Indian Polity
Judicial Majoritarianism
Prelims: Judicial Majoritarianism, Supreme Court, Demonetization, Article 145(5), Article 145(3).
Mains: Judicial Majoritarianism, related Concerns and Solution.
Why in News?
Many people have raised concerns over Judicial Majoritarianism on the Judgement of the Supreme Court on demonetization and the minority judgment has been hailed for its challenge to the RBI’s (Reserve bank of India) institutional acquiescence to the Central government.
What is Judicial Majoritarianism?
- Numerical majorities are of particular importance to cases which involve a substantial interpretation of constitutional provisions.
- The requirement for a majority consensus flows from Article 145(5) of the Constitution which states that no judgment in such cases can be delivered except with the concurrence of a majority. It also provides for judges to freely deliver dissenting judgments or opinions.
- In important cases, Constitutional Benches, consisting of five or more judges, are set up in consonance with Article 145(3) of the Constitution. Such Benches usually consist of five, seven, nine, 11 or even 13 judges.
What are the Concerns?
- Denial of Merit:
- A meritorious minority decision, irrespective of the impeccability of its reasoning, receives little weightage in terms of its outcomes.
- An example is the dissenting opinion of Justice Subba Rao in the Kharak Singh v. State of U.P. (1962) case upholding the Right To Privacy which received the judicial stamp of approval in the K.S. Puttaswamy v. UOI (2017) case.
- The dissenting opinion of Justice H.R. Khanna in A.D.M. Jabalpur v. Shivkant Shukla (1976) upholding the right to life and personal liberty even during situations of constitutional exceptionalism is a prime example.
- It is argued that the weightage given to numerical majorities in judicial decisions by our Constitutional Courts is opposed to the merits in their reasoning.
- A meritorious minority decision, irrespective of the impeccability of its reasoning, receives little weightage in terms of its outcomes.
- Obscure Situations:
- All judges on a particular Bench give their rulings on the same set of facts, laws, arguments and written submissions. In light of the same, any differences in judicial decisions can be attributed to a difference in either the methodology adopted and the logic applied by the judges in their interpretation.
- In such circumstances, it is entirely possible that the majority may fall into either methodological fallacies and errors or be limited by their ‘judicial hunch’ respectively.
- Question on Head Counting Procedure:
- A study also found that the rate of dissent where the Chief Justice was a part of the Bench was lower than in those cases where the Chief Justice was not on the Bench.
- Such situations call into question the efficiency and desirability of head-counting procedures for a judicial determination on questions of national and constitutional importance.
What can be the Solution?
- A system can be devised, which either gives more weightage to the vote of senior judges given that they have more experience or to the junior judges as they may represent popular opinion better. Such alternatives, however, can only be explored once we identify and question the premises and rationales which underlie head-counting in judicial decision-making.
- The absence of a critical discourse on judicial majoritarianism represents one of the most fundamental gaps in our existing knowledge regarding the functioning of our Supreme Court.
- As pending Constitutional Bench matters are listed for hearing and judgments are reserved, we must reflect upon the arguments of judicial majoritarianism on the basis of which these cases are to be decided.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. We adopted parliamentary democracy based on the British model, but how does our model differ from that model? (2021)
- As regards legislation, the British Parliament is supreme or sovereign but in India, the power of the Parliament to legislate is limited.
- In India, matters related to the constitutionality of Amendment of an Act of the Parliament are referred to the Constitution Bench by the Supreme Court.
Select the correct answer using the code given below.
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 only
(c) Both 1 and 2
(d) Neither 1 nor 2
Ans: (c)


Agriculture
Urban Farming
Prelims: Urban Farming, Healthy Food, Environmental Sustainability, Economic Development, Biotechnology, Scientific Innovations & Discoveries.
Mains: Urban Farming, related Challenges and its Potential.
Why in News?
Recently, a Non-Profit Research Organisation has prepared a “Draft Citizen’s Policy for Urban Agriculture in Delhi”, recommending a holistic framework for Urban Farming.
- The Draft recommends building on existing practices, promoting residential and community farming through rooftop and kitchen gardens, allocating vacant land for agricultural use, creating a market, developing policies for animal rearing and spreading awareness.
What is Urban Farming?
- About:
- Urban farming refers to the practice of growing crops, raising livestock, or producing other forms of food within urban areas.
- Despite its potential benefits, such as increased access to fresh and healthy food, environmental sustainability, and economic development, urban farming faces several challenges that limit its widespread adoption and impact.
- Challenges:
- Limited Land Availability:
- One of the biggest challenges facing urban farming is the limited availability of suitable land within urban areas.
- Urban land is often expensive and highly coveted for other uses, making it difficult for farmers to secure the space they need to grow food.
- Soil Contamination:
- Urban soils are often contaminated with heavy metals, pollutants, and other toxic substances, making it difficult to grow crops in a safe and sustainable manner.
- Water Availability:
- In many urban areas, water is a scarce resource, and farmers often struggle to access enough water to meet the needs of their crops and livestock.
- Lack of Infrastructure:
- Urban farming often requires specialized infrastructure, such as greenhouses, irrigation systems, and cooling and storage facilities, which can be expensive and difficult to access in urban areas.
- Limited Land Availability:
How can the Related Challenges be Addressed?
- Developing Partnerships:
- Urban farming can benefit from partnerships with local governments and other organizations that can provide support and resources to help overcome some of the challenges.
- Investment:
- Further research into urban agriculture can help to address some of the key challenges and provide new insights into the best practices for growing food in urban areas.
- Encouraging Community Engagement:
- Community engagement is critical for the success of urban farming, as it can help to build support, bring together resources, and promote sustainability.
- Urban Agriculture Policies:
- Governments and other organizations can play a role in promoting urban agriculture by enacting policies that support the growth and development of urban farming initiatives.
What are Some Related Initiatives in India?
- In 2008, Pune’s civic administration launched a city farming project to train and encourage people to take up farming on allocated land.
- In 2012 Teh Kerala government launched a vegetable development programme to encourage gardening in houses, schools, government and private institutions.
- It also offered subsidies and support for eco-friendly inputs, irrigation, compost and biogas plants.
- In 2014, the Tamil Nadu government introduced a “do-it-yourself” kit for city dwellers to grow vegetables on rooftops, houses and apartment buildings under its Urban Horticulture Development Scheme.
- Since 2021, Bihar has encouraged terrace gardening in five smart cities through subsidy for input cost.
Way Forward
- To promote urban farming, governments must recognise informal practices and link them with agricultural schemes.
- There is a need to make urban agriculture viable. Farming in cramped urban spaces marred by water scarcity and pollution is not easy.
- A 2016 paper titled Future of Urban Agriculture in India by the Hyderabad-based Institute for Resource Analysis and Policy mentions that in Delhi, Hyderabad, Ahmedabad and Chennai, wastewater is directly or indirectly used for urban farming.
- Studies show that excessive use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides in urban farms can lower produce and soil quality. However, urban farmers believe such hurdles can be overcome with innovative techniques.
- Urban farming has the potential to play a major role in addressing some of the biggest challenges facing cities today, including food insecurity, environmental sustainability, and economic development. However, to truly realize its potential, it is essential to overcome the challenges and create an environment that supports and nurtures urban farming initiatives.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. How far is Integrated Farming System (IFS) helpful in sustaining agricultural production? (2019)
Q. What is Integrated Farming System? How is it helpful to small and marginal farmers in India? (2022)


Science & Technology
Space Debris
For Prelims: Space debris, Kessler Syndrome, Project NETRA, European Space Agency (ESA), Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), Peaceful Uses of Outer Space.
For Mains: Potential Hazard related to Space Debris, Initiatives to Curb Space Debris.
Why in News?
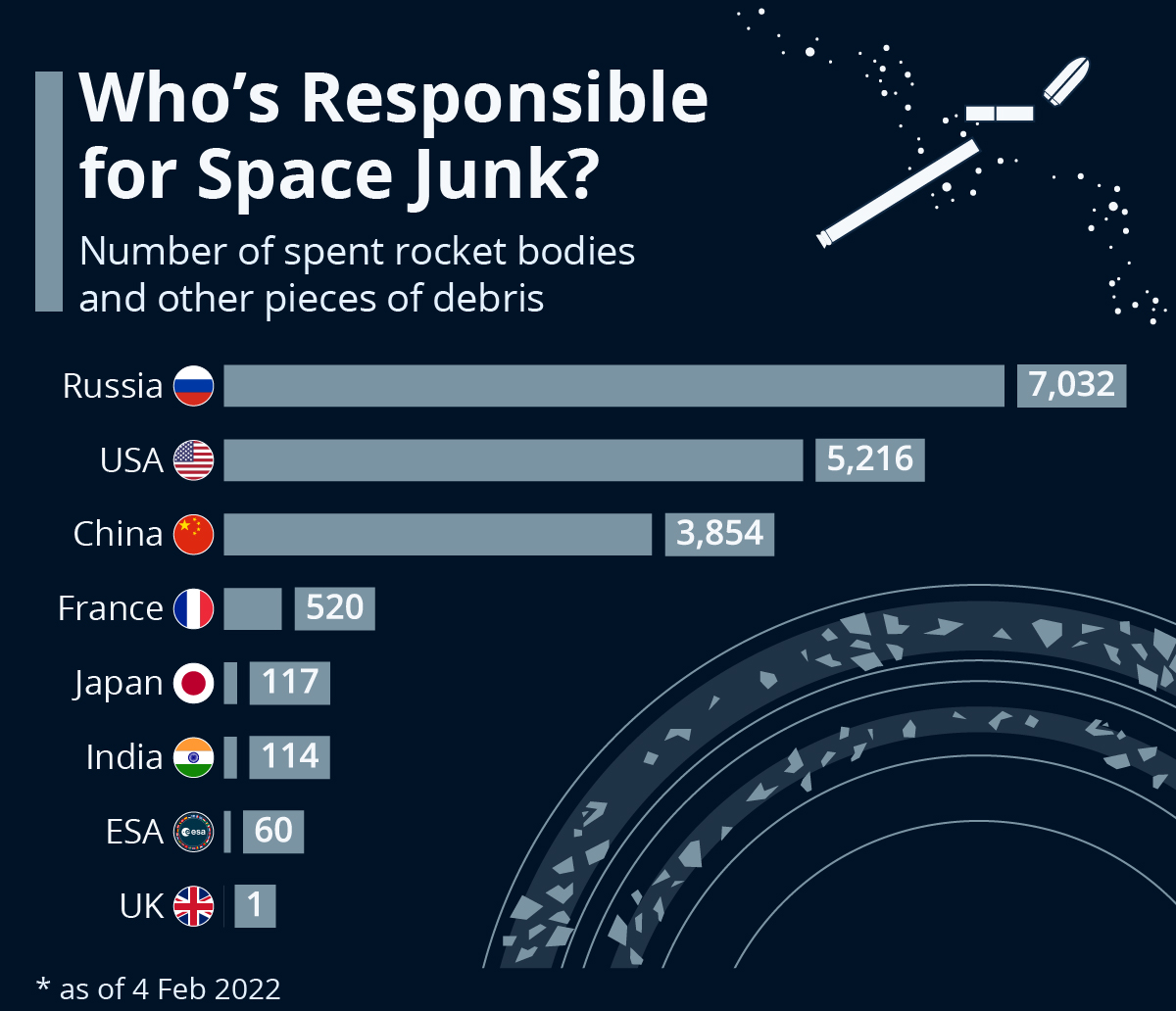
Recently, the Government of India has announced that 111 payloads and 105 space debris have been identified as Indian objects orbiting Earth.
- All orbiting debris will affect the future of outer space and future missions. Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has also been carrying out several studies on the impact of growing space debris on the space environment.
What is Space Debris?
- About:
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth's orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- This includes defunct satellites, spent rocket stages, and fragments of debris from collisions or other events.
- Space debris refers to man-made objects in Earth's orbit that no longer serve a useful purpose.
- Potential Hazard:
- Threat for Operational Satellites:
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- This overpopulation of space with objects and debris is referred to as Kessler Syndrome.
- The floating space debris is a potential hazard for operational satellites and colliding with them can leave the satellites dysfunctional.
- Reduction of Orbital Slots:
- The accumulation of space debris in specific orbital regions can limit the availability of desirable orbital slots for future missions.
- Space Situational Awareness:
- The increasing amount of space debris makes it more challenging for satellite operators and space agencies to accurately track and predict the orbits of objects in space.
- Threat for Operational Satellites:
- Initiatives to Curb Space Debris:
- India:
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- ISRO also carried out 21 collision avoidance manoeuvres of Indian operational space assets in 2022 to avoid collisions with other space objects.
- ISRO has also set up a Centre for Space Debris Research to monitor and mitigate the threat of space debris.
- ‘Project NETRA’ is also an early warning system in space to detect debris and other hazards to Indian satellites.
- In 2022, ISRO set up the System for Safe and Sustainable Operations Management (IS 4 OM) to continually monitor objects posing collision threats, predict the evolution of space debris, and mitigate the risk posed by space debris.
- Global:
- The Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee (IADC), an international governmental forum, was established in 1993 to coordinate efforts between spacefaring nations to address the issue of space debris.
- The United Nations has established the Committee on the Peaceful Uses of Outer Space (COPUOS) to develop guidelines for the long-term sustainability of outer space activities, including the mitigation of space debris.
- The European Space Agency (ESA) has launched the Clean Space initiative, aimed at reducing the amount of space debris and promoting sustainable space activities.
- India:
Way Forward
- Improved Tracking and Monitoring: Improving the ability to track and monitor space debris can help mitigate the risks it poses to operational satellites and human space missions.
- Reusable Launch Vehicles: Using reusable launch vehicles instead of single-use rockets can help reduce the number of new debris generated from launches.
- Materials and Design improvements: Using more durable materials and designing satellites for eventual de-orbiting can reduce the number of debris generated in the long term.
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q.1 In the context of space technology, what is “Bhuvan”, recently in the news? (2010)
(a) A mini satellite launched by ISRO for promoting the distance education in India
(b) The name given to the next Moon Impact Probe, for Chandrayaan-II
(c) A geoportal of ISRO with 3D imaging capabilities of India
(d) A space telescope developed by India
Ans: (c)
Mains
Q.1 What is India’s plan to have its own space station and how will it benefit our space programme? (2019)
Q.2 Discuss India’s achievements in the field of Space Science and Technology. How the application of this technology helped India in its socio-economic development? (2016)


Governance
New Tax Regime
For Prelims: Union Budget 2023-24
For Mains: Main Points Associated with the Budget 2023-24, Changes in the Tax Regime, Finance Bill, 2023.
Why in News?
Recently, during the Union Budget 2023-24 speech, Union Finance Minister announced a change in income tax slabs and rebate limits under the new income tax regime.
- According to the proposed 2023 Finance Bill, startups that offer their shares to foreign investors may be subject to paying the "angel tax," which was previously only applicable to investments raised by Indian residents.
What are the Proposed Changes?
- Tax Rebate Limit Raised:
- The enhancement of this limit to ₹7 lakhs from ₹ 5 lakhs indicates that the person whose income is less than ₹7 lakhs need not invest anything to claim exemptions and the entire income would be tax-free irrespective of the quantum of investment made by such an individual.
- This will result in giving more consumption power to the middle-class income group as they could spend the entire amount of income without bothering too much about investment schemes to take the benefit of exemptions.
- The enhancement of this limit to ₹7 lakhs from ₹ 5 lakhs indicates that the person whose income is less than ₹7 lakhs need not invest anything to claim exemptions and the entire income would be tax-free irrespective of the quantum of investment made by such an individual.
- Changes in Income Tax slabs:
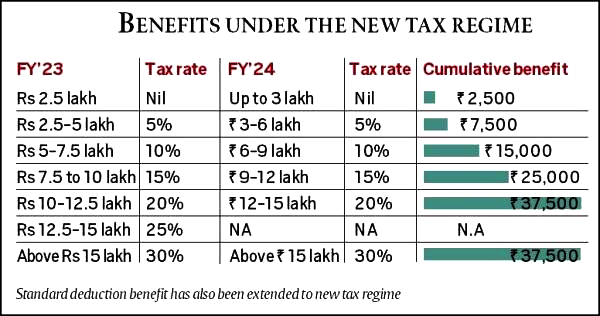
- It was proposed to change the tax structure in the new regime by reducing the number of slabs to five from six income categories and increasing the tax exemption limit to ₹3 lakh.
- Tax assessors will still be able to choose from the prior regime.
- Salaried and Pensioners: The new system's standard deduction for taxable income exceeding Rs15.5 lakhs is ₹52,500.
- For Pensioners:
- The Finance Minister announced extending the benefit of the standard deduction to the new tax regime.
- Each salaried person with an income of ₹15.5 lakh or more will benefit by ₹52,500.
- The Finance Minister announced extending the benefit of the standard deduction to the new tax regime.
- Maximum Tax Along with Surcharge:
- It was proposed to reduce the highest surcharge rate from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime. This would result in the reduction of the maximum tax rate to 39%.
- The highest tax rate in India is 42.74%. This is among the highest in the world.
- Tax rates have been reduced under the new tax regime and the maximum marginal rate drops from 42.74% to 39%.
- It was proposed to reduce the highest surcharge rate from 37% to 25% in the new tax regime. This would result in the reduction of the maximum tax rate to 39%.
- Finance Bill, 2023:
- The Finance Bill, 2023 was also unveiled which has proposed to amend Section 56(2) VII B of the Income Tax Act.
- The provision states that when an unlisted company, such as start-ups receive equity investment for the issue of shares exceeding their face value, it will be considered income for the start-up and be subject to income tax under the heading "Income from other Sources".
- Section 56(2) VII B of the Income Tax Act, colloquially known as the ‘angel tax’ was first introduced in 2012 to deter the generation and use of unaccounted money through the subscription of shares of a closely held company at a value that is higher than the fair market value of the firm’s shares.
- The Finance Bill, 2023 was also unveiled which has proposed to amend Section 56(2) VII B of the Income Tax Act.
- It was also proposed to include foreign investors also, meaning that when a start-up raises funding from a foreign investor, that too will now be counted as income and be taxable.
Why are Startups Concerned?
- Foreign investors are a significant source of funding for startups and have contributed to their increased valuations and the proposed amendments can affect the amount of investment.
- According to a report by PwC India, the funding for India's startups decreased by 33% to $24 billion in 2022.
- The reintroduction of the tax on angel investors in India may cause startups to shift abroad, as foreign investors may not want to pay additional taxes associated with their investment in the startup.
What is Face Value?
- According to the face value definition, it is the dollar value of any stock (or any financial instrument) at the time of issuing. It is also termed as the nominal value or the dollar value.
- Face Value= Equity share capital/ number of outstanding shares.


Important Facts For Prelims
Cholera
Why in News?
African countries are facing Cholera vaccine shortage, that is a looming threat amid increasing cholera cases in the region.
- Since the beginning of 2023, there have been 27,300 new cases of cholera including 687 deaths in five African countries.
- The WHO (World Health Organization) has said Climate Change could make cholera epidemics more common, as the bacteria that causes the disease can reproduce more quickly in warmer water.
What is Cholera?
- About:
- It is a life-threatening infectious disease and a public health hazard.
- Cholera is an acute, diarrheal illness caused by infection of the intestine with the bacterium Vibrio cholerae.
- The infection is often mild or without symptoms, but sometimes can be severe.
- Symptoms:
- Profuse watery diarrhoea, Vomiting, Leg cramps
- Transmission:
- A person may get cholera by drinking water or eating food contaminated with the cholera bacterium.
- The disease can spread rapidly in areas with inadequate treatment of sewage and drinking water.
- Vaccine:
- Currently there are three WHO pre-qualified Oral Cholera Vaccines (OCV), Dukoral, Shanchol, and Euvichol-Plus.
- All three vaccines require two doses for full protection.
What are the Initiatives to Curb Cholera?
- A global strategy on cholera control, Ending Cholera: a global roadmap to 2030, with a target to reduce cholera deaths by 90% was launched in 2017.
- Global Task Force for Cholera Control (GTFCC): WHO revitalized the Global Task Force for Cholera Control (GTFCC) to strengthen WHO’s work in eradicating cholera.
- The purpose of the GTFCC is to support increased implementation of evidence-based strategies to control cholera.


Important Facts For Prelims
Government e-Marketplace
Why in News?
Government e-Marketplace achieves a Gross Merchandise Value (GMV) of Rs. 1.5 Lakh Crores.
- GeM has been effectively contributing to the government’s commitment of “Minimum Government, Maximum Governance”.
What is Gross Merchandise Value (GMV)?
- GMV refers to the value of goods sold via customer-to-customer or e-commerce platforms.
- It is calculated prior to the deduction of any fees or expenses.
- It is a measure of the growth of the business or use of the site to resell products owned by others through consignment.
What is the Government e-marketplace (GeM)?
- About:
- The GeM is an online platform launched by the Ministry of Commerce and Industry, Government of India in 2016 to facilitate procurement of goods and services by various government departments and organisations.
- It is open to all government departments, public sector undertakings, autonomous bodies and other organisations.
- Currently, GeM stands at the third position after Singapore's GeBIZ.
- South Korea's KONEPS is the largest such platform in the world.
- Significance:
- Boost to Digital Economy:
- The e-marketplace can promote the use of technology in government procurement processes, contributing to the growth of India's digital economy.
- In the last 6.5 years, GeM has revolutionised the ecosystem of public procurement in the country through technology, the digitization of processes, the digital integration of all stakeholders, and the use of analytics.
- Improved vendor participation:
- GeM can encourage more vendors, including small and medium enterprises, to participate in government procurement processes, leading to increased competition and better value for money for the government.
- Transparency and Efficiency:
- A government e-marketplace can improve the transparency and efficiency of procurement processes by standardising and automating procedures, reducing the scope for corruption and human error.
- Last Mile Outreach: GeM has integrated with 1.5 lakh+ India Post offices and 5.2+ lakh Village Level Entrepreneurs (VLEs) via the Common Service Centres for last-mile outreach and service delivery.
- Boost to Digital Economy:
- Developments:
- Country of Origin Mandatory: Every time a new product is registered on GeM, sellers are required to list the Country of Origin.
- Bamboo Market Window: The National Bamboo Mission and the Government e-Marketplace (GeM) have collaborated to have a dedicated window on the GeM portal for marketing of the Bamboo Goods (Bamboo based products & Quality Planting Materials).


Rapid Fire
Rapid Fire Current Affairs
APEDA Organises Virtual-Buyer Seller Meet with UAE
As a part of promoting the export of millets, the Agriculture and Processed Food Products Export Development Authority (APEDA) organised a Virtual-Buyer Seller Meet to harness export opportunities in the United Arab Emirates (UAE).
APEDA has also planned to organise millet promotional activities in South Africa, Japan, S Korea, Indonesia, Saudi Arabia, Australia, Germany, the UK and the US.
India’s major millet exporting countries are UAE, Nepal, Saudi, Libya, Oman, Egypt, Tunisia, Yemen, UK and USA with major varieties being - Bajra, Ragi, Canary, Jawar, and Buckwheat.
Read More - APEDA, India's Millet Revolution, India-UAE Relations
Deep Ocean Mission
The Union Budget 2023-24 has allocated Rs 600 crore to the Deep Ocean Mission to explore marine biodiversity for the sustainable use of resources.
Under this mission, a manned submersible will be developed to carry three people to a depth of 6,000 metres to facilitate mineral exploration in the central Indian ocean.
In 2016, India was awarded a 15-year contract to explore an area of 75,000 km2 for mining polymetallic nodules from the Central Indian Ocean Basin at depths of 5,000-6,000 metres.
Read More - Deep Ocean Mission, Samudrayaan Mission
MISHTI Initiative for Mangroves
The Union Budget 2023-24 announced a new initiative for mangrove plantations along the coastline and on salt pan lands - MISHTI (Mangrove Initiative for Shoreline Habitats & Tangible Incomes). Earlier, India joined the Mangrove Alliance for Climate launched during the UNFCCC COP27.
Although Mangroves cover only about 0.1% of the planet’s surface, they can potentially store up to 10x more carbon per hectare (ha) than terrestrial forests. They protect coastal communities by acting as a natural barrier against storm surges.
According to India State of Forest Report (ISFR) 2021, India’s total mangrove cover is 4,992 km2 (0.15% of total geographical area). India lost 40% of its mangrove cover during the last century with Kerala losing 95% of its mangroves in the last 3 decades.
Read More - Mangrove Forests, Mangrove Alliance for Climate
Exercise Trishakti Prahar
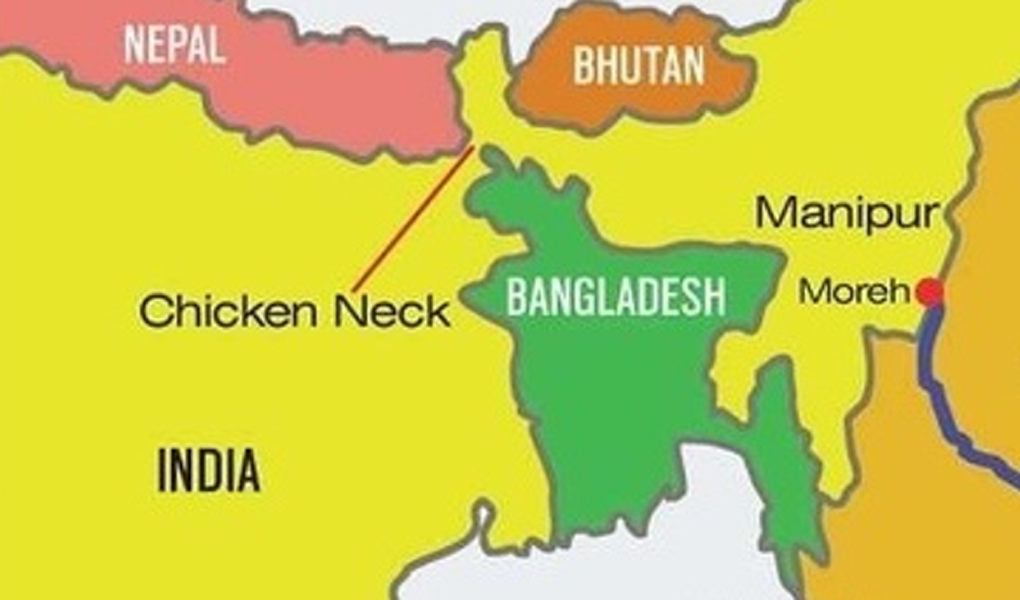
The Indian military recently concluded exercise Trishakti Prahar — a joint training exercise in North Bengal (close to the strategic ‘Siliguri’ corridor). The aim of the exercise was to practise battle preparedness of the security forces, using latest weapons and equipment in a networked, integrated environment, involving the Army, the IAF and CAPFs.
The exercise concluded with an Integrated Fire Power Exercise at the Teesta Field Firing Ranges, aimed at synergising the firepower assets of the Indian Armed Forces and CAPFs to orchestrate an integrated battle.
The Siliguri corridor or Chicken’s neck (West Bengal) is a stretch of land bordering Bangladesh, Bhutan and Nepal, measuring approximately 170x60 km; at the narrowest it is about 20-22 km.