Infographics
Indian Polity
SC Allows Divorce on Irretrievable Breakdown
For Prelims: Article 142(1) of the Constitution, Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), 1955, SC judgements on divorce.
For Mains: Legal challenges faced by people seeking a divorce in India, the significance of Article 142(1) in divorce cases, Supreme Court and Law Commission on Irretrievable breakdown on marriage, Marriage equality in India – challenges faced by women.
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court (SC) ruled that under its power to do ‘complete justice’ granted via Article 142, it can dissolve a marriage on the ground that it had broken down irretrievably, without referring the parties to a family court where they must wait 6-18 months for a decree of divorce by mutual consent.
What is SC’s Ruling?
- Ruling:
- In the case of Shilpa Sailesh vs. Varun Sreenivasan (2023), the SC has ruled that it has the power to dissolve a marriage if it is irretrievably broken down.
- The court can waive the mandatory six-month waiting period for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA), 1955, and allow the dissolution of the marriage on grounds of an irretrievable breakdown even if one of the parties was not willing.
- Conditions:
- Significance of the Ruling:
- The process of obtaining a decree of divorce is often time-consuming and lengthy owing to a large number of similar cases pending before family courts.
- The ruling allows parties to bypass the waiting period and approach the Supreme Court directly for a divorce on grounds of irretrievable breakdown.
- As per SC, if there is no possibility of reconciliation, it would be meaningless to prolong the agony of the parties to the marriage.
- Dissolving such a marriage, even if one of the parties agree, would provide a speedy solution for parties who are unable to live together and have mutually agreed that the marriage should be dissolved.
- The judgment is significant as irretrievable breakdown of marriage is not yet a ground for divorce under the Hindu Marriage Act (HMA) 1955.
- Till date, there is still no codified law for irretrievable breakdown of marriage. Though, the HMA 1955 recognizes a few grounds for dissolution of marriage in Section 13.
- The process of obtaining a decree of divorce is often time-consuming and lengthy owing to a large number of similar cases pending before family courts.
- Implication of the Judgement:
- The recent SC judgement does not imply that people can rush straight to the SC for a quick divorce.
- The grant of divorce by the SC on the ground of irretrievable breakdown of marriage is “not a matter of right, rather a discretion which needs to be exercised with great care and caution”.
- The SC also clarified that a party cannot file a writ petition under Article 32 (or Article 226) of the Constitution of India and seek relief of dissolution of marriage on the ground of irretrievable breakdown of marriage directly from it.
- The recent SC judgement does not imply that people can rush straight to the SC for a quick divorce.
- Need to Shift away from Fault Theory:
- The 5-judge bench highlighted the need of the SC to move away from “fault theory” and “accusatorial principle of divorce” under Section 13 (1) of HMA 1955, which prescribes divorce on grounds where one of the spouses can be held guilty of certain misdeeds such as cruelty, adultery or desertion.
- The HMA 1955 and the Special Marriage Act 1954 are premised on the ‘fault’ or ‘matrimonial offence’ theory for the purpose of divorce.
- It allows the innocent party to obtain a divorce if the other party has committed a matrimonial offense.
- Under HMA 1955, there are 7 fault grounds for divorce: adultery, cruelty, desertion, conversion, insanity, leprosy, venereal disease, and sanyasa.
- There are 4 grounds on which the wife can sue alone: rape, sodomy, bestiality, non-resumption of cohabitation after maintenance order, and decree for maintenance.
- The innocent party must prove that they are blameless for the divorce to be granted under this theory.
Note:
- The Law Commission of India, in its reports in 1978 and 2009 recommended adding irretrievable breakdown as an additional ground of divorce.
- The Law Commission in its 71st report (1978), dealt with the concept of irretrievable breakdown of marriage.
- The Report also mentions that as far back as 1920, New Zealand was the first of the Commonwealth countries to introduce the provision that a three-year or more separation agreement was grounds for filing a petition in the courts for divorce.
- It has become a classic enunciation of the breakdown principle in matrimonial law.
What is HMA 1955?
- About:
- The Hindu Marriage Act 1955 (HMA) is an act of the Parliament of India that codifies and amends the law relating to marriage among Hindus and others.
- It applies to Hindus, Buddhists, Jains, Sikhs and anyone who is not a Muslim, Christian, Parsi, or Jew by religion.
- Current Procedure for Divorce under the HMA:
- Section 13B of the HMA provides for “divorce by mutual consent” under which both parties to the marriage must together file a petition to the district court.
- This will be done on the grounds that they have been living separately for a period of one year or more, that they have not been able to live together and have mutually agreed that the marriage should be dissolved.
- The parties must move a second motion before the court at least 6 months after the date of the presentation of the first petition and not later than 18 months after the said date (provided, the petition is not withdrawn in the meantime).
- The mandatory six-month wait is intended to give the parties time to withdraw their plea.
- A petition for divorce by mutual consent can be moved only after a year of the marriage.
- However, section 14 of the HMA allows a divorce petition sooner in case of “exceptional hardship to the petitioner or of exceptional depravity on the part of the respondent”.
- A waiver of the six-month waiting period under Section 13 B (2) can be sought in an exemption application filed before the family court.
- Section 13B of the HMA provides for “divorce by mutual consent” under which both parties to the marriage must together file a petition to the district court.
What are the Other Judgements Related to Divorce?
- Amit Kumar vs Suman Beniwal (2021): The SC said, “Where there is a chance of reconciliation, however slight, the cooling period of six months from the date of filing of the divorce petition should be enforced. However, if there is no possibility of reconciliation, it would be meaningless to prolong the agony of the parties to the marriage.”
- Bhagwat Pitambar Borse vs. Anusayabai Bhagwat Borse (2018): The Bombay HC held that desertion by the wife for more than seven years without any reasonable cause and without any intention to return is a valid ground for divorce.
- In June 2016, a two-judge bench referred to the larger bench of 5 judges the matter regarding the court’s exercise of powers under Article 142 to grant a divorce without sending the parties to a family court.
- Citing conflicting views taken by different benches of the top court, it also sought clarity on the broad parameters for the exercise of powers under Article 142 to dissolve a marriage between the consenting parties.
- The smaller bench had in 2016 appointed senior advocates Indira Jaising, Dushyant Dave, V Giri, and Meenakshi Arora as amici curiae (friends of court)to assist the Constitution bench.
What is Article 142 (1) of the Constitution?
- Subsection 1 of Article 142 confers sweeping power on the Supreme Court to pass such decree or make such order as is necessary for doing ‘complete justice’ in any cause or matter.
- The decision to exercise the power under Article 142(1) must be “based on considerations of fundamental general and specific public policy”.
- The fundamental general conditions of public policy refer to the fundamental rights, secularism, federalism, and other basic features of the Constitution; specific public policy was defined by the court to mean “some express pre-eminent prohibition in any substantive law, and not stipulations and requirements to a particular statutory scheme”.
What is the Status of Marriage Equality in India?
- Divorce Rate and Trends in India:
- A 2018 survey of 160,000 households revealed that 93% married Indians had ‘an arranged marriage’, as against the global average of about 55%.
- India has a low annual divorce rate of 1.1 per 1,000 people, with only 13 out of every 1,000 marriages resulting in divorce, and men are usually the initiators.
- Prevailing social norms discourage women from seeking a divorce, and when they do, they face legal hassles and socio-economic isolation, especially if they are financially dependent on their spouses.
- A 2018 survey of 160,000 households revealed that 93% married Indians had ‘an arranged marriage’, as against the global average of about 55%.
- Women’s Economic Dependency:
- Indian women’s low labor-force participation rate translates to high levels of financial dependency, forcing them to ‘adjust’ to bad marriages.
- Women’s Socio-Economic Challenges after Divorce:
- The dissolution of a marital union disproportionately affects women, who suffer from chronic strains of divorce, including disproportionate losses in household income, higher risk of losing homeownership, lower chances of re-partnering, and greater responsibilities of single parenting.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q. With reference to the Constitution of India, prohibitions or limitations or provisions contained in ordinary laws cannot act as prohibitions or limitations on the constitutional powers under Article 142. It could mean which one of the following? (2019)
(a) The decisions taken by the Election Commission of India while discharging its duties cannot be challenged in any court of law.
(b) The Supreme Court of India is not constrained in the exercise of its powers by laws made by the Parliament.
(c) In the event of grave financial crisis in the country, the President of India can declare Financial Emergency without the counsel from the Cabinet.
(d) State Legislatures cannot make laws on certain matters without the concurrence of Union Legislature.
Ans: (b)
Buy Now
Indian Economy
Central Counterparties
For Prelims: Central Counterparties (CCPs), EMIR, ESMA
For Mains: CCP and how does it function in financial markets, implications of the ESMA's derecognition of Indian CCPs for European banks.
Why in News?
The European Securities and Markets Authority (ESMA), the European Union's financial markets regulator, has derecognized six Indian Central Counterparties (CCPs) from April 30, 2023, in accordance with the European Market Infrastructure Regulation (EMIR).
- These six CCPs are the Clearing Corporation of India (CCIL), Indian Clearing Corporation Ltd (ICCL), NSE Clearing Ltd (NSCCL), Multi Commodity Exchange Clearing (MCXCCL), India International Clearing Corporation (IFSC) Ltd (IICC) and NSE IFSC Clearing Corporation Ltd (NICCL).
What is CCP?
- About:
- CCP is a financial institution that acts as an intermediary between buyers and sellers in various derivatives and equities markets. CCPs are structures that help facilitate the clearing and settlement process in financial markets.
- The primary goal of CCPs is to increase efficiency and stability in financial markets.
- CCPs reduce risks associated with counterparty, operational, settlement, market, legal, and default issues
- CCPs act as a counterparty to both buyers and sellers in a trade, collecting money from each party involved and guaranteeing the terms of the trade
- Functions:
- Clearing and settlement are the two main functions of a CCP.
- Clearing involves validating the details of the trade and ensuring that both parties have sufficient funds to complete the transaction.
- Settlement involves the transfer of ownership of the asset or security being traded from the seller to the buyer.
- Clearing and settlement are the two main functions of a CCP.
- Regulators in India:
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for CCPs clearing money market instruments and foreign exchange derivatives.
- A CCP is authorized by the RBI to operate in India under the Payment and Settlement Systems Act, 2007.
- The Securities and Exchange Board of India (SEBI) for CCPs clearing securities and commodity derivatives.
- The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) for CCPs clearing money market instruments and foreign exchange derivatives.
Why has ESMA Derecognized Indian CCPs?
- Reason:
- The ESMA derecognized Indian CCPs due to their failure to meet all EMIR requirements.
- The decision came due to ‘no cooperation arrangements’ between ESMA and Indian regulators – the RBI, the SEBI and the International Financial Services Centres Authority (IFSCA).
- While ESMA wants to supervise these six CCPs, Indian regulators are of the view that since these domestic CCPs operate in India and not in the EU, these entities cannot be subjected to the ESMA regulations. They feel that these six CCPs have robust risk management and there is no need for a foreign regulator to inspect them.
- Impact:
- As of the date of application of the withdrawal decisions, these CCPs will no longer be able to provide services to clearing members and trading venues established in the EU.
- The decision will impact European banks in India as they will either need as much as 50 times higher capital to carry out trades involving the Indian central counterparties or will have to unwind positions with the central counterparties over the next 6 to 9 months.
What is ESMA?
- ESMA is an independent EU authority.
- ESMA enhances the protection of investors and promotes stable and orderly financial markets.
- ESMA is the direct supervisor of specific financial entities such as credit rating agencies, securitization repositories, and trade repositories
What is EMIR?
- EMIR is an EU regulation adopted in August 2012
- It aims to reduce systemic, counterparty, and operational risk in the OTC derivatives market
- It sets higher prudential standards for CCPs and trade repositories
- EMIR enhances risk mitigation techniques for non-cleared derivatives
- It establishes a framework for the recognition and supervision of third-country CCPs


Biodiversity & Environment
India to Join International Climate Action in Civil Aviation
For Prelims: ICAO, CORSIA, LTAG
For Mains: Climate Action in Civil Aviation: CORSIA, LTAG, their advantages for India.
Why in News?
The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) has announced has recently announced that India will start participating in the International Civil Aviation Organisation's (ICAO) Carbon Offsetting and Reduction Scheme for International Aviation (CORSIA) and the Long-Term Aspirational Goals (LTAG) from 2027.
- CORSIA Scheme is envisaged in 3 phases: Pilot (2021-2023) and first phases (2024-2026) are voluntary phases whereas second phase (2027-2035) is mandatory for all the member States.
- India has decided not to participate in the voluntary phases of CORSIA.
What are CORSIA and LTAG?
- Background:
- The ICAO has been tasked to reduce carbon emissions from international civil aviation as one of its focus areas.
- In order to mitigate carbon emissions from aviation and its impact on climate change, the global body has adopted several key aspirational goals. Among them are:
- 2% annual fuel efficiency improvement through 2050
- carbon neutral growth
- net zero by 2050
- In order to mitigate carbon emissions from aviation and its impact on climate change, the global body has adopted several key aspirational goals. Among them are:
- The ICAO has clubbed them under CORSIA and LTAG.
- The ICAO has been tasked to reduce carbon emissions from international civil aviation as one of its focus areas.
- CORSIA:
- It is a global scheme established by the ICAO to address the growth in CO2 emissions from international aviation.
- CORSIA aims to stabilize net CO2 emissions at 2020 levels through a combination of measures, including carbon offsetting, carbon credits, and sustainable aviation fuel.
- It offers a harmonized way to reduce emissions from international aviation, minimizing market distortion, while respecting the special circumstances and respective capabilities of ICAO Member States.
- CORSIA complements the other measures by offsetting the amount of CO2 emissions that cannot be reduced through technological improvements, operational improvements, and sustainable aviation fuels with emissions units from the carbon market.
- CORSIA is applicable only to flights originating from one country to another.
- LTAG:
- 41st ICAO Assembly adopted LTAG for international aviation of net-zero carbon emissions by 2050 in support of the UNFCCC Paris Agreement's temperature goal.
- The LTAG does not attribute specific obligations or commitments in the form of emissions reduction goals to individual States. Instead, it recognizes each State's special circumstances and respective capabilities e.g., the level of development, maturity of aviation markets.
What is the ICAO?
- It is a specialized agency of the United Nations that was created in 1944 to promote safe, secure, and efficient air transportation around the world.
- ICAO develops international standards and recommended practices for aviation, including regulations for air navigation, communication, and airport operations.
- It also works to address global aviation issues, such as air traffic management, aviation security, and environmental protection.
- It is headquartered in Montreal, Canada.
What could be the Potential Advantages for Joining such Initiatives?
- Reducing Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Joining CORSIA and striving towards the LTAG will help reduce the greenhouse gas emissions from international aviation. This is essential for combating climate change and protecting the environment.
- India also has set an ambitious target of achieving Net Zero by 2070.
- India also has committed to reduce its Carbon intensity of its economy by 45% by 2030.
- Increasing Sustainability: CORSIA and the LTAG encourage airlines to adopt more sustainable practices, such as using more efficient aircraft, reducing fuel consumption, and investing in renewable energy.
How does Aviation Sector Affect Climate?
- Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Aviation is a significant source of greenhouse gas emissions, particularly carbon dioxide. The burning of fossil fuels in aircraft engines produces carbon dioxide, water vapor, nitrogen oxides, and other greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change.
- Contrails: Contrails are the white, streaky lines that airplanes leave in the sky. They are made up of ice crystals that form when water vapor in the aircraft's exhaust condenses in the cold, high-altitude atmosphere. Contrails can have a warming effect on the planet by trapping heat in the Earth's atmosphere.
- Cirrus Clouds: Similar to contrails, cirrus clouds also form from aircraft emissions. These clouds can have a warming effect on the planet, as they trap heat in the Earth's atmosphere.
What are the Key Initiatives taken by the MoCA to Reduce Carbon Emissions?
- Green Airports: A green airport is an airport that has implemented sustainable practices to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainable development. Green airports aim to minimize their carbon footprint, conserve energy & water resources, and reduce waste and emissions.
- National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP) 2016: It includes a goal of developing a sustainable aviation framework that promotes the use of alternative fuels, energy-efficient aircraft, and infrastructure, among others.
- Sustainable Aviation Fuel (SAF): Initiatives to encourage the use of SAF have been taken for sustainable development and the reduction of carbon emissions at airports.


Geography
India's Climate and Weather Trends
For Prelims: EL Nino, Southwest Monsoon Season, Heatwaves.
For Mains: El Nino on India's monsoon season, role of climate change in the increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events in India.
Why in News?
Although India has received some rain recently, experts predict that the year 2023 will be hotter and drier.
- The Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) has predicted a normal monsoon, but the development of El Nino could lead to a reduction in monsoon rainfall.
- Additionally, the IMD has released data on fatalities caused by extreme weather events, marking the first time they have done so.
What is the Current Situation in India?
- Uneven Rainfall Distribution:
- Despite the recent showers, the entire country has received ample rainfall, except for the northeastern states, Jharkhand, and West Bengal.
- Some areas in Maharashtra, Gujarat, Uttar Pradesh, and Madhya Pradesh have experienced up to 15 times more rainfall than expected due to various local weather phenomena.
- El Nino and Global Warming:
- The IMD has predicted normal monsoon, but the development of El Nino could suppress rainfall over India.
- Globally, 2023 is expected to be one of the top four warmest years on record due to the rapid development of the El Nino event, which has an overall warming impact on the planet.
- India's Warming Trend:
- India's warming trend is slightly lower than the global average, with the year 2022 being 1.15 degree Celsius warmer than pre-industrial times.
- The warming over India is not uniform across regions. Some states like Himachal Pradesh, Goa, and Kerala have become much hotter than others, while eastern states such as Bihar, Jharkhand, and Odisha have experienced the least warming.
- Sea surface temperatures in the tropical Indian Ocean have risen by almost one degree Celsius between 1950 and 2015.
What do the Climate Models Say About the Impact of Upcoming El Nino?
- Weak Monsoon for India: The development of an El Nino in May or June 2023 may cause a weakening of the southwest monsoon season, which brings around 70% of the total rainfall India receives and on which most of its farmers still depend.
- However, sub-seasonal factors such as the Madden-Julian Oscillation (MJO) and monsoon low-pressure systems can temporarily enhance rainfall in some parts as witnessed in the year 2015.
- Hot Temperatures: It may also cause heatwaves and droughts in India and other regions around the world such as South Africa, Australia, Indonesia and the Pacific Islands.
- Heavier Rainfall in the West: It brings heavy rainfall and flooding to other regions such as California in the United States and could cause bleaching and death of coral reefs.
- Rising Global Average Temp:
- The El Nino in 2023 and going into 2024 may push the global average temperature towards 1.5°C warmer than the preindustrial average.
- The warming of the oceans is also one of the major impacts of an El Nino event.
- This is when ocean heat content is already at a record high, according to the World Meteorological Organization (WMO).
Which Weather Event Causes the Most Fatalities?
- Lightning strikes caused more deaths than any other weather event in India.
- In 2022, lightning strikes were responsible for 60% of weather event-related deaths in India (1,608 out of 2,657 recorded deaths).
- Floods and extreme rainfall events claimed 937 lives.
- The actual number of casualties could be higher, as IMD and state governments relied on media reports to compile the list.
What are India's Climate Change Mitigation Initiatives?
- National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC):
- Launched in 2008 to address climate change challenges in India.
- Aims to achieve low-carbon and climate-resilient development for India.
- There are 8 national missions forming the core of the NAPCC which represent multi-pronged, long term and integrated strategies for achieving key goals in climate change. These are-
- National Solar Mission
- National Mission for Enhanced Energy Efficiency
- National Mission on Sustainable Habitat
- National Water Mission
- National Mission for Sustaining the Himalayan Ecosystem
- National Mission for A Green India
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture
- National Mission on Strategic Knowledge for Climate Change.
- Nationally Determined Contributions (NDC):
- India's commitments to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to climate change.
- Pledged to reduce the emissions intensity of GDP by 45% by 2030 from 2005 levels and generate 50% of electricity from non-fossil fuel sources by 2030.
- Pledged to create additional carbon sink and achieve net zero emissions by 2070.
- National Adaptation Fund on Climate Change (NAFCC):
- Established in 2015 to provide financial assistance to state governments for implementing adaptation projects in various sectors.
- State Action Plan on Climate Change (SAPCC):
- Encourages all states and union territories to prepare their own SAPCCs based on their specific needs and priorities.
- SAPCCs outline strategies and actions for addressing climate change at the sub-national level.
- Aligned with the objectives of the NAPCC and the NDC.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. ‘Climate change’ is a global problem. How India will be affected by climate change? How Himalayan and coastal states of India will be affected by climate change? (2017).
Buy Now
Governance
Online Gambling in India
For Prelims: Online Gambling in India, Consumer Protection Act 2019, Public Gambling Act, 1867, Online Gaming.
For Mains: Online Gambling in India, its pros and cons.
Why in News?
Recently, the government of India has instructed states to take action against outdoor advertisements promoting online Betting and Gambling platforms.
- The government had earlier issued an advisory to the media in June 2022, directing them to refrain from publishing such advertisements in the larger public interest.
What is the Government’s Observation?
- The government has observed that some betting and gambling platforms are using outdoor media such as hoardings, posters, banners, and auto rickshaw branding to promote their websites/apps.
- Such advertisements were found to be misleading and not in strict conformity with the Consumer Protection Act 2019.
- Moreover, since betting and gambling are illegal in most parts of the country, they pose financial and social economic risk for the consumers, especially youth and children.
- The government has objected to the promotion of a specific betting platform that encouraged people to watch a sports league on its website in prima facie violation of the Copyright Act.
What is Online Gambling?
- Online gambling involves participating in gambling activities through the internet by placing bets or wagers on games and events to win money or prizes. It can be played on various devices and involves virtual chips or digital currencies instead of cash.
- The global online gambling market was valued at USD 63.53 billion in 2022 and is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.7% from 2023 to 2030, with the Asia-Pacific region being the largest market.
- There are different types of online gambling, including casino games like slots, blackjack, and roulette, sports betting, poker, and lottery. It is regulated in most countries, including India, with varying degrees of restrictions and laws.
What's the Difference Between Online Gaming and Gambling?
- Under the law, the distinction between gaming and gambling depends on the element of skill involved. If an online activity does not require skill, it will be considered gambling rather than gaming.
- Therefore, according to the law, gaming activities that are allowed require skill, while gambling activities rely on chance.
What are the Concerns Related to Online Gambling?
- Financial and Social Trouble:
- Online gambling can be highly addictive, leading to severe financial and social problems. As it is easily accessible, players can spend hours playing games without realizing the amount of time and money they are spending.
- Unregulated:
- Online gambling is often unregulated, making it easy for fraudulent activities to take place. This can lead to players losing their money or their personal information being compromised.
- Gambling has complex laws in India and is not available in most of the states. Each state has its own jurisdiction over gambling.
- Means for Money Laundering:
- Online gambling can be used as a means for money laundering, where players can deposit large amounts of cash into online accounts and then withdraw the money in a legitimate form.
- Prone to Cyber-Attacks:
- Online gambling sites can be vulnerable to cyber-attacks, which can lead to the theft of sensitive personal and financial information of the players.
- Socially Detachment:
- Online gambling can lead to social isolation, as players can spend hours playing games online, leading to a lack of social interaction with family and friends.
What are the Advantages of Online Gambling?
- Convenience: Online gambling can be accessed from the comfort of one's own home or anywhere with an internet connection, making it more convenient than traditional gambling methods.
- Accessibility: Online gambling is often more accessible for people with disabilities or those who have difficulty leaving their homes, allowing them to participate in gambling activities that would otherwise be difficult or impossible for them.
- Revenue Generation: Online gambling has the potential to generate significant revenue for the Indian government through taxation and regulation. Besides, the online gambling industry can create job opportunities for Indian entrepreneurs, who can develop and operate their own online gambling platforms.
What Does Indian Law Say About Online Gambling?
- Public Gambling Act, 1867:
- At present, India has just one central law that governs gambling in all its forms. It's called the Public Gambling Act, 1867, which is an old law, ill-equipped to handle the challenges of digital casinos, online gambling and gaming.
- 7th Schedule of the Constitution:
- Gambling in India is largely a state subject. This means states are expected to create their own laws to regulate gambling in their jurisdictions.
- Laws in Various States:
- States like Delhi, Madhya Pradesh, and Uttar Pradesh have adopted the Public Gambling Act with some amendments.
- However, other regions like Goa, Sikkim, Daman, Meghalaya, and Nagaland, have drafted specific laws to regulate public gambling in their jurisdictions.
Way Forward
- Online gambling poses challenges that need to be addressed by regulators and policymakers to ensure fair and responsible gambling.
- The legal landscape in India is complex and varies by state, so individuals should be aware of their state's laws and only participate in licensed online gambling activities.


Important Facts For Prelims
World Press Freedom Index 2023
Why in News?
On the World Press Freedom Day (WPFD) (3rd May), the World Press Freedom Index 2023 was published by Reporters Without Borders (RSF).
- India ranked 161st among the 180 countries with a score of 36.62. In 2022, India’s rank was 150.
What is World Press Freedom Day?
- About:
- The day was proclaimed by the UN General Assembly in 1993, following the recommendation of UNESCO’s General Conference in 1991.
- The day also marks the 1991 Windhoek Declaration (adopted by UNESCO).
- To raise public awareness of the value of press freedom, the importance of protecting journalists' rights, and the importance of encouraging independent, free media.
- Theme for 2023:
- 'Shaping a Future of Rights: Freedom of Expression as a Driver for All Other Human Rights'
What are the Key Highlights of the World Press Freedom Index 2023?
- Ranking of Countries:
- Top and Worst Performers:
- Norway, Ireland and Denmark occupied the top three positions.
- Vietnam, China and North Korea were at the bottom on the list.
- India’s Neighbours:
- Sri Lanka also made significant improvement on the index, ranking 135th this year as against 146th in 2022.
- Pakistan is ranked at 150th position.
- The situation has gone from ‘problematic’ to ‘very bad’ in three other countries: Tajikistan (down 1 at 153rd), India (down 11 at 161st) and Turkey (down 16 at 165th).
- Top and Worst Performers:
- India’s Performance Analysis:
- India’s position has been consistently falling in the index since 2016 when it was ranked 133.
- The reasons behind the fall in ranking is the increased violence against journalists and a politically partisan media.
- The other phenomenon that dangerously restricts the free flow of information is the acquisition of media outlets by oligarchs who maintain close ties with political leaders.
- The organisation asserts that many journalists in India are forced to censor themselves due to extreme pressure.
What is the World Press Freedom Index?
- About:
- It has been published every year since 2002 by Reporters Without Borders or Reporters Sans Frontieres (RSF).
- RSF is an independent NGO based in Paris that has consultative status with the United Nations, UNESCO, the Council of Europe, and the International Organisation of the Francophonie (OIF).
- OIF is a 54 french speaking nations collective.
- RSF is an independent NGO based in Paris that has consultative status with the United Nations, UNESCO, the Council of Europe, and the International Organisation of the Francophonie (OIF).
- The report ranks 180 countries based on their level of press freedom, taking into account factors such as censorship, media independence, and the safety of journalists. However, it is not an indicator on the quality of journalism.
- It has been published every year since 2002 by Reporters Without Borders or Reporters Sans Frontieres (RSF).
- Scoring Criteria:
- The Index’s rankings are based on a score ranging from 0 to 100 that is assigned to each country or territory, with 100 being the best possible score (the highest possible level of press freedom) and 0 the worst.
- Evaluation Criteria:
- Each country or territory’s score is evaluated using five contextual indicators: political context, legal framework, economic context, sociocultural context and safety.
What about the Freedom of Press in India?
- The Constitution, the supreme law of the land, guarantees freedom of speech and expression under Article 19, which deals with ‘Protection of certain rights regarding freedom of speech, etc.
- Freedom of press is not expressly protected by the Indian legal system but it is impliedly protected under article 19(1) (a) of the constitution, which states - "All citizens shall have the right to freedom of speech and expression".
- In 1950, the Supreme Court in Romesh Thappar v. State of Madras observed that freedom of the press lay at the foundation of all democratic organisations.
- However, Freedom of press is also not absolute. It faces certain restrictions under Article 19(2), which are as follows-
- Matters related to interests of the sovereignty and integrity of India, the security of the State, friendly relations with foreign States, public order, decency or morality or in relation to contempt of court, defamation or incitement to an offence.


Important Facts For Prelims
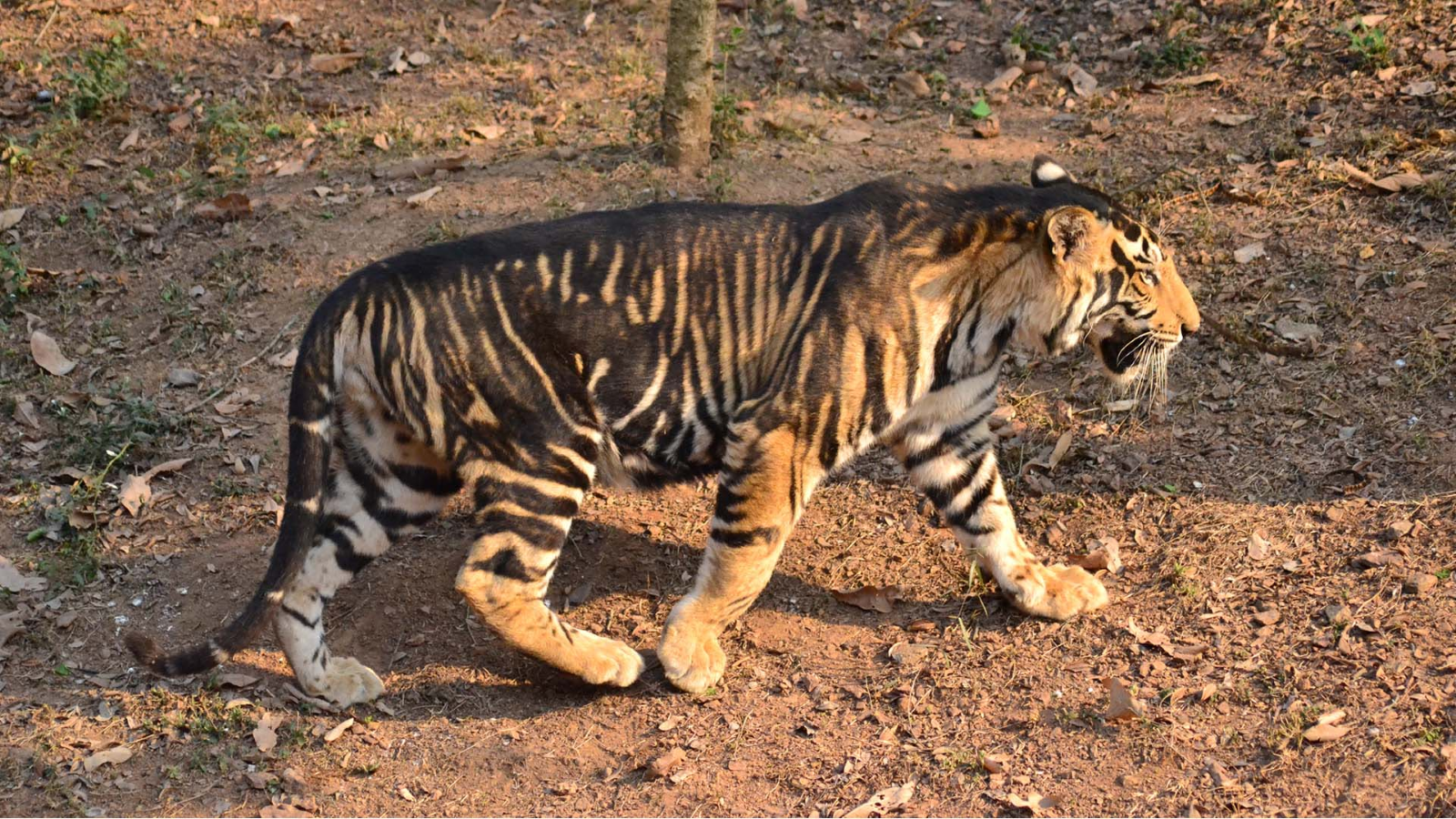
Black Tigers
Why in News?
Recently, the death of a Rare Black Tiger was reported in the Similipal Tiger Reserve in Odisha.
- Simlipal has the world's highest rate of black tiger sightings in the world.
Note:
- The death can have a big impact on the Population of Tiger. The population of black tigers is very limited, and the death of a male tiger will affect the breeding of tigers in the region.
What are the Key Points Related to Black Tigers?
- About:
- Black Tigers are a rare colour variant of the Bengal tiger and are not a distinct species or geographic subspecies.
- The coat colouration and patterning that make the wild cats appear dark boil down to a single mutation in the Transmembrane Aminopeptidase Q (Taqpep) gene.
- Pseudo Melanistic:
- The abnormally dark or black coat in such tigers is termed pseudo melanistic or false coloured.
- Melanistic refers to having very dark skin/hair due to higher-than-normal level of the pigment (substance that gives pigmentation to skin/hair is called melanin).
- There is a high probability (about 60%) that the tiger will have the mutant gene, if randomly selected from Similipal.
- The abnormally dark or black coat in such tigers is termed pseudo melanistic or false coloured.
- Causes for Black Colour:
- The tigers in the Similipal Tiger Reserve are an isolated population in eastern India and gene flow between them and other tiger populations is very restricted.
- Due to Geographic Isolation, genetically related individuals have been mating with each other for many generations, leading to inbreeding.
- This has important implications for tiger conservation as such isolated and inbred populations are prone to extinction over even short periods of time.
What are the Key Points of Similipal Tiger Reserve?
- About:
- It was formally designated a tiger reserve in 1956 and brought under Project Tiger in the year 1973. It was declared a biosphere reserve by the Government of India in June, 1994.
- It has been part of the UNESCO World Network of Biosphere Reserve since 2009.
- It is part of the Similipal-Kuldiha-Hadagarh Elephant Reserve popularly known as Mayurbhanj Elephant Reserve, which includes 3 protected areas i.e., Similipal Tiger Reserve, Hadagarh Wildlife sanctuary and Kuldiha wildlife sanctuary.
- It was formally designated a tiger reserve in 1956 and brought under Project Tiger in the year 1973. It was declared a biosphere reserve by the Government of India in June, 1994.
- Location:
- It is situated in the northern part of Odisha’s Mayurbhanj district. Geographically, it lies in the eastern end of the eastern ghat.
- Wildlife:
- Similipal is home to a wide range of wild animals including tigers and elephants, besides 304 species of birds, 20 species of amphibians and 62 species of reptiles.
- Other Major Protected Areas in Odisha:
- Bhitarkanika National Park.
- Chilika (Nalaban island) WLS.
- Baisipalli WLS.
- Nandankanan WLS.
- Gahirmatha (Marine) WLS.
What are the Tiger Conservation Efforts in India?
- Project Tiger 1973: Project Tiger is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme of the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change (MoEFCC) launched in 1973. It provides havens for tigers in the country’s national parks.
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA): It is a statutory body under the MoEFCC and was established in 2005 following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force. NTCA has been constituted under section 38 L (1) of Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972.
- Conservation Assured | Tiger Standards: CA|TS is a set of criteria which allows tiger sites to check if their management will lead to successful tiger conservation.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims:
Q1. Two important rivers – one with its source in Jharkhand (and known by a different name in Odisha), and another, with its source in Odisha – merge at a place only a short distance from the coast of Bay of Bengal before flowing into the sea. This is an important site of wildlife and biodiversity and a protected area. Which one of the following could be this? (2011)
(a) Bhitarkanika
(b) Chandipur-on-sea
(c) Gopalpur-on-sea
(d) Simlipal
Ans: (a)
Q2. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam
(d) Sundarbans
Ans: (c)
Q3. Consider the following protected areas: (2012)
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Buy Now
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Government to Ease Life for Gay Couples
The Centre informed Supreme Court that it is willing to form a committee headed by the Cabinet Secretary to consider administrative measures for addressing “genuine, human concerns” faced by same-sex couples in their daily lives in areas such as banking, insurance, etc. The SC has suggested that same-sex couples consider this as a building block for future changes, rather than an all-or-none approach. However, the petitioners are seeking a judicial declaration from the court legally recognizing same-sex marriage, arguing that marriage gives meaning, purpose, and identity to a relationship. The court noted that even if it were to recognize same-sex marriage, administrative and legislative changes would still be required to address the human concerns arising out of these relationships. The government is willing to address these human concerns but is reluctant to give same-sex relationships the status of marriage.
Read more: Same-Sex Marriage: Struggle for Equality
Organ Donation and Transplantation Manual
The National Organ and Tissue Transplant Organisation (NOTTO) in India is developing a transplant manual and standard course for training transplant coordinators to better implement organ donation and transplantation programs in hospitals. The NOTTO has also created verticals for coordination, training, and human resources/accounts.
The Indian government has granted Central Government employees who donate an organ special casual leave of up to 42 days as a welfare measure. The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare reported that the number of organ transplants in the country has substantially increased from less than 5,000 in 2013 to over 15,000 in 2022 due to better coordination through the network of Organ & Tissues Transplant Organizations at national, state, and regional levels. In 2016, 2,265 organs were utilized from 930 deceased donors, while 2,765 could be utilized from 904 deceased donors in 2022.
Read more: National Organ Transplantation Guidelines
RVNL Gets Navratna Status
Rail Vikas Nigam Limited (RVNL), a Central Public Sector Enterprise under the Ministry of Railways, has been granted Navratna status. The company, incorporated in 2003, was established to implement railway infrastructure projects and raise extra-budgetary resources for Special Purpose Vehicles (SPVs). RVNL began operations in 2005 and was granted Mini-Ratna status in 2013. RVNL is responsible for undertaking Rail project development and execution of works, creating project specific SPVs, and handing over completed railway projects to the relevant Zonal Railway for operation and maintenance.
The grant of Navratna status to RVNL provides it with more operational freedom, financial autonomy, and enhanced delegation of powers.
Navratna status is a recognition given by the Indian government to select public sector enterprises (PSEs) that have financial and operational autonomy. This status enables PSEs to invest up to Rs. 1000 crore without any approval from the central government, giving them more flexibility in decision making, personnel management, and joint ventures.
Read more: Maharatna Status to REC
Metavalent Bonding
A team of scientists from Jawaharlal Nehru Centre for Advanced Scientific Research, Bengaluru, has discovered a new type of chemical bonding in solids called metavalent bonding. The bonding, which defies the classical octet rule in chemistry, has properties of both the bonding present in metals and those found in glasses. Metavalent bonding can be used to optimize thermoelectric performance in quantum materials and efficiently convert waste heat to electricity. They chose TlBiSe2, a renowned topological insulator, for investigation, and their search for materials with excellent electrical properties drew them to quantum materials. They have shown that TlBiSe2 demonstrates metavalent bonding, which facilitates a fundamentally new way of intrinsically scattering phonons via lattice shearing. By rational chemical designing, they have realized intriguing emergent properties in quantum materials, which shows exciting prospects for green energy production and could pave the way for a new direction for India's newly launched Quantum Mission.
Read more: National Quantum Mission