Infographics
Governance
India’s Vaccination Success Story
For Prelims: Vaccination, Public health Interventions, Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI), National Health Family Survey, Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs), Universal Immunization Programme (UIP), Mission Indradhanush, Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV), Accredited Social Health Activist.
For Mains: Significance of Indian Vaccination Programmes.
Why in News?
As India has achieved remarkable feats with childhood vaccination and continues to do so with Covid-19 vaccination.
- It has overcome challenges across time and geography to reach much of its population, ensure last-mile delivery, finance a sustained large-scale operation at the government level, and develop and sustain trust among the people.
What is Vaccination?
- About:
- The act of administrating the vaccine into the body to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease is termed as vaccination.
- Vaccination is one of the most cost-effective public health interventions, which saves lives by protecting people, especially children, from dreadful vaccine-preventable diseases.
- The act of administrating the vaccine into the body to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease is termed as vaccination.
- Significance:
- According to a recent study, vaccines have prevented up to 3.7 crore deaths in the last 20 years in low- and middle-income countries alone.
- Economic and Social Benefit:
- It's estimated that for every rupee invested in immunization against 10 pathogens in Lower Middle-Income Countries (LMICs) from 2021-30, the return on investment will be 52 rupees.
- Since the discovery of the smallpox vaccine over two centuries ago, vaccines have effectively reduced the burden of diseases such as polio, measles, tetanus, whooping cough, influenza, and lately, Covid-19.
What are the India’s Achievements in Vaccination?
- Background:
- India has a long history of successful vaccination with historical accounts of inoculation dating back to the 18th century.
- After being declared smallpox-free in 1977, India launched the Expanded Programme on Immunization (EPI) in 1978 and introduced the Bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine (BCG), Diphtheria, Tetanus, Pertussis (DPT), and Oral poliovirus vaccines (OPV) vaccines.
- National Health Family Survey (NHFS) Data:
- The childhood vaccination rates have consistently improved over the last two decades with the proportion of children who are ‘fully vaccinated’ reaching 76% as per the latest National Health Family Survey.
- India has a long history of successful vaccination with historical accounts of inoculation dating back to the 18th century.
- Initiatives and Achievements:
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
- India has consistently contributed to the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by focusing on the immunization of newborns, infants, children, and pregnant women.
- Universal Immunization Programme (UIP):
- Under it, India provides vaccines against 11 diseases nationally and one disease sub-nationally.
- Further, targeting close to 2.7 crore newborns and 2.9 crore pregnant women every year.
- Under it, India provides vaccines against 11 diseases nationally and one disease sub-nationally.
- Mass immunization campaigns:
- India launched an ambitious Measles-Rubella (MR) vaccination drive and vaccinated over 3 crore children in three years which prevented tens of thousands of measles deaths in children.
- Mission Indradhanush:
- Since 2014, immunization activities have been intensified with catch-up rounds such as Mission Indradhanush to ensure that full immunization coverage of 90% is achieved and sustained across the country.
- The Pneumococcal Conjugate Vaccine (PCV) was introduced and scaled up using Made-in-India vaccines to prevent rotaviral diarrhea and pneumococcal pneumonia in children.
- Use of Technology:
- The use of technology like the Electronic Vaccine Intelligence Network (eVIN) system that digitizes the entire vaccine stock management, their logistics and temperature tracking at all levels of vaccine storage from national to the sub-district.
- A multi-faceted approach by the government helped the entire population to achieve public ownership to be polio-free in 2014.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs):
What were the challenges faced by India during various vaccination drives?
- Supply chain disruption during Covid-19:
- During the pandemic, lockdowns led to disruptions in routine immunization services and the closure of health facilities.
- Vaccination Hesitancy:
- There was global collaboration to bring out vaccines at an unprecedented speed, also observed an ‘infodemic-fueled’ vaccine hesitancy in people who previously trusted vaccines.
What are the Reasons for India’s Success in Vaccination?
- Capacity Building in Health:
- India has built up its biomedical enterprise including research and development, and manufacturing capacity.
- The indigenously produced Rotavirus and PCV vaccines, and the speed with which India was able to indigenously produce two Covid-19 vaccines, are examples of the return on these investments.
- India has built up its biomedical enterprise including research and development, and manufacturing capacity.
- Infrastructure:
- India also built its delivery infrastructure by establishing cold chain systems, and by developing and training a community health cadre of workers who established last-mile services.
- Behavioural Communication campaign:
- The infrastructural developments were accompanied by an improvement on the demand side through social and behavioural communication campaigns.
- Creating Awareness and Engagement:
- India uses various available platforms of communication to convey consistent and accurate information.
- Community health workers such as Accredited Social Health Activist (ASHAs) and Anganwadi workers go door-to-door to provide information and identify the missed-out children and pregnant women for any due dose.
- While national leaders and celebrities spreading messages through mass media has proven to be useful, engagement with local community influencers who are “closer” to people has also tremendously helped build vaccine confidence.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question:
Prelims:
Q. ‘Mission Indradhanush’ launched by the Government of India pertains to (2016)
(a) immunization of children and pregnant women
(b) construction of smart cities across the country
(c) India’s own search for the Earth-like planets in outer space
(d) New Educational Policy
Ans: A
Exp:
- Mission Indradhanush is an immunization scheme launched by the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, GoI on 25th December, 2014.
- Depicting seven colours of the rainbow, it aimed to cover all those children by 2020 who are either unvaccinated, or are partially vaccinated against seven vaccine preventable diseases which include diphtheria, whooping cough, tetanus, polio, tuberculosis, measles and hepatitis B.
- The mission is technically supported by WHO, UNICEF, Rotary International and other donor partners. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
International Relations
IMF Bailout to Sri Lanka
For Prelims: International Monetary Fund (IMF), GDP growth rate, Trans-Shipment hub, Tamil Community.
For Mains: Sri Lanka crisis and its effects on India.
Why in News?
Recently, The International Monetary Fund (IMF) approved a preliminary agreement with Sri Lanka on a four-year, USD 2.9 billion bailout package which is aimed at restoring economic stability and debt sustainability for the crisis-ridden south Asian nation.
What is the Bailout Package Offered to Sri Lanka?
- Need:
- The Economic Crisis of Sri Lanka with USD 51 billion debt which was caused due to various reasons:
- The Easter bomb blasts of April 2019 in churches in Colombo
- The government policy of lower tax rates and wide-ranging subsidies for farmers during their campaign.
- The Covid-19 pandemic in 2020 which impacted exports of tea, rubber, spices, garments and the tourism sector.
- The Economic Crisis of Sri Lanka with USD 51 billion debt which was caused due to various reasons:
- About:
- The IMF package is to be paid in tranches over the next four years, which is less than what India provided to Sri Lanka over four months.
- The package must be approved by the IMF’s board of directors.
- The approval is contingent on Sri Lanka’s international creditors - commercial lenders such as banks and asset managers, multilateral agencies, as well as bilateral creditors including China, Japan, and India agreeing to restructure its debt.
- Benefits:
- Improve credit rating:
- It can boost the receiving country’s credit ratings, and the confidence of international creditors and investors who may then chip in to provide bridge financing to close the gaps between the tranches.
- Improve credit rating:
- Aim:
- Its program will aim to boost government revenue, encourage fiscal consolidation, introduce new pricing for fuel and electricity, hike social spending, bolster central bank autonomy, and rebuild depleted foreign reserves.
- The programme aims to reach a primary surplus of 2.3% of GDP by 2024.
What Measures are Taken by Sri Lanka’s Economy to Improve its Economy?
- Increase in Revenue:
- The country’s budget aimed at increasing revenue to 15% of GDP by 2025 from 8.2% at the end of 2021 by reducing public debt.
- An increase in VAT from 12 to 15%, and compulsory tax registration for everyone aged 18 years and older in order to widen personal income tax collections are among the measures.
- Some 50 state-owned enterprises are up for privatisation.
- The country’s budget aimed at increasing revenue to 15% of GDP by 2025 from 8.2% at the end of 2021 by reducing public debt.
- Reduce the age of retirement:
- The age of retirement in government and semi-government organisations has been brought down to 60 from 65 and 62 respectively.
- Banking sector:
- Staff and depositors are to be offered a 20% shareholding in state banks to address recapitalization requirements arising out of non-repayment of loans due to the economic meltdown.
What is the International Monetary Fund (IMF)?
- About:
- The International Monetary Fund (IMF) is an international organization that promotes global economic growth and financial stability, encourages international trade, and reduces poverty.
- Conditionalities set by IMF:
- About:
- When a country borrows from the IMF, its government agrees to adjust its economic policies to overcome the problems that led it to seek financial aid.
- These policy adjustments are conditions for IMF loans and serve to ensure that the country will be able to repay the IMF.
- This system of conditionality is designed to promote national ownership of strong and effective policies.
- Conditionality helps countries solve balance-of-payments problems without resorting to measures that are harmful to national or international prosperity.
- When a country borrows from the IMF, its government agrees to adjust its economic policies to overcome the problems that led it to seek financial aid.
- Policy commitments agreed with country authorities can take different forms. They include:
- Prior actions:
- These are the steps a country agrees to take before the IMF approves financing or completes a review.
- They ensure that a program will have the necessary foundation for success.
- These are the steps a country agrees to take before the IMF approves financing or completes a review.
- Quantitative performance criteria (QPCs):
- Specific, measurable conditions for IMF lending always relate to macroeconomic variables under the control of the authorities.
- Such variables include monetary and credit aggregates, international reserves, fiscal balances, and external borrowing.
- Specific, measurable conditions for IMF lending always relate to macroeconomic variables under the control of the authorities.
- Indicative targets (ITs):
- In addition to QPCs, ITs may be set for quantitative indicators to assess progress in meeting a program’s objectives.
- Structural benchmarks (SBs):
- These are reform measures that often are non-quantifiable but are critical for achieving program goals and are intended as markers to assess program implementation.
- Prior actions:
- About:
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Prelims:
Q. Recently, which one of the following currencies has been proposed to be added to the basket of IMF’s SDR? (2016)
(a) Rouble
(b) Rand
(c) Indian Rupee
(d) Renminbi
Ans: D
- Special Drawing Rights (SDR) is an international reserve asset, created by the IMF in 1969 to supplement its member countries’ official reserves.
- The value of the SDR is based on a basket of five currencies – US Dollar, Euro, Chinese Renminbi, Japanese Yen, and British pound sterling.
- The Chinese Renminbi was added to the basket of currencies on October 1, 2016. Therefore, option (d) is the correct answer.
Mains:
Q. The World Bank and the IMF, collectively known as the Bretton Woods Institutions, are the two inter-governmental pillars supporting the structure of the world’s economic and financial order. Superficially, the World Bank and the IMF exhibit many common characteristics, yet their role, functions and mandate are distinctly different. Elucidate. (2013)
International Relations
G20 Education Ministers’ Meeting
For Prelims: G20, International Organization, India and International Groupings
For Mains: India’s foreign policy, Significance of G20 in India’s Foreign Policy, Challenges of global happenings on international groupings
Why in News?
Recently, the Minister of Education addressed the G-20 Education Ministers’ Meeting in Bali, Indonesia.
- Theme: Recovery, Re-imagine and Rebuild Stronger.
- The G20 presidency is scheduled to move from Indonesia to India in December 2022.
What are the Key Highlights?
- Emphasized on the importance of sharing mutual experiences & working together to create a new world in which education remains the nodal point for addressing common challenges.
- The National Education Policy 2020, based on the foundational principles of access, equity, quality, affordability and accountability is India’s guiding light for promoting lifelong learning opportunities and achieving the shared vision of G20.
- Highlighted India’s rapid strides towards building a more resilient and inclusive education and skilling ecosystem and realising the creative potential of each learner through the implementation of NEP 2020.
- India is giving special emphasis on formalizing early childhood care & education, supporting differently-abled children, boosting digital and multi-modal learning, flexible entry-exit pathways, integrating education with skills, which are keys to improve learning outcomes.
What is G20?
- About:
- It is a group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), founded in 1999, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- Its members are Argentina, Australia, Brazil, Canada, China, France, Germany, India, Indonesia, Italy, Japan, Republic of Korea, Mexico, Russia, Saudi Arabia, South Africa, Turkey, the United Kingdom, the United States and the EU.
- Nigeria was meant to be the “20th” member and was dropped at the last minute due to political troubles at the time.
- The membership comprises a mix of the world’s largest advanced and emerging economies, representing about two-thirds of the world’s population.
- The G20 holds a strategic role in securing future global economic growth and prosperity.
- Together, the G20 members represent more than 80% of world GDP, 75% of international trade and 60% of the world population.
- It is a group of 19 countries and the European Union (EU), founded in 1999, with representatives of the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank.
- Functioning of G20:
- The G-20 has no fixed headquarters, and the secretariat moves by rotation between the countries hosting or assuming Presidency of the grouping each year.
- The members are divided into five groups (India is in Group 2, along with Russia, South Africa and Turkey).
- The G-20 agenda that still depends heavily on the guidance of Finance Ministers and central Governors is finalised by a unique system of ‘Sherpas’, who are special envoys of G-20 leaders.
- Another feature of the G-20 is ‘Troika’ meetings, comprising the countries presiding over the G-20 in the past year, present year, and next year. At present, the Troika is made up of Italy, Indonesia and India.
How has the G20 Evolved over the years?
- The Global Financial Crisis (2007-08) cemented G20’s reputation as the premier crisis management and coordination body.
- The US, which held the G20 Presidency in 2008, elevated the meeting of the Finance Ministers and Central Bank Governors to Heads of State, resulting in the first G20 Summit.
- The Summits in Washington DC, London, and Pittsburgh set the scene for some of the most durable global reforms:
- Blacklisting states in an effort to tackle tax evasion and avoidance, provisioning stricter controls on hedge funds and rating agencies, making the Financial Stability Board an effective supervisory and watchdog body for the global financial system, proposing stricter regulations for too-big-to fail banks, refraining members from imposing new barriers to trade etc.
- By the time Covid-19 struck, the G20 had wandered off from its original mission and G20 lost its focus.
- G20 reinvented itself by widening its agenda to include issues such as climate change, jobs and social security issues, inequality, agriculture, migration, corruption, terror financing, drug trafficking, food security and nutrition, disruptive technologies, and meeting the sustainable development goals.
- In recent times, G20 members have made all the right commitments after the pandemic, but there is little to show in action.
- At the Riyadh Summit in October 2020, they prioritised four things: fighting the pandemic, safeguarding the global economy, addressing international trade disruptions, and enhancing global cooperation.
- The Italian Presidency in 2021 had focused on three broad, interconnected pillars of action — People, Planet, Prosperity — vowing to take the lead in ensuring a swift international response to the pandemic.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. In which one of the following groups are all the four countries members of G20? (2020)
(a) Argentina, Mexico, South Africa and Turkey
(b) Australia, Canada, Malaysia and New Zealand
(c) Brazil, Iran, Saudi Arabia and Vietnam
(d) Indonesia, Japan, Singapore and South Korea
Ans: (a)
Ethics
Civil Servants and Digital Literacy
For Mains: Importance of Digital Literacy for Civil Servants
Why in News?
Recently, Microsoft has partnered with the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE), and Capacity Building Commission (CBC) to empower India’s civil servants with future-ready skills.
- The partnership under the project ‘Capacity Building by MSDE in Microsoft Digital Productivity Skills’ aims to enhance the functional computer literacy of nearly 2.5 million civil servants of Government of India (GoI).
- This project is in line with the Mission Karmayogi.
What is Digital Literacy?
- Digital literacy refers to the wide range of skills, which are necessary to emerge successful and adapt to the digital world.
- Since the print mediums are facing stagnation, the ability to grasp information found online becomes important.
- People and students who lack digital literacy skills may soon find themselves tough to gain access to information which is available online.
Why is Digital Literacy important for Civil Servants?
- To Provide Efficient and Effective Citizen Centric Services:
- Digital Literacy will empower India’s civil servants to provide efficient and effective citizen centric services to the vulnerable and underprivileged sections of the society.
- It will enable them to deliver last mile social welfare services.
- Bridging the Competency Gap:
- One of the major competency gaps identified in various job roles among the civil servants is the lack of digital productivity application skills while working on Microsoft Office tools like Word, Excel, and PowerPoint presentation, at a professional level. So digital empowerment will help in bridging competency Gaps.
What Competencies will the Civil servants of the Future Need?
- Unifying Framework across Various Sector:
- There is currently no unifying framework across the public sector, private sector and civil society.
- While the technical competencies that civil servants need are similar to those required in the private sector, the digital governance competencies are something else entirely.
- There is a need for a shared language and understanding of what Artificial Intelligence (AI) for the public good is.
- Scaling up Digital Solutions:
- Public services face difficulties in scaling up digital solutions, due to infrastructure gaps.
- Sometimes, the solutions from the private sector are not ready for the public sector. So, the need is to design technology for the public sector.
- Bridging Cooperation Gap:
- The government should never be viewed as a singular entity, but rather be encouraged to communicate with one another.
- Additionally, the need is to engage existing institutions and foster collaborations instead of reinventing the wheel.
Agriculture
Push to Coarse Cereals
For Prelims: Coarse Cereals & It’s Production
For Mains: Significance of Coarse Cereals, Uses & Features of Coarse Cereals, Government Intervention
Why in News?
Recently, a meeting was organised by the Department of Food and Public Distribution (DFPD), to discuss the procurement of the Kharif produce for 2022-2023.
- The government of India has considered pushing towards coarse cereals as climate change affects wheat and paddy cultivation.
- Procurement target for coarse cereals is doubled from Kharif crop market, more coarse grains likely to be seen in rations.
What are Coarse Cereals?
- About:
- Coarse cereals are traditionally grown in resource poor agro-climatic regions of the country.
- Agro-climatic zone is a land unit in terms of major climates suitable for a certain range of crops and cultivars.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, maize, barley, finger millet and several small millets such as kodo millet, little millet, foxtail millet, proso millet and barnyard millet together called coarse cereals.
- Sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet, maize and small millets (barnyard millet, proso millet, kodo millet and foxtail millet) are also called nutri-cereals.
- Coarse cereals are traditionally grown in resource poor agro-climatic regions of the country.
- Significance:
- Coarse cereals are known for nutria-rich content and having characteristics like drought tolerance, photo-insensitivity and resilient to climate change etc.
- These crops also offer a good potential in the food processing industry and as a promising exportable commodity.
- Their cultivation in drought prone areas for providing food for human consumption, feed & fodder for animal and poultry, use as fuel and industrial uses are common.
- Their nutritious value serves as an excellent tool to combat malnutrition.
- It helps in generating employment in low rainfall areas where other alternative crops are limited and these crops are used as a contingent crop.
- Coarse cereals are known for nutria-rich content and having characteristics like drought tolerance, photo-insensitivity and resilient to climate change etc.
- Coarse Cereals Producing States:
- Karnataka, Rajasthan, Puducherry, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh etc.
- Uses of Coarse Cereals:
- Fodder:
- The cultivation of Millets like sorghum and pearl millet in some Northern States like Haryana, Punjab and Western UP is primarily done for fodder purposes.
- Industrial Products:
- Sorghum: Used in Malting, high fructose syrup, starch, Jaggery, bakery etc.
- Pearl millet: Used in Brewing/malting, starch, bakery, poultry and animal feed.
- Maize: Used in Brewing, starch, bakery, poultry and animal feed, bio-fuel.
- Source of Feed:
- The demand for coarse cereals for animals and poultry feed is on the rise.
- In India, feed requirements are met from waste food grains in general and made especially from coarse cereals.
- Maize is the preferred carbohydrate source in poultry feed.
- Fodder:
Why is the Government Shifting Focus on Coarse Cereals?
- Climate Change:
- Climate change has affected the production of wheat and paddy in the country, indicating a need to shift focus to coarse cereals.
- Cultivation of the wheat and paddy will not be enough to meet the country’s food needs due to erratic weather patterns.
- Climate change has affected the production of wheat and paddy in the country, indicating a need to shift focus to coarse cereals.
- Monsoon:
- Erratic monsoon 2022 has increased the government’s concern for the Kharif season yield.
- The sowing of paddy and pulses was severely affected in most areas in 2022.
- Erratic monsoon 2022 has increased the government’s concern for the Kharif season yield.
- Sustainable Crop:
- Coarse cereals have characteristics like drought tolerance, photo-insensitivity and resilient to climate change etc.
- Low Cost of cultivation:
- The cost of cultivation is less compared to summer paddy cultivation and also it requires lesser quantum of water for irrigation.
- Increased Coarse Cereals Production:
- Coarse cereals have been sown in 17.63 million hectares in 2022 as against 16.93 million hectares in 2021.
- About 50 million tonnes of coarse cereals are produced in the country at present.
- Maize and millets are grown the most.
What Steps are Government Taking to Support Coarse Cereals?
- Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millet Promotion (INSIMP):
- Government announced an allocation of Rs. 300 crores in 2011-12 under Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana for promotion of millets as Nutri-cereals.
- The scheme aimed to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies in an integrated manner with visible impact to catalyze increased production of millets in the country.
- Increase in Minimum Support Price:
- The government has hiked the Minimum Support Price of Millets, which came as a big price incentive for farmers.
- Further, to provide a steady market for the produce, the government has included millets in the public distribution system.
- The government has hiked the Minimum Support Price of Millets, which came as a big price incentive for farmers.
- Input Support:
- The government has introduced provision of seed kits and inputs to farmers, building value chains through Farmer Producer Organisations and supporting the marketability of millets.
- International Year of Millets:
- The United Nation General Assembly adopted an India-sponsored resolution to mark 2023 as the “International Year of Millets”.
- India celebrated 2018 as the “National Year of Millets”.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. With reference to ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2016)
- This initiative aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies, and to demonstrate value addition techniques, in anc integrated manner, with cluster approach.
- Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have larger stake in this scheme.
- An important objective of the scheme is to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation by offering them free kits of critical inputs of nutrients and micro irrigation Equipment.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 2 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Explanation:
- ‘Initiative for Nutritional Security through Intensive Millets Promotion’ Scheme aims to demonstrate the improved production and post-harvest technologies in an integrated manner with visible impact to catalyse increased production of millets in the country. Besides increasing production of millets, the Scheme, through processing and value addition techniques, is expected to generate consumer demand for millet based food products. Hence, statement 1 is correct.
- Technology demonstrations in compact blocks would be organized in selected districts for four categories of millets – sorghum, pearl millet, finger millet and small millets. Poor, small, marginal and tribal farmers have a larger stake in this scheme. Hence, statement 2 is correct.
- There is no such provision to encourage farmers of commercial crops to shift to millet cultivation. Hence, statement 3 is not correct.
- Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Social Justice
Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana
For Prelims: Skill Indian Mission, National Skills Development Corporation, Recognition of Prior Learning.
For Mains: Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana and its Significance.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Education informed Lok Sabha that, during 2021-22, more than 3 Lakh women were trained under Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) scheme.
What is PMKVY?
- Background:
- Skill India Mission was launched by the government in 2015 under which the flagship scheme Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) is run.
- It aims to train over 40 crore people in India in different skills by 2022. It aims at vocational training and certification of Indian youth for a better livelihood and respect in the society.
- PMKVY is implemented by the National Skills Development Corporation (NSDC) under the guidance of the Ministry of Skill Development and Entrepreneurship (MSDE).
- PMKVY 1.0:
- Launch: India’s largest Skill Certification Scheme - Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana (PMKVY) - was launched on 15th July, 2015 (World Youth Skills Day).
- Aim: To encourage and promote skill development in the country by providing free short duration skill training and incentivizing this by providing monetary rewards to youth for skill certification.
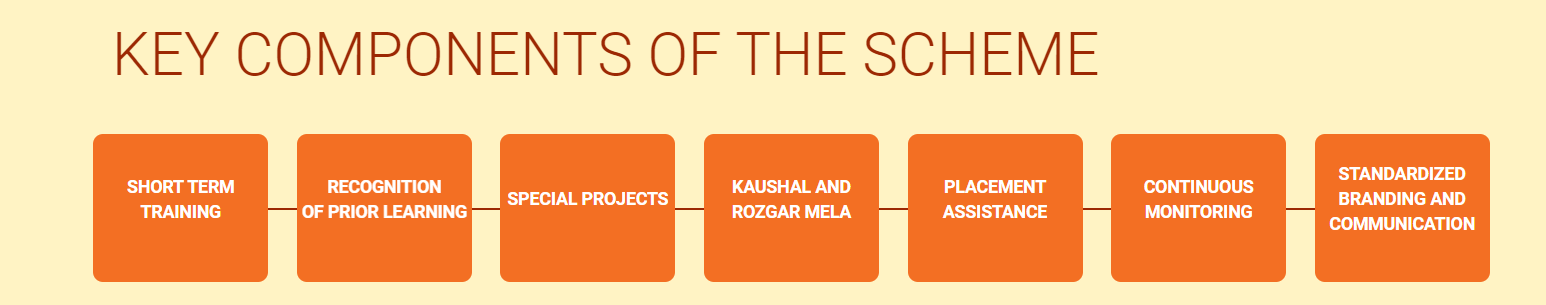
- Key Components: Short Term Training, Special Projects, Recognition of Prior Learning, Kaushal & Rozgar Mela, etc.
- Outcome: In 2015-16, 19.85 lakh candidates were trained.
- PMKVY 2.0:
- Coverage: PMKVY 2016-20 (PMKVY 2.0) was launched by scaling up both in terms of Sector and Geography and by greater alignment with other missions of the Government of India like Make in India, Digital India, Swachh Bharat, etc.
- Budget: Rs. 12,000 Crore.
- Implementation Through Two Components:
- Centrally Sponsored Centrally Managed (CSCM): This component was implemented by National Skill Development Corporation. 75% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSCM.
- Centrally Sponsored State Managed (CSSM): This component was implemented by State Governments through State Skill Development Missions (SSDMs). 25% of the PMKVY 2016-20 funds and corresponding physical targets have been allocated under CSSM.
- Outcome: More than 1.2 Crore youth have been trained/oriented through an improved standardized skilling ecosystem in the country under PMKVY 1.0 and PMKVY 2.0.
- PMKVY 3.0:
- Coverage: Launched in 717 districts, 28 States/eight UTs, PMKVY 3.0 is a step towards ‘Atmnanirbhar Bharat’.
- Implementation: It will be implemented in a more decentralized structure with greater responsibilities and support from States/UTs and Districts.
- District Skill Committees (DSCs), under the guidance of State Skill Development Missions (SSDM), shall play a key role in addressing the skill gap and assessing demand at the district level.
- Features:
- It envisages training of eight lakh candidates over a scheme period of 2020-2021 with an outlay of Rs. 948.90 crore.
- It will be more trainee- and learner-centric. The focus is on bridging the demand-supply gap by promoting skill development in areas of new-age and Industry 4.0 job roles.
- It will be a propagator of vocational education at an early level for youth to capitalize on industry-linked opportunities.
- The National Educational Policy 2020 also puts focus on vocational training for holistic growth and increased employability.
- By taking the bottom-up approach to training, it will identify job roles that have demand at the local level and skill the youth, linking them to these opportunities (Vocal for Local).
- It will encourage healthy competition between states by making available increased allocation to those states that perform better.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question
Q. ‘Recognition of Prior Learning Scheme’ is sometimes mentioned in the news with reference to (2017)
(a) Certifying the skills acquired by construction workers through traditional channels.
(b) Enrolling the persons in Universities for distance learning programmes.
(c) Reserving some skilled jobs to rural and urban poor in some public sector undertakings.
(d) Certifying the skills acquired by trainees under the National Skill Development Programme.
Ans: (a)
Exp:
- Recognition of Prior Learning (RPL), introduced as a component of PMKVY, largely refers to an assessment process used to evaluate a person’s existing skill set, knowledge and experience gained either by formal, non-formal or informal learning and not under the National Skill Development Program.
- It has threefold objectives:
- To align the competencies of the un-regulated workforce of the country to the standardized National Skills Qualification Framework (NSQF).
- To enhance the employability opportunities of an individual as well as provide alternative routes to higher education.
- To provide opportunities for reducing inequalities based on privileging certain forms of knowledge over others.
- Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q. With reference to Pradhan Mantri Kaushal Vikas Yojana, consider the following statements: (2018)
- It is the flagship scheme of the Ministry of Labour and Employment.
- It, among other things, will also impart training in soft skills, entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy.
- It aims to align the competencies of the unregulated workforce of the country to the National Skill Qualification Framework.
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Important Facts For Prelims
Smart Solutions Challenge and Inclusive Cities Awards 2022
Why in News?
Recently, Smart Solutions Challenge and Inclusive Cities Awards 2022 were awarded by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
Why were the Key Highlights of the Event?
- In the category of early-stage innovations, the winner was a wearable technology product, Fifth Sense by Glovatrix Pvt. Ltd.
- This product translates sign language gestures to speech and text using sensors and Artificial Intelligence.
- In the second category of market-ready solutions, Mouseware by Dextroware Devices Pvt. Ltd. was the winner.
- Mouseware is a head-wearable device that enables hands-free control of computers and smart gadgets.
- Belagavi Smarty City’s system for those with disabilities to access education and healthcare was awarded the top prize in the category of implemented solutions.
What should we Know about the Awards?
- About:
- The Smart Solutions Challenge is an initiative of the National Institute of Urban Affairs (NIUA) and the United Nations (UN)) in India.
- NIUA and UN in India are looking for innovative ideas, solutions, technologies, products, and business solutions that can help break-down and resolve complex city-level inclusion and accessibility challenges faced by persons with disabilities, women and girls, and the elderly.
- Significance:
- These solutions will be instrumental in integrating universal design, which will help achieve Sustainable Development Goals’ target 11.7- to provide safe, inclusive and accessible, green and public spaces for all vulnerable communities.
What is National Institute of Urban Affairs?
- NIUA is an institute for research, training and information dissemination in urban development and management. It is located in New Delhi, India.
- It was established in 1976 as an autonomous body under the Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- The Institute is supported by the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, Government of India, State Governments, urban and regional development authorities and other agencies concerned with urban issues.
What are Other Initiatives Related to Urban Development?
- Atal Mission for Urban Rejuvenation and Urban Transformation (AMRUT).
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Urban (PMAY-U).
- Integrated Command and Control Centres (ICCCs).
- Climate Smart Cities Assessment Framework 2.0.
- India Smart Cities Fellowship Program.
- TULIP-The Urban Learning Internship Program.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question
Q. Which of the following statements is/are correct regarding Smart India Hackathon 2017? (2017)
- It is a centrally sponsored scheme for developing every city of our country into Smart Cities in a decade.
- It is an initiative to identify new digital technology innovations for solving the many problems faced by our country.
- It is a programme aimed at making all the financial transactions in our country completely digital in a decade.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 only
(c) 3 only
(d) 2 and 3 only
Ans: B
Exp:
- Smart India Hackathon, 2017 was a 36 hour non-stop digital product development competition during which teams of thousands of technology students tried to build innovative digital solutions for the problems identified by 29 different Ministries/Departments of GoI. Hence, statement 2 is correct and 1, 3 are not correct.
- For the first time, government departments directly engaged with students, challenging them to build digital solutions to improve their efficiency, plug revenue leakages and corruption.
- The ‘Grand Finale’ of Smart India Hackathon, 2017 was organized, simultaneously across 26 different cities and the winners got support for converting their ideas into startups apart from cash prizes.
Important Facts For Prelims
Uyghur Rights Abuse
Why in News?
Recently, according to a report by United Nations, China is conducting serious human rights violations against Uyghurs that may amount to crimes against humanity.
What are the Key Highlights of the Report?
- Persecution of Uyghurs:
- The report accuses China of sweeping a million or more people from minority groups into detention camps where many have said they were tortured, sexually assaulted, and forced to abandon their language and religion.
- Ruthless campaign:
- There is a ruthless campaign against extremism in the far western province of Xinjiang that also included draconian birth control policies and all-encompassing restrictions on people’s movement.
- Set-up Independent International Body:
- Human rights groups renewed calls for the UN Human Rights Council, to set up an independent international body to investigate the allegations.
Who are Uyghurs?
- About:
- The Uyghurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
- The Uyghurs speak their own language, similar to Turkish, and see themselves as culturally and ethnically close to Central Asian nations.
- The Uyghurs are considered to be one of the 55 officially recognized ethnic minority communities in China.
- However, China recognizes the community only as a regional minority and rejects that they are an indigenous group.
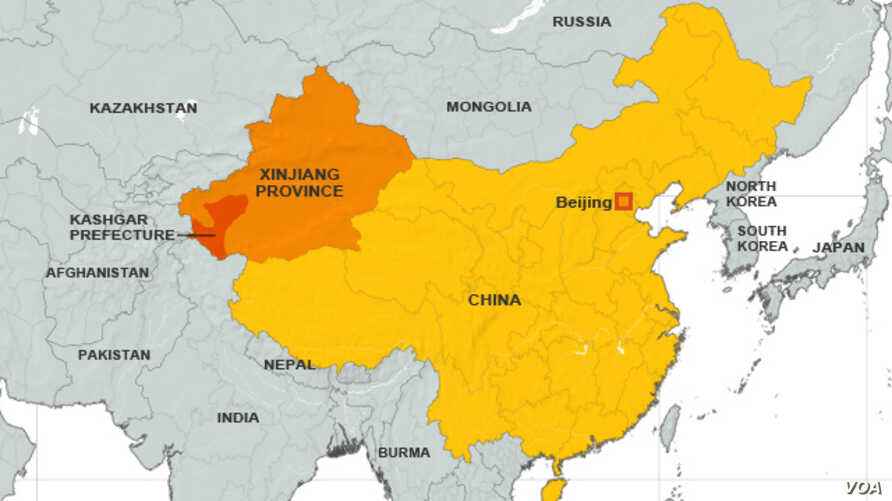
- Currently, the largest population of the Uyghur ethnic community lives in the Xinjiang region of China.
- A significant population of Uyghurs also lives in the neighbouring Central Asian countries such as Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
- Xinjiang is technically an autonomous region within China — its largest region, rich in minerals, and sharing borders with eight countries, including India, Pakistan, Russia and Afghanistan.
- A significant population of Uyghurs also lives in the neighbouring Central Asian countries such as Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan.
- The Uyghurs are a predominantly Muslim minority Turkic ethnic group, whose origins can be traced to Central and East Asia.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2016)
Community sometimes in the affairs of mentioned in the news
- Kurd — Bangladesh
- Madhesi — Nepal
- Rohingya — Myanmar
Which of the pairs given above is/are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 2
(b) 2 only
(c) 2 and 3
(d) 3 only
Ans: (c)
- Kurd: They are one of the indigenous peoples of the Mesopotamian plains and the highlands in what are now South-eastern Turkey, North-eastern Syria, northern Iraq, North-western Iran and South-western Armenia. They also adhere to a number of different religions and creeds, although the majority is Sunni Muslims. Hence, pair 1 is not correctly matched.
- Madhesi: It is an ethnic group living mainly in thesouthern plains of Nepal, close to the border with India. Madhesis are predominantly Hindus with some Muslims and Christians. Hence, pair 2 is correctly matched.
- Rohingya: They are an ethnic group, largely comprising Muslims, who predominantly live in the Western Myanmar province of Rakhine. They speak a dialect of Bengali, as opposed to the commonly spoken Burmese language. According to Myanmar authorities, they are not the authorized citizens of the country. Hence, pair 3 is correctly matched.Therefore, option (c) is the correct answer.
Important Facts For Prelims
Need for Unified Metro Law
Why in News?
Recently, the Parliamentary Standing Committee on Housing and Urban Affairs flagged the need for single and comprehensive legislation for all the Metro rail networks in the country and opposed the existing three central acts.
- All metro rail projects are covered under the legal framework of the Metro Railways (Construction of Works) Act, 1978; the Metro Railways (Operation and Maintenance) Act, 2002; and the Railways Act, 1989.
What are the Issues Highlighted by the Panel?
- Low ridership in all Metros apart from Delhi and Mumbai.
- Leading to a delay in the projects attaining breaking even point.
- Even after six to seven years of continuous operations the issues still exist like:
- faulty Detailed Project Report (DPRs),
- lack of proper planning to provide first and last mile connectivity,
- provision of parking at metro rail stations,
- need for increasing catchment area, etc
What are the Recommendations of the Panel?
- There is a need for the use of the less capital-intensive MetroNeo and MetroLite networks in small cities with low ridership instead of the conventional Metro systems.
- MetroNeo is a mass rapid transit system providing low-cost, energy-efficient and eco-friendly urban transport solutions for tier 2 and tier 3 cities.
- Metrolite system will have a dedicated path separating the road traffic with it.
- For segregation with road traffic, fencing can be provided on either side of the network.
- Further, the Kochi Water Metro project should be included under the Ministry of Heavy Industries’ FAME II scheme as it would be a pollution-free mode of transport using battery-operated boats.