International Relations
United Nations Day 2024
- 26 Oct 2024
- 9 min read
For Prelims: United Nations Day, World War II, UN Charter, ECOSOC, UN General Assembly (UNGA), ICJ, Security Council
For Mains: Challenges Related to the UN and Proposals to Reform the UN
Why in News?
United Nations Day is celebrated each year on 24th October to mark the anniversary of the UN Charter coming into effect in 1945, following the end of World War II.
- The day aims to raise awareness about the goals and achievements of the international body.
What is the UN Charter?
- Background:
- It was signed on 26th June, 1945, in San Francisco at the end of the UN Conference on International Organisation and came into force on 24th October 1945.
- India is one of the founding members and ratified the UN charter on 30th October, 1945.
- The predecessor of the UN was the League of Nations, established in 1919, after World War I, under the Treaty of Versailles "to promote international cooperation and to achieve peace and security."
- It was signed on 26th June, 1945, in San Francisco at the end of the UN Conference on International Organisation and came into force on 24th October 1945.
- About:
- The Charter of the United Nations serves as the foundational document of the UN. It is an instrument of international law, and UN Member States are bound by it.
- It outlines key principles of international relations, including the equal rights of all countries and the ban on using force between nations.
- It has been amended three times since its incorporation – in 1963, 1965, and 1973.
- The Charter of the United Nations serves as the foundational document of the UN. It is an instrument of international law, and UN Member States are bound by it.
- Significance: The UN focuses on maintaining international peace and security, providing humanitarian assistance, protecting human rights, and upholding international law.
- It has been a key player in international cooperation, peace, and development for over 75 years.
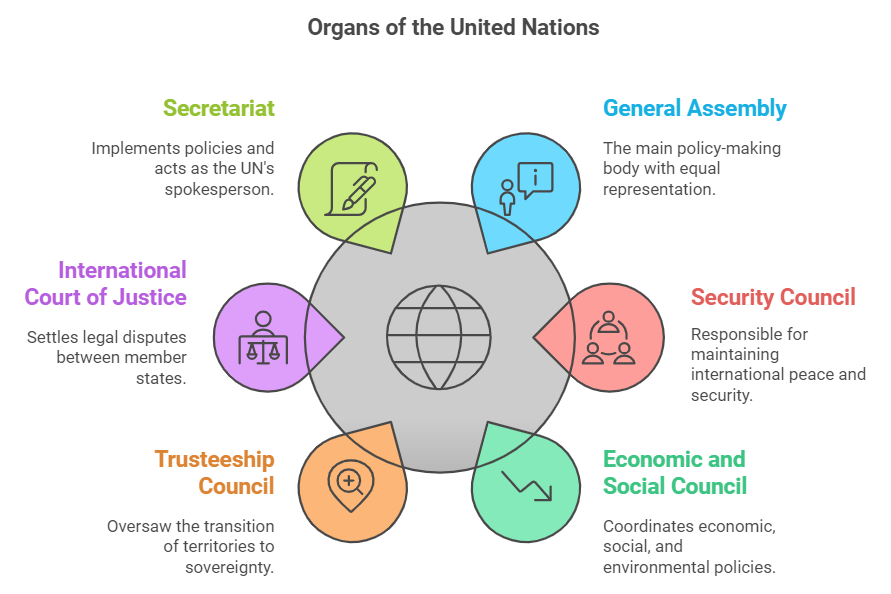
What are the Different Organs of the UN?
- General Assembly: The UN General Assembly (UNGA) is the main policy-making organ of the Organisation. Comprising all Member States, it provides a unique forum for multilateral discussion of the full spectrum of international issues covered by the Charter of the UN.
- Each of the 193 Member States of the UN has an equal vote.
- The UN Security Council: The Security Council consists of 15 members.
- Five permanent members (China, France, Russian Federation, the United Kingdom, and the United States), and ten non-permanent members elected for two-year terms.
- India has been a non-permanent member of the UNSC eight times.
- UN Economic and Social Council: ECOSOC consists of 54 Members of the UN elected by the UNGA.
- It is the principal body for coordination, policy review, policy dialogue and recommendations on economic, social and environmental issues
- Trusteeship Council: One of the main organs of the UN, was established to supervise the administration of trust territories as they transitioned from colonies to sovereign nations.
- International Court of Justice: The ICJ is the only international court that settles disputes between the 193 UN Member States.
- The court can rule on two types of case: “contentious cases” are legal disputes between States and “advisory proceedings” are requests for advisory opinions on legal questions referred to it by UN organs and certain specialised agencies.
- Secretariat: The Secretary-General is appointed by the UNGA based on the Security Council's recommendation and serves as the chief administrative officer of the organisation.
Note:
- Five of the UN’s six principal organs namely, the UNGA, the UNSC, ECOSOC, the Trusteeship Council, and the UN Secretariat are based at UN Headquarters in New York.
- However, the ICJ is located in The Hague, Netherlands.
What are the Challenges Related to the UN?
- Power Alignments: The UN struggles with power imbalances between wealthy and developing nations, making it difficult to implement its goals. These alignments challenge the organisation's ability to act impartially and effectively address global issues.
- Security and Terrorism: The UN faces evolving security challenges, including terrorism and ideological conflicts. While addressing traditional threats, it must also tackle broader issues like human security, poverty, and disease, expanding its role in conflict prevention and global safety.
- Peace-keeping: Modern peacekeeping faces difficulties, particularly in internal conflicts where combatants often ignore UN neutrality. The challenge lies in transitioning from traditional peacekeeping to peace-observation, using rapidly deployable teams to address conflict zones effectively.
- Human Rights Challenges: The UN faces the challenge of establishing and reinforcing national human rights institutions, especially in post-conflict countries. Ensuring these systems adhere to international norms is crucial for long-term protection and promotion of human rights globally.
- Financial Constraints and Arrears: The UN grapples with financial instability due to delays in assessed contributions from member states, hindering its operational effectiveness and capacity to fulfill global commitments.
What are the Proposals to Reform the UN?
- Expanding Permanent Membership & Inclusive Representation:
- Expanding the number of permanent members beyond the P5 and addressing the veto power could result in a more representative and democratic Security Council.
- It would potentially give more countries, especially from underrepresented regions like Africa a voice in decision-making.
- Reducing Inefficiencies in Administrative Processes:
- Streamlining the UN's administrative procedures and reducing bureaucratic complexities can significantly improve its efficiency.
- India's Role in UN Reform:
- India has consistently demonstrated its commitment to global peace, security, and development through its participation in UN peacekeeping missions, humanitarian assistance programs, and contributions to various UN agencies.
- India seeks a permanent seat on the Security Council, emphasising that such a step would make the Council more representative and responsive to the needs of the 21st century.
|
Drishti Mains Question What are the main challenges faced by the UN in fulfilling its objectives? Analyze the proposed reforms to enhance its effectiveness. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to the United Nations, consider the following statements: (2009)
- The Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC) of UN consists of 24 member States.
- It is elected by a 2/3rd majority of the General Assembly for a 3-year term.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Q. Consider the following. (2011)
- Right to education
- Right to equal access to public service
- Right to food.
Which of the above is/are Human Right/Human Rights under “Universal Declaration of Human Rights”?
(a) 1 only
(b) 1 and 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. What are the main functions of the United Nations Economic and Social Council (ECOSOC)? Explain different functional commissions attached to it.150 words (2017)