Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Solar Water Desalination
Why in News?
Indian Institutes of Technology (IIT)- Bombay scientists have developed a new material to enable water desalination and address global freshwater scarcity. 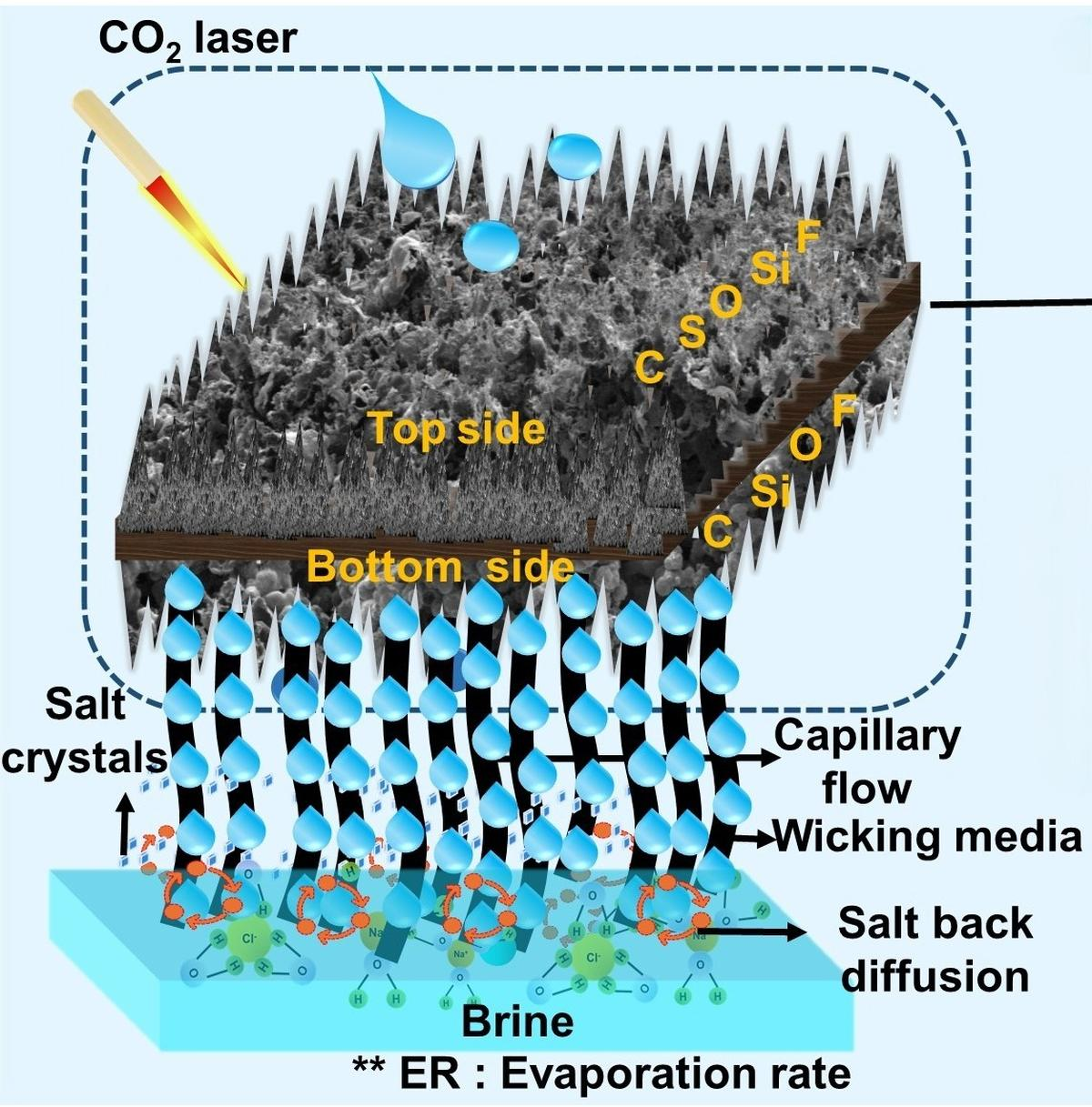
Key Points
- About the Innovation:
- Researchers have developed a Dual-Sided Superhydrophobic Laser-Induced Graphene (DSLIG) evaporator.
- The DSLIG addresses limitations of traditional evaporators and shows promise for large-scale desalination and wastewater treatment.
- The Freshwater Challenge:
- Only 3% of Earth’s water is freshwater, and less than 0.05% is easily accessible.
- Desalination of seawater and brackish water is a key solution to this scarcity.
- However, desalination produces brine, a concentrated salt byproduct, which poses disposal challenges, especially in landlocked areas.
- Industries now aim for zero liquid discharge systems to avoid environmental harm.
- Solar Desalination:
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Yet, sunlight variability and poor light absorption reduce efficiency.
- Interfacial evaporation systems help by heating a thin surface layer of water instead of the whole volume, enhancing efficiency.
- Challenges in Interfacial Evaporation:
- Cloud cover and fluctuating solar intensity hamper consistent performance.
- Evaporation peaks around 2 pm, when solar radiation is highest.
- Salt deposition on the evaporator surface blocks water contact, reducing long-term efficiency.
- DSLIG Overcomes the Challenges:
- DSLIG allows dual heating—solar and Joule heating (electric)—ensuring performance even in low sunlight.
- Superhydrophobic properties (lotus effect) prevent salt from sticking to the evaporator surface.
- Solar energy-based desalination offers a low-carbon solution.
- Fabrication of DSLIG:
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
- PDVF are polymers that can generate electric charges on the surface under pressure/strain thus converting mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- PES is a thermoplastic polymer known for its high thermal stability, excellent chemical resistance, and biocompatibility.
- They used laser engraving to inscribe graphene onto the PVDF layer.
- PES ensures mechanical strength, while PVDF contributes to dual-sided water repellency.
- The result is a durable, superhydrophobic surface effective in both electric and solar modes.
- Applications:
- It is suitable for treating industrial wastewater and brine from desalination plants.
- Researchers observed improved performance by stacking multiple evaporators.
- DSLIG is low-cost, non-toxic, and sustainable, making it ideal for large-scale applications.
- Researchers coated PVDF (polyvinylidene fluoride) on one side of PES (polyether sulfone) polymer.
Desalination
- A desalination plant turns salt water into water that is fit to drink.
- Desalination is the process of removing salts from water to produce water that meets the quality (salinity) requirements of different human uses.
- The most commonly used technology for the process is reverse osmosis.
- An external pressure is applied to push solvents from an area of high-solute concentration to an area of low-solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane.
- The microscopic pores in the membranes allow water molecules through but leave salt and most other impurities behind, releasing clean water from the other side.
- These plants are mostly set up in areas that have access to sea water.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
ATM on Wheels
Why in News?
Indian Railways installed an Automated Teller Machine (ATM) onboard the Manmad-CST Panchvati Express as part of a pilot initiative in Maharashtra.
Key Points
- About the Initiative:
- The initiative aligns with the Railway Board's push to boost non-fare revenue through innovative, out-of-the-box solutions.
- It aims to provide banking access to passengers, especially in regions with limited financial infrastructure.
- This setup could particularly benefit commuters on long-distance routes with fewer banking facilities en route.
- Indian Railways’ Modernisation Drive:
- The ATM initiative is a part of the Viksit Bharat 2047 vision, focusing on passenger convenience and tech-led upgrades.
- Indian Railways is already transforming travel with high-tech trains like Vande Bharat, modern stations, and advanced safety systems.
- Amrit Bharat Station Scheme:
- Under the Amrit Bharat Station Scheme, Indian Railways has selected 1,337 stations for redevelopment, aiming to enhance infrastructure and passenger experience.
- The Scheme was launched in February 2023 by the Ministry of Railways.
Indian Railways
- 169 Years of Heritage:
- The Indian Railways was established on 16th April 1853. The inaugural passenger train covered a 34-kilometer route between Mumbai's Bori Bandar and Thane.
- Unique Mascot:
- The Indian Railways boasts its own mascot, a 'Shubhankar named 'Bholu,' created by the National Institute of Design in 2002. Bholu is an elephant dressed as a railway guard, introduced on the railways' 150th anniversary.
- World's 4th Largest Rail Network:
- The Indian Railways ranks as the world's fourth-largest railway network, encompassing a track length of 67,368 km. Only the US, China, and Russia have larger networks. It's also the world's second-largest network managed under a single administration, spanning 115,000 km.
- UNESCO World Heritage Sites:
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites.
- Darjeeling Himalayan Railway, Chhatrapati Shivaji Terminus in Mumbai, Nilgiri Mountain Railway, and Kalka Shimla Railway.
- The Indian Railways takes pride in owning four UNESCO-recognized world heritage sites.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan


