks among union territories.
What are the Other Major Highlights of the Event?
- Eat Right Challenge for Districts - Phase II: Winners of the Eat Right Challenge for Districts were honoured for their outstanding efforts in improving the food environment and raising awareness about food safety.
- Remarkable achievements were observed in districts from Tamil Nadu, Madhya Pradesh, West Bengal, Uttar Pradesh, and Maharashtra.
Note: FSSAI has initiated the Eat Right India movement. The movement is based on three key themes:
- if it’s not safe, it’s not food’ (safe food),
- food should not only serve the palate but is also meant for body and mind (healthy diets)
- food has to be good both for people and the planet’ (sustainable diets).
- The Eat Right Challenge is envisioned as a competition among districts and cities to recognize their efforts in adopting and scaling up various initiatives under Eat Right India.
- Eat Right Millets Melas: To commemorate India's 75th Independence anniversary and the International Year of Millets, the FSSAI envisioned organising Eat Right Millets Melas nationwide.
- These melas showcase the diversity of cuisines and millet recipes in the country.
- Training Food Business Operators: FSSAI aims to train 25 lakh food business operators in the next three years to ensure food quality standards are met across the country.
- Food Streets: Establishment of 100 Food Streets across the country that meet quality benchmarks for food safety, hygiene, and nutrition, was announced as the part of the event.
- Rapid Food Testing Kit (RAFT) Portal: The RAFT portal was unveiled as part of FSSAI's digitization efforts.
- The portal streamlines the operations of the RAFT Scheme, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Rapid Analytical Food Testing (RAFT) Kit/Equipment/Method facilitates spot field testing by Food Safety Officers (FSOs) or Mobile Testing Labs or to improve speed and reduce testing costs in food laboratories.
- The portal streamlines the operations of the RAFT Scheme, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Manuals for Enhanced Food Safety Practices: The Union Health Minister released three manuals aimed at enhancing food safety practices nationwide.
- Manuals include the analysis methods for Fish & Fish Products, Cereal and Cereal Products (2nd edition), and Beverages: Tea, Coffee & Chicory.
Why is Food Safety Important?
- Food safety is a shared responsibility between governments, producers and consumers.
- According to WHO, an estimated 600 million people – almost 1 in 10 people in the world – fall ill after eating contaminated food and 420 000 die every year.
- Children under 5 years of age carry 40% of the foodborne disease burden, with 1,25,000 deaths every year.
- Foodborne diseases can also have long-term consequences, such as malnutrition, stunting, cancer and chronic diseases.
- Food safety is also essential for achieving several of the UN Sustainable Development Goals, such as ending hunger, improving health, reducing poverty and protecting the environment.
What are the Major Challenges Related to Food Safety in India?
- Lack of Infrastructure and Resources: Insufficient infrastructure and resources pose significant challenges in ensuring food safety across the country.
- Limited laboratory facilities and testing capabilities result in inadequate monitoring and detection of contaminants. Inadequate storage and transportation facilities can lead to improper handling of food, increasing the risk of contamination.
- Contamination and Adulteration:
- Contamination of food with pathogens, chemicals, and toxins remains a major concern in India. Adulteration of food products with substandard ingredients or harmful substances is prevalent, compromising food safety and public health.
- Unregulated use of pesticides and chemical additives in agriculture and food production contribute to the contamination of food.
- Contamination of food with pathogens, chemicals, and toxins remains a major concern in India. Adulteration of food products with substandard ingredients or harmful substances is prevalent, compromising food safety and public health.
- Poor Hygiene and Sanitation Practices:
- Lack of proper handwashing, sanitation facilities, and clean water sources in food handling and processing establishments increase the risk of microbial contamination.
- Unhygienic conditions in food markets, street food vendors, and restaurants contribute to the spread of foodborne illnesses.
- Lack of proper handwashing, sanitation facilities, and clean water sources in food handling and processing establishments increase the risk of microbial contamination.
- Weak Regulatory Framework and Enforcement: Inconsistencies in standards and regulations across different states and regions create challenges in maintaining uniform food safety practices.
- Limited resources and manpower for inspection and enforcement result in inadequate monitoring and control of food safety standards.
- Rapid Urbanization and Changing Food Habits: Rapid urbanisation and changing food habits present challenges in ensuring food safety.
- Increased demand for processed and ready-to-eat foods, as well as street foods, requires robust monitoring and regulation to address safety concerns.
Way Forward
- Strengthening Food Testing Laboratories: There is a need to Establish well-equipped and accredited food testing laboratories across the country, especially in rural areas.
- These labs should be capable of conducting rapid and accurate tests for various contaminants, including pesticides, heavy metals, and pathogens, ensuring timely identification of unsafe food.
- Empowering Local Communities: There is a need to encourage community participation and awareness by organising workshops, seminars, and interactive sessions on food safety.
- There is also a need to empower local communities to take ownership of food safety issues and implement solutions at the grassroots level.
- Ensuring Transparency in Food Stock Holdings: Using IT to improve communication channels with farmers can help them to get a better deal for their produce while improving storage houses with the latest technology is equally important to deal with natural disasters and hoarding.
- Further, foodgrain banks can be deployed at block/village level, from which people may get subsidised food grains against food coupons (that can be provided to Aadhar linked beneficiaries).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of India’s preparation for Climate-Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements: (2021)
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2 With reference to the provisions made under the National Food Security Act, 2013, consider the following statements: (2018)
- The families coming under the category of ‘below poverty line (BPL)’ only are eligible to receive subsidised food grains.
- The eldest woman in a household, of age 18 years or above, shall be the head of the household for the purpose of issuance of a ration card.
- Pregnant women and lactating mothers are entitled to a ‘take-home ration’ of 1600 calories per day during pregnancy and for six months thereafter.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 3 only
Ans: (b)


Geography
El Nino 2023: Unusual Warming Like 2009
For Prelims: El Nino, La Nina, El Nino-Southern Oscillation
For Mains: EL Nino and its impacts, Relationship between El Nino and global warming
Why in News?
Recently, an unusual phenomenon is developing along the equatorial Pacific region, indicating the emergence of El Nino conditions in 2023. Experts warn that this simultaneous warming of the eastern and western regions of the equatorial Pacific, a trend last observed in 2009, could have severe implications for marine life worldwide.
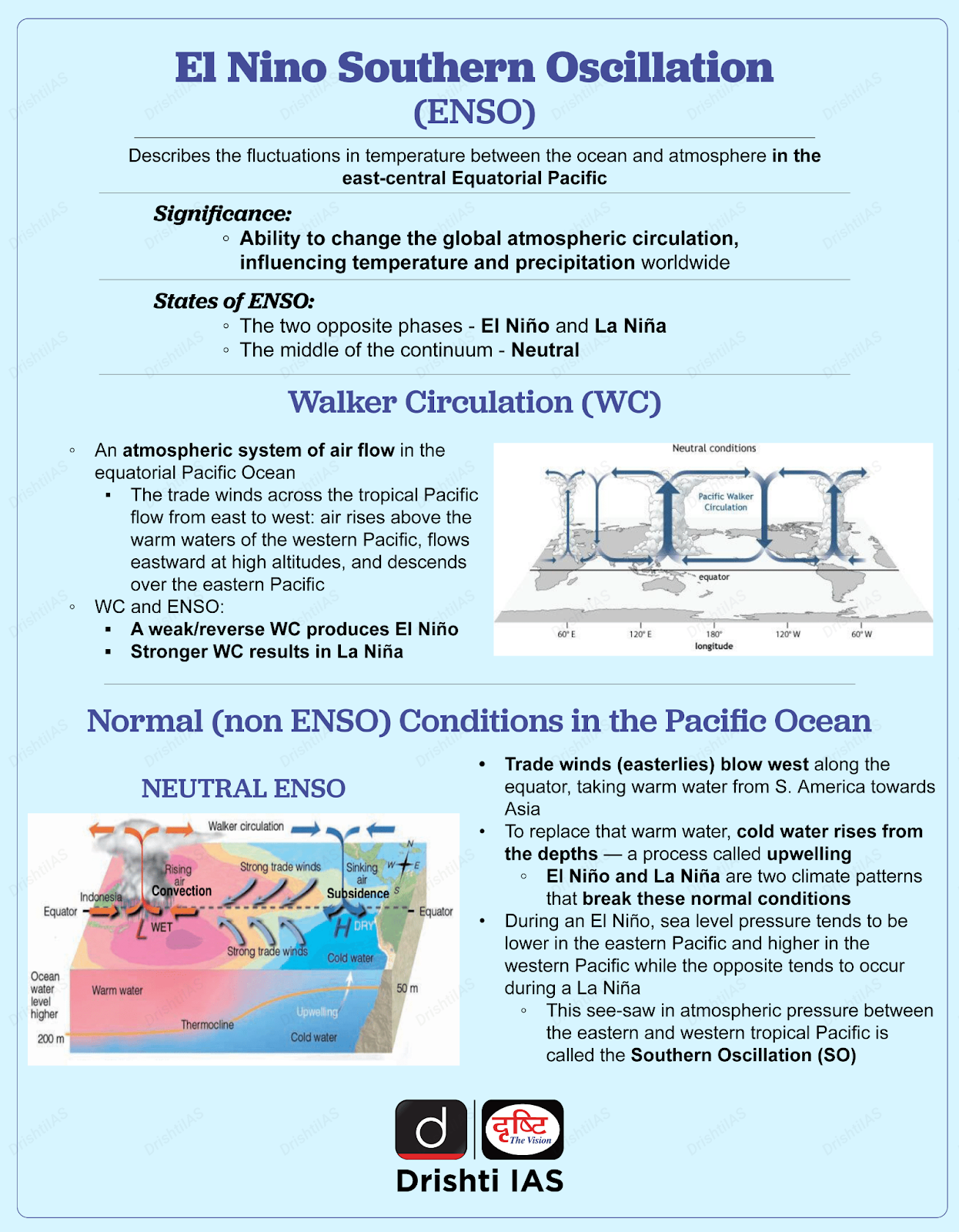
What are the Causes for this Phenomenon?
- The eastern Pacific is getting warmer, which should make the west cooler.
- However, due to global warming, there is basin scale warming across the tropical Pacific.
- Two things could have triggered this phenomenon:
- Global warming in the Pacific and other modes of natural variability
- The transition from La Nina winter into an El Nino summer which is part of the El Nino-Southern Oscillation (ENSO) cycle.
- Basin Scale Warming in the Equatorial Pacific:
- Due to global warming, the equatorial Pacific experiences basin scale warming, causing both eastern and western regions to become warmer.
- The measurement of basin scale refers to the spatial extent of a basin or common water outlet, in this case, the equatorial Pacific region.
- Recent data analysis shows that the ocean temperatures on May 29, 2023, were unusually warm compared to the 2003-2014 average.
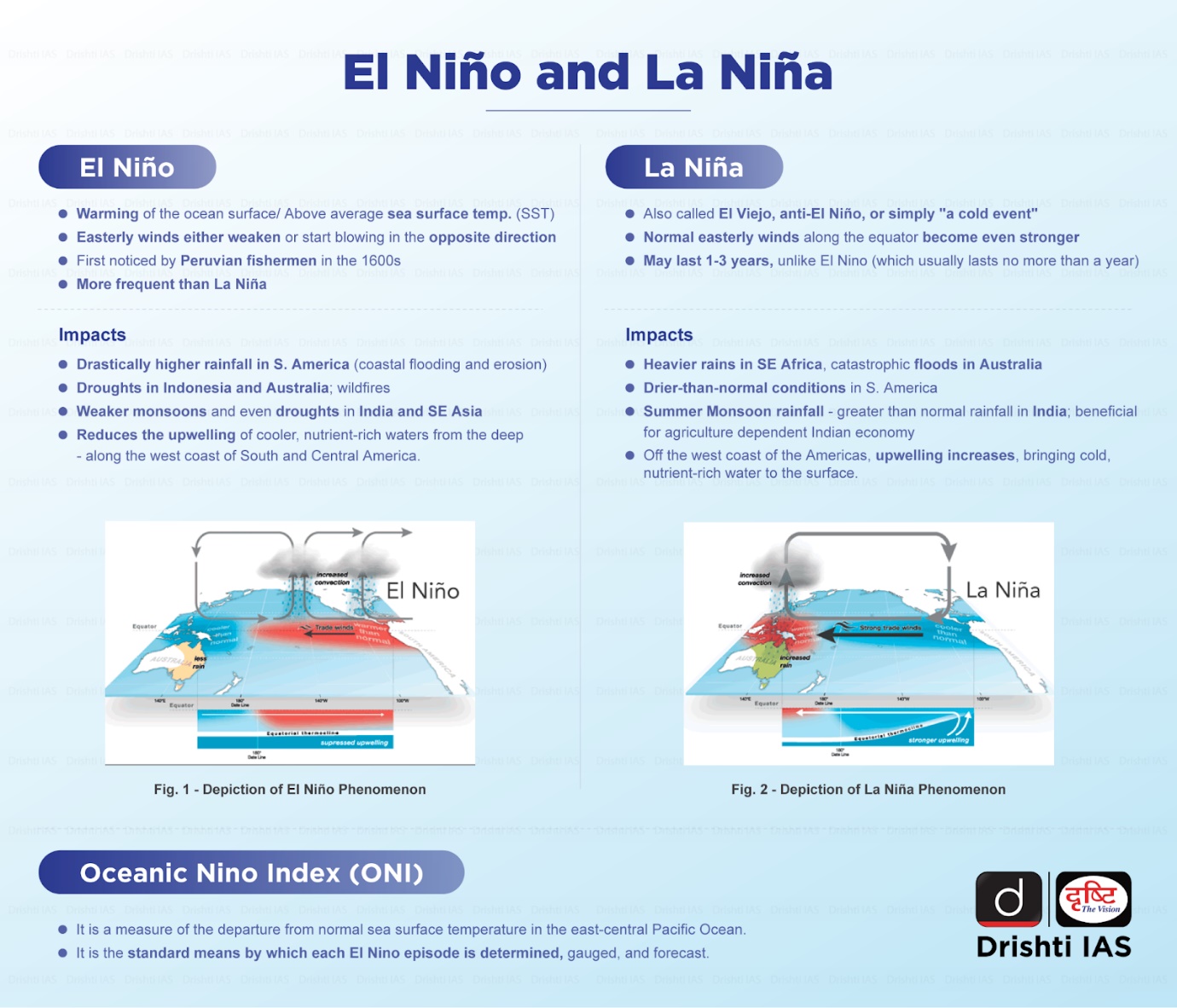
What is ENSO?
What are the Potential Consequences of this Phenomenon?
- Global Warming:
- The end of La Nina means that the ocean is not taking up heat, which will dissipate into the atmosphere.
- If the atmosphere is warmer, then the ocean doesn't lose as much heat, causing it to warm up at the surface.
- This may temporarily push global warming beyond 1.5°C.
- The end of La Nina means that the ocean is not taking up heat, which will dissipate into the atmosphere.
- Geophysical Effect:
- The phenomenon will affect cyclones, hurricanes, and typhoons, with Typhoon Mawar in the western Pacific already being one of the strongest.
- The warming of ocean waters acts as a catalyst for marine heatwaves, the slowing of meridional circulation, which could cause unmitigable losses for marine biodiversity.
- Coral Bleaching:
- A warming of 1.5°C threatens to destroy 70 to 90 per cent of coral reefs, and a 2°C increase means a nearly 100 per cent loss – a point of no return.
Previous El Nino Events:
- El Nino events of 1982-83 and 1997-98 were the most intense of the 20th century.
- During the 1982-83 event, sea surface temperatures in the eastern tropical Pacific were 9-18° F above normal.
- The El Nino event of 1997-98 was the first El Nino event to be scientifically monitored from beginning to end.
- The 1997-98 event produced drought conditions in Indonesia, Malaysia, and the Philippines. Peru and California experienced very heavy rains and severe flooding.
- The Midwest experienced record-breaking warm temperatures during a period known as “the year without a winter.”
- The El Nino, along with global warming, had made 2016 the warmest year on record.
What is the Impact El Nino 2023 on India?
- Weak Monsoon for India: The development of an El Nino in May or June 2023 may cause weakening of the southwest monsoon season, which brings around 70% of the total rainfall India receives and on which most of its farmers still depend.
- However, sub-seasonal factors such as the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and monsoon low-pressure systems can temporarily enhance rainfall in some parts as witnessed in the year 2015.
- Hot Temperatures: It may also cause heatwaves and droughts in India and other regions around the world such as South Africa, Australia, Indonesia and the Pacific Islands.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)


Indian Economy
RBI Monetary Policy Committee: Policy Rates Unchanged
For Prelims: RBI, Monetary Policy Rates, Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), inflation
For Mains: Monetary Policy, Growth & Development, RBI and its Monetary Policy Tools.
Why in News?
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India's Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has decided to keep the policy rates unchanged, taking into account the evolving macroeconomic situation.
- This is the second consecutive pause after a previous conservative rate hike of 250 basis points aimed at curbing inflation.
- The decision reflects a cautious approach to balance inflation management and support economic growth.
What is the Monetary Policy Committee?
- It is a statutory and institutionalized framework under the Reserve Bank of India Act, 1934, for maintaining price stability, while keeping in mind the objective of growth.
- The Governor of RBI is ex-officio Chairman of the committee.
- The MPC determines the policy interest rate (repo rate) required to achieve the inflation target.
What are the Key Announcements?
- Policy Rates Unchanged:
- The policy repo rate under the liquidity adjustment facility (LAF) remains unchanged at 6.50%.
- The standing deposit facility (SDF) rate remains unchanged at 6.25%.
- The marginal standing facility (MSF) rate and Bank Rate are maintained at 6.75%.
- Emphasis on Inflation Management:
- The MPC aims to withdraw accommodation gradually to align inflation with the target while supporting growth.
- The objective is to achieve the medium-term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4% within a band of +/- 2%.
- Inflation Outlook:
- Food Price Dynamics:
- The trajectory of headline inflation will likely be influenced by food price dynamics.
- Monsoon Impact:
- The forecast by India Meteorological Department (IMD) of a normal southwest monsoon is positive for kharif crops.
- Crude Oil Prices and Input Costs:
- Crude oil prices have eased, but the outlook remains uncertain.
- Early survey results indicate expectations of firms' input costs and output prices hardening.
- Food Price Dynamics:
- Inflation and Growth Projections:
- CPI Inflation:
- Assuming a normal monsoon, CPI inflation is projected at 5.1% for 2023-24.
- GDP Growth:
- Higher rabi crop production, anticipated normal monsoon, and robust services sector support private consumption and overall economic activity in the current year.
- Government's emphasis on capital expenditure, moderating commodity prices, and credit growth are expected to nurture investment activity.
- Weak external demand, geopolitical tensions, and geoeconomic fragmentation pose risks to the growth outlook.
- Real GDP growth for 2023-24 projected at 6.5%.
- CPI Inflation:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. With reference to Indian economy, consider the following: (2015)
- Bank rate
- Open market operations
- Public debt
- Public revenue
Which of the above is/are component/ components of Monetary Policy?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)
Q2. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC)? (2017)
- It decides the RBI’s benchmark interest rates.
- It is a 12-member body including the Governor of RBI and is reconstituted every year.
- It functions under the chairmanship of the Union Finance Minister.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: (a)
Q3. If the RBI decides to adopt an expansionist monetary policy, which of the following would it not do? (2020)
- Cut and optimise the Statutory Liquidity Ratio
- Increase the Marginal Standing Facility Rate
- Cut the Bank Rate and Repo Rate
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Fermi Energy in Quantum Physics
Why in News?
Recently, Fermi energy has gained significant attention due to its wide range of daily practical applications in various fields, driven by the principles of quantum physics.
What is Quantum Physics?
- Quantum physics is the branch of physics that deals with the behavior and properties of the smallest particles of matter and energy, such as atoms, electrons, photons, and quarks.
- Quantum physics reveals that these particles can behave in strange and surprising ways, such as being in two places at once (superimposition), tunneling through barriers, or entanglement with each other over long distances.
- Quantum physics also explains how atoms and molecules form the basis of all matter and how light and other electromagnetic waves are produced and interact with matter.
- Quantum physics impacts daily life through electronics, computing, lasers, and optics. It enables technologies like MRI for medical imaging and improves renewable energy systems.
- Quantum cryptography ensures secure communication, while materials science and nanotechnology benefit from quantum principles.
What is Fermi Energy?
- About:
- Fermi energy is the energy of the highest occupied state of electrons in a material at absolute zero temperature (-273º C or 0K).
- Fermi energy determines electron velocity in conduction, as only electrons with energies close to the Fermi energy can participate in the conduction process.
- Metals, such as copper, aluminum, and silver, exhibit high Fermi energies, even at extremely low temperatures.
- The Fermi energy and fermionic behavior of electrons, governed by quantum mechanics, are responsible for various properties of metals, including their reflectivity, electrical conductivity, and thermal conductivity.
- Fermi energy is measured by Fermi level.
- Understanding Fermi energy is essential for comprehending the fundamental behaviors and applications of metals in our daily lives.
- Fermi energy is the energy of the highest occupied state of electrons in a material at absolute zero temperature (-273º C or 0K).
- Importance for Quantum Physics:
- Fermi energy reveals the wave nature and discrete energy levels of electrons in matter.
- Fermi energy determines various physical properties of materials, including electrical and thermal conductivity, heat capacity, magnetism, and superconductivity.
- Fermi energy is relevant in natural phenomena and technological applications like stars, nuclear reactions, lasers, transistors, and solar cells.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. With reference to Visible Light Communication (VLC) technology, which of the following statements are correct? (2020)
- VLC uses electromagnetic spectrum wavelengths 375 to 780 nm.
- VLC is known as long-range optical wireless communication.
- VLC can transmit large amounts of data faster than Bluetooth.
- VLC has no electromagnetic interference.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 1, 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 2, 3 and 4 only
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Visible Light Communication (VLC) systems employ visible light for communication that occupy the electromagnetic spectrum from 375 nm to 780 nm. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- VLC is known as short-range optical wireless communication. Hence, statement 2 is not correct.
- Li-Fi, a kind of VLC, has a range of approximately 10 meters and it cannot pass through walls or any solid object.
- VLC can transmit large amounts of data faster than Bluetooth. The VLC uses visible light for communication to provide high speed internet up to 10 Gb/s while Bluetooth 4.0 promises speeds up to 25 Mb/s. Hence, statement 3 is correct.
- VLC has no electromagnetic interference. The radio frequency (RF) based signals have the problem of interference with other RF signals such as its interference with pilot navigational equipment signals in aircraft. Therefore, in the areas that are sensitive to electromagnetic radiation (such as aircrafts) VLC can be a better solution. Hence, statement 4 is correct. Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q. Which one of the following is the context in which the term "qubit" is mentioned? (2022)
(a) Cloud Services
(b) Quantum Computing
(c) Visible Light Communication Technologies
(d) Wireless Communication Technologies
Ans: (b)
Explanation:
- Quantum Supremacy
- Quantum computers compute in ‘qubits’ (or quantum bits). They exploit the properties of quantum mechanics, the science that governs how matter behaves on the atomic scale.
- Hence, option (b) is correct.


Important Facts For Prelims
First Sustainability Report of NHAI
Why in News?
The National Highways Authority of India (NHAI) has recently released its first Sustainability Report for FY 2021-22. The report highlights NHAI's governance structure, stakeholders, environment, and social responsibility initiatives.
- The Sustainability Report is prepared as per the Global Reporting Initiative (GRI) guidelines and it will help attract ‘Green Finance’ for Infrastructure financing.
What are the Key Findings of the Report?
- Digitization of Highway Network:
- NHAI has developed ‘Data Lake Tool’ for digitizing the highway network in India, enabling NHAI to manage the vast amount of data generated by its infrastructure effectively.
- Reduced Emissions:
- NHAI has reduced direct emissions and fuel consumption by 18.44% and 9.49%, respectively, from FY 2019-20 till 2021-22.
- GHG emissions from energy consumption, operations, transport, and travel saw a decline of 9.7% in FY 2020-21 and 2% in FY 2021-22.
- Use of Recycled Materials:
- NHAI has been using recycled materials for national highway construction, including fly-ash, plastic waste, recycled asphalt (RAP), and recycled aggregates (RA).
- Wildlife Crossings:
- More than 100 wildlife crossings were created in three years across 20 states as a measure for wildlife protection and conservation to reduce man-animal conflict.
- Plantation:
- NHAI has undertaken plantation drives to develop eco-friendly national highways, planting around 2.74 crore saplings till 2021-22 to offset direct emissions from vehicles.
- Inclusive Workforce:
- Women employment and employment of marginalized communities at NHAI have increased over the last three years.
- There has been a steady increase in female hiring by 7.4% and total increase of 3% in overall work force in three financial years.
What is Global Reporting Initiative?
- GRI is the independent, international organization that helps businesses and other organizations take responsibility for their impacts on environment.
- It enables all companies and organisations to report their economic, environmental, social and governance performance.
- The GRI Secretariat is headquartered in Amsterdam, the Netherlands.
What is National Highways Authority of India?
- About: NHAI was set up under NHAI Act, 1988 under the administrative control of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways (MoRTH).
- Objective: It has been entrusted with the National Highways Development Project (NHDP), along with other minor projects for development, maintenance and management.
- NHDP is a project to upgrade, rehabilitate and widen major highways in India to a higher standard. The project was started in 1998.
- Vision: To meet the nation’s need for the provision and maintenance of National Highways network to global standards and to meet user’s expectations in the most time bound and cost effective manner and promote economic well being and quality of life of the people.
What is National Highways (NH)?
- NH are the arterial roads of the country for inter-state movement of passengers and goods.
- They traverse the length and width of the country connecting the National and State capitals, major ports and rail junctions and link up with border roads and foreign highways.
- According to MoRTH, there are 599 NH in India.
- The longest National Highway is NH44, which runs between Srinagar in Jammu and Kashmir and Kanyakumari in Tamil Nadu, covering a distance of 3,806 km (2,365 mi).
- According to Basic Road Statictics 2018-19, National Highways (Total length-1,32,499 kms) constitutes 2.09 % of total road network in the country and carry about 40% of the road traffic.
- Maharashtra has the largest network of National Highways (13.4%) followed by Uttar Pradesh (8.9 %) and Rajasthan (7.8 %).
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims:
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2014)
National Highway : Cities connected
- NH 4 : Chennai and Hyderabad
- NH 6 : Mumbai and Kolkata
- NH 15 : Ahmedabad and Jodhpur
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (d)
Exp:
- In 2010, GoI replaced the old system of numbering of national highways with a new system. According to the new system:
- NH 4 connects Port Blair with Mayabandar in Andaman Islands. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly
- matched.
- NH 6 connects Jorabat (Meghalaya) with Aizawl (Mizoram). Hence, pair 2 is not correctly matched.
- NH 15 connects Baihata-Charali (Assam) with Wakro (Arunachal Pradesh). Hence, pair 3 is not correctly matched.
- Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.


Important Facts For Prelims
Spotted Pond Turtles
Why in News?
Three persons engaged as mahouts (keepers and drivers of an elephant) in the Kaziranga National Park and Tiger Reserve, Assam, have been arrested for capturing and consuming spotted pond turtles, a rare species of a freshwater turtle.
- The incident has raised concerns about the illegal consumption of protected species by park employees, leading to investigations and arrests.
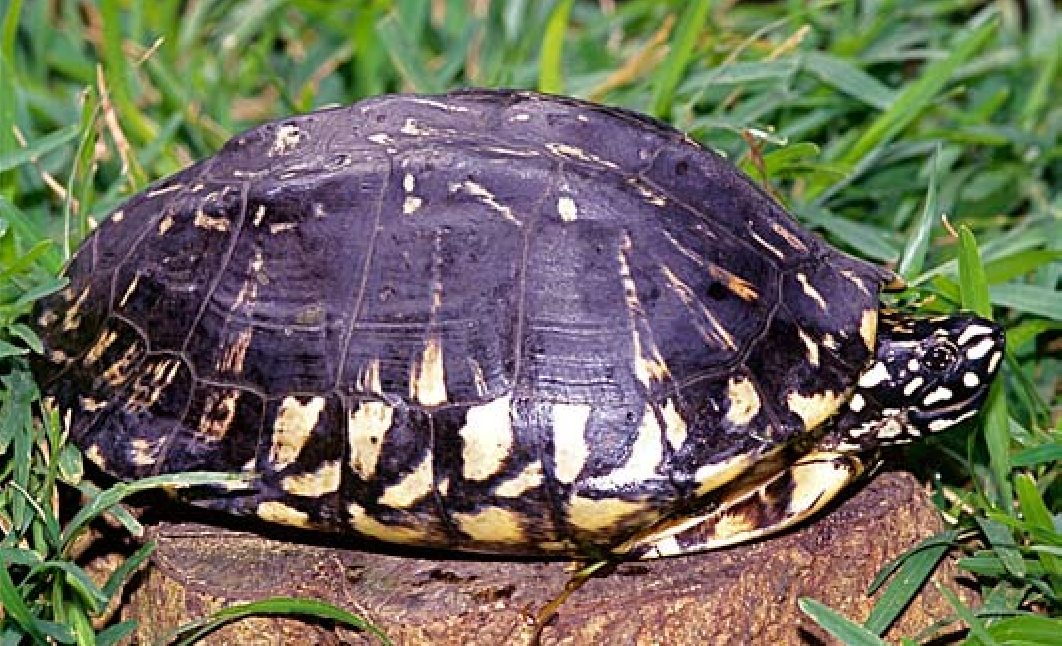
What are Spotted Pond Turtles?
- About: Spotted pond turtles( Geoclemys hamiltonii) are named for the yellow or white spots on their black heads, legs and tails. They have large heads and short snouts, and their webbed feet help them swim.
- They are also known as Black Pond Turtle, Black Spotted Turtle, Hamilton’s Terrapin.
- They bask in the sun to regulate their body temperature. Their need for warm water and an intense basking area is important.
- When they retreat into their shells, spotted pond turtles make a soft croak.
- Range and Habitat: They are found in large, deep rivers in India, Assam, Pakistan and Bangladesh.
- In India, the species is distributed across the north, northeast and a few parts of central India
- Diet Requirements: These turtles are primarily carnivorous and eat aquatic invertebrates.
- Sleep Habits: Spotted pond turtles are crepuscular, meaning they are most active at twilight (dusk and dawn).
- Conservation Status:
- International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) : Endangered
- CITES : Appendix I
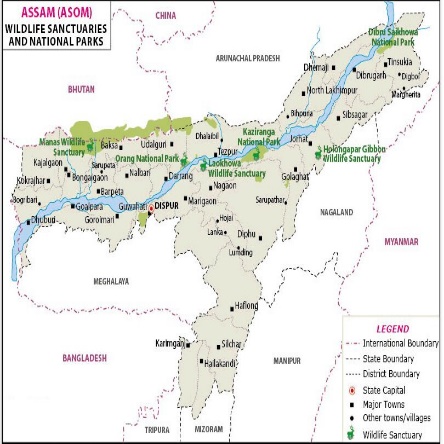
What are the Key Facts about Kaziranga National Park?
- Location: It is in the State of Assam and covers 42,996 Hectare (ha). It is the single largest undisturbed and representative area in the Brahmaputra Valley floodplain.
- Legal Status:
- It was declared as a National Park in 1974.
- It has been declared a tiger reserve since 2007. It has a total tiger reserve area of 1,030 sq km with a core area of 430 sq. km.
- International Status:
- It was declared a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 1985.
- It is recognized as an Important Bird Area by BirdLife International.
- Important Species Found:
- It is the home of the world's most one-horned rhinos. Pobitora Wildlife Sanctuary has the highest density of one-horned rhinos in the world and second highest number of Rhinos in Assam after Kaziranga National Park.
- Much of the focus of conservation efforts in Kaziranga are focused on the 'big four' species— Rhino, Elephant, Royal Bengal tiger and Asiatic water buffalo.
- Kaziranga is also home to 9 of the 14 species of primates found in the Indian subcontinent.
- Rivers and Highways:
- The National Highway 37 passes through the park area.
- The park also has more than 250 seasonal water bodies, besides the Diphlu River running through it.
- Other National Parks in Assam are:
- Dibru-Saikhowa National Park,
- Manas National Park,
- Nameri National Park,
- Rajiv Gandhi Orang National Park.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2013)
| National Park | River flowing through the park | |
| 1. | Corbett National Park | Ganga |
| 2. | Kaziranga National Park | Manas |
| 3. | Silent Valley National Park | Kaveri |
Which of the above pairs is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 3 only
(c) 1 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following fauna of India: (2013)
- Gharial
- Leatherback turtle
- Swamp deer
Which of the above is/are endangered?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 1, 2 and 3
(d) None
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Antardrishti
Recently, the Reserve Bank of India Governor Shaktikanta Das has launched 'Antardrishti', a financial inclusion dashboard aimed at monitoring and evaluating the progress of financial inclusion in India. The primary objective of the dashboard is to assess the current state of financial inclusion by analyzing key metrics and indicators, enabling policymakers and stakeholders to identify areas that require attention and implement targeted interventions. The dashboard presently is intended for internal use in the RBI, it will further facilitate greater financial inclusion through a multi-stakeholder approach.
The development of the Financial Inclusion (FI) Index, introduced by the RBI in 2021, involved collaboration between the government, sectoral regulators, and the central bank. The FI Index provides a comprehensive overview of financial inclusion in India, considering dimensions such as 'Access (35%)', 'Usage (45%) ', and 'Quality (20%) ' across sectors including banking, investments, insurance, postal services, and pensions. This inclusive approach ensures accurate assessment of the progress and challenges in achieving financial inclusion goals, guiding the formulation of policies and initiatives to create a more inclusive financial ecosystem in the country.
Additionally, the index captures information on various aspects of financial inclusion in a single value ranging between 0 and 100, where 0 represents complete financial exclusion and 100 indicates full financial inclusion.
Read more: Financial Inclusion Index
Maiden India-France-UAE Maritime Partnership Exercise
The first edition of India, France, and United Arab Emirates (UAE) Maritime Partnership Exercise commenced on 7th June 2023 in the Gulf of Oman, featuring the participation of INS Tarkash, French Ship Surcouf, French Rafale aircraft, and UAE Navy Maritime Patrol Aircraft. It emphasizes the exchange of best practices and paves the way for greater naval collaboration among India, France, and the UAE.
India and France have established strong cooperation in the defense sector, the two countries regularly conduct joint exercises such as Exercise Shakti, Exercise Varuna, and Exercise Garuda involving their respective army, navy, and air force. Additionally, India has collaborated with France in the construction of six Scorpene submarines through a technology-transfer arrangement in 2005, and France has provided India with 36 Rafale fighter jets under an inter-government agreement.
Additionally, India and the UAE have also established strong cooperation in the defense realm, India and the UAE conduct joint air combat exercises, such as 'Desert Eagle II', to enhance security cooperation and counter terrorist threats.
Read more: India, France, UAE Trilateral Initiative
Agni Prime Ballistic Missile
The recent successful flight test of the new generation ballistic missile, Agni Prime, conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) from Dr A.P.J. Abdul Kalam Island off Odisha marks a significant milestone for India's strategic defence capabilities.
The test involved the deployment of advanced Range Instrumentation such as Radar, Telemetry, and Electro Optical Tracking Systems to capture crucial flight data throughout the vehicle's trajectory, including at the terminal point.
Agni Prime, a two-stage canisterised solid propellant ballistic missile with a range between 1000 to 2000 km, features a dual redundant navigation and guidance system. This technologically advanced missile, which is lighter than its predecessors in the Agni series, plays a vital role in India's nuclear weapons delivery system alongside the Prithvi short-range ballistic missiles and fighter aircraft.
Read more: Agni Prime, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO).
New Appointments in Financial Services Institutions
The Financial Services Institution Bureau (FSIB) has selected N Ramaswamy, the General Manager of General Insurance Corporation of India (GIC Re), as the next Chairman and Managing Director (CMD) of GIC Re, while M Rajeswari Singh, the General Manager and Director of United India Insurance, as the CMD of National Insurance Company (NIC).
FSIB has been constituted in 2022, by Central Government for the purpose of recommending persons for appointment as whole-time directors and non-executive chairpersons on the Boards of financial services institutions and for advising on certain other matters relating to personnel management in these institutions. It replaced Banks Board Bureau (BBB). FSIB is headed by a chairman, a central government nominee. The board comprises the Secretaries of the Department of Financial Services, the chairman of IRDAI, and a deputy governor of the RBI. Additionally, it has three part-time members who are experts in banking and three more from the insurance sector.
Read More: Financial Services Institution Bureau (FSIB)