International Relations
China's Stapled Visas
For Prelims: Stapled Visas, McMahon Line, Line of Actual Control (LAC)
For Mains: Concept of stapled visas, China's unilateral claim to Arunachal Pradesh as South Tibet.
Why in News?
Recently, India withdrew its eight-athlete ‘Wushu’ martial arts athletes contingent from the Summer World University Games in Chengdu, China. The move came in response to China's issuance of stapled visas to three athletes from the Indian team, all of whom were from Arunachal Pradesh.
- The practice of issuing stapled visas started around 2005, and China has consistently issued such visas to residents of Arunachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir.
What are Stapled Visas?
- A stapled visa is an unstamped piece of paper attached to a passport with staples or a pin.
- Unlike regular visas that are affixed and stamped directly on the passport, stapled visas are detachable.
- The issuance of stapled visas is part of China's ongoing territorial disputes with India over Arunachal Pradesh.
- The stapled visas are considered valid by China, but India refuses to accept them as legitimate travel documents.
Note:
- Passports and visas enable authorized, secure international travel, reflecting nation-state sovereignty and control over borders.
- Passports signify identity and citizenship, while visas grant entry permissions to specific destinations.
- A passport is issued by the birth country or current country of residence. A visa is issued by an Embassy/Consulate representing a foreign country.
Why China Issued Stapled Visas?
- Dispute Over Sovereignty:
- China disputes India's sovereignty over Arunachal Pradesh and challenges the legitimacy of the McMahon Line, the boundary between Tibet and British India, agreed upon in the Simla Convention of 1914.
- The disagreement over the Line of Actual Control (LAC) lies at the heart of Chinese claims on the disputed territory and leads to repeated transgressions into Indian territory.
- Unilateral Claim to Indian Territory:
- China claims approximately 90,000 sq km of Arunachal Pradesh as part of its territory, referring to it as "Zangnan" or "South Tibet" in Chinese maps.
- It issues lists of Chinese names for places in Arunachal Pradesh and periodically underlines its unilateral claim to Indian territory.
- Undermining India's Sovereignty:
- Issuing stapled visas to Indian nationals from Arunachal Pradesh and Jammu and Kashmir is part of China's efforts to undermine India's sovereignty over these regions.
- China's actions are seen as attempts to challenge India's control and authority over parts of its own territory.
What are the Impacts and Concerns Regarding Stapled Visas?
- Stapled visas create confusion and uncertainty for travellers, as their validity and acceptance vary.
- India consistently rejects the validity of stapled visas and protests against their issuance.
- These actions by China contribute to diplomatic tensions between the two nations and complicate bilateral relations.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Mains
Q. “China is using its economic relations and positive trade surplus as tools to develop potential military power status in Asia”. In the light of this statement, discuss its impact on India as her neighbour. (2017)
Biodiversity & Environment
Plastic Overshoot Day
For Prelims: Plastic Overshoot, Single-use plastic, Marine pollution, National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management, Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2022, Project REPLAN
For Mains: Issues Associated with Plastic-Waste in India.
Why in News?
Recently, the Earth witnessed Plastic Overshoot Day on July 28, 2023. This marks the point in the year when the amount of plastic waste generated exceeds the global waste management capacity.
- The Plastic Overshoot Day Report by Swiss-based research consultancy Earth Action (EA) sheds light on the alarming issue of plastic pollution and its implications on the environment.
What are the Major Findings of the Report?
- About:
- Plastic Overshoot Day is determined based on a country’s Mismanaged Waste Index (MWI). The gap in waste management capacity and plastic consumption is called MWI.
- Plastic Pollution Crisis: The report highlights that an additional 68,642,999 tonnes of plastic waste will enter nature in 2023, indicating a severe plastic pollution crisis.
- The report identifies 12 countries responsible for 52% of the world's mismanaged plastic waste. India is among them, alongside China, Brazil, Indonesia, Thailand, Russia, Mexico, the United States, Saudi Arabia, the Democratic Republic of Congo, Iran, and Kazakhstan.
- The three countries with the highest mismanaged waste percentages—Mozambique (99.8%), Nigeria (99.44%), and Kenya (98.9%) belong to Africa.
- India ranks fourth in the MWI, with 98.55% of generated waste.
- Short-life Plastics: Short-life plastics, including plastic packaging and single-use plastics, make up approximately 37% of the total plastic used annually. These categories pose a higher risk of leakage into the environment.
- India's Plastic Overshoot: Plastic Overshoot Day for India occurred on January 6, 2023, when the country's plastic waste generation outweighed its waste management capacity.
- India's per-person consumption is 5.3 kg, significantly lower than the global average of 20.9 kg.
What is the Major Significance of Plastic?
- Food Preservation: Plastics are widely used in food packaging, which helps extend the shelf life of perishable goods, reducing food waste and enabling efficient transportation of goods.
- Medical Applications: Plastics play a crucial role in modern medicine. They are used in medical devices, such as syringes, catheters, and artificial joints, which improve patient care and quality of life.
- Safety in Transportation: Plastics are used in automotive applications to make vehicles lighter, which can lead to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions, contributing to a greener environment.
- Insulation: Plastic materials are excellent insulators for electrical and thermal purposes. They help improve energy efficiency in buildings and electronic devices.
- Water Conservation: Certain types of plastics, like those used in pipes and irrigation systems, help conserve water by reducing leakages and improving water distribution efficiency.
What are the Issues Associated with Plastic-Waste in India?
- Poor Waste Management Infrastructure: One of the major problems is the inadequate waste management infrastructure in India.
- The majority of municipal authorities lack proper facilities for segregation, collection, transportation and recycling of plastic waste.
- As a result, a significant portion of plastic waste ends up in landfills, open dumpsites, or even littered in the environment, leading to severe pollution.
- According to the Centre for Science and Environment's report, India recycles 12.3% of its plastic waste and incinerates 20%.
- Single-Use Plastic Products: The widespread use of single-use plastic products, such as bags, bottles, straws, and packaging, exacerbates the plastic waste problem.
- These items are convenient but are discarded after one use, contributing significantly to the accumulation of plastic waste.
- Marine Pollution: India's coastal areas are particularly affected by plastic waste. Rivers and other water bodies act as conduits for plastic waste to reach the oceans, resulting in marine pollution.
- This pollution harms marine life, ecosystem health, and can even have economic impacts on coastal communities reliant on fishing and tourism.
- Health Impacts: Improper plastic waste disposal and the burning of plastic can release harmful chemicals and toxins, leading to adverse health effects for communities living near waste disposal sites or engaged in informal recycling activities.
What are Government Initiatives Related to Plastic Waste Management?
- National Dashboard on Elimination of Single Use Plastic and Plastic Waste Management
- Plastic Waste Management Amendment Rules, 2022
- Project REPLAN
Way Forward
- Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR): India should invest in waste management policies like EPR, which holds producers responsible for the end-of-life disposal of their plastic products and promotes circular economy.
- Waste-to-Energy Plants: There is a need to invest in waste-to-energy plants that use advanced technologies like plasma gasification or anaerobic digestion to convert non-recyclable plastic waste into energy.
- These plants can help reduce the dependence on fossil fuels and generate electricity while managing plastic waste effectively.
- The Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change has indicated that India has the capacity to process 14.2 million tonnes of plastic waste annually, which accounts for 71% of all primary plastic produced.
- Designing Alternatives: Identifying plastic items that can be replaced with non-plastic, recyclable, or biodegradable materials is the first step. Find alternatives to single-use plastics and reusable design goods by working with product designers.
- Promoting the use of Oxo-biodegradable plastics, that are manufactured to be broken down by ultra-violet radiation and heat, more quickly than regular plastics.
- Supporting the UN Treaty to End Plastic Pollution: India's role in addressing plastic pollution is crucial.
- The country was among the first to propose a global ban on single-use plastics in 2019.
- The UN Treaty to End Plastic Pollution represents an opportunity for global action against plastic pollution and should be promoted.
UPSC Civil Services Exam, Previous Year Questions (PYQ)
Q. Why is there a great concern about the ‘microbeads’ that are released into environment? (2019)
(a) They are considered harmful to marine ecosystems.
(b) They are considered to cause skin cancer in children.
(c) They are small enough to be absorbed by crop plants in irrigated fields.
(d) They are often found to be used as food adulterants.
Ans: (a)
Governance
Inclusion of Communities in Jammu and Kashmir's Scheduled Tribes List
For Prelims: Registrar General of India,National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, Scheduled Castes and the Scheduled Tribes (Prevention of Atrocities) Act, 1989., Provisions of the Panchayats (Extension to the Scheduled Areas) Act, 1996., Scheduled Tribes and Other Traditional Forest Dwellers (Recognition of Forest Rights) Act, 2006, Eklavya Model Residential School (EMRS), Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojna (PMAAGY)
For Mains: Process and Criteria of Inclusion in the ST List, Status of Scheduled Tribes in India
Why in News?
The Indian government has introduced the Constitution (Jammu and Kashmir) Scheduled Tribes Order (Amendment) Bill, 2023, aiming to include four communities in the Scheduled Tribes (ST) list in Jammu and Kashmir.
- The proposed inclusion of the "Gadda Brahmin," "Koli," "Paddari Tribe," and "Pahari Ethnic Group" has sparked apprehensions regarding the distribution of reservation benefits.
What is the Process and Criteria of Inclusion in the ST List ?
- Criteria for Inclusion in the Scheduled List: Determining whether a community qualifies as a Scheduled Tribe is based on several criteria, including:
- Ethnological Traits: The community's distinct and identifiable ethnological traits are considered to establish its tribal identity.
- Traditional Characteristics: Traditional practices, customs, and way of life are examined to assess the community's adherence to tribal culture.
- Distinctive Culture: The presence of a unique and distinctive culture that sets the community apart from other groups.
- Geographical Isolation: The community's geographical isolation is taken into account to assess its historic and continuous presence in specific regions.
- Backwardness: Socio-economic backwardness is considered to evaluate the level of disadvantage faced by the community.
- However, The Constitution of India does not define the criteria for recognition of STs.
- Process of Adding a Community to the ST List:
- The process initiates at the State or Union Territory level, where the concerned government or administration recommends the inclusion of a specific community.
- The proposal is sent to the Union Ministry of Tribal Affairs for examination and further deliberations.
- After this, the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, through its own deliberations, examines the proposal, and sends it to the Registrar General of India (RGI).
- Once approved by the RGI, the proposal is sent to the National Commission for Scheduled Tribes, following which the proposal is sent back to the Union government.
- The inclusion of any community in the Scheduled Tribes list takes effect only after the President assents to a Bill that amends the Constitution (Scheduled Tribes) Order, 1950, following its passage in both the Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha.
What is the Status of Scheduled Tribes in India?
- Constitutional; Provisions:
- Article 366(25): It only provides a process to define STs: “STs means such tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to be Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this Constitution.”
- Article 342(1): The President with respect to any State/UT (after consultation with the Governor in case of state) may specify the tribes/tribal communities/part of or groups within tribes/ tribal communities as a Scheduled Tribe in that State/UT.
- Fifth Schedule: It lays out provisions for the Administration and Control of Scheduled Areas and STs in states other than 6th Schedule States.
- Sixth Schedule: Deals with the administration of the tribal areas in Assam, Meghalaya, Tripura and Mizoram.
- Article 366(25): It only provides a process to define STs: “STs means such tribes or tribal communities or parts of or groups within such tribes or tribal communities as are deemed under Article 342 to be Scheduled Tribes for the purposes of this Constitution.”
- Current Number of Officially Recognized Scheduled Tribes:
- As per Census 2011, there are 705 ethnic groups officially listed as Scheduled Tribes under Article 342.
- The STs constitute 8.6% of the total population and 11.3% of the rural population.
- Related Legal Provisions:
- Related Government Initiatives:
- Eklavya Model Residential School (EMRS)
- Pradhan Mantri Adi Adarsh Gram Yojna (PMAAGY)
- Pradhan Mantri Jan Jatiya Vikas Mission (PMJVM)
- Development of Particularly Vulnerable Tribal Groups (PVTGs)
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. Consider the following pairs: (2013)
| Tribe | State |
| 1. Limboo (Limbu) | Sikkim |
| 2. Karbi | Himachal Pradesh |
| 3. Dongaria Kondh | Odisha |
| 4. Bonda | Tamil Nadu |
Which of the above pairs are correctly matched?
(a) 1 and 3 only
(b) 2 and 4 only
(c) 1, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (a)
Q. The provisions in Fifth Schedule and Sixth Schedule in the Constitution of India are made in order to (2015)
(a) protect the interests of Scheduled Tribes
(b) determine the boundaries between States
(c) determine the powers, authority and responsibilities of Panchayats
(d) protect the interests of all the border States
Ans: (a)
Mains:
Q. What are the two major legal initiatives by the State since Independence addressing discrimination against Scheduled Tribes (STs)? (2017)
Q. Why are the tribals in India referred to as ‘the Scheduled Tribes’? Indicate the major provisions enshrined in the Constitution of India for their upliftment. (2016)
Geography
Monsoon, El Nino And Their Impact on Agriculture
For Mains: Impact of Monsoon and El Nino on Indian Agriculture
Why in News?
The 2023 southwest monsoon season in India started late, with the initial two weeks experiencing a significant rainfall deficiency of 52.6% below the normal long-period average(LPA).
- However, as of July 30, 2023 there was an overall 6% surplus rainfall. This turnaround has positively impacted kharif crop plantings. However, concerns persist regarding the potential impact of the approaching El Nino phenomenon on rabi crops.
What is the Long-Period Average (LPA) of Rainfall?
- The IMD defines the "LPA of rainfall" as the average rainfall recorded over a specific region for a long period, like 30 or 50 years. Based on this, the IMD classifies rainfall into five categories on an all-India scale:
- Normal or near normal: Rainfall between 96-104% of LPA.
- Below normal: Rainfall between 90-96% of LPA.
- Above normal: Rainfall between 104-110% of LPA.
- Deficient: Rainfall less than 90% of LPA.
- Excess: Rainfall more than 110% of LPA.
What are Kharif and Rabi Crops?
- Kharif crops:
- Kharif crops are sown during the monsoon season, from June to October, and harvested in the late summer or early autumn.
- They depend on the southwest monsoon for irrigation and growth.
- Major Kharif crops include rice, maize, sorghum, pearl millet (bajra), finger millet (ragi), groundnut and pulses like pigeon pea (arhar) and green gram (moong).
- They account for about 55% of the total foodgrain production in India.
- Rabi Crops:
- These crops are sown around the Retreating Monsoon and Northeast monsoon season, which begins in October and are called rabi or winter crops.
- The harvest for these crops happens typically during April and May, during the summer season.
- Major Rabi crops are wheat, gram, peas, barley etc.
- A warm climate is required for seed germination and cold climate for the growth of crops.
What is the Impact of Monsoon on Indian Agriculture?
- Positive Impacts:
- Increased Crop Production: A major portion of the country's crop area is completely dependent on Monsoon rains as they're not equipped with methods of manual irrigation.
- Adequate rainfall during the monsoon season leads to increased soil moisture and promotes the growth of crops, resulting in higher agricultural output.
- The availability of water supports the cultivation of a variety of crops, including rice, wheat, millets, and pulses.
- Economic Boost: Successful monsoon seasons contribute to rural prosperity by providing income to farmers and laborers, which, in turn, stimulates demand for goods and services in the rural economy.
- This increased economic activity has a positive impact on overall national growth.
- Recharge of Groundwater: The monsoon helps recharge groundwater resources, which is crucial for sustainable agricultural practices in regions where water scarcity is a challenge.
- Increased Crop Production: A major portion of the country's crop area is completely dependent on Monsoon rains as they're not equipped with methods of manual irrigation.
- Negative Impacts:
- Erratic Monsoon Patterns: The monsoon's timing, intensity, and distribution are unpredictable, leading to uncertainties in agricultural planning and crop management.
- Delayed or early monsoons can disrupt planting schedules and affect crop yields.
- Droughts and Floods: Monsoon failure or excess rainfall can lead to droughts or floods, respectively.
- Both scenarios can be disastrous for agriculture. Droughts result in water shortages, crop failures, and reduced yields, while floods can damage crops, wash away fertile topsoil, and lead to livestock losses.
- Crop Losses: Prolonged and excessive monsoon rains can cause crop diseases, reducing crop quality and yield. These conditions also hinder farmers' ability to conduct agricultural operations effectively.
- Soil Erosion: Heavy rainfall can lead to soil erosion, which depletes soil fertility and affects agricultural productivity in the long run.
- Soil erosion also impacts water bodies and can lead to siltation in reservoirs, reducing their storage capacity.
- Food Price Inflation: Inconsistent monsoon patterns can affect crop production and lead to shortages, resulting in food price inflation.
- This can have adverse effects on the economy, especially for low-income households that spend a significant portion of their income on food.
- Erratic Monsoon Patterns: The monsoon's timing, intensity, and distribution are unpredictable, leading to uncertainties in agricultural planning and crop management.
What is El Nino and Its Implications on Agriculture?
- About:
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
- It can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world, including India.
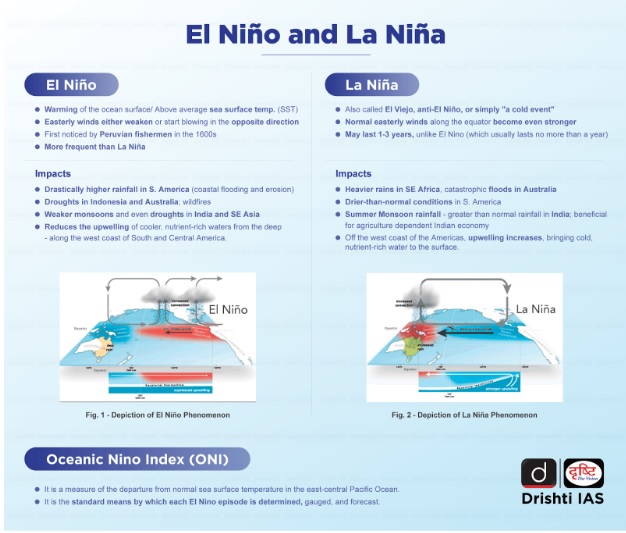
- The Oceanic Nino Index (ONI) reached 0.8 degrees Celsius in June, 2023 surpassing the El Nino threshold of 0.5 degrees.
- Global weather agencies forecast El Nino to persist and strengthen through the 2023-24 winter.
- It can have significant impacts on weather patterns around the world, including India.
- El Nino is a climate phenomenon that occurs irregularly in the tropical Pacific Ocean, characterized by the warming of sea surface temperatures.
- Impacts:
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
- Elevated temperatures can adversely impact crops, leading to heat stress and reduced yields, especially for sensitive crops like fruits and vegetables.
- Pest and Disease Outbreaks: El Nino conditions can create a conducive environment for certain pests and diseases that affect crops.
- Warmer temperatures and altered precipitation patterns can lead to increased pest populations, posing additional challenges to farmers.
- Impact on Livestock: Reduced availability of fodder and water scarcity during El Nino can affect livestock and animal husbandry, leading to lower milk and meat production.
- Temperature Extremes: El Nino is often associated with higher temperatures in some parts of India.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. With reference to ‘Indian Ocean Dipole (IOD)’ sometimes mentioned in the news while forecasting Indian monsoon, which of the following statements is/are correct? (2017)
- IOD phenomenon is characterised by a difference in sea surface temperature between tropical Western Indian Ocean and tropical Eastern Pacific Ocean.
- An IOD phenomenon can influence an El Nino’s impact on the monsoon.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (b)
Mains:
Q. How far do you agree that the behaviour of the Indian monsoon has been changing due to humanizing landscape? Discuss.(2015)
Q. Most of the unusual climatic happenings are explained as an outcome of the El-Nino effect. Do you agree? (2014)
Governance
Schemes For Farmers’ Welfare
For Prelims: Schemes for Farmers’ Welfare, Central Sector Scheme, Centrally Sponsored Scheme.
For Mains: Schemes For Farmers’ Welfare.
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers Welfare has informed Lok Sabha that a comprehensive range of Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes have been implemented for Farmers Welfare.
What are the Central Sector and Centrally Sponsored Schemes?
- Central Sector Scheme:
- Central sector schemes are based on subjects from the union list, and they are formulated by the centre.
- These schemes are designed, planned and comprletely funded by the central government.
- Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, Pradhan Mantri ujjwala Yojana, Khelo India Scheme are some examples of the Central sector schemes.
- Centrally Sponsored Scheme:
- Centrally Sponsored Schemes (CSS) are schemes that are funded partially by both the Central and State Governments.
- It is basically a channel which the central government uses to help the states run their plans financially.
- In these schemes, a certain percentage of the funding is provided by the states, although most of it rests with the centre.
- The amount of state participation varies from state to state.
- Their implementation rests on the Union territories and the States.
What are the Key Government Schemes For Farmers Welfare?
- The Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN):
- The PM-KISAN Scheme aims to provide income support to all landholding Farmers’ families across the country to enable them to take care of expenses related to agriculture and allied activities as well as domestic needs.
- The Scheme provides a payment of Rs.6000/- per year for the farmers’ families with cultivable land holding, subject to certain exclusions.
- Farmer Producer Organizations (FPOs):
- The Government launched the Central Sector Scheme (CSS) for “Formation and Promotion of 10,000 FPOs” in the year 2020.
- Formation & promotion of FPOs are to be done through Implementing Agencies (IAs), which further engage Cluster Based Business Organizations (CBBOs) to form & provide professional handholding support to FPOs for a period of 05 years including preparation and execution of business plan for the concerned FPOs.
- Agriculture Infrastructure Fund (AIF):
- Rs 1 lakh crore Agri Infra Fund was launched in July 2020 under Aatmanirbhar Bharat Abhiyan.
- The AIF is a medium - long term debt financing facility for investment in viable projects for post-harvest management infrastructure and community farming assets through interest subvention and credit guarantee support.
- National Mission on Edible Oil-Oil Palm (NMEO-OP):
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Scheme, launched in 2021 to promote oil palm cultivation for making India Atma Nirbhar in edible oils with special focus on North-Eastern States and A&N Islands.
- The Mission will bring an additional area of 6.5 lakh ha under Oil Palm plantation with 3.28 lakh ha in north-eastern states and 3.22 lakh ha in the rest of India in next 5 years from 2021-22 to 2025-26.
- National Beekeeping & Honey Mission (NBHM):
- It is a Central Sector Scheme, launched in 2020 under AtmaNirbhar Bharat Abhiyan for its implementation in the field for overall promotion and development of scientific beekeeping & to achieve the goal of Sweet Revolution.
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q1. Under the Kisan Credit Card scheme, short-term credit support is given to farmers for which of the following purposes? (2020)
- Working capital for maintenance of farm assets
- Purchase of combine harvesters, tractors and mini trucks
- Consumption requirements of farm households
- Post-harvest expenses
- Construction of family house and setting up of village cold storage facility
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a) 1, 2 and 5 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3, 4 and 5 only
(d) 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5
Ans: (b)
Q2. Consider the following statements: (2017)
- The nation-wide ‘Soil Health Card Scheme’ aims at expanding the cultivable area under irrigation.
- Enabling the banks to assess the quantum of loans to be granted to farmers on the basis of soil quality.
- Checking the overuse of fertilizers in farmlands.
Which of the above statements is/are correct?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 3 only
(c) 2 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (b)
Mains
Q. How is science interwoven deeply with our lives? What are the striking changes in agriculture triggered off by science-based technologies? (2020)
Q. Given the vulnerability of Indian agriculture to vagaries of nature, discuss the need for crop insurance and bring out the salient features of the Pradhan Mantri Fasal Bima Yojana (PMFBY). (2016)
Important Facts For Prelims
Cell-Free DNA
Why in News?
A notable advancement in medical science has emerged in recent years through the discovery of cell-free Deoxyribonucleic Acid (cfDNA), carrying significant implications for disease detection, diagnosis, and treatment.
- cfDNA stands poised to reshape the entire landscape of medical science.
What is Cell-Free DNA (cfDNA)?
- About:
- cfDNA refers to fragments of DNA that exist outside of cells, specifically in various body fluids. Unlike the majority of DNA which is enclosed within cells.
- Scientists have been aware of cfDNA since 1948, but only in the last two decades have they figured out what to do with it.
- cfDNA is released into the extracellular environment under different circumstances, including cell death or other cellular processes.
- These cfDNA fragments contain genetic information and can offer insights into a person's health status, potential diseases, and genetic variations.
- Applications:
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT):
- Cell-free DNA serves as a valuable tool for screening chromosomal abnormalities in developing foetuses, such as Down syndrome.
- NIPT replaces invasive procedures such as amniocentesis, minimizing risks for both expectant mothers and foetuses.
- Analysis of cfDNA in maternal blood provides crucial information about the foetus's genetic health.
- Early Cancer Detection:
- Identifying cancers at their initial stages for prompt treatment.
- The 'GEMINI' test utilizes cfDNA sequencing to detect lung cancer with high accuracy.
- Combining cfDNA analysis with existing methods enhances overall cancer detection.
- Monitoring Organ Transplants:
- Donor-derived cfDNA offers a promising approach to monitor the health and acceptance of transplanted organs.
- Fluctuations in cfDNA levels can indicate organ rejection or acceptance before other markers become evident.
- Early detection of rejection allows for timely intervention and improved outcomes in organ transplantation.
- Neurological Disorder Biomarkers:
- Investigating cfDNA's potential as a biomarker for neurological disorders.
- Aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of conditions like Alzheimer's disease, neuronal tumours, and stroke.
- Metabolic Disorder Insights:
- Exploring cfDNA's role as a biomarker for metabolic disorders.
- Detection and management of conditions such as type-2 diabetes and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
- Advancing Disease Research:
- Researchers use cfDNA analysis to study disease mechanisms, monitor treatment effectiveness, and gain insights into disease pathways.
- The versatility of cfDNA applications contributes to a deeper understanding of complex diseases and their underlying genetic factors.
- Non-Invasive Prenatal Testing (NIPT):
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
PrelimsQ. With reference to the recent developments in science, which one of the following statements is not correct? (2019)
(a) Functional chromosomes can be created by joining segments of DNA taken from cells of different species.
(b) Pieces of artificial functional DNA can be created in laboratories.
(c) A piece of DNA taken out from an animal cell can be made to replicate outside a living cell in a laboratory.
(d) Cells taken out from plasma and animals can be made to undergo cell division in laboratory petri dishes.
Ans: (a)
- In 2017, US researchers were successful in developing new semi-synthetic strain of E. coli bacteria that is a living organism that incorporates both natural and artificial DNA and is capable of creating entirely new, synthetic proteins
- A wide variety of double stranded DNA templates are replicated extensively in an in-vitro DNA replication system containing purified proteins.
- Through micro propagation, plants can be developed in the laboratory, for instance, chlamydomnas cells can be replicated in culture through light variations. Therefore, option (a) is the correct answer.
Q. With reference to agriculture in India, how can the technique of ‘genome sequencing’, often seen in the news, be used in the immediate future? (2017)
- Genome sequencing can be used to identify genetic markers for disease resistance and drought tolerance in various crop plants.
- This technique helps in reducing the time required to develop new varieties of crop plants.
- It can be used to decipher the host-pathogen relationships in crops.
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
(a)1only
(b)2and3only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (d)
- Chinese scientists decoded rice genome in 2002. The Indian Agricultural Research Institute (IARI) scientists used the genome sequencing to develop better varieties of rice such as Pusa Basmati-1 and Pusa Basmati-1121, which currently makes up substantially in India’s rice export.
- In genome sequencing it takes less time. The genome sequencing enables the study of the entire DNA sequence of a crop, thus it aids in understanding of pathogens’ survival or breeding zone.
Important Facts For Prelims
Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023
Why in News?
The Lok Sabha has recently approved the Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023, which introduces a significant shift towards digital birth certificates.
- These certificates are poised to serve as a comprehensive document for a multitude of purposes, ranging from educational admissions to government applications.
What is the Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023?
- About:
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023 seeks to amend the Registration of Births and Deaths Act,1969.
- The Registration of Births and Deaths Act, 1969 provides for the regulation and registration of births and deaths. The registration of births and deaths falls under the Concurrent List, giving powers to both Parliament and state legislatures to make laws on the subject.
- The Registration of Births and Deaths (Amendment) Bill, 2023 seeks to amend the Registration of Births and Deaths Act,1969.
- Key Features:
- Digital Birth Certificates: The bill introduces the concept of digital birth certificates, intended to serve as a comprehensive document for multiple purposes, reducing the need for multiple documents to prove birth details.
- Aadhaar Details: The Bill proposes linking Aadhaar details of parents and informants to birth certificates.
- Expands the scope of Aadhaar inclusion to various reporting authorities, including medical officers, jailors, and managers of institutions.
- Centralized Database: A centralized database will be established to manage birth and death records, facilitating efficient service delivery and maintaining accurate and up-to-date information.
- Apart from birth certificates, the centralized database will also update the National Population Register (NPR), ration cards, and property registrations.
- The Bill proposes to make it obligatory for States to register births and deaths on the Centre’s Civil Registration System (CRS) portal, and to share the data with the Registrar General of India which functions under the Union Home Ministry.
- Benefits:
- The centralized database is expected to enhance administrative efficiency by providing a reliable and unified source of information.
- Citizens will experience streamlined access to various services such as educational admissions, government jobs, passports, and more, using a single digital birth certificate.
- The bill aligns with India's digital transformation efforts, reflecting a commitment to modernize administrative processes for improved citizen services.
- Concerns:
- The Bill's provisions may potentially conflict with constitutional rights, such as the right to education and the right to privacy.
- Denying admission to schools based on the absence of birth certificates could infringe upon the fundamental right to education.
- The bill has sparked a debate about striking a balance between leveraging technology for administrative efficiency and safeguarding citizen’s right to privacy.
- The bill has faced opposition on grounds of transparency, with critics questioning the government's approach to data collection and usage.
- Critics also argue that digital birth certificates may inadvertently exclude individuals who lack access to digital platforms, creating potential disparities in accessing services.
- The Bill's requirements may not align with provisions of the Juvenile Justice Act, 2015, and other relevant legislations.
- The Bill's provisions may potentially conflict with constitutional rights, such as the right to education and the right to privacy.
Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
Relief for Displaced School Children Amid Manipur Ethnic Violence
The ethnic violence in Manipur has led to the displacement of over 14,000 school children, prompting swift measures by the Ministry of Education to ensure their continued education.
- The ethnic clashes in Manipur were ignited by a 'Tribal Solidarity March' on May 3, 2023, organized as a response to the demand for Scheduled Tribe (ST) status by the Meitei community.
- The Meitei people are also known as Manipuri people.
- Their primary language is the Meitei language, which is also called Manipuri and is the only official language of Manipur.
- They are predominantly settled in the Imphal Valley, although a significant number reside in other Indian states, such as Assam, Tripura, Nagaland, Meghalaya, and Mizoram.
- The Meitei people are divided into clans, and members of the same clan do not intermarry.
Read more: Demand of Meities for ST Status
PM-YASASVI SCHEME
Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment is implementing an umbrella scheme namely PM Young Achievers Scholarship Award Scheme for Vibrant India (PM –YASASVI) for students in the Other Backward Class (OBC), SC, Denotified, Nomadic and semi-Nomadic Tribe (DNT) and Economically Backward Caste (EBC) categories.
- The key components of the scheme include
- Pre-Matric Scholarship for OBC, EBC and DNT Students.
- Post-Matric Scholarship for OBC, EBC and DNT Students.
- Top Class School Education for OBC, EBC and DNT Students.
- Top Class College Education for OBC, EBC and DNT Students.
- Construction of Hostel for OBC Boys and Girls.
Read more: Scholarship Schemes in India
Rising Psychiatric Cases in CAPFs
The Ministry of Home Affairs recently reported a concerning increase in psychiatric patients within the Central Armed Police Forces (CAPFs). The number of cases surged from 3,584 in 2020 to 4,940 in 2022, marking a nearly 38% rise in reported psychiatric conditions.
- Psychiatric cases refer to individuals who are experiencing mental health disorders or conditions that require diagnosis, treatment, and care from mental health professionals.
- These cases encompass a wide range of mental health issues, including but not limited to:
- Depression: Persistent feelings of sadness, hopelessness, and loss of interest in activities.
- Bipolar Disorder: Cycles of extreme mood swings, including manic and depressive episodes.
- Schizophrenia: A severe mental disorder characterized by hallucinations, delusions, and disorganized thinking.
- These cases encompass a wide range of mental health issues, including but not limited to:
- Also, the rising number of personnel opting for voluntary retirement in the post-pandemic period remains a concern. In 2022, a record 11,211 personnel took voluntary retirement, signaling possible dissatisfaction and burnout among the workforce.
Read more: Central Armed Police Forces, Issues Related to Mental Health
Aadi Perukku 2023
Aadi Perukku, also known as Pathinettam Perukku, is a significant festival celebrated in Tamil Nadu to express gratitude for the monsoon season and the life-sustaining properties of water.
- Falling on the 18th day of the Aadi month in the Tamil Calendar, this festival marks the onset of the monsoon season, which brings increased water levels to the rivers and benefits sowing and vegetation.
- During Aadi Perukku, people gather near the banks of rivers, especially the Kaveri River, to perform rituals and offer prayers
Read more: Major Festivals of Different States




