6th BIMSTEC Summit
For Prelims:Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation, Indo-Pacific Region, Indian Ocean, South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation. For Mains:Key Highlights of 6th BIMSTEC Summit, Significance of BIMSTEC for Regional Cooperation. |
Source: PIB
Why in News?
The Indian Prime Minister participated in the 6th BIMSTEC Summit, hosted by Thailand under its chairmanship, with the theme "BIMSTEC: Prosperous, Resilient, and Open," focusing on enhancing regional cooperation and addressing key challenges.
- Also, on the sidelines of the summit, India and Thailand announced to elevate their bilateral ties to a Strategic Partnership.
What are the Key Highlights of the 6th BIMSTEC Summit?
- Vision 2030 Document: The Summit adopted the Summit Declaration and Bangkok Vision 2030, outlining a roadmap for regional prosperity with a focus on economic integration, resilience to global challenges, and collaboration in infrastructure, and technology.
-
- BIMSTEC Centres of Excellence: India announced establishment of BIMSTEC Centres of Excellence in India, focusing on Disaster Management, Sustainable Maritime Transport, Traditional Medicine, and Research and Training in Agriculture.
- Also, initiative for linking India's UPI with BIMSTEC payment systems, and operationalizing the BIMSTEC Energy Centre in Bengaluru.
- It also proposed a pilot study on Digital Public Infrastructure (DPI) to enhance governance and service delivery in BIMSTEC.
- BODHI Program: India introduced BODHI Program (BIMSTEC for Organized Development of Human Resource Infrastructure) for skill development, providing training, scholarships, and capacity-building for various professionals across BIMSTEC nations.
- Cancer Care Capacity Building: India proposed a capacity-building program for cancer care in the BIMSTEC region.
- Chamber of Commerce and Business Summit: Establishment of BIMSTEC Chamber of Commerce and hosting an annual BIMSTEC Business Summit was proposed to promote regional economic integration among member nations.Key Action Plans Announced by India: India proposed a 21-point Action Plan and some of the important plan such as:
- People-to-People Linkages: India announced initiatives to strengthen cultural and people-to-people ties, including, BIMSTEC Athletics Meet (2025), First BIMSTEC Games (2027), marking the group's 30th anniversary, BIMSTEC Traditional Music Festival, Young Leaders’ Summit and Hackathon for youth engagement, Young Professional Visitors Program to deepen cultural cooperation.
What are the Key Initiatives Announced under the India-Thailand Strategic Partnership?
- Maritime Cooperation: Collaboration in the Indo-Pacific through frameworks like the ASEAN Outlook on the Indo-Pacific (AOIP) and India’s Indo-Pacific Oceans Initiative (IPOI), with emphasis on maritime security, and regional connectivity via the India-Myanmar-Thailand Trilateral Highway.
- Defence and Security: Expansion of defence dialogues, joint military exercises such as Exercise Maitree, and cooperation in areas like counter-terrorism, cybersecurity, and intelligence sharing.
- Trade and Economic Engagement: Initiatives to boost bilateral trade, enhance supply chain resilience, promote private sector investment, and explore upgradation of the Free Trade Agreement (FTA).
- Cultural and People-to-People Ties: Promotion of educational exchanges, celebration of Buddhist cultural linkages, promotion of tourism, and deeper engagement with the Indian diaspora in Thailand.
- Science, Technology, and Innovation: Joint cooperation in fields such as renewable energy, space technology, development of digital public infrastructure, and innovation in healthcare and biotechnology.
- Regional and Multilateral Cooperation: Strengthening coordinated efforts in regional and international forums such as BIMSTEC, the Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), the Indian Ocean Rim Association (IORA), and the United Nations (UN) to promote a rules-based international order.
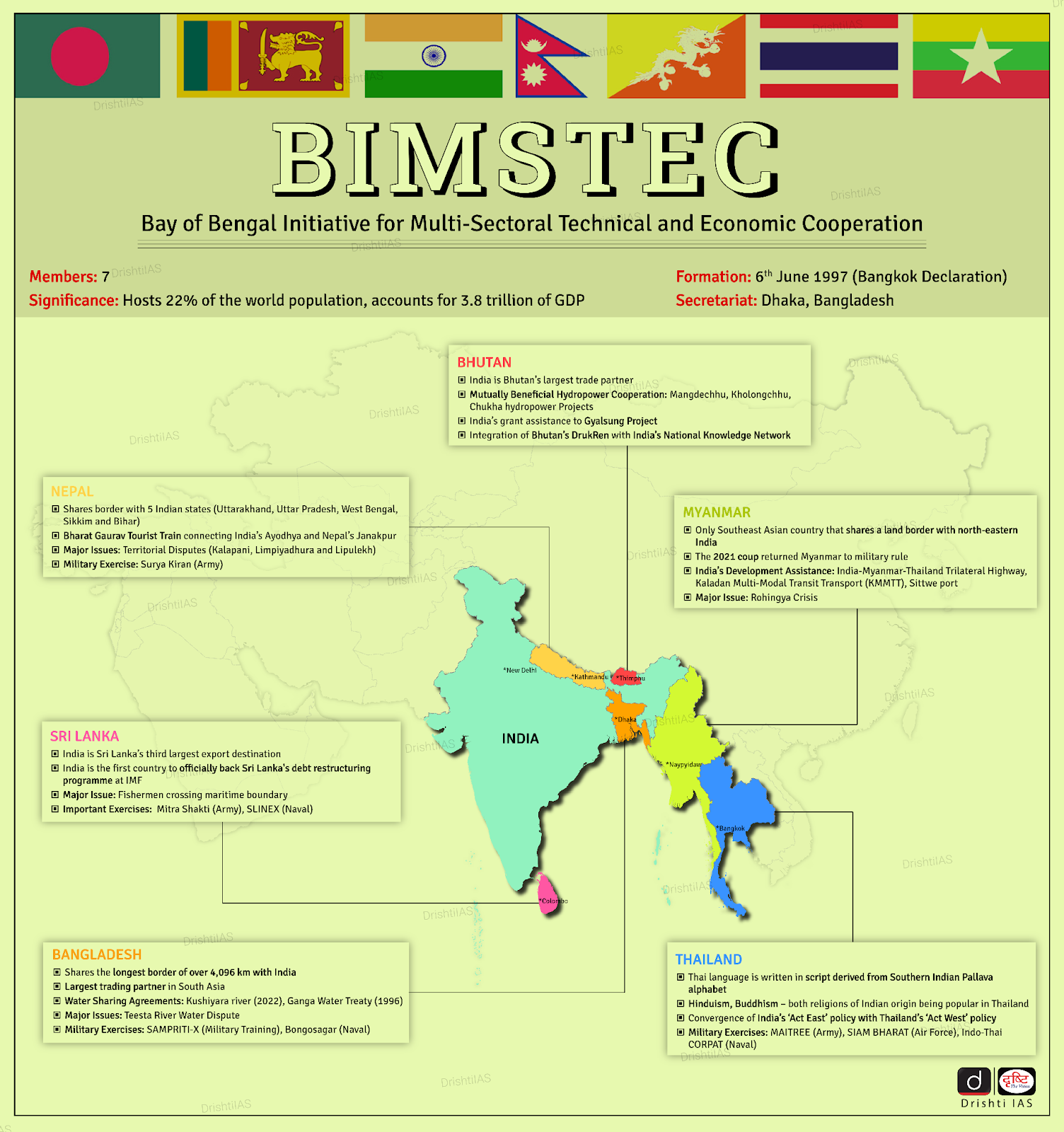
What is BIMSTEC?
- About: BIMSTEC (Bay of Bengal Initiative for Multi-Sectoral Technical and Economic Cooperation) is a regional organization comprising 7 member states as Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Myanmar, Nepal, Sri Lanka, and Thailand.
- Objective: It aims to foster multifaceted technical and economic cooperation among countries in the Bay of Bengal region.
- Origin: It was founded in 1997 with the adoption of the Bangkok Declaration.
- Initially comprising 4 members, it was known as BIST-EC (Bangladesh, India, Sri Lanka, and Thailand Economic Cooperation). In 1997, Myanmar joined, and the grouping was renamed BIMST-EC.
- With the inclusion of Nepal and Bhutan in 2004, the name was further changed to BIMSTEC.
- Significance:
- BIMSTEC countries, with a population of 1.7 billion (22% of the world’s total), have a combined GDP of around USD 5.2 trillion (2023).
What is the Significance of BIMSTEC?
- Alignment with Act East Policy: BIMSTEC aligns with India’s Act East Policy, enhancing India’s trade and security prominence in the Indian Ocean and Indo-Pacific regions.
- Alternative to SAARC: It has emerged as a preferred platform for regional cooperation, offering a viable alternative to SAARC in South Asia.
- Platform for Regional Cooperation: It serves as a key platform for fostering deeper cooperation among South and Southeast Asian countries, particularly in security matters and Humanitarian Assistance and Disaster Relief (HADR) management.
- It also serves as a platform for regional cooperation to balance China’s growing influence through the Belt and Road Initiative (BRI).
- Promotion of Intangible Culture: India’s initiatives, like the Centre for Bay of Bengal Studies (CBS) at Nalanda University, aim to preserve the region’s intangible cultural heritage, while BIMSTEC fosters regional collaboration and cultural exchange.
What are the Challenges Related to BIMSTEC?
Click Here to Read: Challenges
What are the Suggested Measures for Enhancing BIMSTEC’s Effectiveness?
Click Here to Read: Way Forward for BIMSTEC
Conclusion
The 6th BIMSTEC Summit advanced regional cooperation, focusing on economic integration, disaster resilience, and cultural ties. India’s leadership through initiatives like Centres of Excellence and skill development programs strengthens the region’s future prospects. As BIMSTEC celebrates its 30th anniversary in 2027, the Summit’s outcomes foster a more prosperous and resilient Bay of Bengal region.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. How successful has BIMSTEC been in achieving its goals of economic and technical cooperation among its member countries? |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)Q. Do you think that BIMSTEC is a parallel organisation like the SAARC? What are the similarities and dissimilarities between the two? How are Indian foreign policy objectives realized by forming this new organisation? (2022) |
Audible Enclaves and PAL Technology
Sound waves are longitudinal, propagating through compression and rarefaction, but they also spread due to diffraction, leading to dispersion (which increases with frequency), making precise sound delivery to a specific individual difficult in noisy environments.
- However, audible enclaves and parametric array loudspeakers (PAL) solve this by focusing sound into narrow beams, ensuring only the intended listener hears it.
- Audible Enclaves (AE): These are focused pockets of sound created using 2 high-frequency waves that are individually inaudible but produce audible sound at specific locations through nonlinear interactions.
- This ensures precision sound delivery without external disturbance, enhancing privacy and customization.
- PAL: PAL uses high-frequency ultrasonic waves modulated with an audio signal to create a highly directional sound beam, ensuring only targeted listeners hear the audio.
- By self-demodulating in the air, they generate focused sound while preventing unwanted dispersion.
- Applications of PAL and AE: PAL and AE find applications in museums, retail, public announcements, immersive entertainment, assistive technology, and security, offering precise audio without disturbing surrounding areas.
Reforming Indian Railways
For Prelims:Comptroller and Auditor General (CAG), KAVACH, Vande Bharat Train, Hydrogen Train, Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs), Extra-Budgetary Resources (EBRs), Mission Raftar, Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK). For Mains:Significance of Railways for India, Issues related to Indian Railways and way forward. |
Source: TH
Why in News?
The Comptroller and Auditor General’s (CAG) audit report on the Ministry of Railways highlighted the various concerns in the functioning of Indian Railways.
What are Key Facts About Indian Railways?
- About: India has the 4th largest railway network in the world, with over 65,000 km of route length.
- In 2022, Indian Railways carried 8 billion passengers, 1.4 billion tons of freight, and is expected to contribute to 40% of global rail activity by 2050.
- Infrastructure Spending: The government plans to invest USD 750 billion by 2030, as part of a broader USD 1.4 trillion investment target (2019–2023) in infrastructure.
- 100% FDI allowed in the railway sector, encouraging global participation.
- Innovation: KAVACH, India’s own Train Collision Avoidance System, will be deployed over 37,000 km of railway lines.
- 15,000 km of tracks will be converted into automatic signaling zones, enhancing safety and efficiency.
- Vande Bharat trains feature quick acceleration, automatic doors, CCTV, bio-toilets, GPS info systems, and onboard infotainment.
- Financial Performance: In 2023–24, Indian Railways earned USD 32.18 billion in traffic revenue, 99.8% of its total income, showing strong efficiency and public reliance.
- Future Plans:
- High-Speed Rail: Mumbai–Ahmedabad bullet train and other semi-high speed trains.
- Signaling & Telecom: Plans to upgrade around 15,000 km to automatic signaling and 37,000 km with KAVACH.
- Digitalization: Railway puts emphasis on predictive maintenance, asset management, and GPS info systems.
- Intermodal Transport: Integration of rail, road, and ports for smoother logistics.
- Net Zero Carbon Emissions Target: Indian Railways aims for net zero carbon emissions by 2030. As a start, it plans to run 35 hydrogen trains under the Hydrogen for Heritage program.
What is the Significance of Indian Railways?
- Lifeline for the Nation: Indian Railways is the backbone of India's transport, providing affordable, reliable travel and boosting economic integration nationwide.
- Industrial Expansion: It enables the transport of essential commodities like coal, iron ore, cement, and agricultural products, ensuring uninterrupted industrial operations.
- Dedicated Freight Corridors (DFCs) lowers logistics costs, making Indian manufacturing more competitive in the global market.
- Employment: With over 1.2 million employees, it is the 9th-largest employer in the world.
- Regional Development: Railways play a pivotal role in linking rural regions to urban markets, improving access to education, healthcare, and jobs in underdeveloped regions.
- Green Transport: The use of energy-efficient locomotives, green bio-toilets, and electrified routes reflects the commitment to environmental responsibility.
- National Security: Strategic rail links in sensitive areas like the North-East bolster national security and rapid mobilization.
What Concerns are Associated with Indian Railways?
- High Operating Ratio: The operating ratio (OR) for 2024–2025 is estimated at Rs 98.2—slightly better than Rs 98.7 in 2023–2024, but worse than Rs 97.8 in 2016.
- A higher OR (amount spent to earn Rs 100) leaves less resources for capex and makes the Railways more dependent on budgetary support and Extra-Budgetary Resources (EBRs).
- Slow Infrastructure Development: Among the DFCs (proposed in 2005), only the eastern DFC is fully operational and western DFC nears completion.
- The east coast, east-west, and north-south sub-corridor DFC remain in the planning stage.
- The Mumbai-Ahmedabad bullet train project has been delayed from 2023 to 2028 due to land acquisition issues.
- Inadequate Safety Technologies: While Kavach can prevent collisions through automated braking and alerts, its limited rollout reduces its overall impact.
- As of February 2024, it had been installed on only 1,465 route km—just 2% of the total railway network.
- Slow Journeys: Mail and express trains continue to run at an average speed of just 50–51 kmph, falling short of the goals set under Mission Raftar.
- Mission Raftaar (2016–17 Budget) aims to double freight train speeds and raise passenger train speeds by 25 kmph within 5 years.
What Recommendations Have Various Committees Made to Improve Railways?
- Rakesh Mohan Committee (2010): Emphasized development of long-distance and inter-city transport, including High-Speed Rail corridors.
- Establishment of National Transport Infrastructure Finance, ensuring neutrality regarding mobility, sustainability, and inclusion goals.
- Kakodkar Committee (2012): Called for establishing a statutory Railway Safety Authority.
- Proposed a non-lapsable Rashtriya Rail Sanraksha Kosh (RRSK) of Rs 1 lakh crore over 5 years for safety-related projects.
- Bibek Debroy Committee (2014): Recommended creation of a Railway Infrastructure Authority as an advisory body to help the government make informed decisions on issues like promoting competition, efficiency, and economy.
- Suggested outsourcing of non-core activities (e.g., schools, hospitals) to increase efficiency and reduce operational load on Indian Railways.
Way Forward
- Broaden Freight Portfolio: Focus should be on specialized freight solutions for high-value and sensitive commodities such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and perishable goods.
- High-Speed Railways: Upgrading railway infrastructure to support speeds of 160–200 km/h could significantly cut travel time, making rail a strong alternative to air travel on key intercity routes.
- Multimodal Logistics Infrastructure: Integrated multimodal logistics parks should be prioritized, featuring automation, smart inventory systems, and smooth intermodal transfers for higher efficiency.
- Private Sector Participation: Indian Railways should boost private participation in areas like rolling stock, catering, and logistics.
- Competitive bidding on busy routes can raise efficiency and ease the government's burden.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Q. Railways act as an engine for inclusive economic growth and regional development. Discuss. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)MainsQ. The setting up of a Rail Tariff Authority to regulate fares will subject the cash strapped Indian Railways to demand subsidy for the obligation to operate nonprofitable routes and services. Taking into account the experience in the power sector, discuss if the proposed reform is expected to benefit the consumers, the Indian Railways or the private container operators. (2014) |
GI Tag to Tomato Chilli and Kannadippaya
Why in News?
Telangana’s Warangal Chapata Chilli (Tomato Chilli) and Kerala’s tribal handicraft Kannadippaya have been granted the Geographical Indication (GI) tag, further enriching India’s GI registry, which now has over 600 products listed.
Geographical Indication (GI) Tag
- About: A GI tag is a name or sign used on certain products that correspond to a specific geographical location or origin.
- The GI tag ensures that only authorised users or those residing in the geographical territory are allowed to use the popular product name.
- It also protects the product from being copied or imitated by others.
- A registered GI is valid for 10 years and can be renewed.
- GI registration is overseen by the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade under the Ministry of Commerce and Industry.
- The GI tag ensures that only authorised users or those residing in the geographical territory are allowed to use the popular product name.
- Legal Framework:
What are the Key Facts About Warangal Chapata Chilli?
- About: It is Telangana’s 18th GI-tagged product and the third agricultural GI, after Banaganapalli Mango and Tandur Red Gram.
- Features: It is known for its bright red colour and round tomato-like shape.
- The chilli is less spicy but lends a bright red colour with extensive flavour due to its capsicum oleoresin properties (anti-obesogenic, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective properties).
- Types: It exists in three fruit types: Single Patti, Double Patti, and Odalu.
- Cultivation: The Warangal Chapata is under cultivation in the villages of Nagaram of Jammikunta mandal for more than 80 years while Nadikuda village and mandal could be the oldest source.
- Its unique characteristics can be attributed to the red and black soil of the region.
- The area's unique soil, water, and weather make it hard to grow this crop anywhere else.
What are the Key Facts About Kannadippaya?
- About: The recognition makes Kannadippaya the first tribal handicraft product from Kerala to receive the GI tag.
- Origin: The craft is primarily preserved by the Oorali, Mannan, Muthuva, Malayan, and Kadar tribal communities and by the Ulladan, Malayarayan, and Hill Pulaya artisans in Idukki, Thrissur, Ernakulam, and Palakkad districts.
- In the past, Kannadippaya was once presented to kings by tribal communities as a mark of honour.
- Key Features: The product derives its name, which literally means mirror mat, from its unique reflective pattern
- It is made from the soft inner layers of reed bamboo (Teinostachyum wightii), the mat is known for its unique properties like providing warmth during winter and cooling effects in summer.
What are the Other Recent GI Tagged Products?
|
Product |
State |
Year |
Fact |
|
Banaras Thandai |
Uttar Pradesh |
2024 |
Traditional spiced beverage associated with Varanasi. |
|
Assam Bihu Dhol |
Assam |
2024 |
Traditional drum integral to Bihu celebrations. |
|
Kasti Coriander |
Maharashtra |
2023 |
Known for its distinctive fragrance and taste |
|
Koraput Kalajeera Rice |
Odisha |
2023 |
Aromatic black paddy rice, often referred to as the 'Prince of Rice'. |
|
Uttarakhand Red Rice |
Uttarakhand |
2023 |
High-altitude rice known for its nutritional benefits and distinct aroma. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Which of the following has/have been accorded ‘Geographical Indication’ status? (2015)
- Banaras Brocades and Sarees
- Rajasthani Daal-Bati-Churma
- Tirupathi Laddu
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Q. India enacted the Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection) Act, 1999 in order to comply with the obligations to (2018)
(a) ILO
(b) IMF
(c) UNCTAD
(d) WTO
Ans: (d)
NITI NCAER States Economic Forum Portal
Source: ET
The Union Finance Minister launched the "NITI NCAER States Economic Forum" portal, developed by NITI Aayog in collaboration with the National Council of Applied Economic Research (NCAER).
- About NITI NCAER States Economic Forum Portal: The portal is a comprehensive repository of 30 years (1990–91 to 2022–23) of data on Indian states, covering demography, economy, fiscal indicators, health, education, and expert research on state finances.
4 Main Components of the Portal:
- State Reports: It summarizes the macro and fiscal landscape of 28 States, highlighting indicators in demography, economic structure, socio-economic, and fiscal areas.
- Data Repository: Offers direct access to a comprehensive database categorized under five key verticals — Demography, Economic Structure, Fiscal Indicators, Health, and Education.
- State Fiscal and Economic Dashboard: Provides graphical representations of key economic variables and quick access to raw data and summary tables.
- Research and Commentary: It offers extensive research on State finances and critical aspects of fiscal policy and financial management at the State and national levels.
Significance of the Portal:
- User-Friendly & Comparative Tool: Enables benchmarking of states against each other and the national average.
- Aid for Policymaking: Supports evidence-based policymaking through historical trends and real-time analytics.
- One-Stop Research Hub: Acts as a centralized platform for scholars, policymakers, and stakeholders to access long-term data in a consolidated manner.
Read More: Forging the Future of Federalism in India
Chandrayaan’s ChaSTE
India's Chandrayaan-3 mission’s ChaSTE (Chandra’s Surface Thermophysical Experiment) became the first-ever instrument to successfully measure subsurface temperature near the Moon’s south pole.
- ChaSTE was deployed by the Vikram lander after Chandrayaan-3's successful lunar landing in August 2023.
- The ChaSTE probe features 10 temperature sensors spaced 1 cm apart along its needle, with a rotation-based deployment mechanism, rather than a hammering one.
- The probe successfully descended up to 10 cm into the lunar surface and collected thermal data until September, 2023.
- The data suggested the presence of more water ice near the south pole than previously estimated, a crucial discovery for future lunar missions.
- ChaSTE’s success was attributed to its rotating probe mechanism, which proved more effective than the hammering technique used by earlier missions.
- Previous Missions: ESA's Philae lander (2014) couldn’t deploy the MUPUS (Multi-Purpose Sensors for Surface and Subsurface Science) thermal probe due to an awkward landing on comet 67P.
- NASA’s InSight (2018) on Mars also failed to gather subsurface data due to mechanical issues with the Heat Flow and Physical Properties Package (HP3) instrument.
| Read more: Chandrayaan-3 Successfully Lands on Moon's South Pole |
Euphaea wayanadensi
Source: TH
A new damselfly species, Euphaea wayanadensis, has been discovered in Kerala’s Wayanad region of the Western Ghats, marking an important addition to India’s biodiversity records.
- Scientific Significance: The species is Kerala’s 191st odonate species and the 223rd recorded species in the Western Ghats.
- Unique Characteristics: Longer black patch on hind wings, especially in males, setting it apart visually.
- Broader and uninterrupted humeral and antehumeral stripes in the thorax region of males, which are key taxonomic identifiers.
- Habitat Preferences: The species prefers fast-flowing rocky streams with aquatic vegetation in areas surrounded by evergreen and semi-evergreen forests.
- Observed year-round except in the dry season (March–April), it has a highly restricted distribution, necessitating conservation measures.
Read more: Platygomphus Benritarum
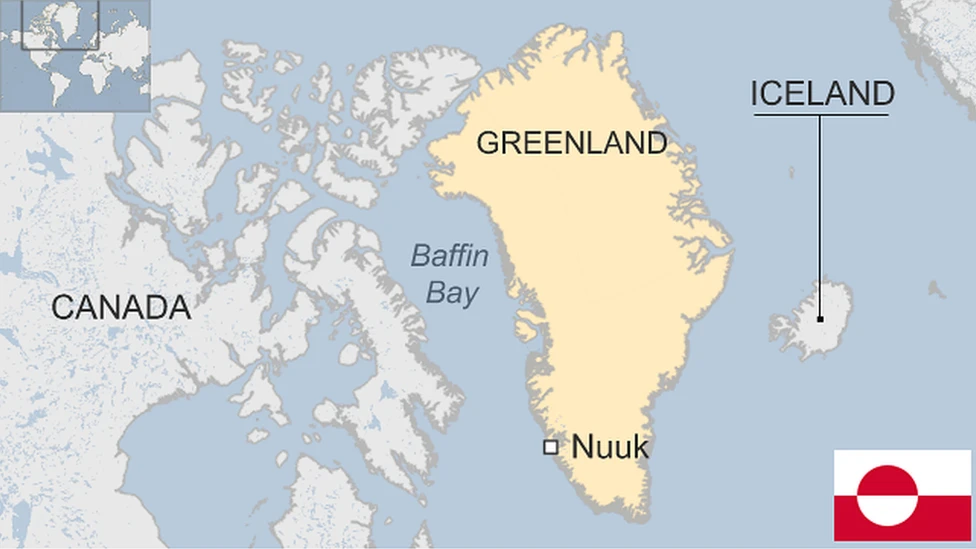
Denmark Reaffirms Greenland’s Sovereignty
Recently, Denmark's Prime Minister dismissed U.S. suggestions regarding the annexation of Greenland, emphasizing that such actions are unacceptable even when justified on the grounds of national security.
- Greenland holds strategic significance for the U.S. due to the Pituffik Space Base, vital for missile defense and positioned along the shortest route between North America and Europe.
- Greenland's rich mineral resources, including rare earth minerals, attract US interest.
- Greenland: It is the world's largest island, lying in the North Atlantic Ocean, between North America and Europe.
- It features major mountain ranges like the Watkins Range and Stauning Alps, and rivers such as Borglum, and Majorqaq.
- It has an Arctic climate with over 80% ice cover (up to 4 km thick), harsh winters (-50°C), short summers (10–15°C), and 2 months of continuous daylight.
- It functions as an autonomous territory under the Kingdom of Denmark, with self-government and its own Parliament (Inatsisartut).
| Read More: US Territorial Acquisitions and Interest in Greenland |