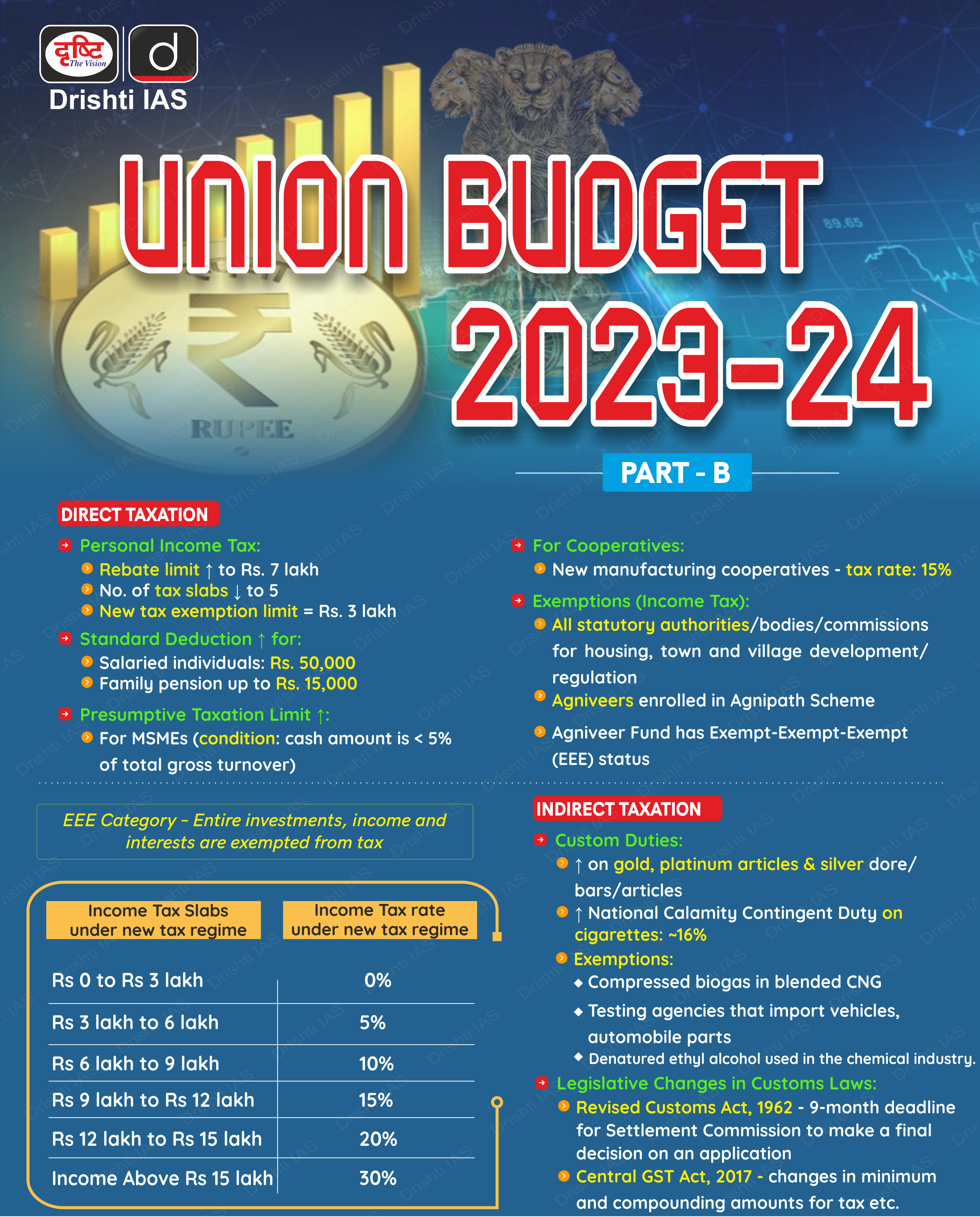
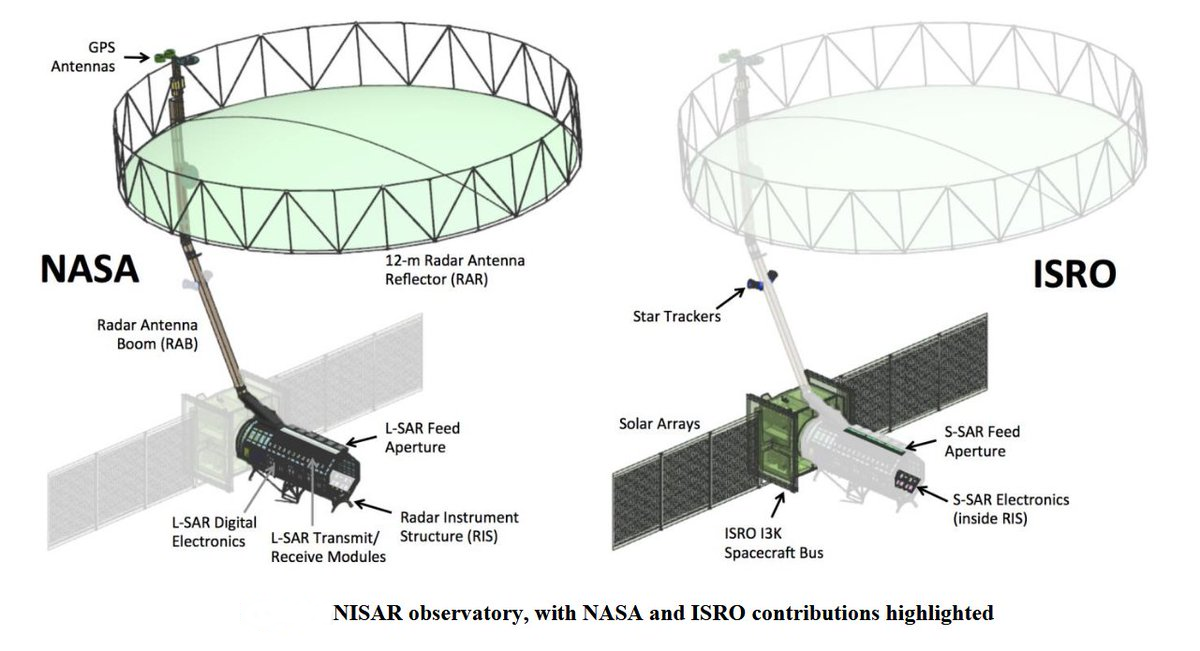
NISAR Mission
Prelims: NASA, ISRO, S band radars, GPS, Synthetic Aperture Radar.
Mains: NISAR Mission, Achievements of Indians in Science & Technology.
Why in News?
Recently, NISAR (NASA-ISRO Synthetic Aperture Radar) has received a send-off ceremony at the NASA’s (National Aeronautics and Space Administration) Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in California, USA.
- NISAR will be the first radar of its kind in space to systematically map Earth, using two different radar frequencies (L-band and S-band) to measure changes in our planet's surface less than a centimeter across.
What is the NISAR Mission?
- About:
- NISAR has been built by space agencies of the US and India under a partnership agreement signed in 2014.
- It is expected to be launched in January 2024 from Satish Dhawan Space Centre into a near-polar orbit.
- The satellite will operate for a minimum of three years.
- It is a Low Earth Orbit (LEO) observatory.
- NISAR will map the entire globe in 12 days.
- Features
- It is a 2,800 kilograms satellite consisting of both L-band and S-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR) instruments, which makes it a dual-frequency imaging radar satellite.
- While NASA has provided the L-band radar, GPS, a high-capacity solid-state recorder to store data, and a payload data subsystem, ISRO (Indian Space Research Organisation) has provided the S-band radar, the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) launch system and spacecraft.
- S band radars operate on a wavelength of 8-15 cm and a frequency of 2-4 GHz. Because of the wavelength and frequency, they are not easily attenuated. This makes them useful for near and far range weather observation.
- It has a 39-foot stationary antenna reflector, made of a gold-plated wire mesh; the reflector will be used to focus “the radar signals emitted and received by the upward-facing feed on the instrument structure.
- By using SAR, NISAR will produce high-resolution images. SAR is capable of penetrating clouds and can collect data day and night regardless of the weather conditions.
- NASA requires the L-band radar for its global science operations for at least three years. Meanwhile, ISRO will utilise the S-band radar for a minimum of five years.
What are the Expected Benefits of NISAR?
- Earth Science: NISAR will provide a wealth of data and information about the Earth's surface changes, natural hazards, and ecosystem disturbances, helping to advance our understanding of Earth system processes and climate change.
- Disaster Management: The mission will provide critical information to help manage natural disasters such as earthquakes, tsunamis, and volcanic eruptions, enabling faster response times and better risk assessments.
- Agriculture: NISAR data will be used to improve agriculture management and food security by providing information about crop growth, soil moisture, and land-use changes.
- Infrastructure Monitoring: The mission will provide data for infrastructure monitoring and management, such as monitoring of oil spills, urbanization, and deforestation.
- Climate Change: NISAR will help to monitor and understand the impacts of climate change on the Earth's land surface, including melting glaciers, sea-level rise, and changes in carbon storage.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q1. What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q2. Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology has helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)
International Marine Protected Areas Congress
Prelims: Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity, CCAMLR, Marine Protected Areas in India.
Mains: Marine Protected Areas.
Why in News?
Recently, the 5th International Marine Protected Areas Congress (IMPAC5) was held in Canada in order to discuss the solutions to address the Funding Gap of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs).
- This meeting is crucial since nations agreed to protect 30% of Earh’s lands and oceans by 2030 at the 15th Conference of the Parties to the Convention on Biological Diversity held in 2022.
Note: Canada is bordered by three oceans - the Pacific, Arctic and Atlantic - and has the longest coastline in the world.
What are the Highlights of the Meet?
- Sustainable and Resilient MPA networks:
- As many as 70% of MPAs are underfunded. A well-managed and sufficiently funded MPA can restore good health to vulnerable ecosystems.
- Achieving sustainable and resilient MPA networks depends on an overall commitment to protection, leadership, engagement from stakeholders, institutions, governments and organizations, Indigenous peoples, coastal communities, and individuals in an inclusive and equitable manner to advance ocean protection.
- IMPAC5 aims to provide a forum for sharing knowledge, successes and best practices in an open and respectful environment for the exchanging of ideas among a diversity of views.
- Significance of MPAs:
- MPAs can generate sustainable revenues for their own management.
- Revenue can be generated from statutory and non-statutory MPA fees for tourism programmes, blue carbon credits generated from mangrove conservation and avoided deforestation as well as seaweed farming and sustainable coastal fisheries.
What are Marine Protected Areas?
- About:
- MPAs are designated areas of the ocean that are set aside for the protection and conservation of marine ecosystems and their biodiversity.
- Within the region, certain activities are limited, or entirely prohibited, to meet specific conservation, habitat protection, ecosystem monitoring or fisheries management objectives.
- MPAs do not necessarily exclude fishing, research or other human activities; in fact, many MPAs are multi-purpose areas.
- Need for Establishing MPAs:
- Biodiversity Conservation:
- MPAs help to conserve the diversity of marine species and their habitats, preserving the delicate balance of marine ecosystems and the services they provide, such as food and oxygen production.
- Sustainable Fisheries:
- MPAs can help to regulate fishing activities and prevent overfishing, ensuring that fish populations are able to recover and remain healthy, which in turn supports sustainable fishing practices.
- Climate Change Mitigation:
- MPAs can serve as carbon sinks, helping to absorb and store carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and mitigate the impacts of climate change on marine ecosystems.
- Research and Education:
- MPAs can provide valuable opportunities for scientific research and educational activities, helping to increase our understanding of the marine environment and promote ocean literacy.
- Economic Benefits:
- MPAs can contribute to local economies by attracting tourists, providing opportunities for sustainable tourism and recreation, and supporting local fishing communities.
- Biodiversity Conservation:
- Treaties, Conventions and Agreements:
- Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area:
- It specifically aims to establish a network of 'specially protected areas to conserve cetaceans. It prohibits the deliberate killing of cetaceans in national waters.
- Bern Convention:
- Formulated under the aegis of the European Community Council in 1979, it has been in force since 1982 and covers European states.
- CITES:
- Formulated under UNEP in 1973, Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES) has been in force since 1975 and has worldwide application. CITES regulates international trade of species listed on three appendices.
- EU Habitats Directive:
- Formulated by the European Community Council in 1992, the EU Habitats Directive applies to all EU states, including the Azores and Madeira (part of Portugal) and the Canary Islands.
- CCAMLR:
- Commission for the Conservation of Antarctic Marine Living Resources (CCAMLR) is a multilateral response to concerns that unregulated increases in krill catches in the Southern Ocean could be detrimental for Antarctic marine ecosystems particularly for seabirds, seals, whales and fish that depend on krill for food.
- Agreement on the Conservation of Cetaceans of the Black Sea, Mediterranean Sea and Contiguous Atlantic Area:
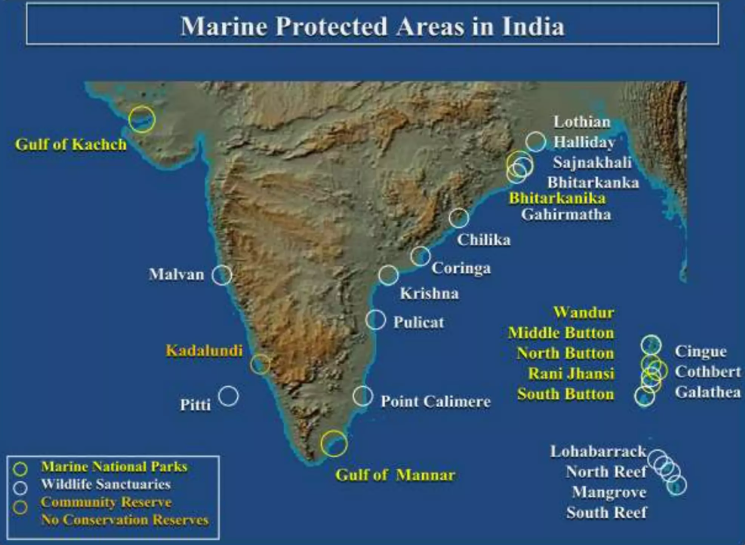
What are the Marine Protected Areas in India?
- In India, there are 33 national parks and wildlife sanctuaries designated under the Wildlife (Protection) Act of 1972 that make up the country's MPAs.
- Marine National Park and Marine Sanctuary in the Gulf of Kutch form one unit and Bhitarkanika National Park and Bhitarkanika Sanctuary are an integral part of one MPA. Thus, there a total of 31 MPAs in India.
- MPAs cover less than 4.01% of the total area of all Protected Areas of India.
What is IMPAC?
- IMPAC congresses are a collaborative effort between the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN) and the chosen host country.
- The congress brings together scientists, policy makers, practitioners, and stakeholders from around the world to discuss the latest scientific knowledge, best practices and challenges in the management of MPAs.
- The goal of IMPAC is to advance the conservation and sustainable use of the world's marine biodiversity and to support the implementation of the United Nations Convention on Biological Diversity's goals for marine conservation and management.
NCAER Report on Farm Machinery Industry in India
For Prelims: Farm Machinery Industry, Farm power, Science & Technology (S&T) Cluster programme, Make in India, Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization Scheme.
For Mains: Major Challenges Related to the Farm Machinery Industry, Ways to Revitalise Farm Machinery Industry.
Why in News?
National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER) Report on "Making India a Global Power House on Farm Machinery Industry" released recently.
- NCAER has analysed the non-tractor farm machinery industry from both demand and supply side perspectives, bringing out the challenges in the sector, and recommending measures & reforms by benchmarking global practices.
What is the Farm Machinery Industry?
- The Farm Machinery Industry is an industry sector that produces and supplies a range of machinery, equipment, and tools used in agriculture and farming activities such as ploughing, planting, harvesting, and more.
- These machines are designed to improve productivity and efficiency in farming operations, and the industry encompasses both small-scale and large-scale farming equipment.
- Some examples of products offered by this industry include tractors, combine harvesters, irrigation systems, tillers, and more.
What are the Major Challenges Related to the Farm Machinery Industry?
- Limited Domestic Demand:
- There is a mismatch between what the organised farm machinery sector produces and the needs of small and marginal Indian farmers.
- Although there is high State-level variation, in 2018–19 barely 4.4% of farmer households in India owned a tractor, 2.4 % used a power tiller and 5.3 % owned one of the four machinery items.
- Dependence on Imports for Non-Tractor Machinery:
- Farm machinery exports are driven by the tractors, and farm machinery imports are driven by non-tractor farm machinery imports.
- Further, the direction of trade is lopsided where 53% of non-tractor farm machinery imports are coming from China.
- Lack of Adequate Power:
- With the increase in intensity of cropping, the turnaround time is drastically reduced. Availability of adequate farm power is very crucial for timely farm operations for increasing production and productivity and reducing losses.
- However, our farm power availability is at 2.49 Kw/ha in 2018-19 which is much lower as compared to Korea (+7 kw/ha), Japan (+14kw/ha), USA(+7kw/ha)
How can the Farm Machinery Industry be Revitalized?
- Encourage Local Innovation:
- Entrepreneurship ecosystems should be created and encouraged in local education institutes; they may also partner with farm machinery firms.
- For help on patents, district-level patent offices need to be opened and strengthened and state agricultural universities’ patent offices need to cater to the needs of local communities.
- Research-linked incentive (RLI) is also recommended for innovations in light farm machinery and futuristic precision farming.
- Non-tractor Farm Machinery Cluster:
- There is a need to set up a non-tractor farm machinery Science & Technology Cluster under the aegis of the Science & Technology (S&T) Cluster programme.
- Level-playing Field for Indian Manufacturers:
- Given the unfair competition that Indian manufacturers face, it should be mandated that farm machinery that is sold under government subsidy on government DBT portals (both Central and State) follow the revised public procurement norms with regard to preference to ‘Make in India’ goods.
- Localisation should be promoted by simultaneously maintaining international quality standards.
- Vision for Export Hub:
- The Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare is already promoting farm mechanization through various schemes and programmes like the Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization Scheme. But India needs a vision for the next 15 years to translate itself into a production and export hub for the non-tractor farm machinery.
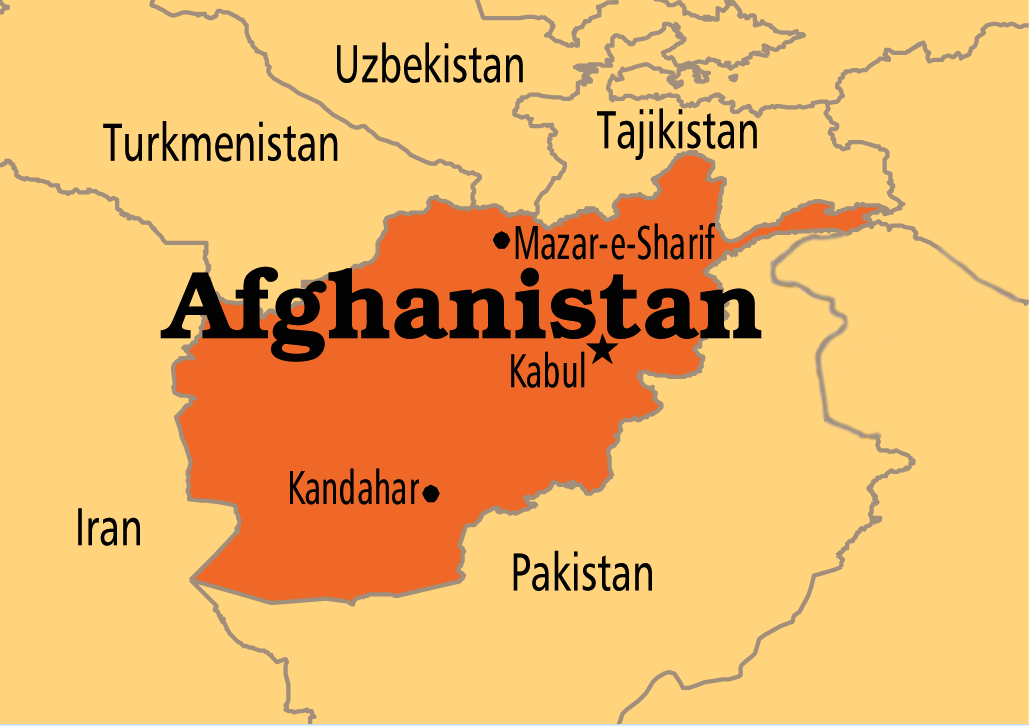
Multilateral Security Dialogue on Afghanistan
For Prelims: National Security Advisor, Multilateral Security Dialogue on Afghanistan, UN Security Council resolution 2593, Terrorism, Chabahar port.
For Mains: Significance of Afghanistan for India, India-Afghanistan Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, the National Security Advisor(NSG) addressed a Multilateral Security Dialogue on Afghanistan in Moscow.
- The discussion revolved around issues related to Afghanistan, including security and humanitarian challenges and was attended by representatives from various countries including Russia, China, and Iran.
What are Key Highlights of the Dialogue?
- NSG emphasized that no country should be allowed to use Afghan territory for exporting terrorism and that India will always support the people of Afghanistan in their time of need.
- NSG also spoke about the importance of UN Security Council resolution 2593 that calls for denying sanctuary to terror outfits in the region.
How is India’s Relations with Afghanistan?
- About:
- India and Afghanistan have had close historical, cultural, and economic ties for centuries.
- The relationship between the two countries has undergone significant changes in the post-9/11 era, with India playing an increasingly active role in the reconstruction and development of Afghanistan.
- Political Relations:
- India has been a strong supporter of Afghan democracy and has consistently advocated for a stable, peaceful, and prosperous Afghanistan.
- But India is still yet to recognize the Taliban regime in Afghanistan and has been advocating for the formation of an inclusive government in Kabul.
- Also, India re-established its diplomatic presence in Kabul in June 2022.
- India has been a strong supporter of Afghan democracy and has consistently advocated for a stable, peaceful, and prosperous Afghanistan.
- Humanitarian Assistance:
- India has been providing humanitarian aid to Afghanistan, including 40,000 metric tonnes of wheat, 60 tonnes of medicines, 5,00,000 Covid vaccines, winter clothing, and 28 tonnes of disaster relief.
- India has also granted scholarships to 2,260 Afghan students, including 300 girls, over the past two years.
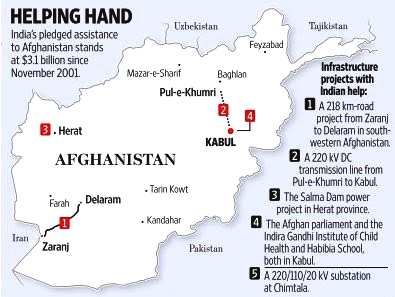
- Economic Relations:
- India has undertaken more than 400 key infrastructure projects in all 34 Afghan provinces and has signed strategic agreements to enhance trade and bilateral relations.
- From 2002 to 2021, India spent USD 4 billion in development assistance in Afghanistan, building high-visibility projects such as highways, hospitals, the parliament building, rural schools, and electricity transmission lines.
- India has undertaken more than 400 key infrastructure projects in all 34 Afghan provinces and has signed strategic agreements to enhance trade and bilateral relations.
- Connectivity:
- India has been working towards building regional connectivity with Afghanistan by developing the Chabahar port and providing access to markets in the region.
What is the Significance of Afghanistan for India?
- Geopolitical Location: Afghanistan is located at the crossroads of Central and South Asia, and its stability and security have a direct impact on India's interests in the region.
- Afghanistan serves as a bridge between South and Central Asia and is critical for India's pursuit of regional connectivity and economic integration.
- Countering Terrorism:
- Afghanistan has been a hotbed of terrorism, with various terrorist groups operating from its territory.
- India has a direct interest in ensuring that Afghanistan does not become a safe haven for terrorists who threaten its security.
- Afghanistan has been a hotbed of terrorism, with various terrorist groups operating from its territory.
- Strategic Interests:
- Afghanistan is important to India's strategic interests as it is located at the heart of the historic Silk Road.
- India's presence in Afghanistan helps to counterbalance the influence of Pakistan and China in the region.
- Afghanistan is important to India's strategic interests as it is located at the heart of the historic Silk Road.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following countries: (2022)
- Azerbaijan
- Kyrgyzstan
- Tajikistan
- Turkmenistan
- Uzbekistan
Which of the above have borders with Afghanistan?
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. The proposed withdrawal of the International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) from Afghanistan in 2014 is fraught with major security implications for the countries of the region. Examine in light of the fact that India is faced with a plethora of challenges and needs to safeguard its own strategic interests. (2013)
CAR T-cell Therapy
Why in News?
The main treatments for cancer are surgery, radiotherapy and systemic therapy.
- Surgery and radiotherapy have improved over time, but advances in systemic therapy have been particularly impressive, with Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy being a recent breakthrough attracting global attention.
What are the Major Interventions in Systemic Therapy for Cancer Treatment?
- Systemic therapy began with chemotherapy, which attacks cancer cells due to their fast growth.
- Chemotherapy drugs have limited success and significant side effects because they affect many types of cells in the body.
- The next advancement was targeted agents, also known as immunotherapy, which work by binding to specific targets on the cancer or immune cells supporting its growth.
- This approach is less toxic as it affects fewer non-tumor cells, but only works on tumours that have these targets.
What is CAR T-cell Therapy?
- About:
- CAR T-cell therapies are a major breakthrough in cancer treatment.
- Unlike chemotherapy or immunotherapy which involve taking drugs, CAR T-cell therapies use a patient's own cells. They are modified in the laboratory to activate T-cells and target tumor cells.
- CAR T-cell therapy has been approved for leukaemias (cancers arising from the cells that produce white blood cells) and lymphomas (arising from the lymphatic system).
- CAR T-cell therapies are a major breakthrough in cancer treatment.
- Procedure:
- T cells are taken from a patient’s blood and then the gene for a special receptor that binds to a certain protein on the patient’s cancer cells is added to the T cells in the laboratory.
- The special receptor is called a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR). Large numbers of the CAR T cells are grown in the laboratory and given to the patient by infusion.
- T cells are taken from a patient’s blood and then the gene for a special receptor that binds to a certain protein on the patient’s cancer cells is added to the T cells in the laboratory.
- Significance:
- CAR T-cell therapies are even more specific than targeted agents and directly stimulate the patient's immune system to fight cancer, leading to greater clinical efficacy.
- That's why they're referred to as "living drugs."
- CAR T-cell therapies are even more specific than targeted agents and directly stimulate the patient's immune system to fight cancer, leading to greater clinical efficacy.
- Challenges:
- Preparation:
- The difficulty of preparing CAR T-cell therapies has been a major hindrance to their widespread use.
- The first successful clinical trial was published a decade ago, and the first indigenously developed therapy in India was performed in 2021.
- Side Effects:
- In certain kinds of leukaemias and lymphomas, the efficacy is as high as 90%, whereas in other types of cancers it is significantly lower.
- The potential side-effects are also significant, associated with cytokine release syndrome (a widespread activation of the immune system and collateral damage to the body’s normal cells) and neurological symptoms (severe confusion, seizures, and speech impairment).
- Preparation:
- Affordability:
- Introduction of CAR T-cell therapy in India can face challenges of cost and value.
- Critics argue that developing CAR T-cell therapy in India may not be cost-effective as it will still be unaffordable for most people.
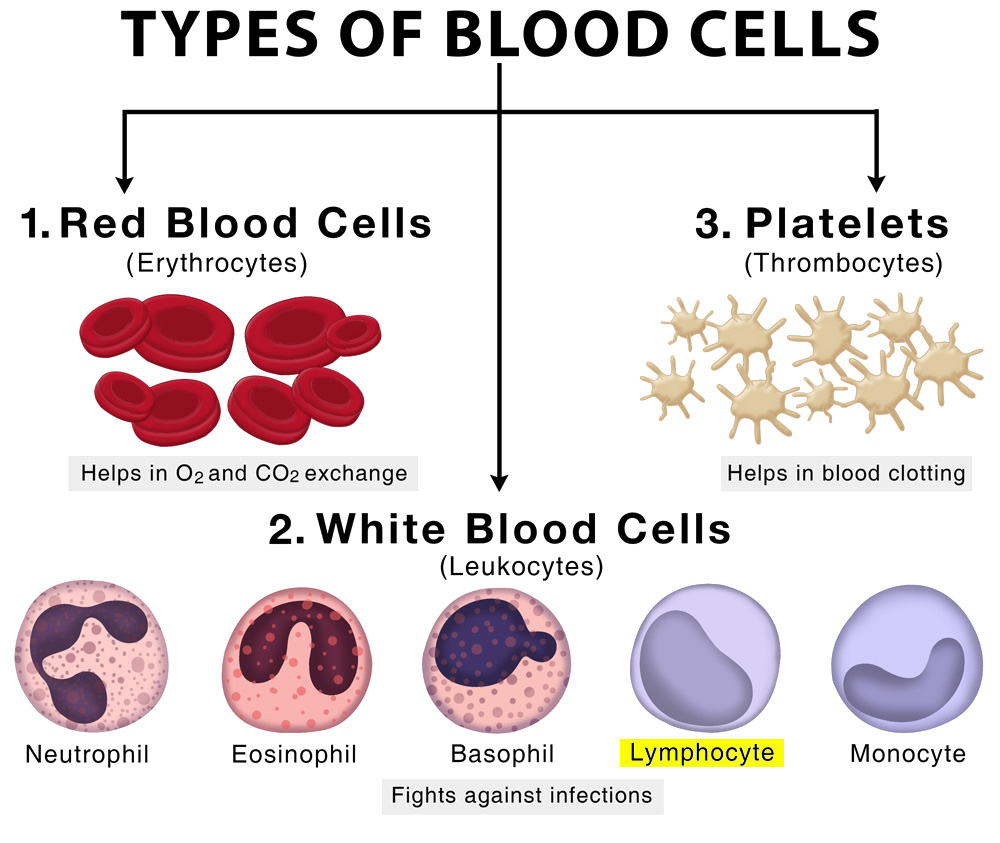
What are T Cells?
- T cells, also known as T lymphocytes, are a type of white blood cell that play a central role in the immune response.
- T cells are involved in cell-mediated immunity, which means they help the body recognize and respond to foreign substances, such as viruses, bacteria, and abnormal cells, such as cancer cells.
- There are two major types of T cells: the helper T cell and the cytotoxic T cell.
- As the names suggest, helper T cells ‘help’ other cells of the immune system, whilst cytotoxic T cells kill virally infected cells and tumors.
What are the Government Initiatives Related to Cancer Treatment?
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which one of the following statements best describes the role of B cells and T cells in the human body?(2022)
(a) They protect the environmental allergens. body
(b) They alleviate the body’s pain and inflammation.
(c) They act as immunosuppressants in the body.
(d) They protect the body from the diseases caused by pathogens.
Ans: (d)
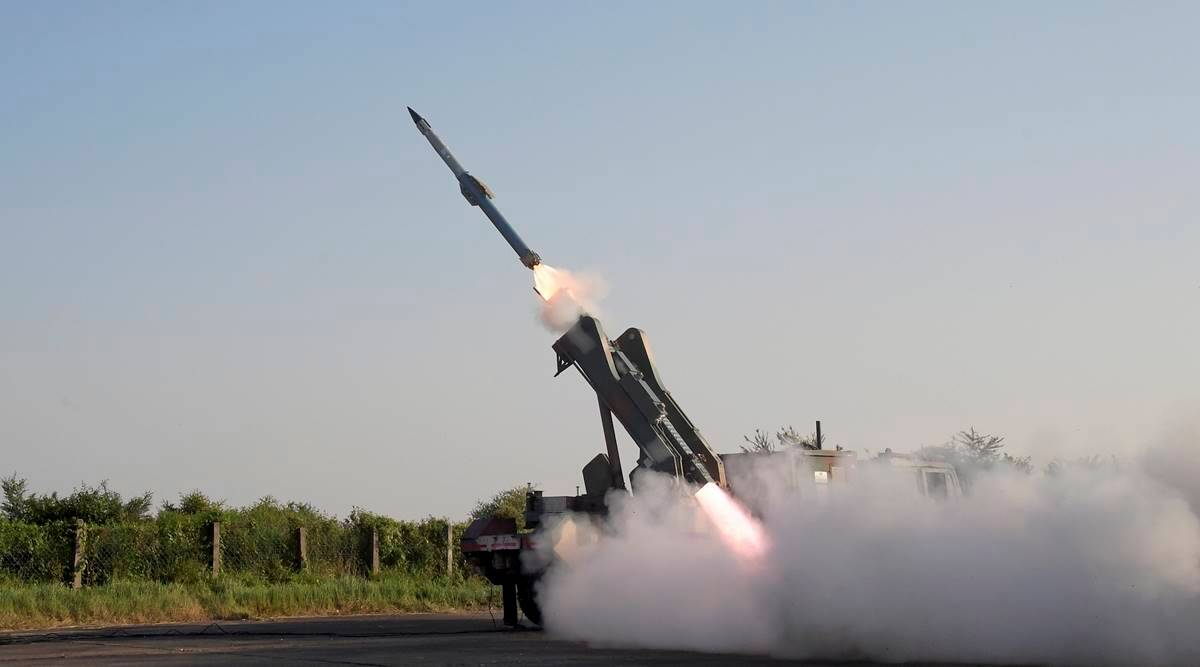
Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile System
Why in News?
Indigenous Quick Reaction Surface to Air Missile (QRSAM) being developed by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) is set to be tested again in April 2023.
- And a Medium Range SAM is being developed by the DRDO in collaboration with Israel Aerospace Industries (IAI). The maiden launch of MRSAM Army Version was conducted in December 2020 and its induction is on and is ready for deployment.
What is QRSAM?
- About:
- QRSAM is a canister-based system, which means that it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- In the canister, the inside environment is controlled, thus along with making its transport and storage easier, the shelf life of weapons also improves significantly.
- The system is capable of detecting and tracking targets on the move and engaging targets with short halts.
- QRSAM is a canister-based system, which means that it is stored and operated from specially designed compartments.
- Range and Mobility:
- It is a short-range surface-to-air missile (SAM) system, primarily designed and developed by DRDO to provide a protective shield to moving armoured columns of the Army from enemy aerial attacks.
- The entire weapon system has been configured on a mobile and manoeuvrable platform and is capable of providing air defence on the move.
- It has been designed for induction into the Army and has a range of 25 to 30 km.
- Functioning:
- The QRSAM weapon ensemble consists of a fully automated command and control system.
- It also consists of two radars - Active Array Battery Surveillance Radar and Active Array Battery Multifunction Radar - with one launcher.
- Both radars have 360-degree coverage with “search on move” and “track on move” capabilities.
- The system is compact, uses a single stage solid propelled missile and has a mid-course inertial navigation system with two-way data link and terminal active seeker developed indigenously by DRDO.
- The QRSAM weapon ensemble consists of a fully automated command and control system.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Years Questions (PYQs)
Q1. What is “Terminal High Altitude Area Defense (THAAD)”, sometimes seen in the news? (2018)
(a) An Israeli radar system
(b) India’s indigenous anti-missile programme
(c) An American anti-missile system
(d) A defence collaboration between Japan and South Korea
Ans: (c)
Exp:
- Terminal High Altitude Area Defence (THAAD) is an American anti-missile system designed to intercept and destroy short and medium-range ballistic missiles during their “terminal” phase of flight when they are falling towards the target.
- They have the ability to intercept missile inside and outside the atmosphere.
- It is interoperable with other ballistic missile defence systems and is highly mobile and deployable worldwide.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Q2. With reference to Agni-IV Missile, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2014)
- It is a surface-to-surface missile.
- It is fuelled by liquid propellant only.
- It can deliver one-tonne nuclear warheads about 7500 km away.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Agni-IV is a nuclear-capable long-range ballistic missile of India, with a strike range of 4,000 km.
- The indigenously developed Agni-IV is a two-stage surface-to-surface missile. It is 20 metres long with a weight of 17 tonnes. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- It is a two stage solid fuelled system that can carry a one-tonne nuclear warhead over a distance of 4,000 kilometres. Hence, statements 2 and 3 are not correct.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Amrit Sarovar Mission
Why in News?
A target of 50,000 Amrit Sarovars was set to be completed by August 15, 2023. So far, 60% of the target has been achieved with over 30,000 Amrit Sarovars constructed in the span of 9 months.
What is the Amrit Sarovar Mission?
- About:
- On April 24, 2022, Mission Amrit Sarovar was launched as part of India's "Azadi Ka Amrit Mahotsav" celebrations for the 75th year of independence.
- The mission aims to construct/rejuvenate at least 75 Amrit Sarovars in each district across India to overcome the water crisis in rural areas.
- Major Features of Mission Amrit Sarovar:
- Whole of the Government Approach:
- Six central government Ministries are working together in conjunction with technical organisations like Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geo-Informatics (BISAG-N) and state/union territory governments in a "Whole of Government" approach.
- Six ministries are Ministry of Rural Development, Ministry of Jal Shakti, Ministry of Culture, Ministry of Panchayati Raj, Ministry of Environment, Forest & Climate Change.
- Six central government Ministries are working together in conjunction with technical organisations like Bhaskaracharya National Institute of Space Applications and Geo-Informatics (BISAG-N) and state/union territory governments in a "Whole of Government" approach.
- Jan Bhagidari:
- It has been the core of this Mission and involves people’s participation at all levels.
- States/UTs are leveraging the participation of freedom fighters, eldest members of the panchayat, family members of freedom fighters and martyrs, Padma Awardees, etc.
- Innovative Measures:
- The Ministries of Railways and Road Transport and Highways are using the excavated soil/silt for infrastructure projects near the Amrit Sarovar sites.
- Also, Public and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) bodies are playing a significant role in the construction and rejuvenation of several Amrit Sarovars across India.
- Boosting Rural Livelihood:
- The completed Sarovars are boosting rural livelihoods by being used for activities such as irrigation, fisheries, duckery, cultivation of water chestnut and animal husbandry, among others.
- These activities are carried out by different user groups linked to each Amrit Sarovar.
- The completed Sarovars are boosting rural livelihoods by being used for activities such as irrigation, fisheries, duckery, cultivation of water chestnut and animal husbandry, among others.
- Whole of the Government Approach:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Which of the following best describes/describe the aim of ‘Green India Mission’ of the Government of India? (2016)
- Incorporating environmental benefits and costs into the Union and State Budgets thereby implementing the ‘green accounting’.
- Launching the second green revolution to enhance agricultural output so as to ensure food security to one and all in the future.
- Restoring and enhancing forest cover and responding to climate change by a combination of adaptation and mitigation measures.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Quad Cyber Challenge
The Quad Nations are launching Quad Cyber Challenge - a public campaign to improve cyber security across the 4 nations. The Internet-users are being invited across the Indo-Pacific and beyond to join the Challenge and pledge to practice safe and responsible cyber habits.
(India’s National Cyber Security Coordinator with National Security Council Secretariat is the coordinating body in this challenge.
Internet-users worldwide are targets of cybercrime and other malicious cyber threats that can cost trillions of dollars each year and compromise sensitive, personal data. Many successful cyber-attacks can be guarded against by simple preventative measures such as; routinely installing security updates, utilising stronger and regularly changing passwords, and awareness of common online scams, like phishing.
QUAD is the grouping of four democracies –India, Australia, the US, and Japan that aims to ensure and support a “free, open and prosperous” Indo-Pacific region.
Read More - Quad, Cyber Security
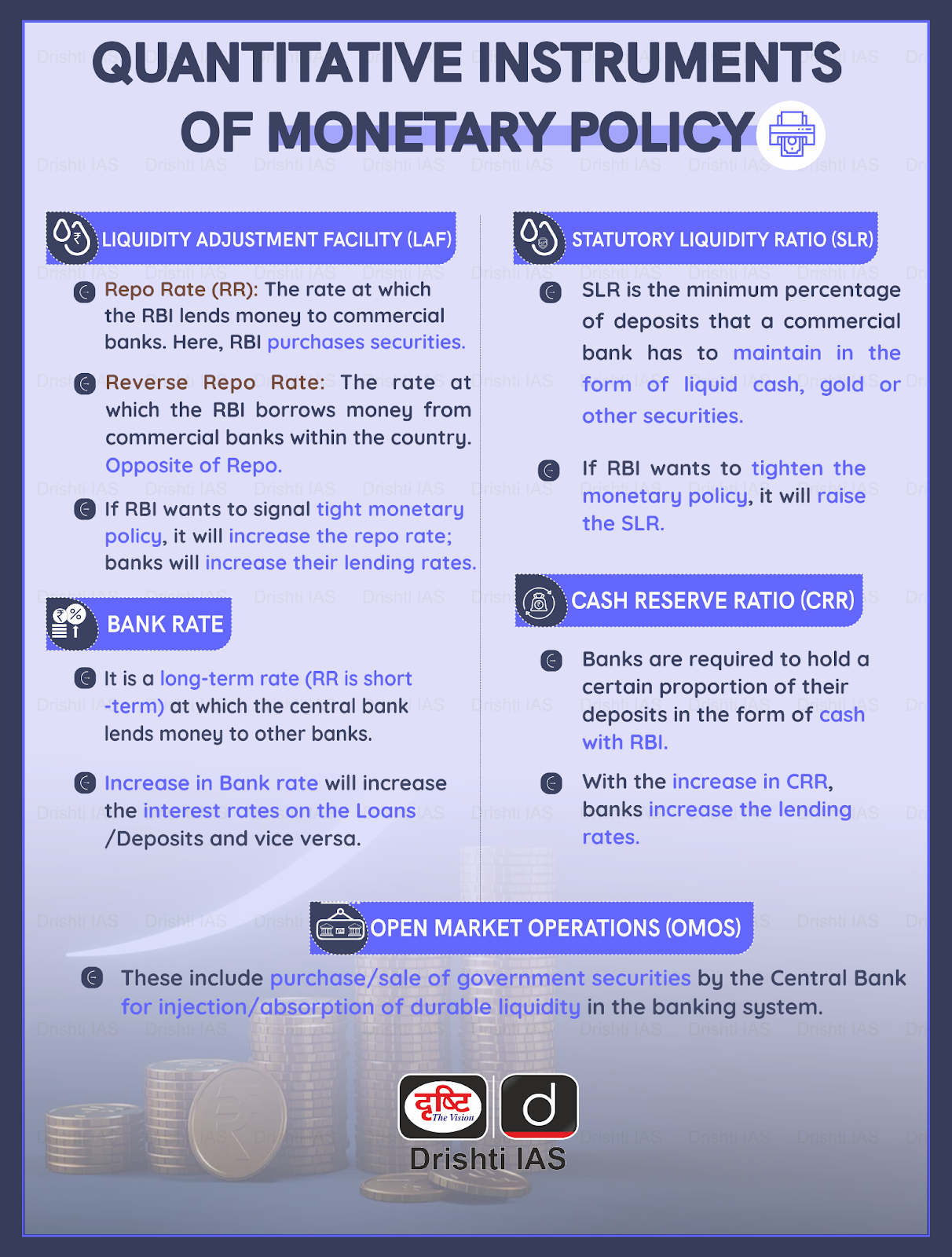
RBI Hikes Repo Rate
In a move to further increase the lending/deposit rates, the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) raised the repo rate by 25 bps to 6.5% - 6th rate hike in a row.
In the last meeting for the current fiscal (2022-23), the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) projected the real GDP growth at 6.4% (for FY 23-24).
Repo Rate is the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks.
Read More - Monetary Policy Committee (Infographic)
Israel’s Sniffing Robot with Locust Antennae
The scientists in Israel have developed a new sniffing robot equipped with a biological sensor that uses the antennae of locusts (locusts smell with their antennae and have an acute sense of smell).
This makes the robot far more sensitive than existing electronic sniffers and helpful in advance disease diagnosis and better security checks.
The researchers placed the insect’s antenna between two electrodes on the robot that send electrical signals as a response to a nearby odour. The robot is able to identify different scents with machine learning.
Read More - Locust, Machine Learning
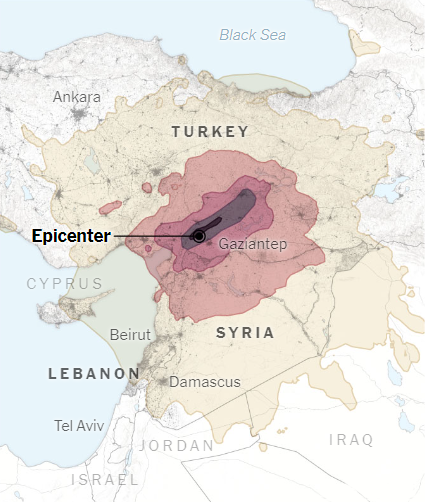
Operation Dost
India, under ‘Operation Dost’ has sent its sixth plane carrying National Disaster Response Force (NDRF) personnel, essentials, and medical equipment for the earthquake-hit Turkey. The 6th flight carries more rescue teams, dog squads, and essential medicines. A field hospital under Operation Dost has been set up by the Indian Army in Hatay province of Turkey. India has also sent a transport aircraft with medical supplies to Syria.
The earthquake of magnitude 7.7 on the Richter scale hit Turkey and Syria on 6 Feb 2023 followed by a series of aftershocks causing huge devastation, major loss of lives and damage to infrastructure in the two countries.
Operation Dost symbolises that India is a friend of Turkey and the two must deepen their relations.
Earlier, the NDRF was sent to two similar international operations – the 2011 Japan triple disaster (earthquake, tsunami and nuclear meltdown) and the 2015 Nepal earthquake.
Read More - India-Turkey Relations, India's Humanitarian Assistance