India, France, UAE Trilateral Initiative
For Prelims: India, France, United Arab Emirates, Nuclear Energy, Solar Energy, Climate Change, World Health Organization, Gavi-the Vaccine Alliance, Exercise Shakti (Army), Exercise Varuna (Navy), Exercise Garuda (Air Force), International Solar Alliance, VIRAL (Venus Infrared Atmospheric Gases Linker).
For Mains: Major Highlights of the Trilateral Initiative, India France Relations, India UAE Relations.
Why in News?
Recently, India, France, and the United Arab Emirates (UAE) have agreed to form a partnership to work together in the fields of nuclear and solar energy, as well as in tackling climate change and preserving biodiversity.
- The idea of this partnership was first discussed at a meeting in New York during the United Nations General Assembly in September 2022.
What Are the Major Highlights of the Trilateral Initiative?
- This trilateral initiative will serve as a forum to promote the design and execution of cooperation projects in the fields of energy, with a focus on solar and nuclear energy, as well as in the fight against climate change and the protection of biodiversity, particularly in the Indian Ocean region.
- The three countries have also agreed to work together in defence, countering infectious diseases, and promoting cooperation in global health organisations such as the World Health Organization, Gavi-the Vaccine Alliance, the Global Fund, and Unitaid.
- Further, the three countries will attempt to identify tangible cooperation on implementing the “One Health” approach, and support the development of local capacities in biomedical innovation and production within developing countries.
- The three countries also agreed to expand their cooperation through initiatives such as the Mangrove Alliance for Climate led by the UAE and the Indo-Pacific Parks Partnership led by India and France.
What are the Other Areas of Cooperation between India and France?
- Defence Cooperation:
- The three services of both countries have regular defence exercises; viz.
- Exercise Shakti (Army)
- Exercise Varuna (Navy)
- Exercise Garuda (Air Force)
- India entered into a contract with a French firm to build six Scorpene submarines in India’s Malegaon dockyards through a technology-transfer arrangement in 2005.
- Also, India and France had signed the inter-government agreement in 2016, under which France agreed to provide 36 Rafale fighter jets at a cost of around 60,000 crore rupees to India.
- The three services of both countries have regular defence exercises; viz.
- Other Initiatives:
- India and France are in joint efforts to limit climate change and develop the International Solar Alliance.
- France has agreed to be part of India's Venus mission, scheduled for 2025.
- Also, ISRO’s Venus instrument, VIRAL (Venus Infrared Atmospheric Gases Linker) has been co-developed by French and Russian agencies.
What are the Other Areas of Cooperation between India and UAE?
- Collaboration: They both are the members of I2U2 Grouping.
- Economic Partnership: In 2022 India & UAE signed a Comprehensive Economic Partnership Agreement (CEPA) with an aim of taking bilateral trade to USD 100 billion within 5 years.
- Also, India and UAE are discussing ways to boost non-oil commerce in rupees that will promote internationalisation of rupees.
- UAE is the second largest export destination of India (after the US) with an amount of over US$ 28 billion for the year 2021-22.
- For the UAE, India is the second largest trading partner for the year 2021 with an amount of around USD 45 billion (non-oil trade).
- Defence Cooperation: With the spread of radicalism in the Gulf and South Asia, India looks to enhance security cooperation with the UAE to counter terrorist threats and combat radicalization.
- ‘Desert Eagle II’, is a joint air combat exercise, between air forces of India and UAE.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The International Solar Alliance was launched at the United Nations Climate Change Conference in 2015.
- The Alliance includes all the member countries of the United Nations.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (a)
Mains
Q. How will I2U2 (India, Israel, UAE and USA) grouping transform India's position in global politics? (2022)
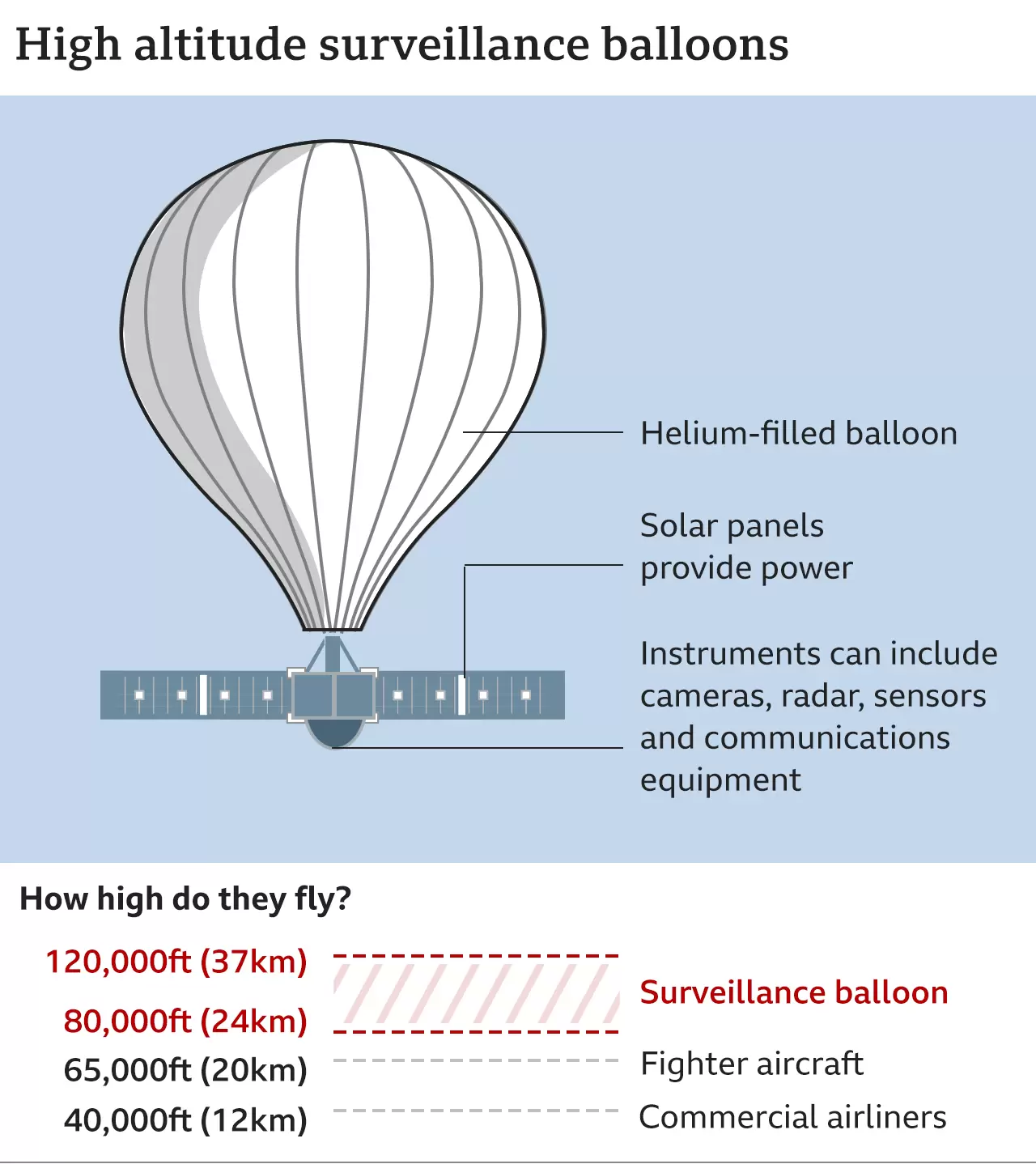
Surveillance Balloon
For Prelims: Surveillance Balloon, Human Intelligence, Outer Space Treaty 1967.
For Mains: Ways of Surveillance Techniques, Air Space and Related Laws.
Why in News?
The United States (US) shot down a Chinese surveillance balloon that has been spotted over US airspace for a couple of days.
What is a Surveillance Balloon?
- About:
- These cheap, quiet and hard-to-reach balloons have been used for reconnaissance purposes, including in conflicts like the American Civil War.
- The practice became widespread during World War I and was used extensively during the Cold War when the US launched hundreds of balloons to gather intelligence on the Soviet Union and China.
- While their use has declined with the rise of unmanned drones and satellites, many countries still employ spy balloons.
- The Purpose of Sending the Balloon:
- China has for decades complained about US surveillance by ships and spy planes near its own territory, leading to occasional confrontations over the years. According to China, the balloon was for research but got off track.
Why do Governments use Surveillance Balloons?
- Close-range Monitoring: In the age of satellites, surveillance balloons which are typically advanced balloons equipped with high-tech, downward-pointing imaging gear offer close-range monitoring.
- Image Quality: The lower-flying balloons, which hover at about the same height as commercial airlines fly, can typically take clearer images than the lowest orbiting satellites.
- Satellites that rotate in sync with Earth capture continuous but hazier images due to farther orbit.
- Intercepting Communication: Surveillance balloons can also be capable of “gathering electronic signals” and intercepting communications.
What are the Other Ways of Surveillance Techniques?
- Electronic Surveillance: It can be used in intercepting communication signals, tapping phone calls, and monitoring emails and other forms of digital communication.
- Human Intelligence (HUMINT): It is one of the main components used in surveillance by recruiting individuals with access to sensitive information, such as embassy staff, military personnel, or government officials.
- Cyber Espionage: It is a form of cyber-attack that steals classified, sensitive data or intellectual property to gain an advantage over a competitive company or government entity.
- Satellite Imagery: Satellites are sometimes used to gather information about foreign countries.
- Drone Technology: Drones, also known as unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) can be used for surveillance and espionage purposes. Drones equipped with cameras, listening devices, and other sensors can fly over foreign territories and gather intelligence.
What is Air Space and its Related Laws?
- About:
- Air space, in international law, is the space above a particular national territory, treated as belonging to the government controlling the territory.
- It does not include outer space, which, under the Outer Space Treaty of 1967 is declared to be free and not subject to national appropriation.
- The treaty, however, did not define the altitude at which outer space begins and air space ends.
- Air Sovereignty:
- It is the fundamental right of a sovereign state to regulate the use of its air space and enforce its own aviation law.
- The State controls the entry of foreign aircraft into its territory and that persons within its territory are subject to its laws.
- The principle of air space sovereignty is established through the Paris Convention on the Regulation of Aerial Navigation (1919) and subsequently by other multilateral treaties.
- Under the 1944 Chicago Convention, contracting states agree to permit aircraft registered in the other contracting states and engaged in commercial non-scheduled flights to fly into their territory without prior diplomatic permission and, moreover, to pick up and discharge passengers, cargo, and mail.
- This provision, in practice, has become a dead letter.
- Prohibited Air Space:
- It refers to an area of air space within which flight of aircraft is not allowed, usually due to security concerns. It is one of many types of special use airspace designations and is depicted on aeronautical charts with the letter "P" followed by a serial number.
- Restricted Air Space:
- Different from prohibited air space, in this space, entry is typically forbidden for all aircraft and is not subjected to clearance from ATC (Air Traffic Control) or the air space's controlling body.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. International civil aviation laws provide all countries complete and exclusive sovereignty over the airspace above their territory. What do you understand by ‘airspace’? What are the implications of these laws on the space above this airspace? Discuss the challenges which this poses and suggest ways to contain the threat. (2014)
Paris Club
For Prelims: Paris Club, International Monetary Fund, Sri Lanka Economic Crisis, Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD)
For Mains: India's Position on Bilateral Negotiation with Sri Lanka, India’s Neighborhood First Policy.
Why in News?
The Paris Club, an informal group of creditor nations, will provide financial assurances to the International Monetary Fund (IMF) on Sri Lanka’s debt.
- Sri Lanka needs assurance from the Paris Club and other creditors in order to receive a USD 2.9 billion bailout package from the IMF, following an economic crisis in 2022.
What is the Paris Club?
- About:
- The Paris Club is a group of mostly western creditor countries that grew from a 1956 meeting in which Argentina agreed to meet its public creditors in Paris.
- It describes itself as a forum where official creditors meet to solve payment difficulties faced by debtor countries.
- Their objective is to find sustainable debt-relief solutions for countries that are unable to repay their bilateral loans.
- The Paris Club is a group of mostly western creditor countries that grew from a 1956 meeting in which Argentina agreed to meet its public creditors in Paris.
- Members:
- The members are: Australia, Austria, Belgium, Canada, Denmark, Finland, France, Germany, Ireland, Israel, Japan, Netherlands, Norway, Russia, South Korea, Spain, Sweden, Switzerland, the United Kingdom and the United States.
- All 22 are members of the group called Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
- Involved in Debt Agreements:
- According to its official website, Paris Club has reached 478 agreements with 102 different debtor countries.
- Since 1956, the debt treated in the framework of Paris Club agreements amounts to USD 614 billion.
- Recent Developments:
- The Paris group countries dominated bilateral lending in the last century, but their importance has receded over the last two decades or so with the emergence of China as the world’s biggest bilateral lender.
- In Sri Lanka’s case, for instance, India, China, and Japan are the largest bilateral creditors.
- Sri Lanka’s debt to China is 52% of its bilateral debt, 19.5% to Japan, and 12% to India.
What is India's Position on Bilateral Negotiation with Sri Lanka?
- India launched its own bilateral negotiations with Sri Lanka in January 2023.
- The Indian External Affairs Minister announced that India had written to the IMF providing the necessary financial assurances, adding that it hoped others would follow suit.
- The decision of financing assurance was also a reassertion of India’s belief in the principle of “neighborhood first”, and not leaving a partner to fend for themselves.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q1. "Rapid Financing Instrument" and "Rapid Credit Facility" are related to the provisions of lending by which one of the following? (2022)
(a) Asian Development Bank
(b) International Monetary Fund
(c) United Nations Environment Programme Finance Initiative
(d) World Bank
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Rapid Financing Instrument (RFI) provides quick financial assistance, which is available to all member countries facing urgent balance of payments requirements. The RFI was created as part of a broader reform to make IMF financial support more flexible to meet the diverse needs of member states. The RFI replaces the IMF's previous emergency assistance policy and can be used in a wide variety of circumstances.
- The Rapid Credit Facility (RCF) provides immediate balance of payments (BoP) requirements to low-income countries (LICs) with no ex-post condition, where a full economic program is neither necessary nor feasible. RCF was set up as part of a comprehensive reform to make the fund's financial support more flexible and better suited to suit the diverse needs of LIC including times of crisis.
- There are three areas under the RCF: (i) a "regular window" for immediate BoP needs due to a wide range of sources such as household instability, emergencies and fragility (ii) for immediate BoP needs due to sudden, exogenous shocks. an “exogenous shock window” and (iii) a “large natural disaster window” for immediate BoP needs due to natural disasters where the damage is estimated to be equal to or greater than 20% of the member's GDP.
Q2. “Gold Tranche” (Reserve Tranche) refers to (2020)
(a) a loan system of the World Bank
(b) one of the operations of a Central Bank
(c) a credit system granted by WTO to its members
(d) a credit system granted by IMF to its members
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q1. In respect of India-Sri Lanka relations, discuss how domestic factors influence foreign policy. (2013)
Q2. ‘India is an age-old friend of Sri Lanka.’ Discuss India's role in the recent crisis in Sri Lanka in the light of the preceding statement. (2022)
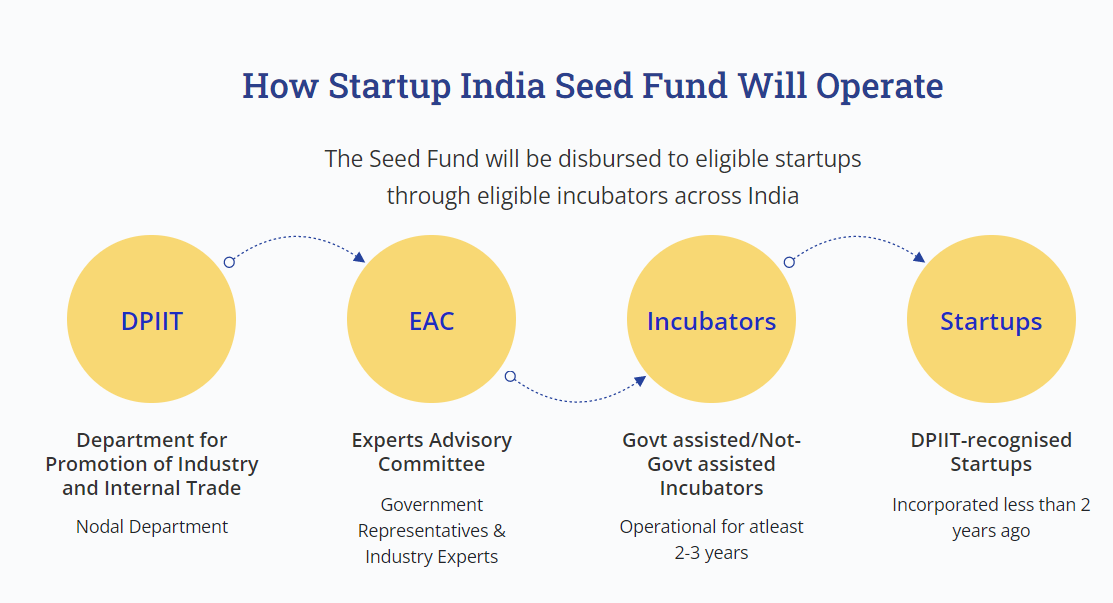
Startup India Seed Fund Scheme
Prelims: Startup India Seed Fund Scheme, Startup India Initiative, DPIIT, Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems, Make in India, Invest India.
Mains: Startup India Seed Fund Scheme and the Need for early-stage Seed Fund.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Commerce and Industry has approved Rs. 477.25 crore under the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme (SISFS), which is a flagship Scheme under Startup India Initiative.
- Seed Funding is an early stage of investment in a start-up or a new business idea. The goal of seed funding is to help the company reach a point where it can secure additional rounds of funding or generate revenue to become self-sustaining.
What is the Startup India Initiative?
- The Startup India initiative envisages building a robust Start-up ecosystem in the country for nurturing innovation and providing opportunities to budding entrepreneurs.
- Under the Initiative, an Action Plan of 19 Action Points was unveiled by the Prime Minister in January, 2016.
- This Action Plan laid down a roadmap for the creation of a conducive ecosystem for Startups in India.
- The flagship schemes under Startup India initiative namely, Fund of Funds for Startups (FFS), SISFS and Credit Guarantee Scheme for Startups (CGSS) extend support to startups at various stages of their business cycle.
What is SISFS?
- About:
- The scheme was announced at Startup India International Summit on 16th January 2021.
- Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT) approved an outlay of Rs. 945 Crore for the period of 4 years starting from 2021-22 to provide financial assistance to startups for Proof of Concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry, and commercialization.
- Execution and Monitoring:
- An Experts Advisory Committee (EAC) has been constituted by DPIIT, which will be responsible for the overall execution and monitoring of the Startup India Seed Fund Scheme.
- The EAC will evaluate and select incubators for allotment of Seed Funds, monitor progress, and take all necessary measures for efficient utilization of funds towards fulfilment of objectives of Startup India Seed Fund Scheme.
- Eligibility:
- A startup, recognized by DPIIT (Ministry of Commerce and Industry), incorporated not more than 2 years ago at the time of application.
- Startups should not have received more than Rs. 10 lakhs of monetary support under any other Central or State Government scheme.
- Preference would be given to startups creating innovative solutions in sectors such as social impact, waste management, water management, financial inclusion, education, agriculture, food processing, biotechnology, healthcare, energy, mobility, defence, space, railways, oil and gas, textiles, etc.
- Grants and Support:
- It will support an estimated 3,600 entrepreneurs through 300 incubators in the next 4 years.
- Grants of upto Rs. 5 crores will be provided to the eligible incubators selected by the committee.
- The selected incubators will provide grants of up to Rs. 20 lakhs for validation of proof of concept, or prototype development, or product trials to startups.
- Investments of up to Rs. 50 lakhs will be provided to the startups for market entry, commercialization, or scaling up through convertible debentures or debt-linked instruments.
What is the Need for Seed Fund?
- Easy availability of capital is essential for entrepreneurs at the early stages of growth of an enterprise.
- The Indian startup ecosystem suffers from capital inadequacy in the seed and ‘Proof of Concept’ development stage.
- The capital required at this stage often presents a make-or-break situation for startups with good business ideas.
- Many innovative business ideas fail to take off due to the absence of this critical capital required at an early stage for proof of concept, prototype development, product trials, market entry and commercialization.
- Seed Fund offered to such promising cases can have a multiplier effect in validation of business ideas of many startups, leading to employment generation.
What are the other Initiatives Pertaining to Startups?
- Startup Innovation Challenges: It is a fantastic opportunity for any startup to leverage their networking and fund-raising efforts.
- National Startup Awards: It seeks to recognize and reward outstanding startups and ecosystem enablers that are contributing to economic dynamism by spurring innovation and injecting competition.
- Ranking of States on Support to Startup Ecosystems: It is an evolved evaluation tool aimed to strengthen the support of States and UTs to holistically build their startup ecosystems.
- SCO Startup Forum: The first-ever Shanghai Cooperation Organisation (SCO) Startup Forum was launched in October 2020 to develop and improve startup ecosystems collectively.
- Prarambh: The ‘Prarambh’ Summit aims to provide a platform to the startups and young minds from around the world to come with new ideas, innovation and invention.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. What does venture capital mean? (2014)
(a) A short-term capital provided to industries
(b) A long-term start-up capital provided to new entrepreneurs
(c) Funds provided to industries at times of incurring losses
(d) Funds provided for replacement and renovation of industries
Ans: (b)
Exp:
- Venture capital is a form of fund for a new or growing business. It usually comes from venture capital firms that specialize in building high risk financial portfolios.
- With venture capital, the venture capital firm gives funding to the startup company in exchange for equity in the startup.
- The people who invest this money are called venture capitalists (VCs). Venture capital investment is also referred as risk capital or patient risk capital, as it includes the risk of losing the money if the venture does not succeed and takes a medium to long term period for the investments to fructify.
- Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Generative Artificial Intelligence
Prelims: Generative Artificial Intelligence, AI, Generative Adversarial Network, Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence.
Mains: Applications of Generative AI, Issues Associated with Generative AI, AI and Ethics.
Why in News?
The use of Generative Artificial Intelligence (GAI) is still in its early stages but its impact is likely to grow as technology continues to evolve and improve.
- The Government of India is cognizant of the emergence of the technologies related to GAI and their rapid proliferation in sectors like education, manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and others.
What is Generative Artificial Intelligence?
- About:
- GAI is a rapidly growing branch of AI that focuses on generating new content (such as images, audio, text, etc.) based on patterns and rules learned from data.
- The rise of GAI can be attributed to the development of advanced generative models, such as Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) and Variational Autoencoders (VAEs).
- These models are trained on large amounts of data and are able to generate new outputs that are similar to the training data. For example, a GAN trained on images of faces can generate new, synthetic images of faces that look realistic.
- While GAI is often associated with ChatGPT and deep fakes, the technology was initially used to automate the repetitive processes used in digital image correction and digital audio correction.
- Arguably, because machine learning and deep learning are inherently focused on generative processes, they can be considered types of GAI, too.
- Applications:
- Art and Creativity:
- It can be used to generate new works of art that are unique and innovative, helping artists and creatives explore new ideas and push the boundaries of traditional art forms.
- DeepDream Generator - An open-source platform that uses deep learning algorithms to create surrealistic, dream-like images.
- DALL·E2 - This AI model from OpenAI generates new images from text descriptions.
- It can be used to generate new works of art that are unique and innovative, helping artists and creatives explore new ideas and push the boundaries of traditional art forms.
- Music:
- It can help musicians and music producers explore new sounds and styles, leading to more diverse and interesting music.
- Amper Music - creates musical tracks from pre-recorded samples.
- AIVA - uses AI algorithms to compose original music in various genres and styles.
- It can help musicians and music producers explore new sounds and styles, leading to more diverse and interesting music.
- Computer Graphics:
- It can generate new 3D models, animations, and special effects, helping movie studios and game developers create more realistic and engaging experiences.
- Healthcare:
- By generating new medical images and simulations, improving the accuracy and efficiency of medical diagnoses and treatments.
- Manufacturing and Robotics:
- It can help optimize manufacturing processes, improving the efficiency and quality of these processes.
- Art and Creativity:
- Significance for India:
- As per NASSCOM data, the overall AI employment in India is estimated at about 416,000 professionals.
- The growth rate for the sector is estimated at about 20-25%. Further, AI is expected to contribute an additional USD 957 billion to India’s economy, by 2035.
What are the Concerns Related to GAI?
- Accuracy:
- One of the biggest challenges is ensuring that the outputs generated by GAI are of high quality and accurate.
- This requires the development of advanced generative models that can accurately capture the patterns and rules learned from data.
- Partisan GAI Models:
- GAI models are trained on large amounts of data, and if that data is biased, the outputs generated by GAI may also be biased. This can lead to discrimination and reinforce existing societal biases.
- Privacy:
- Training GAI models requires access to large amounts of data, which could include personal and sensitive information.
- There is a risk that this data could be used for unethical purposes, such as for targeted advertising or for political manipulation.
- Responsibility:
- Since GAI models can generate new content, such as images, audio, or text it may be used to generate fake news or other malicious content, without knowing who is responsible for the output. This could lead to ethical dilemmas over responsibility.
- Automation and Lowering Job:
- GAI has the potential to automate many processes, which could lead to job displacement for people who are skilled in those areas.
- This raises questions about the ethics of using AI for job displacement and the potential impact on workers and society.
What are the Related Indian Initiatives?
- National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence:
- The Government has published the National Strategy for Artificial Intelligence with the objective of developing an ecosystem for the research and adoption of Artificial Intelligence.
- National Mission on Interdisciplinary Cyber-Physical Systems:
- Under this Mission, Technology Innovation Hubs (TIH) has been established on Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning at the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Kharagpur, which aims to provide the state-of-the-art training and capacity building for the creation of next-generation scientists, engineers, technicians, and technocrats in the field of Artificial Intelligence.
- Artificial Intelligence Research, Analytics and Knowledge Assimilation Platform:
- It is a Cloud computing platform, aiming to make India a pioneer amongst emerging economies with regards to AI and transform sectors like education, health, agriculture, urbanization and mobility.
Way Forward
- More research and development is needed to improve the accuracy and reliability of GAI models and to address ethical concerns related to the technology. This includes developing new algorithms and models that are more transparent and accountable for their outputs.
- Regulations and standards must be put in place to ensure that GAI is used in a responsible and ethical manner. This includes establishing guidelines for data privacy, bias, and accountability, as well as ensuring that GAI is used for the benefit of society and not to the detriment of individuals or groups.
- Collaboration between stakeholders, including industry, government, academia, and civil society, is crucial to ensure that GAI is used in a responsible and ethical manner.
- GAI models are only as good as the data they are trained on, so it is important to ensure that the data used for training GAI models is ethical and unbiased. This includes ensuring that the data used for training is collected and used in a way that respects the privacy of individuals and does not reinforce existing biases.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. With the present state of development, Artificial Intelligence can effectively do which of the following? (2020)
- Bring down electricity consumption in industrial units
- Create meaningful short stories and songs
- Disease diagnosis
- Text-to-Speech Conversion
- Wireless transmission of electrical energy
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2, 3 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following pairs: (2018)
| Terms sometimes seen in news | Context/Topic | |
| 1. | Belle II experiment | Artificial Intelligence |
| 2. | Blockchain technology | Digital/Cryptocurrency |
| 3. | CRISPR–Cas9 | Particle Physics |
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
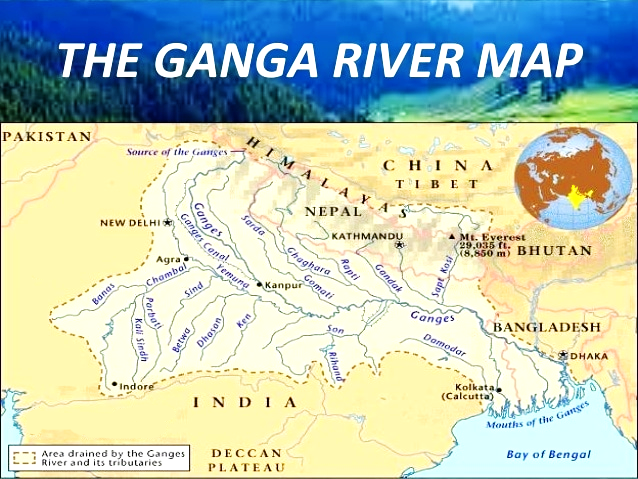
Groundwater loss for the Indian Ganga Basin
Why in News?
A recent report, "Estimation of groundwater storage loss for the Indian Ganga Basin using multiple lines of evidence," estimates that groundwater storage levels in the Ganga basin have been declining by 2.6 centimeters per year.
- The Ganga Basin’s aquifers are one of the largest reservoirs of groundwater in the world.
What are the Findings?
- The average groundwater levels have been declining at a rate of 2.6 cm year-1 between 1996-2017.
- The analysis of satellite data from the Gravity Recovery and Climate Experiment (GRACE), yielded an average loss of 1.7 cm per year-1.
- GRACE satellites, launched in 2002, assess Earth’s water reservoirs over land, ice and ocean.
- The average storage decline in Uttar Pradesh, Bihar and West Bengal was estimated to be roughly 2 cm year−1, 1 cm year−1 and 0.6 cm year−1, respectively.
- The impacts were more pronounced in Rajasthan, Haryana and Delhi, with average storage declines of roughly 14 cm year−1, 7.5 cm year−1 and 7.2 cm year−1, respectively.
- West and southwest areas, including agriculturally intensive regions and urban areas like Delhi and Agra, took the biggest hit.
- Delhi and Haryana have high groundwater abstraction rates, which explains the steep decline.
- The Brahmaputra basin shows more groundwater level reduction than the Ganga and Indus basins.
What is the Ganga River System?
- It is the longest river of India flowing over 2,510 km of mountains, valleys and plains and is revered by Hindus as the most sacred river on earth.
- The Ganga basin outspreads in India, Tibet (China), Nepal and Bangladesh over an area of 10,86,000 Sq.km.
- In India, it covers states of Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Bihar, West Bengal, Uttarakhand, Jharkhand, Haryana, Chhattisgarh, Himachal Pradesh and Union Territory of Delhi draining nearly 26% of the total geographical area of the country.
- It originates in the snowfields of the Gangotri Glacier in the Himalayas.
- At its source, the river is called as the Bhagirathi. It descends down the valley upto Devprayag where after joining another hill stream Alaknanda, it is called Ganga.
- The principal tributaries joining the river from right are the Yamuna and the Son.
- The Ramganga, the Ghaghra, the Gandak, the Kosi and the Mahananda join the river from left. The Chambal and the Betwa are the two other important sub- tributaries.
- The Ganges River Dolphin is an endangered animal that specifically habitats this river.
- The Ganga joins the Brahmaputra (Jamuna) in Bangladesh and continues its run under the name Padma.
- The Ganga widens out into the Ganges Delta in the Sundarbans swamp of Bangladesh, before it ends its journey by emptying into the Bay of Bengal.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Consider the following statements: (2020)
- 36% of India’s districts are classified as “overexploited” or “critical” by the Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA).
- CGWA was formed under the Environment (Protection) Act.
- India has the largest area under groundwater irrigation in the world.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 2 only
(d) 1 and 3 only
Ans: (b)
- Based on groundwater levels, areas across the country are split into three categories: Over-exploited, Critical and Semi critical. The first refers to groundwater being extracted more than what’s recharged i.e. extraction is more than 100%. Critical where the groundwater taken out is 90-100% of what’s recharged and semi-critical where extraction rate is 70%-90%.
- As per the report ‘National Compilation on Dynamic Groundwater Resources of India, 2017’ of CGWA, out of the total 6881 assessment units (Blocks/ Mandals/Talukas) in the country, 1186 units in various States (17%) have been categorized as ‘OverExploited’, 313 units (5%) are ‘Critical’, and 972 are semi-critical units (14%). Hence, statement 1 is not correct.
- Note: As per National Compilation on Dynamic Groundwater Resources of India 2020; Out of the total 6965 assessment units (Blocks/ Mandals/ Talukas/ Firkas) in the country, 16 % have been categorized as ‘Over-exploited, 4 % as Çritical, 15 % as Semi-critical and 64 %) as ‘Safe‘ units. Apart from these, there are 97 (1%) assessment units, which have been categorised as ‘Saline’.
- The Central Ground Water Authority (CGWA) was constituted under Section 3(3) of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986 to regulate, control development and management of ground water resources. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- As per report of Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) of UN, the countries with the largest extent of areas equipped for irrigation with groundwater, in absolute terms, are India (39 million ha), China (19 million ha) and the USA (17 million ha). Hence, statement 3 is correct. Therefore, option (b) is the correct answer.
Mains
Q1. India is well endowed with fresh water resources. Critically examine why it still suffers from water scarcity. (2015)
Q2. The idealsolution of depleting ground water resources in India is water harvesting system”. How can it be made effective in urban areas? (2018)
Q3. Discuss the Namami Gange and National Mission for Clean Ganga (NMCG) programmes and causes of mixed results from the previous schemes. What quantum leaps can help preserve the river Ganga better than incremental inputs? (2015)
Magnetite Pollution
Why in News?
Recently, some Geologists have found the presence of Magnetite Pollution on the roadside Dust of Kolkata.
- The frequency of pollutants is higher in areas with heavy vehicular traffic and other polluting sources. The amount of magnetite is proportional to the traffic on a given road.
What is Magnetic Pollution?
- About:
- Magnetite pollution refers to the presence of a magnetic mineral called Magnetite (Fe3O4) in the environment, as a result of human activities such as mining, steel production and industrial processes.
- Magnetite is an oxide of iron. It is the most magnetic of all the naturally occurring minerals on earth. It is a natural magnet.
- Magnetite contains about 72% metallic iron in it. It is found in Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Rajasthan, Tamil Nadu, Goa and Kerala.
- Magnetite pollution refers to the presence of a magnetic mineral called Magnetite (Fe3O4) in the environment, as a result of human activities such as mining, steel production and industrial processes.
- Impact:
- Ecological Impacts:
- Magnetic particles can interfere with the migratory patterns of birds and other animals, affecting their survival and reproduction.
- Soil and Water Contamination:
- Magnetite particles can settle in the soil and water, contaminating these environments and affecting the growth of plants and the health of aquatic life.
- Human Health:
- Inhaling magnetic particles can cause respiratory problems and other health problems, such as lung cancer, cardiovascular disease, and central nervous system damage.
- Building and Infrastructure Damage:
- Magnetic particles can cause corrosion of steel structures and other metal objects, leading to damage over time.
- Electronic Equipment Damage:
- Magnetic pollution can also interfere with the operation of electronic equipment, such as compasses and navigation systems.
- Ecological Impacts:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. In the cities of our country, which among the following atmospheric gases are normally considered in calculating the value of Air Quality Index? (2016)
- Carbon dioxide
- Carbon monoxide
- Nitrogen dioxide
- Sulfur dioxide
- Methane
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 3 only
(b) 2, 3 and 4 only
(c) 1, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. Describe the key points of the revised Global Air Quality Guidelines (AQGs) recently released by the World Health Organisation (WHO). How are these different from its last update in 2005? What changes in India’s National Clean Air Programme are required to achieve revised standards? (2021)
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
World Wetlands Day 2023
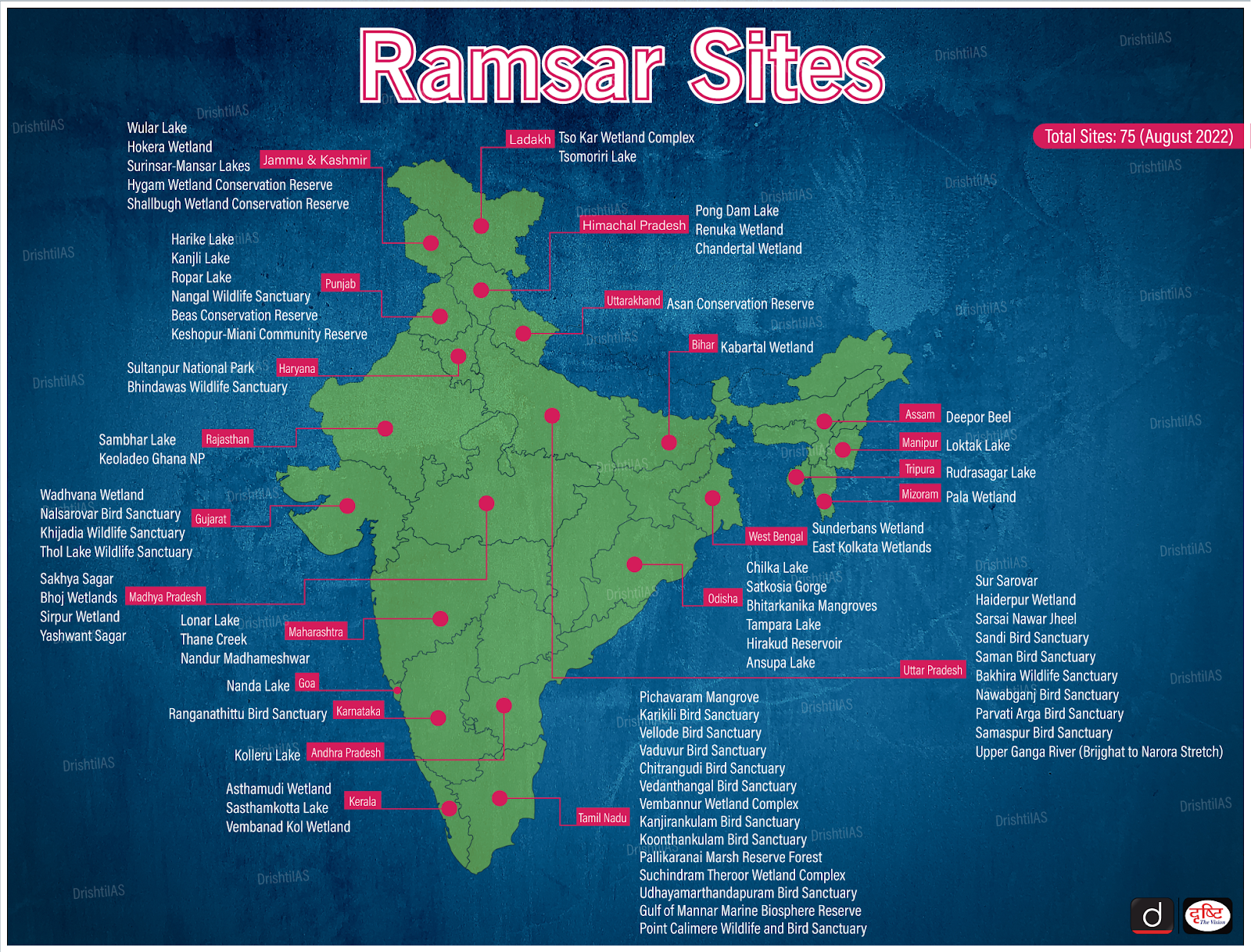
The State Govts and UT administrations across India celebrated World Wetlands Day (WWD) at all 75 Ramsar sites on 02nd Feb 2023.
The 2023 theme for World Wetlands Day is ‘Wetland Restoration’ highlighting the urgent need to prioritise wetland restoration.
The Union Minister for Environment, Forest and Climate Change launched the ‘Save Wetlands Campaign’ structured on a “whole of society” approach for wetlands conservation.
World Wetlands Day is celebrated all over the world to commemorate the signing of the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance (1971).
India has been a party to the Convention since 1982 and has so far declared 75 wetlands as Ramsar across 23 states/UTs. India has the largest network of Ramsar Sites in Asia.
Read More - World Wetlands Day, Ramsar Sites, Ramsar Convention (Infographics)
Sant Guru Ravidas Jayanti
The birthday of Sant Guru Ravidas was observed on 05th Feb 2023. Guru Ravidas Jayanti is celebrated on Magh Purnima (full moon day in the Magh month of the Hindu lunar calendar).
Guru Ravidas was a 15th century saint and reformer of the Bhakti movement who gained prominence due to his belief in one God and his unbiased religious poems. He dedicated his whole life to the abolition of the caste system and openly despised the notion of a Brahminical society. Around 41 of his poems were included in ‘Guru Granth Sahib’, the religious text of the Sikhs.
Read More - Guru Ravidas Jayanti
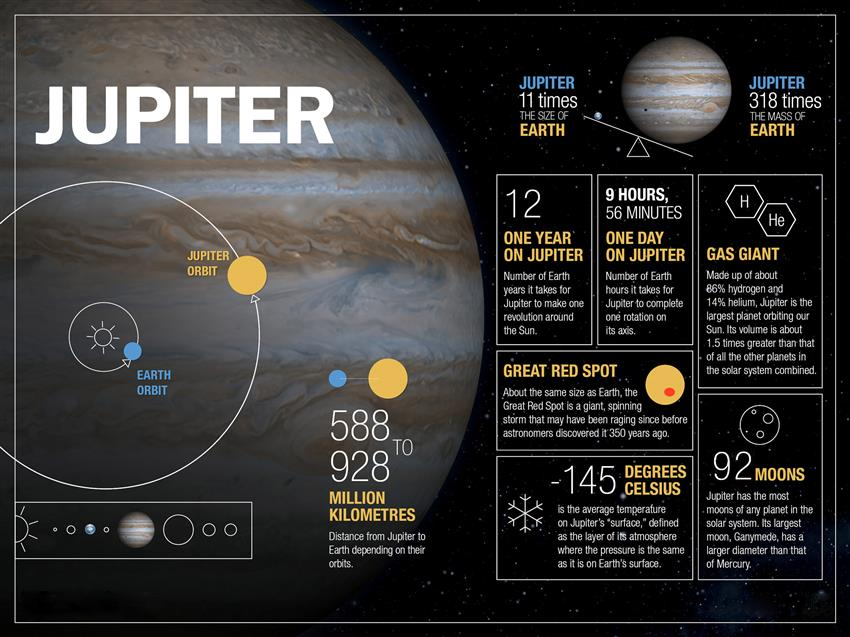
Jupiter Becomes the Planet with Most Moons
Astronomers recently discovered 12 new moons around Jupiter, increasing the total number of moons it has to 92 - the largest number any planet on our solar system has (Saturn has 83 moons).
The moons were discovered using telescopes in Hawaii and Chile in 2021 and 2022 and have been added to a list kept by the International Astronomical Union's Minor Planet Centre (size of these moons ranges from 1-3 kms).
Upcoming missions to Jupiter include - (a) ESA’s spacecraft to Jupiter to study the planet and some of its biggest, icy moons (in 2023), (b) NASA’s Europa Clipper to explore Jupiter's moon Europa which could harbour an ocean beneath its frozen crust (in 2024). NASA earlier launched Mission Lucy to explore the Jupiter Trojan Asteroids.
Apart from Jupiter and Saturn, Uranus has 27 confirmed moons, Neptune 14, Mars 2 and Earth has 1 moon while Venus and Mercury have no moons.
Read More - Jupiter and Europa
Medium Density Amorphous Ice
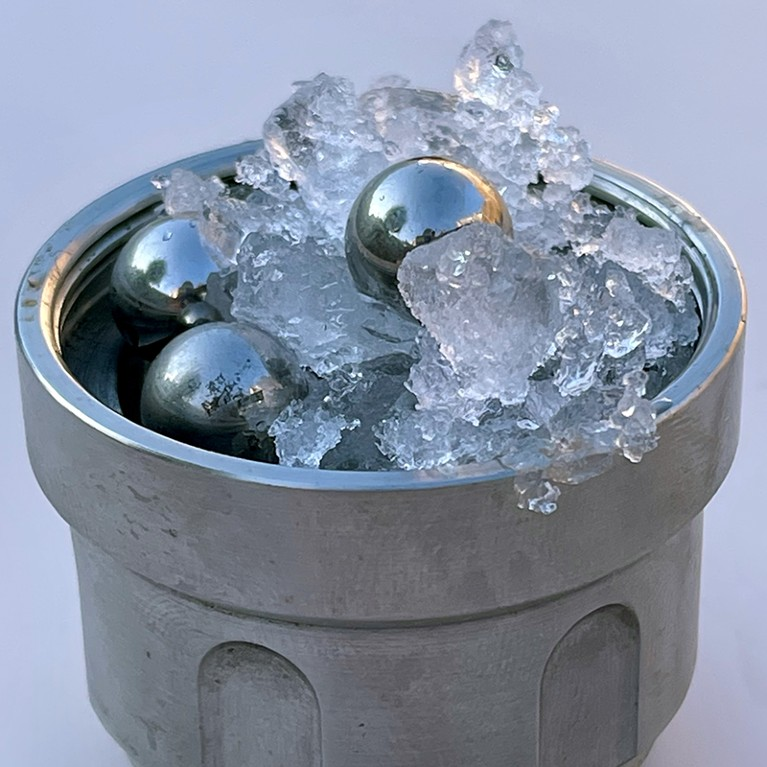
Scientists at University College London (UCL) have recently created a new type of ice that matches the density and structure of water. The ice is called medium-density amorphous ice.
The ice was created by shaking regular ice in a small container with centimetre-wide stainless-steel balls at temperatures of -200°C to produce the novel variant. The ice appeared as a white granular powder that stuck to the metal balls.
Normally, when water freezes, it crystallises and its molecules are arranged into the familiar hexagonal, solid structure - ice. Ice is less dense than its liquid form - an unusual property for a crystal.
Depending on conditions such as pressure and the speed of freezing, water can also solidify in many other regular arrangements. Amorphous ice, however, is different as it has no such order. Hence, this study could probably help in studying water’s mysterious properties.