Infographics
Governance
WHO Report on Tobacco Control
For Prelims: World Health Organisation, E-cigarettes, National Tobacco Control Programme, Promulgation of the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes Ordinance, 2019, National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS).
For Mains: Status of Tobacco Consumption in India
Why in News?
The World Health Organisation (WHO) recently released a comprehensive report on tobacco control measures. The report evaluates the progress made globally since the introduction of the MPOWER measures - a set of strategies developed by WHO to combat tobacco use and its detrimental effects on health.
What are MPOWER Measures?
- In 2008, the WHO established MPOWER, a plan consisting of the six most important and effective tobacco control methods. The six MPOWER strategies include:
- M: Monitor tobacco use and prevention policies
- P: Protect people from tobacco smoke
- O: Offer help to quit smoking
- W: Warn about the dangers of tobacco
- E: Enforce bans on tobacco advertising, promotion and sponsorship
- R: Raise taxes on tobacco
What are the Major Highlights of the Report?
- Global Tobacco Control Progress:
- Worldwide, there has been a decline in smoking prevalence from 22.8% in 2007 to 17% in 2021, resulting in 300 million fewer smokers today.
- The WHO's MPOWER measures have played a vital role in tobacco control over the past 15 years, protecting 5.6 billion people (71% of the global population) with at least one measure.
- The number of countries implementing at least one MPOWER measure has risen from 44 in 2008 to 151 in 2022, and four countries - Brazil, Turkiye, Netherlands, and Mauritius - have successfully implemented all measures.
- Addressing the Challenges:
- The report also sheds light on the challenges that need to be addressed for more effective tobacco control.
- At least 44 countries still do not implement any MPOWER measure, and 53 countries do not have a complete ban on smoking in healthcare facilities.
- Additionally, only half of the countries enforce smoke-free workplaces and restaurants.
- WHO emphasizes the dangers of e-cigarettes, noting that the tobacco industry's aggressive promotion of e-cigarettes as a safer alternative undermines progress.
- E-cigarettes pose risks to both users and those around them, especially in indoor environments.
- Second-hand Smoking:
- Of the estimated 8.7 million tobacco-related deaths annually, 1.3 million are non-smokers exposed to second-hand smoke.
- Second-hand smoke is linked to almost 400,000 deaths due to heart disease. Moreover, second-hand smoke adversely affects children, leading to severe asthma, respiratory tract infections, and sudden infant death syndrome.
- Around 51,000 deaths in children and adolescents under 20 years are attributed to exposure to second-hand smoke.
- India's Progress in Tobacco Control:
- India excels in implementing health warning labels on tobacco products and providing tobacco dependence treatment.
- About 85% of cigarette packs in India carry health warnings on both the front and back, placing the country among the top 10 in terms of warning label size.
- India has also banned the sale of e-cigarettes and implemented smoking bans in healthcare facilities and educational institutions.
- Bengaluru has seen significant progress in tobacco control due to hundreds of enforcement drives, 'No Smoking' sign displays, and extensive awareness campaigns about the hazards of smoking and second-hand smoke.
- The city's efforts have led to a commendable 27% reduction in smoking in public places.
What is the Status of Tobacco Consumption in India?
- About:
- Nearly 267 million adults (15 years and above) in India (29% of all adults) are users of tobacco, according to the Global Adult Tobacco Survey India, 2016-17.
- The most prevalent form of tobacco use in India is smokeless tobacco.
- It is one of the major causes of death and disease in India and accounts for nearly 1.35 million deaths every year. India is also the second largest consumer and producer of tobacco.
- Nearly 267 million adults (15 years and above) in India (29% of all adults) are users of tobacco, according to the Global Adult Tobacco Survey India, 2016-17.
- Related Government Initiatives:
- National Tobacco Control Programme
- Promulgation of the Prohibition of Electronic Cigarettes Ordinance, 2019
- Cigarettes and other Tobacco Products (Prohibition of Advertisement and Regulation of Trade and Commerce, Production, Supply and Distribution) Amendment Rules, 2023.
- National Tobacco Quitline Services (NTQLS)
- The Union Finance Minister of India announced a 16% increase in National Calamity Contingent Duty (NCCD) on cigarettes in the Budget 2023-24.
- The Union Health Ministry of India has announced new regulations requiring Over-The-Top (OTT) platforms to display tobacco-related health warnings during streamed content.


Indian Economy
State of Formal Employment In India
For Prelims: State of Formal Employment In India, Employees Provident Fund (EPF), Labor Rights, Pandemic, Labour Force Survey Report, Labour codes.
For Mains: State of Formal Employment In India.
Why in News?
Employees Provident Fund’s (EPF) data indicates net increases in contributors, but this contradicts ground reports of Unemployment and Job Scarcity in India.
- The Indian government has been using the EPF’s data to measure the Formal Employment creation since 2017.
What is Formal Employment?
- About:
- Formal employment refers to a type of employment where the terms and conditions of work are regulated and protected by labor laws and employment contracts.
- It is characterized by certain features that distinguish it from informal or casual employment.
- Key Features:
- Written Contracts: Formal employment typically involves a written employment contract that outlines the terms of employment, including job responsibilities, working hours, compensation, benefits, and other terms and conditions.
- Social Security: Formal employees are often entitled to social security benefits such as health insurance, retirement funds, Provident fund, unemployment benefits, and other forms of financial protection.
- Labor Rights: Formal employees have specific Labor Rights protected by law, such as the right to join trade unions, collective bargaining, protection against unfair dismissal, and access to legal recourse in case of disputes.
- Regular Payment: Formal employees receive regular wages or salaries, usually on a fixed schedule, which provides a stable income source.
- Informal Employment:
- Informal employment refers to work that is not regulated or protected by labor laws, lacks formal employment arrangements, and often operates outside the scope of government oversight.
- Informal employment can lead to precarious working conditions and hinder economic growth as it may result in lower productivity and higher income inequality.
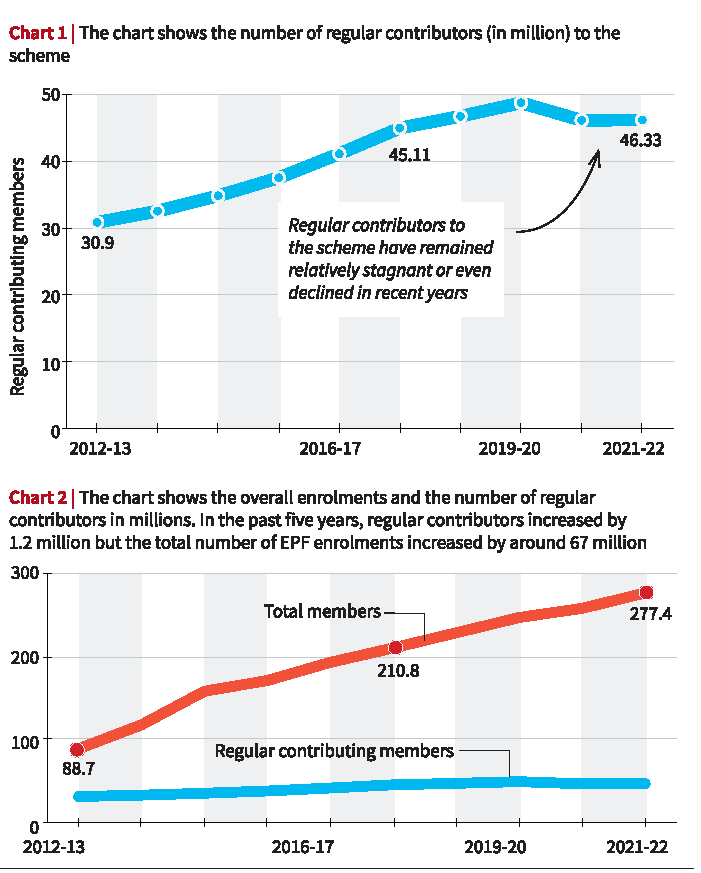
What does the EPF Data Say about Formal Jobs?
- EPFO's annual reports show a stagnant or declining number of regular contributors, those with consistent PF contributions, in recent years.
- Between 2012 and 2022, the number of regular contributors to the EPF increased from 30.9 million to 46.3 million.
- Between 2017 and 2022, the number of regular contributors increased only from 45.11 million to 46.33 million, showing a slowdown in growth during this period.
- Total EPF enrollments increased significantly, but the corresponding increase in regular contributors was minimal.
- Between 2017-2022, overall EPF enrollments increased from 210.8 million to 277.4 million.
- The difference between the total number of EPF enrollments (277.4 million) and the number of regular contributors (46.33 million) indicates that a significant portion of enrollments is not resulting in regular contributions.
- The majority of EPF enrollments are linked to temporary or casual jobs with irregular PF contributions.
- Factors Leading to the Decline in Contributors:
- The EPFO disputed its own data and stopped publishing monthly reports on regular contributors.
- The Pandemic further worsened the situation, leading to a decline in EPF contributors.
- The Indian government neglected other sources of formal employment data, like the Directorate General of Employment and Training (DGET) , which has not been published since 2013.
What is the Scenario of the Job Crisis in India?
- Unemployment Rate:
- According to the National Statistical Office’s (NSO) Periodic Labour Force Survey (PLFS) report for the year 2021-22, the unemployment rate for 2021-22 was 4.1%.
- Low Labor Force Participation Rates (LFPR):
- According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), India’s LFPR fell to 39.5% in the financial year (2022-23).
- This is the lowest LFPR reading since 2016-17.
- The LFPR for men stood at a seven-year low of 66% while that of women was pegged at a mere 8.8%.
- The LFPR is the share of the working-age population (aged 15 years and above) that is employed or unemployed, willing and looking for employment.
- According to Centre for Monitoring Indian Economy (CMIE), India’s LFPR fell to 39.5% in the financial year (2022-23).
What are the Causes of Low Employment in India?
- Absence of Formal and Quality Job:
- The absence of formal, well-paid, and regular employment inhibits the expansion of India's middle class, unlike China's growth model.
- Lack of quality jobs leads to over-qualified youth competing for limited job openings, raising concerns about claims of strong economic growth.
- Social Factors:
- In India, the caste system is prevalent. The work is prohibited for specific castes in some areas.
- In big joint families having big business, many such persons will be available who do not do any work and depend on the joint income of the family.
- Dominance of Agriculture:
- In India nearly half of the workforce is dependent on Agriculture. However, Agriculture is underdeveloped in India. Also, it provides seasonal employment.
- Fall Small industries:
- The industrial development had adverse effects on cottage and small industries.
- The production of cottage industries began to fall and many artisans became unemployed.
- Limitations in Education System:
- Jobs in the capitalist world have become highly specialized but India’s education system does not provide the right training and specialization needed for these jobs.
- Thus, many people who are willing to work become unemployed due to lack of skills.
How are the Rights of Labour Protected in India?
- Constitutional Framework:
- Under the Constitution of India, Labour as a subject is in the Concurrent List and, therefore, both the Central and the State governments are competent to enact legislations subject to certain matters being reserved for the Centre.
- Judicial Interpretation:
- In the case of Randhir Singh vs Union of India, the Supreme Court stated that “Even though the principle of ‘Equal pay for Equal work’ is not defined in the Constitution of India, it is a goal which is to be achieved through Article 14,16 and 39 (c) of the Constitution of India.
- Legislative Framework:
- There have been several legislative and administrative initiatives taken by the government to improve working conditions and simplify labour laws. Most recent is the consolidated sets of 4 labour codes.
What are Government’s Initiatives to Curb Unemployment?
Way Forward
- Relying on a single data source, like the EPF, overlooks the complexity of India's labor market. Comprehensive labor statistics, like the PLFS, provide a more accurate picture and call for urgent policy interventions to address the jobs crisis in the country.
- The formal job crisis in India requires a multi-faceted approach to address the underlying issues and create a conducive environment for formal employment generation.
- There is a need to encourage industries that have a higher labor intensity, such as manufacturing and certain services, to create more formal job opportunities and reduce reliance on informal sectors.
- There is a need to Investing in skill development programs that align with industry demands can enhance the employability of the workforce and lead to better-quality formal jobs.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. How globalization has led to the reduction of employment in the formal sector of the Indian economy? Is increased informalization detrimental to the development of the country? (2016)


Governance
Enhancing Social Security for Unorganized Workers
For Prelims: Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana , Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana, Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana, eShram Portal, Unorganized Sector
For Mains: Unorganized Workers in India and Related Initiatives
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of State for Labour and Employment shed light on the significant strides made in the realm of Social Security for Unorganized Workers during a written reply in the Lok Sabha.
- Aligned with the Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008, the government has formulated a range of welfare programs, spanning life and disability coverage, health benefits, maternity support, and old age protection.
- Unorganized Workers constitute about 93% of the total workforce or around 43.7 crore workers in India.
- Social Security Code, 2020 aims to regulate the organized/unorganized (or any other) sectors and extend social security benefits, during sickness, maternity, disability, etc. to all employees and workers across different organizations.
What are the Various Initiatives Related to Social Security for Unorganized Workers?
- Life and Disability Cover:
- Pradhan Mantri Jeevan Jyoti Bima Yojana (PMJJBY): Offers a life cover of Rs. 2.00 Lakh for insured individuals, regardless of the cause of death, at an annual premium of Rs. 436/-.
- Pradhan Mantri Suraksha Bima Yojana (PMSBY): Available to the people in the age group of 18 to 70 years with a bank/post office account. Provides accidental death or disability cover of Rs. 2.00 Lakh and Rs. 1.00 Lakh respectively, at a nominal premium of Rs. 20/- per annum.
- Over 16.92 crore beneficiaries enrolled under PMJJBY and 36.17 crore beneficiaries under PMSBY nationwide.
- Health and Maternity Benefits:
- Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): Ensures health insurance coverage of up to Rs. 5.00 lakhs per family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- As of July 2023, Verified approx. 24.19 crore beneficiaries and created Ayushman Cards across the country.
- Ayushman Bharat- Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB-PMJAY): Ensures health insurance coverage of up to Rs. 5.00 lakhs per family for secondary and tertiary care hospitalization.
- Old Age Protection:
- Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan (PM-SYM): Launched in 2019, provides a monthly minimum assured pension of Rs. 3000/- for workers aged 60 or above with a monthly income of Rs. 15000/- or less.
- Beneficiary contributes 50% monthly, matched by equal contribution from the Central Government.
- Enrolled around 49.47 lakh beneficiaries nationwide.
- Pradhan Mantri Shram Yogi Maan-Dhan (PM-SYM): Launched in 2019, provides a monthly minimum assured pension of Rs. 3000/- for workers aged 60 or above with a monthly income of Rs. 15000/- or less.
- eShram Portal:
- Launched by the Ministry of Labour & Employment in 2021.
- Aims to create a comprehensive database of unorganized workers.
- Approx. 28.97 crore workers registered on eShram Portal, including details like name, occupation, address, education, skills, and family information.
- Additional Schemes for Unorganized Workers:
- One Nation One Ration Card: Public Distribution System under the National Food Security Act.
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA): Provides employment opportunities.
- Deen Dayal Upadhyay Gramin Kausal Yojana: Skill development programs.
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana: Affordable housing scheme.
- Pradhan Mantri Gareeb Kalyan Rojgar Yojana: Employment generation during the pandemic.
- Mahatma Gandhi Bunkar Bima Yojana: Provides enhanced insurance cover to the handloom weavers in the case of natural as well as accidental death and in cases of total or partial disability.
- Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana: Promotion of multiple livelihoods and improved access to financial services for rural poor households across the country.
- Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana: Vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in society.
Unorganised Workers’ Social Security Act, 2008
- The Act defines unorganized workers as those who work in the informal sector or households, without any regular employment or social security benefits.
- The Act empowers the Central Government and the State Governments to frame schemes for providing various social security benefits to unorganized workers, such as life and disability cover, health and maternity benefits, old age protection, education, housing, etc.
- The Act also provides for the constitution of a National Social Security Board and State Social Security Boards for unorganized workers, which will advise and monitor the implementation of the schemes.
- The Act mandates the registration of unorganized workers by the District Administration and the issuance of identity cards to them.
- The Act also envisages the establishment of workers facilitation centers to provide information and facilitate access to the schemes.
Code on Social Security, 2020
- The Code on Social Security, 2020 aims to extend social security to all employees and workers either in the organized or unorganized or any other sectors and for matters connected therewith or incidental thereto.
- The Code can be applied to establishments subject to size-threshold through notification by the central government.
- Separate Social Security Funds will be set up by the Central and State Governments for unorganized workers, gig workers, and platform workers.
- Registration provisions are specified for unorganized workers, gig workers, and platform workers.
- A National Social Security Board will be established to recommend and monitor schemes for these categories of workers.
- Funding for schemes of gig workers and platform workers may come from contributions by central and state governments, as well as aggregators.
- Penalties for certain offenses have been reduced, including obstructing inspectors and unlawfully deducting contributions from wages.
- During an epidemic, the central government may defer or reduce employer and employee contributions (under Employee State Insurance (ESI) and Provident Fund (PF) for up to three months.


Biodiversity & Environment
Urban Flooding
For Prelims: Urban Flooding, Rainfall, Rural floods, Drainage System, Wetlands, Climate Change, Sewage and solid waste, Illegal Mining, Riverbank Erosion.
For Mains: Urban Flooding, Causes and Curtailment.
Why in News?
There has been an increased incidence of high intensity Rainfall in short duration, causing Urban Flooding which is further compounded by unplanned growth, encroachment of natural water bodies, and Poor Drainage System.
What is Urban Flooding?
- About:
- Urban flooding is the inundation of land or property in a built environment, particularly in more densely populated areas (like cities), caused by rainfall overwhelming the capacity of drainage systems.
- Unlike Rural floods (Heavy rain over a flat or low-lying area), urban flooding is not only caused by just higher precipitation but also unplanned urbanisation (catchments) that:
- Increases the flood peaks from 1.8 to 8 times
- Increases the flood volumes by up to 6 times.
- Causes:
- Encroachments on Drainage Channels: Due to increased land prices and less availability of land new developments have come up in low-lying areas of cities, such as encroachments over lakes, Wetlands and riverbeds.
- Ideally, the natural drains should have been widened to accommodate the higher flows of stormwater.
- But on the contrary, there have been large scale encroachments without widening the natural drains, leading to decrease in the capacity of the natural drains resulting in flooding.
- Climate Change: Climate Change has caused an increase in the frequency of short duration heavy rainfall leading to higher water run-off.
- Whenever the rain bearing clouds pass over the urban heat island, the hot air pushes the clouds up, resulting in highly localised rainfall which may sometimes be of high intensity.
- Uninformed Release of Water from Dams: Unplanned and sudden release of water from dams and lakes lead to floods in an urban area, without giving the public enough time to respond.
- Example: Chennai Floods 2015 due to release of water from Chembarambakkam Lake.
- The July 2023 flood in Delhi was magnified by 2 lakh cusecs of water discharged from the Hathnikund Barrage into the Yamuna river.
- Illegal Mining: Illegal mining of river sand and quartzite for use in building construction deplete the natural bed of the rivers and lakes.
- It causes soil erosion and reduces the water retention capacity of the waterbody increasing the speed and scale of water flow.
- Example: Jaisamand Lake- Jodhpur, Cauvery river- Tamil Nadu.
- Encroachments on Drainage Channels: Due to increased land prices and less availability of land new developments have come up in low-lying areas of cities, such as encroachments over lakes, Wetlands and riverbeds.
What are the Implications of Urban Flooding?
- Loss of Life and Property:
- Urban floods are often associated with loss of life and physical injury either directly due to the effect of floods or indirectly due to infections by water-borne diseases spreading during the inundated period.
- Ecological and Environmental:
- Trees and plants are washed away during extreme flood events and riverbank erosion is caused by high-speed flood water.
- Impact on Animal and Human Health:
- Stagnation of stormwater in the localities, and Contamination of consumable water leads to various health problems resulting in plagues/epidemics.
- The sewage and solid waste washing into houses and neighborhoods also causes a variety of diseases to spread.
- Psychological Impacts:
- Loss of shelter and relatives creates emotional turmoil in the mental health of the stranded. The recovery process in case of such incidents is a tiresome process and time consuming that often leads to long lasting psychological trauma.
What are the Government Initiatives to Curtail Urban Flooding?
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA)
- Amrit Sarovar Mission
- Atal Bhujal Yojana
- Atal Mission for Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT) 2.0
- Model Building Bye Laws (MBBL), 2016
- Standard Operating Procedures (SoPs) on Urban Flooding by MInistry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Way Forward
- Implement sustainable urban planning practices that prioritize green spaces, retention ponds, and permeable surfaces to absorb and manage stormwater. Avoid construction in flood-prone areas and preserve natural drainage systems.
- Invest in upgrading and expanding drainage infrastructure, including natural drains, stormwater channels, and flood-control systems. Regular maintenance and cleaning of drains are essential to ensure effective water flow.
- Identify and map flood-prone areas and develop appropriate floodplain management strategies. Restrict construction and development in these vulnerable zones to reduce the risk of flooding.
- Establish and improve Early Warning Systems to alert residents about impending floods. Timely warnings can help people evacuate and take necessary precautions.


Governance
The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023
For Prelims: Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957, Mineral sector, Net-Zero emission by 2070.
For Mains: The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023.
Why in News?
The Rajya Sabha has passed the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Bill, 2023 for making amendments to the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957.
What is the Background?
- The MMDR Act, 1957 was amended in 2015 to introduce auction-based mineral concession allocation for transparency, create District Mineral Foundation (DMF) for the welfare of affected communities, establish National Mineral Exploration Trust (NMET) to promote exploration, and impose stricter penalties for illegal mining.
- The Act was further amended in 2016 and 2020 to address specific emergent issues and was last amended in 2021 to bring further reforms in the sector, such as, removing the distinction between captive and merchant mines, etc.
- However, the mineral sector required more reforms particularly for increasing exploration and mining of Critical Minerals that are essential for economic development and national security in the country.
- The lack of availability of the critical minerals or concentration of their extraction or processing in a few geographical locations may lead to supply chain vulnerabilities and even disruption of supplies.
- Critical minerals have gained significance in view of India's commitment towards energy transition and achieving Net-Zero emission by 2070.
What are the Key Provisions under the Bill?
| Key Provisions | MMDR Act 1957 | MMDR Amendment Bill |
| Private Sector to Mine Atomic Minerals | The Act allows the only State agencies in the exploration of the atomic minerals such as lithium, beryllium, niobium, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. |
The Bill allows the private sector to mine six out of 12 atomic minerals such as lithium, beryllium, niobium, titanium, tantalum and zirconium. When it becomes an Act, Centre will have powers to auction mining lease and composite licence for critical minerals such as gold, silver, copper, zinc, lead, nickel etc.. |
| Auction for Exploration Licence |
The exploration licence will be granted by the state government through competitive bidding. The central government will prescribe details such as manner of auction, terms and conditions, and bidding parameters for exploration licence through rules. |
|
| Maximum Area in which Activities are Permitted | Under the Act, a prospecting licence allows activities in an area up to 25 square kilometres, and a single reconnaissance permit allows activities in an area up to 5,000 square kilometres. |
The Bill allows activities under a single exploration licence in an area up to 1,000 square kilometres. After the first three years, the licencee will be allowed to retain up to 25% of the originally authorised area. |
| Incentive for exploration Licence | If the resources are proven after exploration, the state government must conduct an auction for mining lease within six months of the submission of the report by the exploration licencee. The licencee will receive a share in the auction value of the mining lease for the mineral prospected by them. |
What is the Scenario of the Mining Sector in India?
- Backbone of Manufacturing:
- Mining industry plays a crucial role in the country's economy, serving as the backbone for manufacturing and infrastructure sectors.
- According to the Ministry of Mines, the total value of mineral production (excluding atomic and fuel minerals) during 2021-22 amounted to Rs 2,11,857 crore.
- Scope:
- India ranks 4th globally in terms of iron ore production and is the world's 2nd largest coal producer as of 2021.
- Combined Aluminium production (primary and secondary) in India stood at 4.1 MT per annum in FY21 becoming the 2nd largest in the world.
- In 2023, the mineral’s demand is likely to increase by 3%, driven by expanded electrification and overall economic growth in India.
- India holds a fair advantage in production and conversion costs in steel and alumina. Its strategic location enables export opportunities to develop as well as fast-developing Asian markets.
- India ranks 4th globally in terms of iron ore production and is the world's 2nd largest coal producer as of 2021.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Mains
Q. Despite India being one of the countries of Gondwanaland, its mining industry contributes much less to its Gross Domestic Product (GDP) in percentage. Discuss. (2021)
Q. “In spite of adverse environmental impact, coal mining is still inevitable for development”. Discuss. (2017)


Important Facts For Prelims
Palaeo Proxies
Why in News?
Recently, it was proclaimed that a particular day in July 2023 as the Warmest in over 100,000 Years is scientifically unfounded.
- This claim is based on temperature estimates from before the invention of thermometers, which rely on "Palaeo Proxies" that cannot provide daily timescale temperatures.
What are Palaeo Proxies?
- About:
- Palaeo proxies, short for paleoclimate proxies or paleoenvironmental proxies, are indicators or records used by scientists to reconstruct past climate and environmental conditions.
- These proxies are typically derived from physical, biological, or chemical processes that respond to changes in temperature or other climatic factors.
- Since direct measurements of climate from the distant past are not possible, scientists rely on these proxy records to understand past climate variations and long-term trends.
- Examples:
- Ice Cores: Ice cores drilled from glaciers and polar ice sheets contain trapped air bubbles and isotopic compositions that provide information about past atmospheric conditions, including temperature and Greenhouse Gas concentrations.
- Tree Rings: The width, density, and isotopic composition of tree rings can reveal past climate variations and growth conditions of trees, serving as a valuable proxy for temperature and precipitation changes.
- Coral Records: The growth patterns and Isotopic Compositions of corals offer information about past sea surface temperatures and ocean conditions.
- Pollen Records: The presence and abundance of specific pollen types preserved in sediment cores can indicate past vegetation and climate changes.
- Limitations:
- A major assumption required to make the “paleo proxy” technique workable is that the processes that produced the proxies have operated similarly back then as they do today.
- However, proxies buried in ocean and lake sediments can only record temperature anomalies on timescales of centuries or thousands of years, making daily temperature estimations impossible.
- Temperature proxies provide only local or regional estimates of historical temperature anomalies with significant uncertainties.
- Global estimates based on averaging all local proxies have even higher uncertainties, making claims about daily temperatures at a global scale unreliable.
What are the other Methods to Estimate Temperature over longer Timescales?
- Some isotopes with known radioactive decay rates can provide estimates of temperature changes over longer timescales like Holocene Epoch.
- The Holocene Epoch is a geological times scale that began approximately 11,650 years ago and continues to the present day. It is the current and most recent epoch within the Quaternary Period.
- Carbon or lead isotopes with half-lives ranging from 5,000 to over 10 million years can be used to estimate past temperatures.
- Nonetheless, these methods are also limited to longer timescales and cannot provide daily temperature data.


Important Facts For Prelims
Modernization of Fire Services
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Home Affairs, Government of India has launched a “Scheme for Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services in the States” under the National Disaster Response Fund (NDRF) for strengthening fire services in the States.
What is the Scheme for Expansion and Modernization of Fire Services in the States?
- About:
- The Scheme finds its origin from the recommendation of the Fifteenth Finance Commission (XV-FC) which allows an allocation of 12.5% of each of the NDRF and State Disaster Response Fund (SDRF) for the Funding Window of Preparedness and Capacity Building.
- Objective:
- It aims to expand and modernize Fire Services in the States with a view that activities for strengthening of fire services at the State-level through preparedness and capacity-building components of the NDRF will be ensured.
- Measures under the Scheme:
- Setting up of new fire stations
- Strengthening of State Training Centres and capacity building
- Provisions for modern fire-fighting equipment
- Strengthening of State Headquarters and Urban Fire Stations
- Technological upgradation and installation and augmentation of online systems.
- Fund Allocation:
- Fund allocation under the scheme is on a cost sharing basis of 75:25 with the States, except for North Eastern Hill States which is in the ratio of 90:10.
- While the Centre will provide Rs. 5000 crore to the States for identified activities, the States’ contribution will be of Rs. 1387.99 Crore.
- An amount of Rs. 500 crore, out of the total central outlay of Rs. 5000 crore will be available for incentivizing the States for adoption of legal and infrastructure-based reforms.
What are the Government Initiatives for Disaster Risk Reduction?
- National Disaster Management Plan
- Aapda Mitra Scheme
- Common Alerting Protocol based Integrated Alert System (Sachet).
- School Safety Programme (SSP) of NDRF
- National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP)
- NGO-Coordination Centres at States/UTs and District levels.
- NDRF Mock Exercises scheme on community disaster Awareness.
- NDMA Guidelines for Management of Disaster Risks.
- National Cyclone Risk Mitigation Project (NCRMP)


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Great Nicobar Island Project
 The Government's Great Nicobar Project may require the felling of 9.64 lakh trees, higher than the earlier estimate of 8.5 lakh trees. The project has faced challenges from the National Green Tribunal (NGT) regarding the issue of deforestation.
The Government's Great Nicobar Project may require the felling of 9.64 lakh trees, higher than the earlier estimate of 8.5 lakh trees. The project has faced challenges from the National Green Tribunal (NGT) regarding the issue of deforestation.
- The Great Nicobar Island (GNI) Project is a mega project to be implemented at the southern end of the Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The project includes an international container transshipment terminal, a greenfield international airport, township development, and a 450 MVA gas and solar based power plant over an extent of 16,610 hectares in the island.
Read More: Great Nicobar Island Project
Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF)
Since the launch of the Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) in 2020, only 15% of the Rs 1 lakh crore aimed at developing post-harvest infrastructure, has been distributed.
- AIF aims to provide all-around financial support to the farmers, agri-entrepreneurs, farmer groups like Farmer Producer Organisations (FPOs), Self Help Groups (SHGs), Joint Liability Groups (JLGs) etc. and many others to create post-harvest management infrastructure and build community farming assets throughout the country.
- It provides support of 3% interest subvention, credit guarantee support through the Credit Guarantee Fund Trust for Micro and Small Enterprises (CGTMSE) scheme for loans of up to Rs. 2 crore and facility of convergence with other Central and State Government schemes.
Read More: Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF) & Post Harvest Management
Gukesh D Overtakes Viswanathan Anand in FIDE Rankings
Gukesh D, a protege of five-time world chess champion Viswanathan Anand, will become the top-ranked Indian in the International Chess Federation (FIDE) monthly rating list for classical chess, surpassing Anand after 36 years. He will also break into the top 10 rankings for the first time, making him the third Indian to achieve this feat.
He became the youngest player to defeat World No. 1 chess player, Magnus Carlsen.
- FIDE is the governing body of the sport of chess, and it regulates all international chess competitions. It's constituted as a non-governmental institution.
Viswanathan Anand
- The most successful Indian chess player, who won the FIDE World Chess Championship in 2000, 2007, 2008, 2010 and 2012.
- He also won the World Rapid Chess Championship in 2003 and 2017, and the World Blitz Chess Championship in 2000 and 2017. He is the only player to have won the world title in all three formats of chess.
Read More: The Rising Popularity of Chess in India, FIDE
Western Tragopan
The Western Tragopan (Tragopan melanocephalus), Himachal Pradesh's state bird, has faced habitat loss but has shown a gradual increase in population at the Sarahan pheasantry due to conservation efforts.
- The western tragopan, also known as the western horned tragopan, is amongst the rarest of all living pheasants.
- Due to its beautiful plumage and large size, this bird is locally known as ‘jujurana’ or ‘king of birds’.
- It is endemic to the northwest Himalaya, within north Pakistan through Jammu and Kashmir and Himachal Pradesh, to the western part of Garhwal.
- They feed mostly on leaves, shoots and seeds, but also consumes insects and other invertebrates.
- IUCN Status: Vulnerable










-min.jpg)