Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
India’s First Pilot Project for Underground Coal Gasification
Why in News?
The Ministry of Coal, Eastern Coalfields Limited (ECL) is conducting a pilot project for Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) at the Kasta coal block in Jamtara District, Jharkhand.
Key Points
- It aims to revolutionise the coal industry by using in-situ coal gasification to convert it into valuable gases such as methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
- These gases can be utilised to produce synthetic natural gas, chemical feedstocks for fuels, fertilizers, explosives, and other industrial applications.
- The Ministry of Coal is fully committed to promoting coal gasification projects, recognizing their potential to transform coal into various high-value chemical products.
- The first phase involves creating a Technical Feasibility Report through borehole drilling and core testing. The next phase will focus on coal gasification at a pilot scale.
- The successful execution of this pilot project is expected to create transformative opportunities for India's energy sector, highlighting the sustainable and efficient use of the country's coal resources.
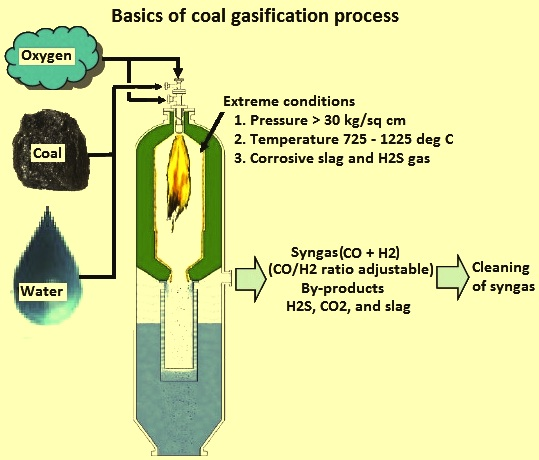
Coal Gasification
- Process: Coal gasification is a process in which coal is partially oxidised with air, oxygen, steam or carbon dioxide to form a fuel gas.
- This gas is then used instead of piped natural gas, methane and others for deriving energy.
- In-situ gasification of coal – or Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) – is the technique of converting coal into gas while it is still in the seam and then extracting it through wells.
- Production of Syngas: It produces Syngas which is a mixture consisting primarily of methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas can be used to produce a wide range of fertilizers, fuels, solvent and synthetic materials.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan