Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Maharashtra Reduces Women’s Welfare Aid
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government has reduced stipends for around eight lakh beneficiaries of the Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana as they also receive benefits under the Namo Shetkari Mahasanman Nidhi (NSMN) scheme.
Key Points
- Reduction in Monthly Assistance:
- Under the revised structure, affected women will now receive Rs 500 per month instead of Rs 1,500 under the Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana.
- The reduction applies to those already receiving Rs 1,000 monthly under the NSMN scheme.
- As per the scheme’s guidelines, the total government aid per woman cannot exceed Rs 1,500.
- Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana:
- About:
- Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana, launched in 2024, is a flagship welfare programme aimed at supporting women financially across Maharashtra.
- Benefits:
- The original Rs 1,500 monthly payout was designed to empower women economically and enhance their social security.
- Beneficiaries receive three free LPG cylinders each year.
- Poor girls from Other Backward Classes (OBC) and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) are eligible for fee waivers during college admissions.
- Eligibility:
- The scheme covers women aged 21 to 65 including married, widowed, divorced, abandoned, and destitute women.
- About:
- Namo Shetkari Mahasanman Nidhi (NSMN) Scheme:
- About:
- Introduced in 2023 by the Maharashtra government, it aims to provide additional financial support to small and marginal farmers.
- It complements the Central government’s Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme.
- Eligibility:
- Farmers must be registered under PM-KISAN.
- Must meet Maharashtra’s criteria for small or marginal farmers.
- Benefits:
- Provides Rs 6,000 annually in three equal installments of Rs 2,000.
- This is over and above the Rs 6,000 received under PM-KISAN, totaling Rs 12,000 annually.
- About:
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- Under the scheme, the Centre transfers an amount of Rs 6,000 per year, in three equal installments, directly into the bank accounts of all landholding farmers irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- It was launched in February 2019.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The entire responsibility of identification of beneficiary farmer families rests with the State / UT Governments.
- Objective:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Exercise DUSTLIK-VI
Why in News?
India and Uzbekistan began the 6th edition of Joint Military Exercise DUSTLIK-VI at Aundh, Pune. The exercise will take place from 16 to 28 April 2025.
- The previous edition took place in Termez District, Uzbekistan, in April 2024.
Key Points
- Exercise Theme and Focus:
- The core theme is Joint Multi-Domain Sub-Conventional Operations in a Semi-Urban Scenario.
- The focus is on responding to terrorist actions involving the capture of a defined territory.
- A Joint Operations Centre will be established at the battalion level for continuous coordination.
- Participation and Representation:
- The Indian contingent includes 60 personnel from a battalion of the JAT Regiment and the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The Uzbekistan Army is representing the Uzbek side.
- Strategic Objectives:
- The joint drill will promote interoperability, tactical cooperation, and mutual learning in sub-conventional warfare.
- It aims to enhance defence cooperation and deepen bilateral military relations between India and Uzbekistan.
- The exercise fosters camaraderie and trust between both armies through shared training and strategic alignment.
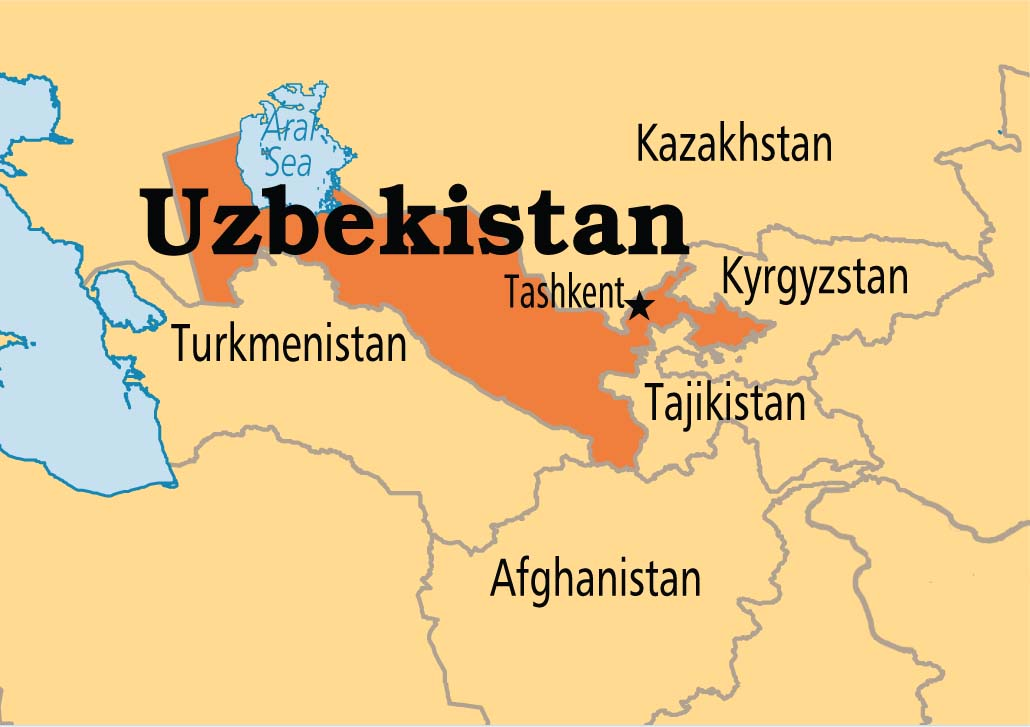
Uzbekistan
- About:
- Landlocked country in Central Asia, situated between the Syr Darya (northeast) and Amu Darya (southwest) rivers.
- Lies in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres.
- One of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world (the other is Liechtenstein).
- Neighbouring Countries:
- Kazakhstan (north and northwest)
- Kyrgyzstan (northeast)
- Tajikistan (southeast)
- Afghanistan (south)
- Turkmenistan (southwest)
- Topographical Features:
- Around 80% of the land is sandy desert, mostly the Kyzyl Kum Desert.
- Lowlands dominate the west; foothills and mountains (Tian Shan range) rise in the northeast and southeast.
- The highest peak is Adelunga Toghi (4,301 m) in the northeast.
- Fergana Valley is the most fertile and agriculturally productive region.
- Rivers and Lakes:
- Major rivers: Amu Darya and Syr Darya.
- The Aral Sea, shared with Kazakhstan, is a major environmental disaster due to water mismanagement.
- Important lakes: Lake Aydarkul and Lake Sarykamish.
- Major rivers: Amu Darya and Syr Darya.
- Vegetation and Climate:
- Dominated by desert scrub in arid zones.
- Fertile valleys, especially Fergana, support intensive agriculture.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in natural gas, oil, coal, and minerals like gold, uranium, and copper.
- Holds the 4th largest gold reserves globally.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan