Infographics
Governance
PRITHvi VIgyan Scheme
For Prelims: PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI) Scheme, ACROSS Scheme, O-SMART Scheme, PACER
For Mains: Earth System Sciences, Modeling systems for understanding climate change science, Government Policies, Disaster Management
Why in News?
The Union Cabinet recently approved the comprehensive scheme "PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI)" by the Ministry of Earth Sciences.
- This initiative spans five sub-schemes, aiming to enhance Earth System Sciences and provide crucial services for societal, environmental, and economic well-being.
- The Cabinet also approved an agreement between the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and Mauritius Research and Innovation Council (MRIC) to jointly develop a “small satellite.”
Note
- India and Mauritius have a history of cooperation since the 1980s when ISRO established a ground station in Mauritius for tracking and telemetry support for ISRO’s launch vehicle and satellite missions.
What is the "PRITHvi VIgyan (PRITHVI)" Scheme?
- About:
- It is an overarching scheme of the Ministry of Earth Sciences (MoES) for the period from 2021 to 2026.
- It encompasses five ongoing sub-schemes, namely:
- ACROSS: Atmosphere and Climate Research-Modelling Observing Systems & Services.
- O-SMART: Ocean Services, Modelling Application, Resources and Technology.
- PACER: Polar Science and Cryosphere Research.
- SAGE: Seismology and Geosciences
- The scheme includes six activities, including seismological monitoring and microzonation. SAGE aims to strengthen earthquake monitoring and research on the Earth's solid components.
- REACHOUT: Research, Education, Training and Outreach.
- PRITHVI scheme comprehensively addresses the five components of Earth System Sciences: atmosphere, hydrosphere, geosphere, cryosphere, and biosphere.
- This holistic approach aims to enhance understanding and deliver reliable services for the country.
- Objectives:
- To augment and sustain long-term observations of the atmosphere, ocean, geosphere, cryosphere and solid earth to record the vital signs of the Earth System and change
- Development of modelling systems for understanding and predicting weather, ocean and climate hazards and understanding the science of climate change.
- Exploration of polar and high seas regions of the Earth towards discovery of new phenomena and resources;
- Development of technology for exploration and sustainable harnessing of oceanic resources for societal applications.
- Translation of knowledge and insights from Earth systems science into services for societal, environmental and economic benefit.
- Benefits for India:
- PRITHVI provides advanced warning services for natural disasters like cyclones, floods, heatwaves, and earthquakes, facilitating prompt and effective disaster management.
- Additionally, the scheme ensures precise weather forecasts for both land and oceans, enhancing safety and minimizing property damages in adverse weather conditions.
- PRITHVI extends its reach to explore the three poles of the Earth; Arctic, Antarctic, and Himalayas facilitating valuable insights and knowledge about these regions.
- The scheme encourages the development of technology for exploration and sustainable harnessing of oceanic resources, aligning with modern advancements in Earth Science.
- PRITHVI provides advanced warning services for natural disasters like cyclones, floods, heatwaves, and earthquakes, facilitating prompt and effective disaster management.


Indian Polity
Supreme Court Legal Services Committee
For Prelims: Supreme Court Legal Services Committee, Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, Supreme Court, National Legal Services Authority (NALSA), State Legal Services Authorities (SLSA).
For Mains: Supreme Court Legal Services Committee, Legal Services Authority Act, 1987.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court judge Justice BR Gavai has been nominated as the Chairman of the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee (SCLSC).
What is the Supreme Court Legal Services Committee?
- Background:
- The idea of a legal aid programme was earlier floated in the 1950s, it was in 1980 that a committee at the national level was established under the chairmanship of then SC judge Justice PN Bhagwati.
- The Committee for Implementing Legal Aid Schemes started monitoring legal aid activities throughout India.
- About:
- The SCLSC was constituted under Section 3A of the Legal Services Authorities Act, 1987, to provide “free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of society”, in cases falling under the top court’s jurisdiction.
- Section 3A of the Act states that the National Legal Services Authority (NALSA) shall constitute the committee.
- It consists of a sitting SC judge, who is the chairman, along with other members possessing the experience and qualifications prescribed by the Centre. Both the chairman and other members will be nominated by the CJI (Chief Justice of India).
- Further, the CJI can appoint the Secretary to the Committee.
- Members:
- The SCLSC consists of a chairperson and nine members nominated by the CJI. The Committee, in turn, can appoint officers and other employees as prescribed by the Centre, in consultation with the CJI.
- Besides this, Rule 10 of the NALSA Rules, 1995, entails the numbers, experience, and qualifications of the SCLSC members.
- Under Section 27 of the 1987 Act, the Centre is empowered to make rules in consultation with the CJI, by notification, to carry out the provisions of the Act.
What is the Legal Services Authority Act, 1987?
- About:
- In 1987, the Legal Services Authorities Act was enacted to give a statutory base to legal aid programmes. It aims to provide free and competent legal services to eligible groups, including women, children, SC (Scheduled Castes)/ST (Scheduled Tribes) and EWS (Economically Weaker Section) categories, industrial workers, disabled persons, and others.
- NALSA:
- Under the Act, NALSA was constituted in 1995 to monitor and evaluate the implementation of legal aid programmes and to lay down policies for making legal services available.
- A nationwide network has been envisaged under the Act for providing legal aid and assistance.
- It also disburses funds and grants to State Legal Services Authorities and NGOs for implementing legal aid schemes and programmes.
- State Legal Services Authorities:
- Subsequently, in every state, State Legal Services Authorities (SLSA) were established to implement NALSA’s policies and directions, give free legal services to people, and conduct Lok Adalats.
- An SLSA is headed by the Chief Justice of the respective High Court and includes the senior HC judge as its Executive Chairman. While the HC Chief Justice is the patron-in-chief of the SLSA, the CJI is the patron-in-chief of NALSA.
- District Legal Services Authorities:
- Similarly, District Legal Services Authorities (DLSAs) and Taluk Legal Services Committees were established in districts and most taluks. Situated in the District Courts Complex in every district, each DLSA is chaired by the District Judge of the respective district.
- The Taluka or Sub-Divisional Legal Services Committees are headed by a senior civil judge. Collectively, these bodies organise legal awareness camps, provide free legal services, and supply and obtain certified order copies and other legal documents, among other functions.
What are the Constitutional Provisions that Mandate the Provision of Legal Services in India?
- The need for providing legal services has been underlined in many provisions of the Indian Constitution. Article 39A states, the State shall secure that the operation of the legal system promotes justice, on a basis of equal opportunity, and shall, in particular, provide free legal aid, by suitable legislation or schemes or in any other way, to ensure that opportunities for securing justice are not denied to any citizen by reason of economic or other disabilities.
- Moreover, Articles 14 (right to equality) and 22(1) (rights to be informed of grounds for arrest) also make it obligatory for the State to ensure equality before the law and a legal system that promotes justice based on equal opportunity.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. With reference to National Legal Services Authority, consider the following statements: (2013)
- Its objective is to provide free and competent legal services to the weaker sections of the society on the basis of equal opportunity.
- It issues guidelines for the State Legal Services Authorities to implement the legal programmes and schemes throughout the country.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)


Social Issues
Rise of Child Marriages in West Bengal
For Prelims: Child marriage, Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006 (PCMA), Kanyashree Prakalpa Scheme,
For Mains: Major Factors Associated with Child Marriage, Legislative Framework and Initiatives Related to Child Marriage in India.
Why in News?
A recent Lancet study on child marriage in India highlighted an overall decrease in child marriage across the country. However, it emphasized that certain states, specifically Bihar (16.7%), West Bengal (15.2%), Uttar Pradesh (12.5%), and Maharashtra (8.2%), collectively contributed to over half of the total headcount burden of child marriages in girls.
- Despite the implementation of multiple policy interventions in West Bengal aimed at curbing child marriage, the region has experienced a substantial surge of 32.3% in the incidence of child marriages. This increase corresponds to over 500,000 additional girls getting married as children.
Note
- National Family Health Survey-5 ( 2019-21):
- The National Family Health Survey-5 indicates that the prevalence of women aged 20-24 years married before 18 remains high in West Bengal at 41.6%, compared to the national figure of 23.3%.
Has Policy Intervention in West Bengal Effectively Curbed Child Marriage?
- Policy Interventions to Stop CHild Marriage in West Bengal:
- The Kanyashree Prakalpa Scheme:
- Launched in 2013, Kanyashree Prakalpa incentivizes the schooling of teenage girls aged 13 to 18 while simultaneously discouraging child marriage. The scheme has covered 81 lakh girls, according to the West Bengal Budget for 2023-24.
- The scheme received international recognition with the United Nations Public Service Award in 2017.
- While the school enrolment of girls has increased in the State, questions are being posed based on National Family Health Survey data and the Lancet study of whether the scheme has achieved its promise of arresting child marriage.
- Launched in 2013, Kanyashree Prakalpa incentivizes the schooling of teenage girls aged 13 to 18 while simultaneously discouraging child marriage. The scheme has covered 81 lakh girls, according to the West Bengal Budget for 2023-24.
- Rupashree Prakalpa:
- In addition to Kanyashree, the state government runs the Rupashree Prakalpa, providing cash incentives for girls' marriages.
- Some families utilize benefits from both schemes, organizing marriages shortly after cashing in on the school scheme.
- In addition to Kanyashree, the state government runs the Rupashree Prakalpa, providing cash incentives for girls' marriages.
- The Kanyashree Prakalpa Scheme:
- Educational Stride and Child Marriage Rates:
- Despite girl’s enrolment in schools has “significantly increased over the past few years and yet the incidence of child marriage remains high in West Bengal”.
- The All-India Survey of Higher Education for 2020-21 puts the number of estimated enrolment of girls in West Bengal at 9.29 lakh, which is higher than the boys enrolment which stood at 8.63 lakh.
- As per NFHS- 5, the Purba Medinipur district with over 88% literacy rate has the highest incidence of child marriage of more than 57.6%.
- Experts noted migration in West Bengal fuels child marriage as families fear leaving unmarried daughters behind, driven by societal norms and economic factors.
- This perpetuates a cycle where cultural expectations prioritize early marriages for wives to bear children while men work.
- Despite girl’s enrolment in schools has “significantly increased over the past few years and yet the incidence of child marriage remains high in West Bengal”.
- Challenges in Law Implementation:
- Beyond social issues, challenges in law implementation contribute to the persistence of child marriage.
- As West Bengal's 105 cases under The Prohibition of Child Marriage Act (PCMA), 2006 in 2021 raise concerns. Because comparatively, states with smaller populations reported more cases.
- The Ministry introduced the Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2021, proposing raising the age of marriage for women to 21, currently under Parliamentary review.
- The data suggests gaps in law enforcement and highlights the need for comprehensive strategies.
- Beyond social issues, challenges in law implementation contribute to the persistence of child marriage.
What are the Impacts of Child Marriage?
- Ending Childhood:
- Child marriage is a global problem and is compounded by poverty. It abruptly ends a boy’s/girl's childhood, pushing them into adulthood before they are physically and mentally prepared.
- Arranged marriages often involve girls marrying significantly older men, intensifying the challenges they face.
- Early marriage significantly decreases the likelihood of girls staying in school, leading to lifelong economic repercussions.
- Child marriage leads childhood grooms to drop out of school and often settle for low-paying jobs to provide for their families.
- Child brides and grooms often experience isolation and have their freedom curtailed, limiting their social interactions and personal autonomy.
- Child marriage is a global problem and is compounded by poverty. It abruptly ends a boy’s/girl's childhood, pushing them into adulthood before they are physically and mentally prepared.
- Human Rights Violation:
- Child marriage is considered a human rights violation and a recognised form of sexual and gender-based violence, the adverse impact of child marriage is manifested across maternal and child health in the State.
- Child brides are frequently denied their fundamental rights, including access to health, education, safety, and the opportunity for active participation.
- United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) categorizes child marriage as a human rights violation due to its adverse impacts on the development of both girls and boys.
- Each year, some 12 million more girls will marry before reaching age 18 and of those, 4 million are under age 15.
- Save the Children’s Global Girlhood Report estimates that an additional 2.5 million girls are at risk of child marriage globally between 2020 and 2025, as a result of reported increases in all types of gender-based violence due to the Covid-19 pandemic.
- Maternal and Child Health Implications:
- The adverse impact of child marriage extends to maternal and child health.
- Child brides often become pregnant during adolescence, when the risk of complications during pregnancy and childbirth increases. The practice can also isolate girls from family and friends, taking a heavy toll on their mental health.
- Child brides are also more susceptible to contracting Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV).
- The adverse impact of child marriage extends to maternal and child health.
What are the Initiatives to Tackle Child Marriage?
- Prohibition of Child Marriage Act, 2006 (PCMA)
- BetiBachaoBetiPadhao (BBBP) scheme.
- National Commission for Protection of Child Rights (NCPCR).
- Protection of Children from Sexual Offences Act 2012.
- CHILDLINE.
Way Forward
- Mobilize political will at both state and national levels to prioritize the eradication of child marriage through legislative measures.
- Conduct social campaigns involving all stakeholders including panchayats, schools and local communities and without a political will to enforce the existing laws the situation at the grass roots will not improve as rapidly as it has in other parts of the country.
- Promote a culture of reporting and transparency by regularly updating and providing detailed information on child marriage cases under PCMA 2006.
- Facilitate a comprehensive review of PCMA 2006 to identify loopholes and areas for improvement in enforcement.
- Advocate for the swift approval of the Prohibition of Child Marriage (Amendment) Bill, 2021, by the Parliamentary Standing Committee.
- The Bill amends the PCMA 2006 to increase the minimum age of marriage of females to 21 years. Further, the Bill will override any other law, custom, or practice.
- Empower girls with information, skills, and support networks for increased autonomy and decision-making.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Examine the main provisions of the National Child Policy and throw light on the status of its implementation. (2016).


Indian Economy
Supreme Court Verdict on Adani-Hindenburg Case
For Prelims: Supreme Court of India, Securities and Exchange Board of India, Short-selling, Naked Short selling, Tax havens, Justice Sapre Committee, Futures and Options.
For Mains: Regulation of Short-selling in India, Supreme Court’s Recent Verdicts Related to Capital Market.
Why in News?
The Supreme Court of India recently concluded its judgment on a series of petitions pertaining to allegations made by the US-based firm, Hindenburg Research, against the Adani group.
- The apex court refused to transfer the investigation from the Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) to other bodies, affirming its confidence in SEBI's handling of the case.
- Also, SC instructed SEBI to utilize its investigative authority to determine if the Hindenburg report's short-selling actions violated laws, resulting in investor harm.
What is the Supreme Court's Position Regarding the Adani-Hindenburg Dispute and SEBI's Inquiry?
- Background:
- Hindenburg's Allegations: In January 2023, Hindenburg Research accused the Adani group of stock manipulation, accounting fraud, and using improper tax havens and shell companies to manage funds, significantly impacting the stock market.
- Petitions and Arguments:
- Petitions Filed: Various petitions were filed seeking a court-monitored investigation, citing implications for national security and the economy.
- They also alleged that SEBI, the market regulator, was not competent or independent enough to conduct a fair and impartial probe.
- Counter Arguments: The Adani group refuted the allegations, attributing them to false information and vested interests.
- SEBI defended its competence and independence in handling the investigation.
- Petitions Filed: Various petitions were filed seeking a court-monitored investigation, citing implications for national security and the economy.
- Recent Judgment:
- The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the Adani group and SEBI, rejecting the transfer of the probe to other investigative bodies.
- The court held that the power to transfer investigation must be exercised in exceptional circumstances and not in the absence of cogent justifications.
- The Court deemed the Hindenburg report unreliable and aimed at influencing the market through selective and distorted information.
- While upholding SEBI's integrity, the Court directed an expedited completion of SEBI's investigation within three months.
- The Supreme Court ruled in favor of the Adani group and SEBI, rejecting the transfer of the probe to other investigative bodies.
Note
The Supreme Court formed the Justice Sapre Committee in March 2023 to probe potential regulatory failures after investors suffered significant losses due to market volatility following Hindenburg Research's allegations against the Adani Group for share price manipulation and accounting fraud.
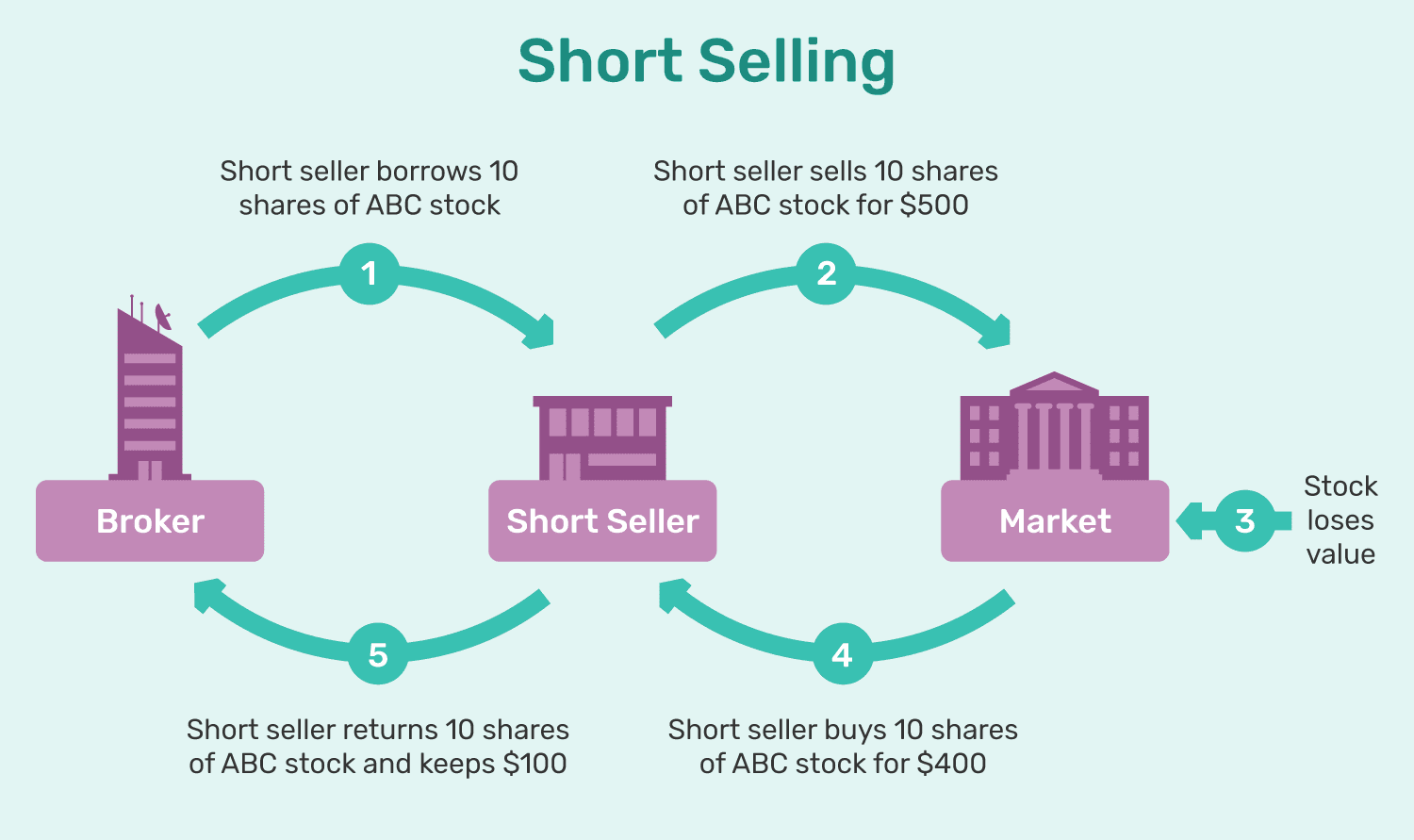
What is Short Selling?
- About:
- Short selling is the practice wherein an investor borrows a stock or security, sells it in the open market, foreseeing a potential future price decline, aiming to repurchase the same asset at a lower price point later on.
- SEBI defines short selling as selling a stock that the seller does not own at the time of trade.
- Short selling is the practice wherein an investor borrows a stock or security, sells it in the open market, foreseeing a potential future price decline, aiming to repurchase the same asset at a lower price point later on.
- Regulation of Short-selling in India:
- SEBI has recently stated that investors across all categories will be allowed for short-selling, but naked short-selling will not be permitted.
- Consequently, all investors are required to fulfill their duty of delivering securities during the settlement period
- Naked short selling occurs when an investor sells stocks or securities without first arranging to borrow them or ensuring they can be borrowed.
- Institutional investors must disclose upfront whether a transaction is a short sale, while retail investors can make a similar disclosure by the trading day's end.
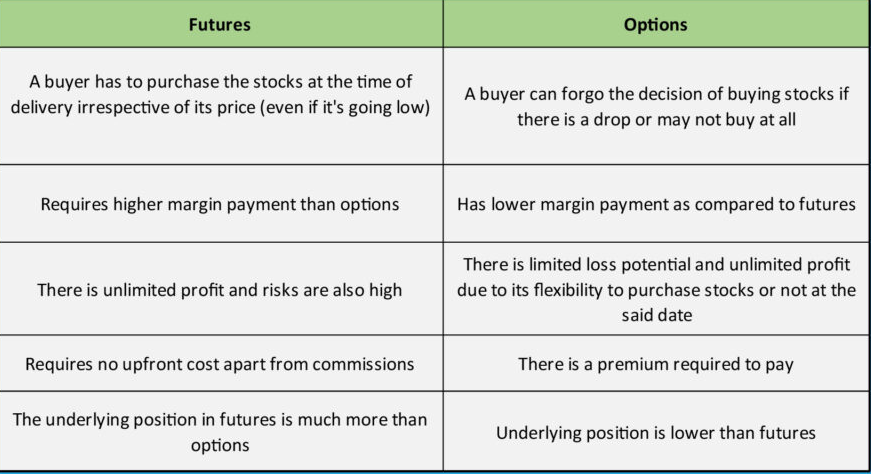
- Also, short selling is permitted for securities traded in the F&O (Futures & Options) segment, subject to SEBI's periodic review of eligible stocks.
- Futures and Options (F&O) are derivative instruments. Futures involve an obligation to buy/sell assets at an agreed price on a set date, carrying unlimited risk.
- Options grant the right (but not obligation) to buy/sell assets by a certain date, with a premium paid upfront limiting potential losses.
- Futures and Options (F&O) are derivative instruments. Futures involve an obligation to buy/sell assets at an agreed price on a set date, carrying unlimited risk.
- SEBI has recently stated that investors across all categories will be allowed for short-selling, but naked short-selling will not be permitted.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. In the parlance of financial investments, the term ‘bear’ denotes (2010)
(a) An investor who feels that the price of a particular security is going to fall
(b) An investor who expects the price of particular shares to rise
(c) A shareholder or a bondholder who has an interest in a company, financial or otherwise
(d) Any lender whether by making a loan or buying a bond
Ans: (a)


Governance
Outlook of OTT in 2024
For Prelims: Outlook of OTT in 2024, Over-The-Top (OTT) Market, Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021.
For Mains: Outlook of OTT in 2024.
Why in News?
The OTT market in India is currently battling the dilemma between growth and profitability in a price-sensitive market. In 2023, the Over-The-Top (OTT) Market in India experienced significant disruptions and challenges that shaped its trajectory.
What is Over-The-Top?
- About:
- OTT stands for "Over-The-Top," a term used to describe content delivery over the internet directly to viewers, bypassing traditional broadcast, cable, or satellite TV platforms.
- The OTT market refers to the industry that provides streaming media services, delivering movies, TV shows, music, and other content to users via the internet.
- Examples: Netflix, Disney+, Hulu, Amazon Prime Video, Peacock, CuriosityStream, Pluto TV, and so many more.
- Benefits of OTT:
- Flexibility and Convenience:
- Users can access content anytime, anywhere, across multiple devices, providing unparalleled convenience.
- Diverse Content:
- OTT platforms offer a wide array of content, including movies, TV shows, documentaries, and original productions, catering to varied tastes and interests.
- Personalization:
- These platforms use algorithms to recommend content based on viewing habits, enhancing user experience and content discovery.
- Cost-Effectiveness:
- Compared to traditional cable or satellite TV subscriptions, OTT services often offer more affordable pricing options, including free content with ad support or subscription tiers.
- Global Accessibility:
- OTT platforms transcend geographical barriers, allowing users worldwide to access content regardless of their location.
- Flexibility and Convenience:
- Limitations of OTT:
- Internet Dependence:
- Reliable high-speed internet is crucial for seamless streaming. In areas with poor connectivity, accessing content can be frustrating.
- Content Fragmentation:
- Exclusive content rights on different platforms result in fragmentation. To access specific shows or movies, users may need multiple subscriptions.
- Data Privacy Concerns:
- OTT platforms collect user data for personalization, raising privacy concerns if mishandled or if data is shared with third parties without consent.
- Content Quality and Quantity:
- While there's a vast selection of content, quality can vary. Additionally, the sheer volume of content can make discovering quality material overwhelming for users.
- Internet Dependence:
What was the State of OTT in 2023 and Outlook for 2024?
- In 2023, the OTT landscape saw disruptive moves with platforms offering premium content for free, impacting subscription revenue.
- Monetization challenges persisted, none reaching break-even due to high content costs.
- Freemium models emerged, curbing password sharing and integrating ads. Regulatory concerns lingered but censorship wasn't favored, fostering selective data sharing.
- Looking to 2024, expect cost-efficient content strategies with a decline in experimental content. Mergers among major players like Zee/Sony and potential collaborations like RIL/Disney may restructure market dynamics, influencing bargaining power and content costs.
- Pricing strategies will continue evolving, likely intensifying limitations on sharing and embedding ads.
- Regulatory compliance may tighten, emphasizing sensitivity toward religious or minority sentiments. Increased transparency in viewership trends will aid advertisers and creators.
What are the Laws regulating OTT Platforms?
- In 2022, the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) had notified the Information Technology (Intermediary Guidelines and Digital Media Ethics Code) Rules 2021 to regulate OTT platforms.
- The rules establish a soft-touch self-regulatory architecture with a Code of Ethics and three-tier grievance redressal mechanism for OTT platforms.
- Every publisher should appoint a Grievance Officer based in India for receiving and redressing grievances in 15 days.
- Also, every publisher needs to become a member of a self-regulating body. Such a body will have to register with the Ministry of Information and Broadcasting and address grievances that have not been resolved by the publisher within 15 days.
- The Ministry of Information Broadcasting and the Inter-Departmental Committee constituted by the Ministry constitute the third-tier Oversight Mechanism.
- They provide for self-classification of the content without any involvement of Central Board of Film Certification.
What Can be Done for Better Regulation of OTT?
- Self-Regulation Frameworks:
- There is a need to encourage OTT platforms to establish transparent content guidelines and rating systems akin to traditional media.
- Industry-led self-regulation can address concerns without stifling creativity.
- Collaborative Oversight Bodies:
- It is imperative to form independent bodies comprising industry experts, stakeholders, and government representatives. These bodies can monitor content, review complaints, and set industry standards.
- Clear Content Classification and Ratings:
- There is a need to implement standardized content classification systems to help users make informed viewing choices based on age-appropriateness and content themes.
- Transparency in Data Sharing:
- Encourage OTT platforms to share viewership trends selectively with oversight bodies, aiding in content evaluation and ensuring compliance with guidelines.
- Regular Audits and Compliance Checks:
- There is a need to conduct periodic audits to ensure platforms adhere to established guidelines, fostering accountability and responsible content curation.
Conclusion
- OTT has transformed the way people consume entertainment, providing flexibility, choice, and convenience.
- The market continues to evolve, driven by technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and the dynamic landscape of media and entertainment.


Important Facts For Prelims
GSAT-20 (GSAT-N2) Aboard SpaceX’s Falcon-9
Why in News?
The commercial arm of the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO), NewSpace India Limited (NSIL) is set to launch GSAT-20 (GSAT-N2), aboard SpaceX's Falcon-9 in 2024.
- Falcon 9 is the world’s first orbital class reusable, two-stage rocket designed and manufactured by SpaceX for the reliable and safe transport of people and payloads into Earth orbit and beyond.
What is GSAT-20?
- GSAT-20 is a high throughput Ka-band satellite that provides high-speed broadband internet connectivity, digital video transmission, and audio transmission.
- It is being launched to address the growing broadband communication needs of India.It is designed to provide comprehensive coverage across India, including remote regions like Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Lakshadweep Islands.
- This satellite offers an impressive HTS (High Throughput Satellite) capacity of nearly 48Gbps. Notably, it comprises 32 beams specifically designed to meet the demanding service needs of underserved areas, aiming to bridge the connectivity gap.
Note
The Ka-band refers to radio frequencies ranging from 27 to 40 GHz. It allows high-speed satellite data transfers with wide coverage through focused spot beams.
What is NewSpace India Limited (NSIL)?
- NSIL, incorporated on 6th March 2019 (under the Companies Act, 2013), is a wholly owned Government of India company, under the administrative control of Department of Space (DOS).
- Its primary responsibility is enabling Indian industries to take up high technology space related activities and is also responsible for promotion and commercial exploitation of the products and services emanating from the Indian space programme.
- The Major Business Areas of NSIL include:
- Production of Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) and Small Satellite Launch Vehicle (SSLV) through industry
- Production and marketing of space-based services, including launch services and space-based applications like transponder leasing, remote sensing and mission support services;
- Building of Satellites (both Communication and Earth Observation) as per user requirements.
- Transfer of technology developed by ISRO centres/ units and constituent institutions of Dept. of Space;
- Marketing spin off technologies and products/ services emanating out of ISRO activities
- Consultancy services
- In June 2022, NSIL successfully completed its first demand-driven satellite mission, GSAT-24, which was fully secured by Tata Play, a satellite television service.
- Currently, NSIL manages and operates 11 communication satellites in orbit.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. With reference to India’s satellite launch vehicles, consider the following statements: (2018)
- PSLVs launch the satellites useful for Earth resources monitoring whereas GSLVs are designed mainly to launch communication satellites.
- Satellites launched by PSLV appear to remain permanently fixed in the same position in the sky, as viewed from a particular location on Earth.
- GSLV Mk III is a four-staged launch vehicle with the first and third stages using solid rocket motors, and the second and fourth stages using liquid rocket engines.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3
(c) 1 and 2
(d) 3 only
Ans: (a)


Important Facts For Prelims
Peregrine Mission One
Why in News?
The United States embarked on the Peregrine Mission One, its first attempt to land on the Moon in over 50 years. However, the landing attempt was seemingly doomed after the spacecraft developed a “critical” fuel leak just hours after launch.
- The mission is spearheaded by private space enterprises, Astrobotic Technology and United Launch Alliance, this collaborative mission, signals a shift towards leveraging private sector capabilities for space exploration.
What are the Key Highlights of Peregrine Mission One?
- The Peregrine Lander is expected to be one of the first American spacecraft to land on the Moon since the Apollo program.
- The Peregrine Lunar Lander, also known as Peregrine Mission One, is a lunar lander built by Astrobotic Technology.
- It is part of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)’s Commercial Lunar Payload Services (CLPS) programme, which aims to stimulate a broader lunar economy.
- NASA is partnering with diverse American companies under the CLPS initiative to transport science and technology payloads to the lunar surface.
- The CLPS contracts aim to facilitate lunar exploration, experimentation, and technology demonstrations in preparation for upcoming human missions.
- It is expected to touch down on a mid-latitude region of the Moon called Sinus Viscositatis, or Bay of Stickiness.
- This mission will also help prepare for Artemis, the NASA-led programme to return astronauts to the Moon later this decade, in preparation for missions to Mars.
- Artemis is NASA's ambitious initiative named after the moon goddess in Greek mythology. With a mission to land humans on the Moon by 2024, including the first woman and person of colour on the lunar surface.
- The program envisions an Artemis Base Camp on the lunar surface and a strategic Gateway in lunar orbit.
Note
- Until now, a soft landing on the Moon has only been accomplished by a handful of national space agencies: the Soviet Union was first, in 1966, followed by the United States, which is still the only country to put people on the Moon. China has successfully landed three times over the past decade, while India with Chandrayaan-3 is the most recent to achieve the feat on its second attempt, in 2023.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. What is the purpose of the US Space Agency’s Themis Mission, which was recently in the news? (2008)
(a) To study the possibility of life on Mars
(b) To study the satellites of Saturn
(c) To study the colourful display of high latitude skies
(d) To build a space laboratory to study the stellar explosions
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
BIS: 77 Years of Shaping Standards
Recently, the Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS), a body under the Ministry of Consumer Affairs, Food, and Public Distribution, Government of India, celebrated its 77th Foundation Day on 6th January 2024.
- BIS is the National Standard Body of India established under the BIS Act 2016 for the harmonious development of the activities of standardization, marking and quality certification of goods. BIS has its headquarters at New Delhi.
- It operates various schemes like Product Certification (ISI mark), Hallmarking of Gold and Silver Jeweller, ECO Mark Scheme (for labeling of environment friendly products).
- The BIS Act, 2016, has been implemented since October 2017. The major highlights of the act are:
- Enables the government to authorize any agency apart from BIS to certify and enforce conformity to a standard.
- Provides consumer protection measures like recall of non-conforming standard marked products, compensation to the consumer and more stringent penal provisions.
Read more: Bureau of Indian standards (BIS) Act 2016


Rapid Fire
Martian Plasma Waves
Scientists from the Indian Institute of Geomagnetism studied high-frequency plasma waves in Mars' upper atmosphere using data from NASA's MAVEN spacecraft.
- The study found two types of waves in Mars' magnetic environment—some below and some above the electron plasma frequency. These waves are important because they help us understand how electrons behave around Mars.
- NASA’s MAVEN (Mars Atmosphere and Volatile Evolution) was launched in November 2013 with the mission to gain insights of the planet's atmospheric conditions.
- Plasma waves are oscillations or disturbances in the electric and magnetic fields that propagate through plasma, which is a state of matter consisting of charged particles like ions and electrons.
- These waves play a significant role in various plasma phenomena, influencing energy transfer, particle acceleration, and the behavior of charged particles within plasmas found in space.
Read more: NASA's MAVEN spacecraft


Rapid Fire
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas
Pravasi Bharatiya Divas (PBD) has been celebrated on 9th January every year since 2003 to honor the Indian diaspora and the contribution of the overseas Indian community to the country's development.
- January 9 was chosen as the day to celebrate this occasion since it was on this day in 1915 that Mahatma Gandhi, the greatest Pravasi, returned to India from South Africa, and led India’s freedom struggle.
- Since 2015, its format has been revised to celebrate the PBD once every two years and to hold theme-based PBD Conferences during the intervening period
Read more: Pravasi Bharatiya Divas


Rapid Fire
National Birds Day
National Bird Day, which has American origins, is celebrated annually on 5th of January, to raise awareness about the value of birds in the ecosystem.
- The day also aims to raise awareness for the conservation of avian species affected by habitat destruction, reducing food choices, and climate change.
- India's Union Cabinet Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change, called for saving the wetlands to preserve bird populations in the country.
- Wetlands become home to various species of birds in India and sustain ecosystems vital to feed local avian populations.
- National Bird Day is different from occasions such as International Migratory National Bird Day, World Migratory National Bird Day (May 13) , and several other National Bird Days.


Rapid Fire
World Typing Day
8th January is observed as World Typing Day to encourage people to express themselves via written communication.
- Celebration of the day started in Malaysia in 2011. It commemorates the 2011 Malaysian Speed Typing Contest, which broke records for the fastest typist and largest participation.
- The day holds special significance as it celebrates the ability to type and communicate with one another.