Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Sets Minimum Teacher Requirements for Primary & Middle Schools
Why in News?
The Bihar Education Department has established new standards for the minimum number of teachers required in primary and middle schools.
Key Points
- According to these new guidelines, primary schools (classes 1 to 5) must have at least five teachers, including the head teacher.
- For schools encompassing classes 1 to 8, a minimum of nine teachers, including the principal, is mandated.
- District Education Officers have been instructed to upload reports detailing the approved and required number of teachers for each school on the e-ShikshaKosh portal by 31 January 2025.
- The department emphasizes that each teacher should have at least one dedicated classroom, and the actual assessment of teacher requirements will be based on the availability of rooms in each school.
- In primary schools with student numbers ranging from 1 to 120, five teachers are mandatory.
- For student numbers between 121 and 150, six teachers are required. For every additional 40 students beyond 150, one extra teacher will be appointed.
- In classes 6 to 8, for student numbers up to 105, the staffing requirements are as follows:
- One teacher for Science and Mathematics
- One teacher for Social Studies
- One teacher for Hindi
- One teacher for English
- Additionally, provisions can be made for Urdu and Sanskrit teachers as needed.
- For every additional 35 students beyond 105, one extra teacher will be appointed.
- These measures aim to ensure adequate teacher-student ratios and improve the quality of education in Bihar's schools.
e-ShikshaKosh Portal
- About:
- e-ShikshaKosh is an integrated digital platform designed to streamline educational data management, enhancing decision-making, optimizing resources, and enabling real-time monitoring by consolidating data from various sources.
- Key Benefits
- Enhanced Decision-Making: Consolidates data to improve decision-making and resource optimization.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides up-to-date information for continuous monitoring.
- Efficiency: Addresses inefficiencies, reduces redundancy, and ensures strong governance.
- Comprehensive View: Offers a holistic view of educational metrics.
- Academic Improvement: Supports continuous improvement in academic quality and equity.
- Sustainability & Inclusion: Promotes a sustainable, inclusive, and well-managed learning environment.
- Integrated Functions: Combines multiple educational functions like teaching standards, student performance monitoring, and e-learning programs into one platform.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Potential Petroleum Reserves in Ballia
Why in News?
The Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) has started drilling operations in Ballia, Uttar Pradesh, after geological surveys indicated the possibility of petroleum reserves in the region.
Key Points
- Survey and Exploration: ONGC conducted satellite, geochemical, gravity-magnetic, and magneto-telluric (MT) surveys over the last three years, confirming the possibility of oil and natural gas reserves.
- Magnetotellurics (MT) is a geophysical method that uses natural changes in the Earth's magnetic and electric fields to study underground electrical resistivity.
- Drilling Operations: The project, with an estimated cost of ₹100 crore, involves drilling up to 3,001 meters at a site near Sagar Pali village in Gram Sabha Vaina (Rattuchak).
- Land and Infrastructure: ONGC has leased eight acres of land for three years.
- Potential Impact: If petroleum reserves are confirmed, the project could significantly contribute to the energy sector, boost local employment, and transform the economy of eastern Uttar Pradesh.
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC)
- Oil and Natural Gas Corporation Limited (ONGC), formerly Oil and Natural Gas Commission, was established in 1956.
- In 1994, Oil and Natural Gas Commission was converted into a Corporation, and in 1997 it was recognized as one of the Navratnas by the Government of India.
- Subsequently, it had been conferred with Maharatna status in the year 2010.
- It is the largest crude oil and natural gas company in India, contributing around 70% to Indian domestic production.
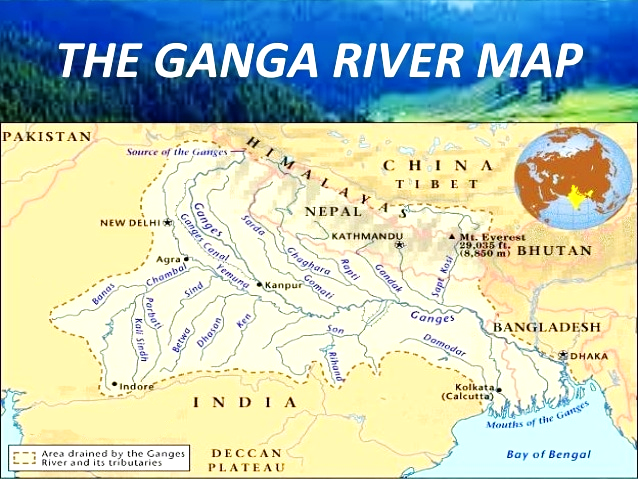
Ganga Basin
- The headwaters of the Ganga called the ‘Bhagirathi’ are fed by the Gangotri Glacier and joined by the Alaknanda at Devprayag in Uttarakhand.
- At Haridwar, Ganga emerges from the mountains to the plains.
- The Ganga is joined by many tributaries from the Himalayas, a few of them being major rivers such as the Yamuna, the Ghaghara, the Gandak, and the Kosi.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan Govt to Introduce Suicide Prevention Bill for Coaching Students
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government, has informed the Rajasthan High Court that it has announced plans to introduce a bill aimed at suicide prevention among coaching students. The Rajasthan HC took suo motu cognizance of the issue.
- This move comes in response to the alarming increase in student suicides, particularly in Kota, known as India’s coaching hub.
Key Points
- Rising Suicides in Kota: Since the start of 2025, six coaching students have died by suicide, adding to the long-standing crisis. Over the past decade, 127 suicide cases have been recorded, with 26 cases in 2023 and 17 in 2024.
- Impact on Kota’s Reputation: The ongoing crisis has negatively affected Kota's status as a coaching hub, leading to declining student enrollments.
- Need for Mental Health Support: The rising cases of student suicides highlight the inadequacy of current measures, emphasizing the need for stronger mental health support and stress management strategies.
Suo Moto Cognizance
- A Suo Moto cognizance is a Latin term which means an action taken by a government agency, court or other central authority on their own apprehension.
- A court takes a Suo Moto Cognizance of a legal matter when it receives information about the violation of rights or breach of duty through media or a third party’s notification.
- Article 32 of the Indian Constitution and Article 226 of the Indian Constitution lay down the provisions for filing Public Interest Litigation (PIL) in Supreme Court and High Courts respectively.
- This has given rise to the court's power to initiate legal action on their cognizance of a matter.
- Suo Moto’s actions by Indian courts are a reflection of judicial activism.
Other Initiatives Related to Suicide Prevention in India
- National Mental Health Programme (NMHP):
- District Mental Health Programme (DMHP) is implemented in 738 districts, offering outpatient services, counselling, continuing care, and a 10-bedded inpatient facility at the district level.
- National Tele Mental Health Programme: Launched in 2022 to improve access to quality mental health counselling and care services across the country.
- As of December 2023, 34 States/UTs have established 46 Tele MANAS Cells, handling over 500,000 calls on the helpline.
- The Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment has launched a 24/7 toll-free helpline "KIRAN" to provide mental health support.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand Implements UCC and Launches Portal
Why in News?
The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) was officially implemented in Uttarakhand making it the first Indian state to implement the UCC post Independence and second state overall after Goa.
- The newly launched UCC portal has enabled individuals to register their marriages online by submitting necessary documents and undergoing a live witness verification process.
Key Points
- Features:
- The UCC Bill, passed by the State Assembly in February 2024, bans practices such as halala, iddat, and talaq (customs related to marriage and divorce in the Muslim Personal Law).
- The UCC mandates online registration of marriages, divorce and live-in relationships.
- A government portal has been formed for the purpose on which people can access records, register complaints and also upload their will on the portal.
- Online Registration Process: The UCC portal requires individuals to submit essential documents, including a birth certificate, Aadhaar card, PAN card, domicile certificate, and details of the spouse. Additionally, two witnesses, either parents or local guardians, must testify via live video.
- The portal features an AI-based translation service that will translate the content into 22 languages, including English.
- Chief Minister’s Endorsement: CM Pushkar Singh Dhami also registered his marriage on the UCC portal and shared his certificate on social media, assuring the
Uniform Civil Code
- About UCC:
- The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) is outlined in Article 44 of the Constitution as part of the Directive Principles of State Policy, which states that the government should strive to establish a uniform civil code for all citizens across India.
- However, its implementation is left to the discretion of the government.
- The Uniform Civil Code (UCC) is outlined in Article 44 of the Constitution as part of the Directive Principles of State Policy, which states that the government should strive to establish a uniform civil code for all citizens across India.
- UCC in Goa:
- Goa follows the Portuguese Civil Code of 1867. The Goa, Daman and Diu Administration Act of 1962 permitted it to retain the colonial-era civil code.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana-Delhi Yamuna Water Dispute
Why in News?
The Haryana-Delhi dispute over the Yamuna river has once again become a key political issue. Delhi Chief Minister (CM) has accused the Haryana government of contaminating the Yamuna with untreated sewage and industrial waste.
Key Points
- Water Contamination Allegations:
- Delhi Chief Minister termed Haryana’s actions as "water terrorism" and wrote to the Election Commission, citing a Delhi Jal Board (DJB) report that claimed ammonia levels in the Yamuna had surged beyond treatable limits.
- The ammonia levels have steadily increased in the water coming from Haryana to Delhi via River Yamuna due to mixing of untreated sewage or industrial waste from Haryana.
- Delhi Chief Minister termed Haryana’s actions as "water terrorism" and wrote to the Election Commission, citing a Delhi Jal Board (DJB) report that claimed ammonia levels in the Yamuna had surged beyond treatable limits.
- Legal and Political History:
- The Yamuna water-sharing dispute is a long-standing dispute, ongoing since 1995.
- 1994 Memorandum of Understanding (MoU): Five states (Delhi, Haryana, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, and Himachal Pradesh) signed an MoU in 1994 to regulate Yamuna water distribution.
- The Supreme Court had intervened in 1995 and 1996 to ensure Delhi’s water supply from Haryana. Despite multiple petitions and legal battles, the issue remains unresolved.
- The Supreme Court has ruled multiple times that Haryana must ensure Delhi’s rightful share of water.
- Recent Developments:
- In 2018, the Supreme Court directed the Chief Secretaries of Delhi and Haryana to resolve water disputes.
- In 2021, the Delhi government accused Haryana of withholding Yamuna water, Haryana countered that Delhi’s crisis was due to "internal mismanagement."
- In July 2023, floods in Delhi led to fresh accusations, with the Delhi Government claiming Haryana deliberately released excess water from the Hathnikund Barrage.
- In June 2024, Delhi CM accused Haryana of "conspiring against Delhi" and launched an indefinite hunger strike, which she ended after five days due to health concerns.
- Impact on Delhi Residents:
- The dispute has led to severe water shortages in Delhi, particularly in summer months.
- Elevated ammonia levels pose a threat to public health, complicating water treatment processes.
- Future Outlook:
- The dispute remains unresolved despite legal interventions.
- The upcoming elections could further intensify political rhetoric around the issue.
- A long-term sustainable solution is needed to address Delhi’s water security concerns.
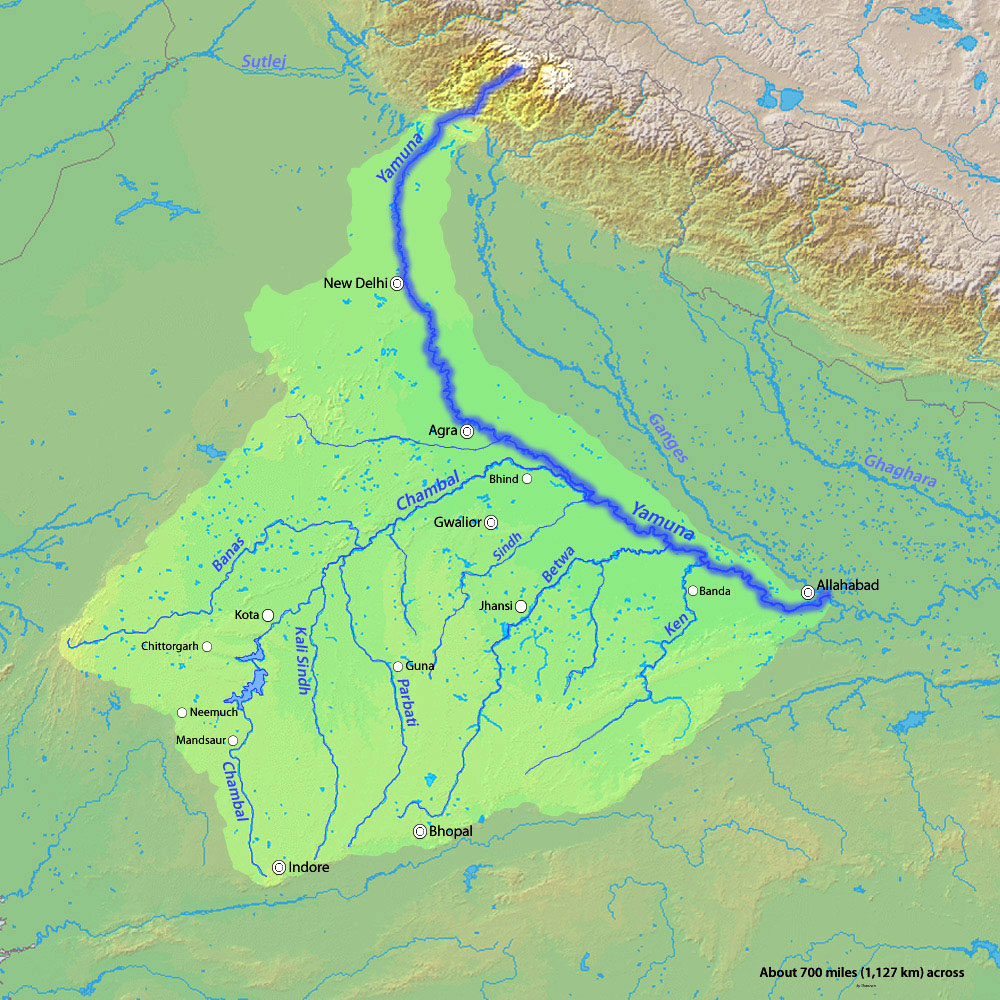
Yamuna
- The river Yamuna, a major tributary of river Ganges, originates from the Yamunotri glacier near Bandarpoonch peaks in the Mussoorie range of the lower Himalayas in Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
- It meets the Ganges at the Sangam in Prayagraj, Uttar Pradesh after flowing through Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Haryana and Delhi.
- Length: 1376 km
- Important Dam: Lakhwar-Vyasi Dam (Uttarakhand), Tajewala Barrage Dam (Haryana) etc.
- Important Tributaries: Chambal, Sindh, Betwa and Ken.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.jpg)
.jpg)