Agriculture
Agricultural Initiatives and their Implementation
For Prelims: Agriculture, Kisan Credit Card (KCC) Scheme, Modified Interest Subvention Scheme, PMFBY, RWBCIS, Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), RKVY, Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI), FPOs, Formation and Promotion of 10,000 FPOs Scheme, PMKMY, PDMC, Meghdoot and Mausam Mobile Apps, AIF, Horticultural Crops, Millet, Swarna-Sub1 Rice.
For Mains: Agricultural initiatives and their status of implementation, Concerts associated with agriculture and way forward.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers' Welfare has initiated and is implementing a number of initiatives for promotion of agriculture.
What are the Various Initiatives for Promotion of Agriculture?
- KCC Scheme: The Kisan Credit Card (KCC) scheme was expanded in 2019 to include animal husbandry, dairying, and fisheries.
- As of March 2024, India has 7.75 crore operational KCC accounts with a loan outstanding of Rs 9.81 lakh crore.
- KCC provides farmers with easy access to credit for their agricultural needs.
- Crop Insurance Schemes: The number of farmer applications under PMFBY and RWBCIS has grown by 35.12% and 27.50% year-on-year during 2022-23 and 2023-24.
- PMFBY covers risks from pre-sowing to post-harvest losses, while RWBCIS addresses weather-related risks.
- Agricultural Mechanization: Under the Sub Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM), Farm Machinery Training & Testing Institutes (FMTTIs) provide skill training on equipment selection, operation, maintenance, and energy management.
- Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana (RKVY): RKVY allows states to choose their own agriculture and allied sector development activities as per the district/state agriculture plan.
- RKVY is an umbrella scheme that supports the holistic development of agriculture and allied sectors.
- National Research Centre for Makhana (NRCM): It has developed machines for Makhana processing, such as seed washers, graders, and roasting machines.
- It has supported 24 enterprises, including Mithila Naturals, to boost Makhana industries and the agricultural economy.
- Project VISTAAR: Project VISTAAR (Virtually Integrated System To Access Agricultural Resources) aims to create a unified digital agriculture ecosystem, enhancing scalability, accessibility, inclusivity, and enabling two-way communication with farmers.
- It supports Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) for agricultural extension, and integrates AI chatbots and Agristack for real-time farmer support and feedback.
- Paramparagat Krishi Vikas Yojana (PKVY): PKVY has covered 14.99 lakh hectares through clusters, benefiting over 25 lakh farmers since 2015-16.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs): As December 2024, 9268 FPOs have been registered under the Formation and Promotion of 10,000 FPOs scheme for sourcing inputs, accessing credit, and marketing for farmers.
- Pradhan Mantri Kisan Maandhan Yojana (PMKMY): As of November 2024, 24.66 lakh farmers are enrolled under PMKMY, providing a minimum pension of Rs 3,000 per month after reaching 60 years of age.
- Per Drop More Crop (PDMC): The Government provides financial assistance of 55% to the small and marginal farmers and of 45% to other farmers of the project cost for installation of drip and sprinkler systems under the PDMC.
- Gramin Krishi Mausam Sewa (GKMS): 130 Agromet Field Units (AMFUs) disseminate weather and crop-related information through multiple channels, including SMS, radio, and social media.
- Meghdoot and Mausam mobile apps also help farmers get weather information.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF): AIF aims to enhance post-harvest infrastructure, reduce losses and intermediaries, and enable farmers to sell directly to consumers at better prices.
- Interest rate for loans capped at 9%, with a 3% subvention for loans up to Rs 2 crore.
- Skill Development Initiatives:
- Skill Training of Rural Youth (STRY): Offers 7-day short-term skill training in agriculture and allied sectors for self-employment.
- Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK): Provides training in agriculture, horticulture, livestock, and allied sectors to strengthen rural skills.
- Agriculture Technology Management Agency (ATMA): Delivers decentralized extension services to update farmers on new technologies and practices.
- Student READY Programme: Focuses on skill development and hands-on learning through training, rural awareness, internships, and projects.
What Plagues Indian Agriculture Despite Several Initiatives?
- Fragmented Land: The average farm size decreased from 2.3 hectares in 1970-71 to 1.08 hectares in 2015-16.
- 86.1% of farmers have less than 2 hectares that limits productivity, mechanization, and access to credit.
- Innovation Gap: Low adoption of modern technology like precision farming, drones, and AI contributes to lower yields.
- Post-Harvest Losses: Postharvest losses in India are estimated at 10-25%, with only 11% of produce stored in cold storage, causing distress sales and lower income.
- Diversification Dilemma: Indian agriculture is mainly focused on rice and wheat, with just 17% of land used for horticultural crops, despite millet promotion efforts.
- Irrigation Challenges: Over-reliance on monsoons and inefficient irrigation hinder productivity, with 52% of land irrigated by 2022-23.
- Climate change may cut agricultural incomes by 15-18%, with heat waves damaging crops.
Way Forward
- Boosting Productivity: Precision agriculture using GPS-guided machinery, IoT sensors, and data analytics can optimize resources, boost crop yields, and save millions of liters of water.
- Crop Diversification: Encouraging crop diversification, like the government's push for millets, can enhance income, soil health, and nutritional security.
- Strengthening FPOs: Strengthening FPOs can boost farmer incomes by 25-30% through collective bargaining and direct market access.
- Agri-Tech Startups: Supporting agri-tech startups like DeHaat can and speeding up tech adoption through funding and incubation.
- Climate-Smart Agriculture: Promoting drought and flood resistant crops (e.g., Swarna-Sub1 rice), and water conservation can boost farming sustainability and resilience.
|
Drishti Mains Question: What are the key initiatives launched by the Government of India to promote agriculture? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the context of India’s preparation for Climate -Smart Agriculture, consider the following statements:
- The ‘Climate-Smart Village’ approach in India is a part of a project led by the Climate Change, Agriculture and Food Security (CCAFS), an international research programme.
- The project of CCAFS is carried out under Consultative Group on International Agricultural Research (CGIAR) headquartered in France.
- The International Crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics (ICRISAT) in India is one of the CGIAR’s research centres.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q. In India, which of the following can be considered as public investment in agriculture? (2020)
- Fixing Minimum Support Price for agricultural produce of all crops
- Computerization of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies
- Social Capital development
- Free electricity supply to farmers
- Waiver of agricultural loans by the banking system
- Setting up of cold storage facilities by the governments
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3, 4 and 5 only
(c) 2, 3 and 6 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 and 6
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q. Explain various types of revolutions, took place in Agriculture after Independence in India. How have these revolutions helped in poverty alleviation and food security in India? (2017)
Q. Given the vulnerability of Indian agriculture to vagaries of nature, discuss the need for crop insurance and bring out the salient features of the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY). (2016)


Indian Economy
Union Budget 2025-26 Measures to Boost MSMEs
For Prelims: Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises, Udyam portal, Stand-Up India, Make in India, Gross Value Added, Export Factoring, Self-Reliant India Fund
For Mains: Role of MSMEs in India’s economic growth, Challenges and opportunities for MSMEs, Make in India
Why in News?
The Union Budget for 2025-26 has introduced a series of significant measures to enhance the Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises (MSME) sector, recognising its vital role in driving India's economic growth.
What are the Key Budgetary Measures for MSMEs?
- Increased Investment and Turnover Limits: Investment limits raised by 2.5 times and turnover limits by 2 times to allow MSMEs to scale operations and adopt better technology.
- This will enable more businesses to qualify as MSMEs and avail government incentives.
- Enhanced Credit Availability: Credit guarantee cover increased from Rs 5 crore to Rs 10 crore for micro and small enterprises, unlocking Rs 1.5 lakh crore in additional credit over five years.
- Startups’ guarantee cover doubled from Rs 10 crore to Rs 20 crore, with a reduced fee of 1% for loans in 27 priority sectors.
- Exporter MSMEs eligible for Rs 20 crore term loans with enhanced guarantee cover, encouraging international trade.
- MSME Credit Cards: The 2025 budget introduces MSME credit cards to boost growth and streamline loan access, with experts urging reduced bureaucratic hurdles.
- Rs 5 lakh credit facility will be provided for micro-enterprises registered on the Udyam portal, with 10 lakh cards to be issued in the first year.
- Support for Startups: A new Fund of Funds with Rs 10,000 crore will be established to expand support for startups.
- Scheme for First-time Entrepreneurs: A new scheme aimed at empowering 5 lakh first-time entrepreneurs from women, Scheduled Castes (SC) and Scheduled Tribes (ST).
- This initiative will offer term loans up to Rs 2 crore over the next five years.
- Drawing inspiration from the Stand-Up India scheme, the scheme will also include online capacity-building programs to enhance entrepreneurial and managerial skills.
- National Manufacturing Mission (NMM): The NMM, announced in Budget 2025-26, supports Make in India with a focus on clean tech manufacturing, including solar photovoltaic (PV) cells, Electric Vehicles batteries, wind turbines, and transmission equipment.
- It aims to boost domestic value addition and reduce reliance on Chinese imports.
- Labour-Intensive Sector Support:
- Focus Product Scheme: Supports design, component manufacturing, and non-leather footwear production, expected to create 22 lakh jobs and generate Rs 4 lakh crore turnover.
- Toy Sector: A new Scheme for the Toy Sector will promote cluster development and skill-building, aiming to position India as a global toy manufacturing hub.
- Food Processing: Establishment of a National Institute of Food Technology in Bihar to boost Eastern India’s food industries.
- Cross-Border Factoring: The government aims to scale cross-border factoring services to reach about 3% of India’s merchandise exports, aligning with the global average.
- This will help MSMEs access financing through export factoring, thereby improving cash flow and reducing financial strain.
- Export factoring is a financing method where exporters sell their receivables to a third party (factor) at a discount in exchange for immediate payment, reducing bank dependence and aiding growth.
- This will help MSMEs access financing through export factoring, thereby improving cash flow and reducing financial strain.
What is the Current Landscape of MSMEs in India?
- Employment: MSMEs employ over 25.18 crore individuals in India and play a pivotal role in economic growth and job creation.
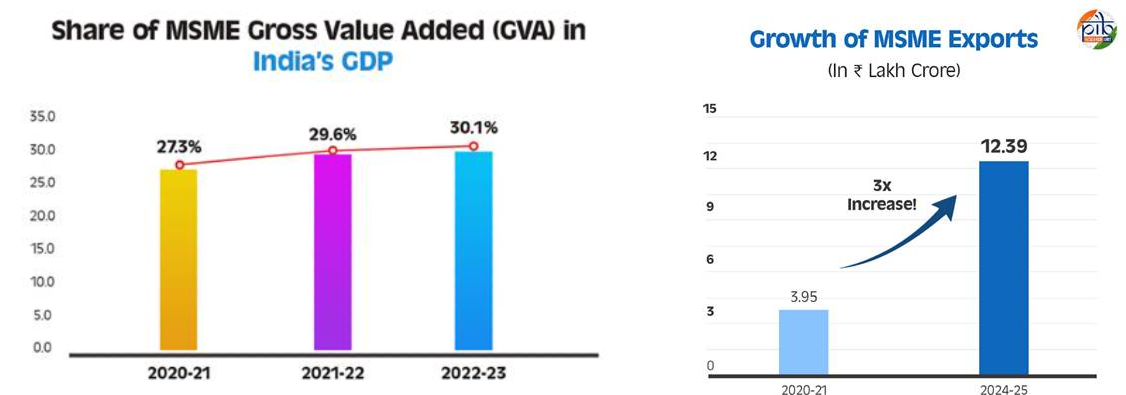
- Economic Contribution: The share of MSMEs in India’s Gross Value Added (GVA) has grown from 27.3% in 2020-21 to 30.1% in 2022-23, highlighting its growing importance in national economic output.
- Export Growth: Exports from MSMEs increased from Rs 3.95 lakh crore in 2020-21 to Rs 12.39 lakh crore in 2024-25.
- The number of exporting MSMEs surged from 52,849 in 2020-21 to 1,73,350 in 2024-25.
- The contribution of MSMEs to India's overall exports has steadily risen. MSMEs accounted for 43.59% of total exports in 2022-23, 45.73% in 2023-24, and 45.79% in 2024-25 (up to May 2024).
What are the Challenges Faced by MSMEs in India?
- Labour Issues: Labour-related issues, such as the absence of well-defined trial periods for new hires, an unskilled workforce, wage disparities across states, and inefficient training centres, hinder MSME growth and productivity.
- Lack of Clarity: There is a lack of awareness and confusion about various government schemes, coupled with poor coordination between the Centre and State, hindering MSMEs from fully benefiting from them.
- Export Issues: MSMEs struggle with inadequate export infrastructure and face challenges due to the lack of Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) reports, which negatively impacts their competitiveness in global markets.
- Formalisation and Inclusion Despite efforts like the Udyam Registration Portal, the formalisation of informal micro-enterprises is a significant challenge, as many do not have Permanent Account Number (PAN) or Goods and Services Tax (GST), limiting their access to government benefits.
- Regulatory Burden: MSMEs are burdened with complex licensing, inspection, and compliance requirements imposed by various government levels, making it particularly challenging for smaller businesses to meet regulations.
What are the Government Initiatives for MSMEs?
- PM Vishwakarma Scheme
- Udyam Assist Platform
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP)
- Scheme of Fund for Regeneration of Traditional Industries (SFURTI)
- Self-Reliant India (SRI) Fund
- MSME Samadhan
- CHAMPIONS Portal
- MSE-CDP (Cluster Development Programme)
- Pradhan Mantri MUDRA Yojana
- Government e-Marketplace
- Trade Receivables Discounting System (TReDS)
- Public Procurement Policy for MSEs: 25% of annual procurement by Central Ministries and CPSEs must be sourced from MSEs.
- 4% reserved for SC/ST-owned MSEs, 3% for women-owned MSEs.
- In 2023-24, Rs 74,717 crore worth of goods/services procured from MSEs, 43.71% of total procurement.
Way Forward
- Simplifying Regulations: A reduction in the regulatory burden (deregulation) is crucial for improving MSME productivity. Efforts should focus on creating a business-friendly environment that encourages innovation and scaling.
- Continued Support for Financing: Increasing access to funding through platforms like the SRI Fund and expanding the reach of MSME-focused initiatives will be key to unlocking the sector's potential.
- Technology and Skill Development: Ongoing efforts to upgrade technology and enhance skills will help MSMEs adapt to global standards and boost their competitiveness.
- Improving Market Access: Promote market awareness and standardization of products to increase market access of MSMEs. Also, work on reducing tariff and non-tariff barriers through trade agreements.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question:(PYQ)
Prelims:
Q1. What is/are the recent policy initiative(s)of Government of India to promote the growth of the manufacturing sector? (2012)
- Setting up of National Investment and Manufacturing Zones
- Providing the benefit of ‘single window clearance’
- Establishing the Technology Acquisition and Development Fund
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q.2. Which of the following can aid in furthering the Government’s objective of inclusive growth? (2011)
- Promoting Self-Help Groups
- Promoting Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises
- Implementing the Right to Education Act
Select the correct answer using the codes given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Q3. Consider the following statements with reference to India : (2023)
- According to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises Development (MSMED) Act, 2006, the ‘medium enterprises’ are those with investments in plant and machinery between `15 crore and `25 crore.
- All bank loans to the Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises qualify under the priority sector.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)


Important Facts For Prelims
Indo-European Languages
Why in News?
A Study published in the journal Nature identifies the Caucasus Lower Volga people as the probable originators of Indo-European languages, challenging the earlier Yamnaya theory.
What are the Key Findings of the Study?
- Genetic Origin: The Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived 6,500 years ago on the Eurasian steppe, stretching from the Volga River to the Caucasus Mountains, are identified as the genetic progenitors of the Indo-European language family.
- Yamnaya People’s Role: The Yamnaya people (5,700–5,300 years ago), descendants of the Caucasus Lower Volga, played a significant role in spreading Proto-Indo-European languages across Europe, the Indian subcontinent, and China.
- These ancient populations migrated west, mixed with locals, and formed the distinct Yamnaya genome.
- Earlier researches suggested the ancient Yamnaya people of the steppe as the originators of Proto-Indo-European, the precursor to modern Indo-European languages.
- Economic Transformation: The Yamnaya people’s new economic practices, such as livestock herding and the use of oxen-drawn wagons, enabled their migration and expansion.
- The Yamnaya underwent a demographic explosion, expanding from a few thousand people to tens of thousands within a few centuries.
Indo-European Language Family
- The Indo-European language family is the world’s largest language family, comprising over 400 languages. These languages are divided into several sub-families.
|
Indo-European Language Sub-family |
Languages |
Region |
|
Celtic |
Breton, Cornish, Manx, Irish, Scottish Gaelic, Welsh |
Western Europe, British Isles |
|
Germanic |
English, German, Dutch, Swedish, Danish, Norwegian |
Northern and Western Europe |
|
Romance |
Latin (classical), French, Spanish, Italian, Portuguese, Romanian |
Southern and Western Europe |
|
Hellenic |
Greek (Modern and Ancient) |
Greece, Cyprus |
|
Albanian |
Albanian |
Albania, Kosovo, parts of Macedonia, Montenegro |
|
Armenian |
Armenian |
Armenia |
|
Balto-Slavic |
Latvian, Lithuanian, Russian, Polish, Czech, Slovak, Ukrainian, Belarusian |
Eastern Europe, Baltic region |
|
Indo-Iranian |
Persian (Farsi), Kurdish, Pashto, Baloch, Sanskrit, Punjabi, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Dogri, Gujarati, Urdu, Hindi, Marathi, Maithili, Nepali, Bangla, Assamese, Odia, Sinhala, Dhivehi |
Indian subcontinent, Iran, Central Asia |
Note: In South Asia, languages belong to four major families: Indo-European (primarily Indo-Aryan), Dravidian, Austro-Asiatic, and Sino-Tibetan.
- Indo-Aryan languages: The largest group, with 574 languages spoken by 73.30% of the population.
- Dravidian languages: 153 languages, spoken by 24.47% of the population.
- Sino-Tibetan languages: 226 languages, with less than 1% of the population speaking them, including Khampti from the Siamese-Chinese subfamily.
- Austro-Asiatic languages: 65 languages with 6.19 million speakers.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. With reference to India, the terms ‘HaIbi, Ho and Kui’ pertain to (2021)
(a) dance forms of Northwest India
(b) musical instruments
(c) pre-historic cave paintings
(d) tribal languages
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following languages: (2014)
- Gujarati
- Kannada
- Telugu
Which of the above has/have been declared as ‘Classical Language/Languages’ by the Government?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)


Important Facts For Prelims
Tribal Welfare Measures in Budget 2025-26
Why in News?
The Union Budget 2025-26 has increased the Ministry of Tribal Affairs' allocation by 45.79% from 2024, emphasizing education, infrastructure, and socio-economic development.
What are the Key Highlights of Union Budget 2025-26 for Tribal Welfare?
- Increased Budgetary Allocation: The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) received Rs 14,925.81 crore in Budget 2025-26, a 45.79% increase from 2024-25.
- The Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment received Rs 13,611 crore (35.75% increase).
- The Ministry of Tribal Affairs (MoTA) focuses on the welfare and development of Scheduled Tribes (STs), while the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment (MoSJE) works for the welfare of SCs, STs, OBCs, PwDs, the elderly, and the transgender community.
- Expansion of Eklavya Model Residential Schools (EMRS): The Budget 2025-26 allocates Rs 7,088.60 crore for EMRS, with the aim to operationalize 728 schools by March 2026, benefiting 3.5 lakh tribal students with quality education and residential facilities.
- DA-JGUA: The Dharti Aaba Janjatiya Gram Utkarsh Abhiyan (DA-JGUA), originally named the PM Janjatiya Unnat Gram Abhiyan (PM-JUGA) received Rs 2,000 crore, a fourfold increase from Rs 500 crore, to enhance infrastructure, education, and livelihoods in tribal regions.
- Expediting PM-JANMAN: The Pradhan Mantri Janjati Adivasi Nyaya Maha Abhiyan (PM-JANMAN) allocation has doubled to Rs 300 crore in Budget 2025-26 to enhance healthcare, education, and livelihoods for Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs).
- To expedite the PM-JANMAN Housing Scheme, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs revised the approval process for PM-AWAS homes, aiming for 4.90 lakh houses for PVTGs.
What are the Various Government Initiatives Related to Tribals?
What are the Challenges Faced by Tribes in India?
Click to Read: Problems Faced By Tribes in India
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. At the national level, which ministry is the nodal agency to ensure effective implementation of the Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006?
(a) Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change
(b) Ministry of Panchayati Raj
(c) Ministry of Rural Development
(d) Ministry of Tribal Affairs
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements about Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs) in India: (2019)
- PVTGs reside in 18 States and one Union Territory.
- A stagnant or declining population is one of the criteria for determining PVTG status.
- There are 95 PVTGs officially notified in the country so far.
- Irular and Konda Reddi tribes are included in the list of PVTGs.
Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) 1, 2 and 3
(b) 2, 3 and 4
(c) 1, 2 and 4
(d) 1, 3 and 4
Ans: (c)


Rapid Fire
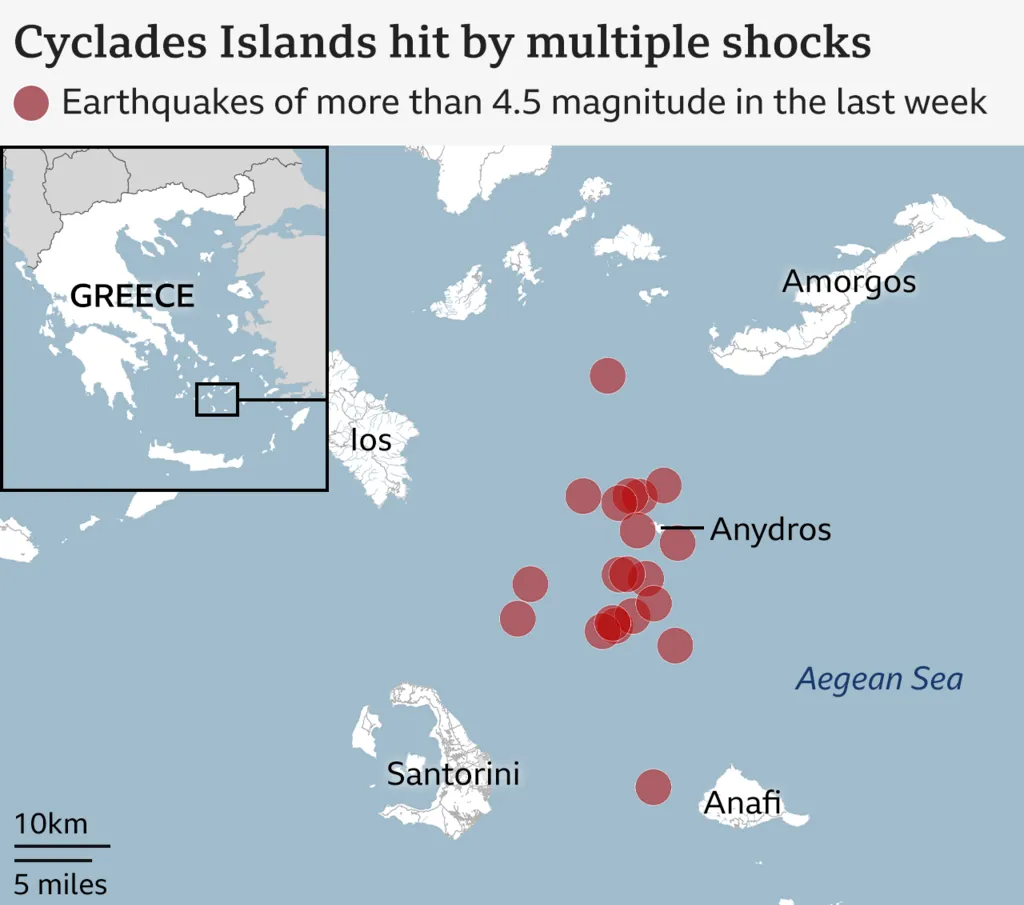
Santorini Islands
Santorini, a popular tourist destination in Greece's volcanic island, has experienced frequent earthquakes.
- These tremors have been linked to tectonic plate movements from the African-Eurasian Plate interaction, rather than volcanic activity.
- Santorini: It lies in the southern Aegean Sea, 200 km southeast from the mainland. Its capital is Fira.
- It is a part of the southern Cyclades (group of around 2200 Greek islands in the southern Aegean Sea), with an area of approximately 73 km2 located on the Hellenic Volcanic Arc, a chain of islands formed by volcanic activity.
- Other Unique Features: Santorini is also famous for its beaches, wines, Akrotiri ruins, and year-round Mediterranean climate.
Read More: Samos Island


Rapid Fire
Very Short-Range Air Defence System
The Defence Research & Development Organisation (DRDO) has successfully completed three successive flight trials of the Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS) off the Odisha coast.
- VSHORADS: It is a man-portable system developed by Research Center Imarat in collaboration with other DRDO laboratories.
- It is lightweight, and has a maximum range of 8 km and can engage targets at altitudes of up to 4.5 km.
- The system has the ability to neutralize aerial threats, including drones, flying at very low altitudes and high speeds.
- It is designed to meet the needs of all three branches of the Indian Armed Forces: the Army, Navy, and Air Force.
- The VSHORADS missile incorporates advanced technologies like the miniaturized Reaction Control System (RCS) (a system used for attitude control) and integrated avionics (missile control and navigation), successfully tested for neutralizing low-altitude aerial threats.
- Importance: The VSHORADS system is a critical air defence tool, offering close protection against aerial threats in battlefield scenarios.
- It is especially vital in combating the emerging threat of drones and other loitering munitions, which are increasingly used in modern warfare.
Read more: Very Short-Range Air Defence System (VSHORADS)


Rapid Fire
Gaia BH3 Black Hole
Astronomers have discovered Gaia BH3, the largest known stellar-mass black hole in the Milky Way, located in the constellation Aquila.
- This marks the 3rd black hole found using the Gaia telescope of the European Space Agency. (Previous discoveries: Gaia BH1 in 2022 and Gaia BH2 in 2023)
- Gaia BH3 has a mass 33 times that of the Sun, making it the most massive stellar-mass black hole in the Milky Way.
- A stellar-mass black hole is a type of black hole that forms when massive stars, weighing 5 to 10 times the Sun, collapse.
- Gaia BH3 is not actively pulling in matter and does not emit X-rays showing evidence of "silent" black holes without X-ray emissions.
- Rings of gas and dust around black holes emit light, including X-rays, making them detectable.
- The 2020 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded for confirming black hole formation as a key prediction of general theory of relativity and discovering a supermassive compact object at the center of our Milky Way galaxy.
Read More: Ultramassive Black Hole


Rapid Fire
3rd India-Japan Steel Dialogue
The 3rd India-Japan Steel Dialogue, held in New Delhi, brought both nations to discuss economic developments, steel trade, and technological collaboration.
- Institutional Mechanism: The dialogue is part of the Memorandum of Cooperation (MoC) on the steel sector, signed between the two countries in 2020, to promote sustainable growth, innovation, and workplace safety.
- Outcomes: India assured ease of doing business for Japanese companies, while Japan reaffirmed its support for investments in new steel technologies.
- Both sides shared perspectives on the European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (EU CBAM) and its impact on steel trade.
- EU CBAM: It is the EU's mechanism to price carbon emissions on imported goods and promote cleaner industrial production globally.
- CBAM's transitional phase (2023-2025) involves reporting obligations, with full financial implementation from 2026, covering iron, steel, cement, fertilizers, aluminum, electricity, and hydrogen.
Read more: Green Steel Policy