Biodiversity & Environment
Mangroves in Coastal Resilience
For Prelims: Bhitarkanika National Park, Indian State Forest Report 2021, MISHTI, Tropical cyclones, Extra Tropical cyclones, MAC
For Mains: Initiatives for protection and conservation of Mangroves, Challenges with Mangrove Conservation, Role of Mangroves in Cyclone Mitigation.
Why in News?
Recently, Cyclone Dana's landfall near Bhitarkanika National Park and Dhamra Port in Odisha underscored the essential role of mangrove forests in reducing cyclone impacts.
- The cyclone did not cause as significant damage as anticipated due to the rich mangrove forest cover of Bhitarkanika.
- Bhitarkanika National Park has withstood the onslaught of several cyclones in the past including the Super Cyclone, which took place in October 1999.
What are Mangroves?
- About: Mangroves are salt-tolerant trees and shrubs that thrive in estuarine and intertidal regions where freshwater meets saltwater.
- They possess unique adaptations, such as aerial roots and waxy leaves, allowing them to survive in saline environments.
- They represent a littoral forest ecosystem, which means they thrive in saline or brackish waters in coastal regions
- Some common mangrove trees include Red mangrove, Grey mangrove, and Rhizophora.
- Mangrove Cover in India: According to the Indian State Forest Report 2021, Mangrove cover in India is 4992 sq. Km which is 0.15% of the country's total geographical area.
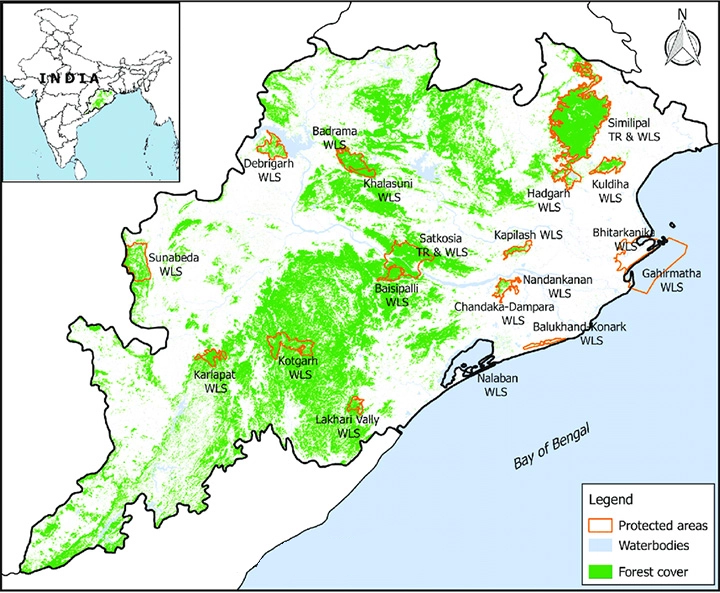
- Geographical Distribution: India hosts significant mangrove ecosystems in various states, including Odisha (Bhitarkanika), Andhra Pradesh (Godavari-Krishna delta), Gujarat, Kerala, and the Andaman Islands.
- The Sundarbans (spread across India and Bangladesh) is the largest contiguous mangrove forest in the world. Bhitarkanika is second only to Sunderbans in terms of mangrove cover in India
- Role of Mangroves in Cyclone Mitigation:
- Coastal Defence: Mangroves are the first line of defence for coastal communities. They stabilise shorelines by slowing erosion and provide natural barriers protecting coastal communities.
- Storm Surge Protection: Mangrove forests act as natural barriers against cyclone-driven surges, significantly reducing surge height, water flow velocity, and minimising flooding and coastal damage.".
- Integration with Infrastructure: The effectiveness of mangroves can be enhanced when combined with built infrastructure, such as embankments.
- Initiatives for Protection and Conservation of Mangroves:
- MISHTI Initiative: The Union Budget 2023-24 announced MISHTI initiative for mangrove plantations along the coastline and on salt pan lands.
- Mangrove Alliance for Climate: MAC includes UAE, Indonesia, India, Sri Lanka, Australia, Japan, and Spain. It seeks to educate and spread awareness worldwide on the role of mangroves in curbing global warming and its potential as a solution for climate change.
- Blue Carbon Initiative: It is focused on mitigating climate change through the conservation and restoration of coastal and marine ecosystems.
- It is coordinated by Conservation International (CI), IUCN, and the Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission-UNESCO (IOC-UNESCO)
What are the Challenges with Mangrove Conservation ?
- Commercialisation of Coastal Areas: Aquaculture, coastal development, rice and palm oil farming and industrial activities are rapidly replacing these salt-tolerant trees and the ecosystems they support.
- Temperature Related Issues: A fluctuation of ten degrees in a short period of time is enough stress to damage the plant and freezing temperatures for even a few hours can kill some mangrove species.
- Soil Related Issues: The soil in which mangroves grow presents a challenge for plants due to its severe lack of oxygen.
- Pollution and Contamination: Pollution from agricultural runoff, industrial discharges, and improper waste disposal contaminate mangrove habitats.
- Lack of Integrated Management: The management of mangroves often occurs in isolation, failing to recognize their crucial interconnectedness with adjacent ecosystems, such as coral reefs and seagrass beds, which is essential for holistic environmental health.
Bhitarkanika National Park:
- Bhitarkanika National Park is spread in a vast area of 672 Kms in Orissa.
- The National Park is essentially a network of creeks and canals which are inundated with waters from rivers Brahmani, Baitarani, Dhamra and Patasala forming a unique ecosystem.
- It is the breeding place for the Saltwater Crocodiles. The crocodile conservation project in Bhitarkanika was started in 1975.
- The Gahirmatha Beach which forms the boundary of the sanctuary in the east is the largest colony of the Olive Ridley Sea Turtles.
What can be Done to Preserve Mangroves?
- Utilise bio-restoration techniques like Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) to revive degraded mangrove areas, helping to maintain original biodiversity.
- Assisted Natural Regeneration (ANR) is a complementary solution to planting. This solution consists of a soft forest management method that preserves and strengthens existing forests through forest maintenance work that respects and mimics the natural reproduction cycle of trees.
- There is a pressing need for policies aimed at conserving existing mangrove forests and restoring degraded areas. Sustainable management practices should be adopted to enhance the resilience of coastal ecosystems.
- Engaging local communities in mangrove conservation efforts can foster a sense of ownership and ensure the sustainability of these ecosystems. Education and awareness programs about the benefits of mangroves can promote community-driven conservation initiatives.
Conclusion
Strengthening mangrove conservation efforts is imperative for enhancing India's resilience to cyclones and safeguarding coastal communities. The integration of ecological and infrastructural approaches will be key to achieving long-term sustainability and disaster risk reduction.
|
Drishti Mains Question: Examine the role of mangrove ecosystems in mitigating the impacts of cyclones. Discuss the significance of mangrove preservation in India’s coastal disaster management strategy. |
UPSC Civil Services Examination Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Prelims
Q. Which one of the following regions of India has a combination of mangrove forest, evergreen forest and deciduous forest? (2015)
(a) North Coastal Andhra Pradesh
(b) South-West Bengal
(c) Southern Saurashtra
(d) Andaman and Nicobar Islands
Ans: (d)
Mains
Q. Discuss the causes of depletion of mangroves and explain their importance in maintaining coastal ecology. (2019)
Important Facts For Prelims
Biotechnology Experiments for India's Upcoming Space Station
Why in News?
Recently, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) and the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) have signed an agreement to design and conduct experiments that will later be integrated with the Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS), slated for development between 2028 and 2035.
Note
The ISRO-DBT collaboration stems from another initiative this year called the BIOE3 (Biotechnology for Economy, Environment and Employment) policy by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT) that aims to stimulate ‘bio-manufacturing’ in India. The bio-economy, officials in the DBT said, would be worth USD 300 billion by 2030.
Why have ISRO and DBT Collaborated for Space Experiments?
- The key challenges in space missions are the continuous availability of nutrients, preservation of food, microgravity and radiation, health hazards such as cancers, cataracts, bone and muscle loss among others. The MoU will help address these issues using biotechnology.
- Potential Experiments:
- Investigating the effects of weightlessness on muscle loss in astronauts.
- Identifying algae species that could serve as nutrients or extend food preservation.
- Exploring the processing of specific algae for jet fuel production.
- Assessing the impact of radiation on the health of individuals aboard space stations.
What is Bharatiya Antariksh Station (BAS)?
- BAS is India's proposed indigenous space station for scientific research. It will be built in three phases and will have five modules.
- The first module, known as BAS-1, is expected to be launched in 2028, and the station will be fully operational by 2035.
- Key Details about the BAS:
- Orbit: The BAS will orbit the Earth at a height of around 400–450 kilometres.
- Weight: The station will weigh about 52 tonnes.
- Crew: Astronauts will be able to stay in orbit for 15–20 days.
- Modules: The BAS will have a crew command module, habitat module, propulsion module, and docking ports.
- Purpose: The BAS will be used for scientific research, including microgravity experiments, earth observation, and fostering innovation.
- Collaboration: The BAS will promote international collaboration with other countries and space agencies.
- Program: The ISRO will lead the program, which will also involve industry, academia, and other national agencies.
Other Space Stations
- International Space Station (ISS) Context:
- The ISS has been operational since 1998, with collaboration from multiple countries including the US, Canada, Russia, and Japan.
- Due to shifting geopolitical dynamics and cost factors, the ISS is projected to be decommissioned by 2030, prompting countries to consider their own space stations.
- Tiangong:
- China has successfully established its Tiangong space station, which has been fully operational since November 2022.
Recent Major Developments in the Space Sector in India
- Recent Major Successful Missions:
- Advancements in Launch Vehicles:
- Missions for International Clients:
- Other Key Developments:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Question (PYQ)
Q. “The experiment will employ a trio of spacecraft flying in formation in the shape of an equilateral triangle that has sides one million kilometres long, with lasers shining between the craft.” The experiment in question refers to (2020)
(a) Voyager-2
(b) New Horizons
(c) LISA Pathfinder
(d) Evolved LISA
Ans: (d)
Q. Consider the following statements: (2016)
- The Mangalyaan launched by ISRO
- is also called the Mars Orbiter Mission
- made India the second country to have a spacecraft orbit the Mars after USA
- made India the only country to be successful in making its spacecraft orbit the Mars in its very first attempt
Which of the statements given above is/are correct?
(a) 1 only
(b) 2 and 3 only
(c) 1 and 3 only
(d) 1, 2 and 3
Ans: (c)
Important Facts For Prelims
Tiger Translocation for Genetic Diversity
Why in News?
Recently, the Odisha government translocated a tigress named Jamuna from Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve in Maharashtra to the Similipal Tiger Reserve (STR) in Odisha.
- Translocation was aimed at enhancing genetic diversity in Similipal, where there are concerns about inbreeding due to a small population.
What are Key Facts About this Translocation?
- Previous Translocation Attempts: In 2018, a tigress named Sundari was relocated to Satkosia Tiger Reserve, Odisha.
- The National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) gives approval for the translocation project.
- Translocation of Black Tigers:
- Population: The Odisha Tiger Estimation conducted in 2024 found a total 24 adult tigers in Similipal, with a notable presence of pseudo-melanistic tigers.
- STR is the only habitat where these black tigers are found in the wild.
- Inbreeding Concerns: The high number of pseudo-melanistic tigers (13 out of 24 adults) in Similipal raises concerns about inbreeding and lack of genetic flow, prompting the need for external genetic input.
- Future Initiatives: Plans are in place to establish a melanistic tiger safari in Similipal, which would be the first of its kind in the world.
- Population: The Odisha Tiger Estimation conducted in 2024 found a total 24 adult tigers in Similipal, with a notable presence of pseudo-melanistic tigers.
Note:
- Black or pseudo-melanistic tigers exist because of a genetic trait that creates a unique phenotype and indicates a lack of genetic diversity.
- They are characterised by wide and merged stripes
What are the Key Facts About Similipal Tiger Reserve?
- Location: Similipal tiger reserve and national park is located in Odisha's Mayurbhanj district.
- It was designated as a tiger reserve under Project Tiger in 1973.
- In 2009, UNESCO included Simlipal National Park in its list of Biosphere Reserve.
- Geography: Joranda and Barehipani waterfalls and Khairiburu and Meghashini peaks are located in Simlipal national park.
- Burhabalanga, Palpala Bandan, Salandi, Kahairi, and Deo rivers pass through it.
- It is named after the ‘Simul’ (Silk Cotton) tree.
- Biodiversity: Forest type is primarily dominated by tropical moist deciduous forests.
- Mammals: Tigers, leopards, sambar deer, barking deer, gaurs, jungle cats, wild boars, four-horned antelopes, giant squirrels, and common langurs.
- Avian Species: Grey hornbills, Indian pied hornbills, and Malabar pied hornbills.
- Reptile: Mugger crocodiles inhabit Khairi and Deo Rivers.
- Indigenous Population: It is inhabited by indigenous tribes like Kolha, Santhala, Bhumija, Bhatudi, Gondas, Khadia, Mankadia, and Sahara.
- The tribals worship sacred groves called Jharia.
What are the Key Facts About Tadoba Andhari Tiger Reserve?
- Location: It is situated in Maharashtra and is the oldest and largest national park in the state.
- Tadoba/Taru is the local deity revered by the tribal people in the area.
- Andhari is derived from the Andhari river which flows through the reserve.
- Geography: It contains two primary lakes, Tadoba Lake and Kolsa Lake, along with the Tadoba River.
- Biodiversity:
UPSC Civil Services Examination, Previous Year Questions (PYQs)
Prelims
Q. Among the following Tiger Reserves, which one has the largest area under “Critical Tiger Habitat”? (2020)
(a) Corbett
(b) Ranthambore
(c) Nagarjunasagar-Srisailam
(d) Sundarbans
Ans: (c)
Q. Consider the following protected areas: (2012)
- Bandipur
- Bhitarkanika
- Manas
- Sunderbans
Which of the above are declared Tiger Reserves?
(a) 1 and 2 only
(b) 1, 3 and 4 only
(c) 2, 3 and 4 only
(d) 1, 2, 3 and 4
Ans: (b)
Rapid Fire
SC Expands Rights for Disabled in Medical Admissions
The Supreme Court has ruled against denying individuals educational opportunities based on strict disability criteria. It directed the disability assessment boards to evaluate whether an individual’s impairment genuinely prevents them from completing the course successfully.
- The ruling comes amid challenges to the Graduate Medical Education Regulation of 1997, which previously excluded individuals with a disability of 40% or more from MBBS courses.
- The SC held that mere existence of benchmark disability of 40% or above (or such other prescribed percentages depending on the disability) will not disqualify a candidate from being eligible for the course applied for.
- It reinforces the importance of individual assessments, advocating for inclusive policies under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- The 2016 RPwD Act supports UN conventions on disability rights, aiming to promote and protect the full rights and freedoms of persons with disabilities.
- It reinforces the importance of individual assessments, advocating for inclusive policies under the Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016.
- The Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD) oversees the implementation of the RPwD Act. Disability Assessment Board (DAB) is a designated panel established to evaluate and certify the extent of disability in individuals.
- As per the latest SC ruling, the DABs should positively record whether the disability of the candidate will or will not come in the way of the candidate pursuing the course in question and shall state reasons if the latter appears to be the case.
Read More: PwDs in India, Medical College Seats and New Regulations in India


Rapid Fire
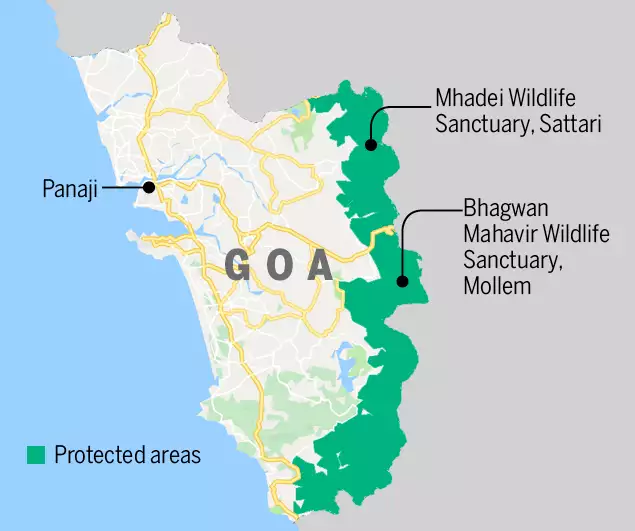
Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary
Recently, an adult tigress and three cubs were spotted in the Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary (WLS), Goa for the first time since 2020.
- Location and Geography:
- WLS is located near the Chorla Ghat, situated between North Goa and Belgavi. It borders both Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- The Mhadei River flows through this sanctuary.
- Ecological Significance:
- Mhadei WLS, along with other protected areas in Goa like Mollem National Park, forms part of the Western Ghats. This region is globally renowned for hosting the world's largest tiger population.
- The sanctuary plays a vital role in a network of wildlife corridors that connect tiger populations across the Sahyadri Tiger Reserve (Maharashtra) and the Kali Tiger Reserve (Karnataka).
- Unique Flora and Fauna:
- Notably, Vazra Falls in Mhadei WLS serves as a nesting ground for critically endangered Long-billed vultures, underscoring the sanctuary's importance for avian conservation.
- Conservation Status and Recommendations:
- Goa stands as the only state in India to have its entire portion of the Western Ghats under state protection, with Mhadei WLS being a critical part of this area.
- Previously, the National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) recommended the designation of Mhadei WLS as a tiger reserve under the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972, to enhance conservation efforts for the tiger population in this unique region.
Read More: Mhadei Wildlife Sanctuary

Rapid Fire
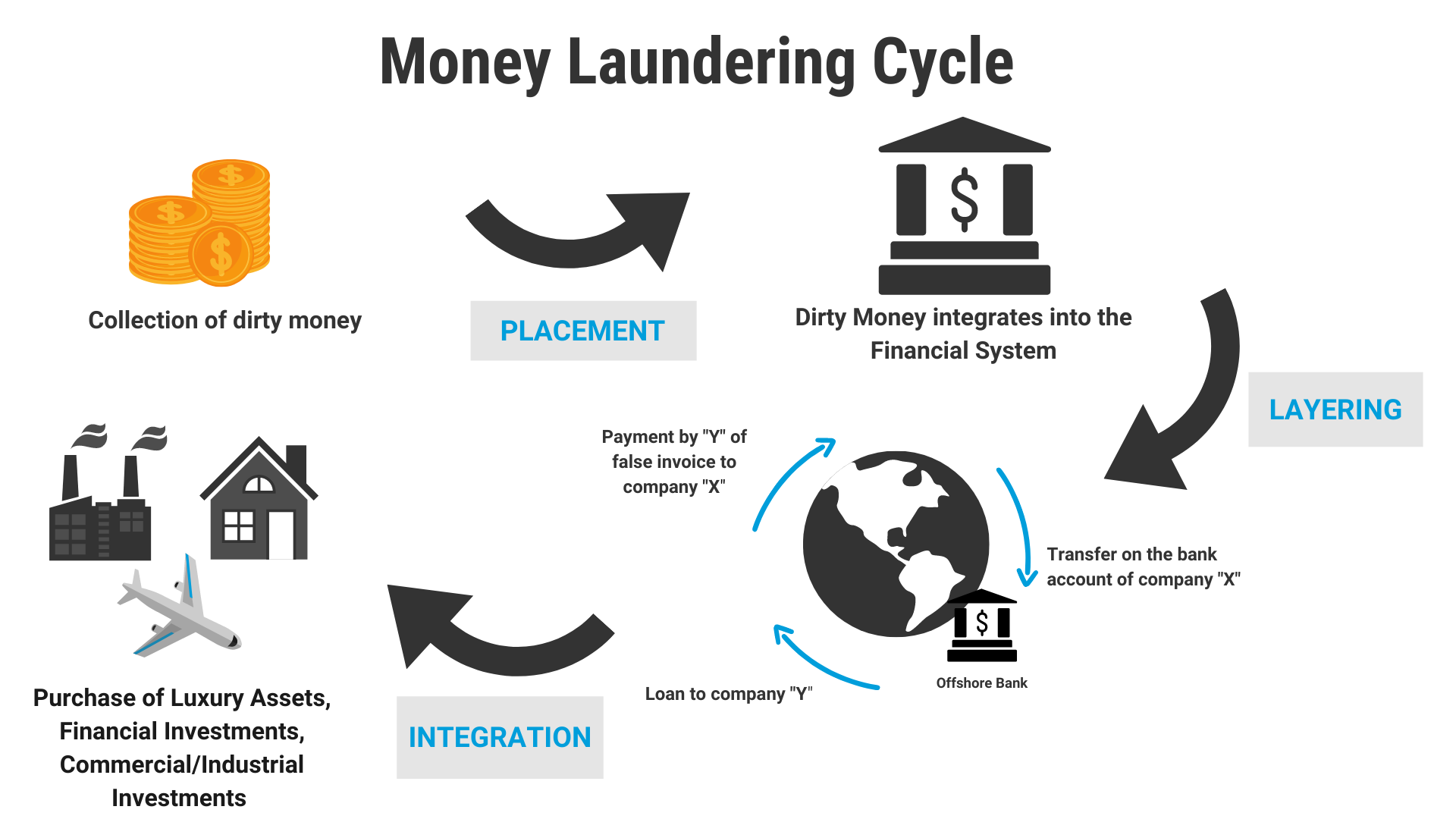
Mule Accounts for Money Laundering
Recently, the Union Ministry of Home Affairs has issued an alert about illegal payment gateways like PeacePay, RTX Pay etc set up by transnational cybercriminals using mule bank accounts for money laundering.
- A mule account is a bank account used to facilitate illegal activities.
- A money mule is someone who transfers or moves illegally acquired money on behalf of someone else.
- Transnational cybercriminals use accounts of shell companies and individuals as mule accounts, exploiting the bulk payout facility provided by banks.
- A shell company is a company without active business operations or significant assets.
- They are not all necessarily illegal, but they can be used illegitimately to conceal business ownership from law enforcement or the public.
- The Bulk Payout facility offered by banks allows businesses and organisations to make multiple payments to various beneficiaries in a single transaction.
Read More: Money Laundering


Rapid Fire
New Guidelines for Import of Seaweeds
Recently, the Centre issued the 'Guidelines for Import of Live Seaweeds into India' to support the import of high-quality seed materials or germplasm, aimed at enhancing livelihood opportunities for coastal communities.
- Guidelines:
- Framework and Procedures for Importing Seaweed:
- Establishes a regulatory framework with clear guidelines for live seaweed import into India, covering quarantine, risk assessment, and post-import monitoring to prevent pests, diseases, and biosecurity risks.
- India's seaweed industry faces challenges from limited seed availability and quality issues, especially in the widely farmed Kappaphycus species.
- Pradhan Mantri Matsya Sampada Yojana (PMMSY):
- The PMMSY targets raising India’s seaweed production to over 1.12 million tonnes by 2025, with major initiatives such as a Multipurpose Seaweed Park in Tamil Nadu to bolster seaweed farming.
- Encouragement for Sustainable and Responsible Cultivation:
- The guidelines encourage environmentally sustainable and economically beneficial seaweed cultivation.
- Introducing new strains drives research and development, boosting the production of diverse seaweed species including red, brown, and green algae.
- Framework and Procedures for Importing Seaweed:
Read More: National Conference on Promotion of Seaweed Cultivation