Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Lead in Filing GST Return
Why in News?
According to the Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN), Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Maharashtra are leading in filing Goods and Services Tax (GST) returns monthly, indicating their economic potential.
- GST is a value-added tax levied on most goods and services sold for domestic consumption.
Key Points
- In April 2024, UP, the most populous state in the country, reported over 908,900 GST returns summarizing their monthly transactions (in the form of GSTR-3B).
- While industrialised Tamil Nadu reported over 880,200 GST returns.
- Maharashtra was in third position with over 798,600 GST returns.
- Monthly return filings reflect business activity, compliance levels, revenue potential, tax administration efficiency, and demand for goods and services in the state.
Goods and Services Tax Network (GSTN)
- GSTN has developed an Indirect Taxation platform for GST in India.
- The platform helps taxpayers in preparing, filing returns, making payments, and complying with indirect tax regulations.
- It provides IT infrastructure and services to the Central and State Governments, taxpayers, and other stakeholders.
- GSTN is a not for profit, limited by shares, Government Company. It was incorporated in 2013 under Section 25 of the Companies Act, 1956 (Now Section 8 of the Companies Act, 2013).
- The company is headed by a chairman who is appointed by the Government.
- The Board of GSTN in its 49th Board Meeting held in June 2022 has approved the conversion of GSTN into Government Company and hence 100% of the shareholding being held by Government (50% with Union Government and 50% jointly with State Governments & UTs) in GSTN.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
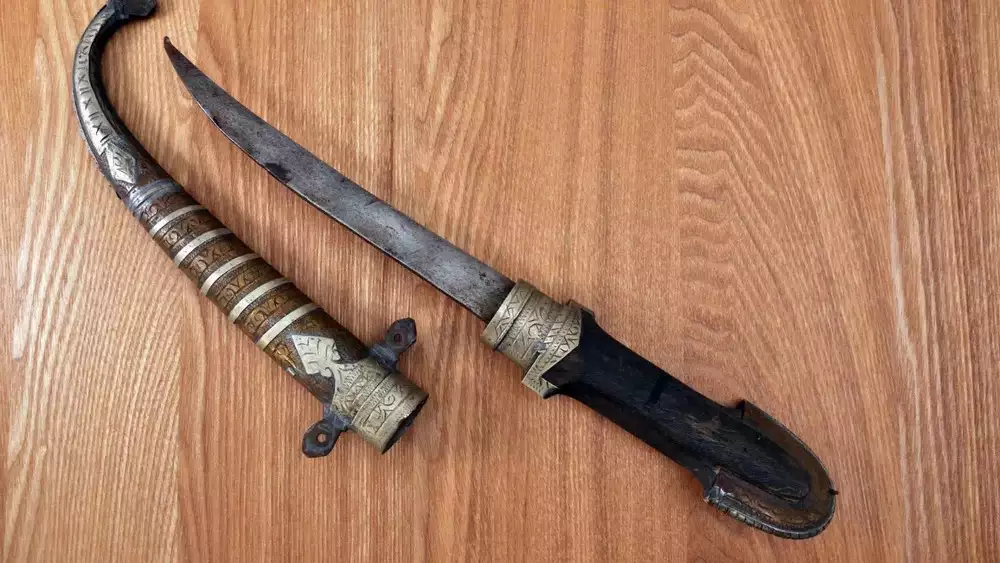
Rampur: City of Knives
Why in News?
Rampur district, in Uttar Pradesh, is celebrated as the "City of Knives" for its renowned Rampuri chaku, a historic blade crafted since the 18th century.
Key Points
- Rampuri chaku were a symbol of the city’s artisanship and a reflection of the royal patronage that valued skill and precision.
- The blade, forged from high-quality steel, was complemented by a handle crafted from various materials, including bone, horn, and ivory.
- The handles were often embellished with ornate carvings, making each knife a piece of art.
- In the mid-1990s, Uttar Pradesh banned the manufacture of knives with blades longer than 4.5 inches. This regulation, aimed at reducing violence, had struck a blow to the traditional knife-making industry of Rampur.
- Despite regulatory challenges in recent decades, artisans uphold its legacy with legal adaptations, maintaining its sharpness and intricate craftsmanship.
- This title honors Rampur's rich cultural heritage, resilience, and commitment to preserving a craft that has defined its identity and captivated knife enthusiasts worldwide.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP-PRAGATI Accelerator Programs (UPPAP)
Why in News?
KisanKraft Ltd, the Bengaluru-based agri-firm has joined the World Bank’s Water Resource Group (WRG)’s low methane rice project to promote the Direct Seeded Rice (DSR) in Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- The company partnered with seed companies Delta Agri Genetics and Savannah Seeds to provide its DSR seed varieties for multi-location trials.
- It has developed 15 new paddy varieties suitable for the DSR cultivation method, which requires less water.
- These varieties do not need stagnant water, reduce water needs by half, and also decrease the use of pesticides and fertilizers.
- The company will conduct the pilots in Rae Bareli, Sitapur, Pratapgarh, Barabanki, Unnao, and Ayodhya districts.
- Rice is India's most crucial food crop, using the largest portion of freshwater and occupying 28% of irrigated lands.
- Due to increasing freshwater scarcity and soil degradation, new technologies like Dry Direct Seeded Rice (dry-DSR) are becoming more popular.
UP-PRAGATI
- UP has launched an accelerator program called UP-PRAGATI in collaboration with the 2030 Water Resources Group, Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation, and the private sector.
- The program aims to promote water-use efficiency and low-carbon practices in agriculture through technological and institutional innovations to boost incomes across the state.
- The UP PRAGATI program aims to promote Direct Seeding of Rice (DSR) across the state over the next five years on 250,000 hectares in collaboration with stakeholders.
Direct Seeded Rice (DSR)
- Direct Seeded Rice (DSR), also known as the 'broadcasting seed technique,' is a water-saving method of sowing paddy.
- In this method, seeds are directly drilled into the fields. In contrast to the traditional water-intensive method of transplanting rice seedlings from a nursery to waterlogged fields, this method saves groundwater.
- There is no nursery preparation or transplantation involved in this method.
- Farmers have to only level their land and give one pre-sowing irrigation.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Birth Anniversary of Sucheta Kriplani
Why in News?
Sucheta Kripalani birth anniversary is celebrated on 25 June, 2024 to commemorate her remarkable contributions as a pioneering figure in the independence movement and Indian politics.
Key Points
- About:
- She was an Indian politician and freedom fighter, born on 25 June 1908 in the Ambala district of Haryana.
- She was among the 15 women who were elected in 1946 as members of the new Indian Constituent Assembly formed to draft the Constitution of India.
- Key Contributions:
- Sucheta Kripalani came to the forefront during the Quit India Movement and was arrested by the British in 1944 for her involvement.
- She was the founder of the women’s wing All India Mahila Congress (AIMC) for the freedom movement during the 1940s.
- She played a crucial role in the rehabilitation of refugees in Noakhali in 1946.
- She became the first woman Chief Minister (Uttar Pradesh, 1963) in India.
Quit India Movement
- On 8th August 1942, Mahatma Gandhi called to end British rule and launched the Quit India Movement at the session of the All-India Congress Committee in Mumbai.
- Gandhiji gave the call “Do or Die” in his speech delivered at the Gowalia Tank Maidan, now popularly known as August Kranti Maidan.
- Aruna Asaf Ali popularly known as the 'Grand Old Lady' of the Independence Movement is known for hoisting the Indian flag at the Gowalia Tank Maidan in Mumbai during the Quit India Movement.
- The slogan ‘Quit India’ was coined by Yusuf Meherally, a socialist and trade unionist who also served as Mayor of Mumbai.
- Meherally had also coined the slogan “Simon Go Back”.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh: Tiger State of India
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has the highest tiger population in the country. Among approximately 3,800 big cats in the wild, 785 of them are in Madhya Pradesh.
- Karnataka for a brief period between 2011 and 2018 had surpassed Madhya Pradesh for the most number of tigers.
Key Points
- The tiger census of 2022 put the population in the country between 3,682 and 3,925, out of which MP tops the list with 785 tigers followed by Karnataka (563), Uttarakhand (560) and Maharashtra (444) respectively.
- Jim Corbett National Park in Uttarakhand tops the list with 260 tigers amongst all the tiger reserves across the country.
- Efforts made by stakeholders including tribals and jungle dwellers besides forest officials who made remarkable progress has also led to conservation of big cat species.
- The first tiger census was conducted in 1972, which recorded the tiger population as 1,827.
- India's tiger population has faced severe threats due to habitat loss, poaching, and human-wildlife conflict.
- In the early 20th century, India had a robust tiger population, but by the 1970s, their numbers had diminished alarmingly.
- In response, the government launched 'Project Tiger' in 1973, which aimed at creating a network of tiger reserves across the country to provide safe habitats for tigers and to curb poaching activities.
- Maintaining the ecological balance and biodiversity of India's forests was also an objective of the project.
Tiger Reserves
- A protected area designated for the conservation of the striped big cats (tigers) is referred to as Tiger Reserve. However, a tiger reserve may also be a national park or wildlife sanctuary.
- For Example: The Sariska Tiger Reserve is also a national park. It is so because the place was originally created as a national park and later dedicated to tiger conservation.
- Tiger Reserves are notified by State Governments as per provisions of Section 38V of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972 on advice of the National Tiger Conservation Authority.
- Presently, India accommodates a total of 54 Tiger Reserves (with the most recent addition being the Dholpur-Karauli Tiger Reserve).


Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
India’s First Pilot Project for Underground Coal Gasification
Why in News?
The Ministry of Coal, Eastern Coalfields Limited (ECL) is conducting a pilot project for Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) at the Kasta coal block in Jamtara District, Jharkhand.
Key Points
- It aims to revolutionise the coal industry by using in-situ coal gasification to convert it into valuable gases such as methane, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and carbon dioxide.
- These gases can be utilised to produce synthetic natural gas, chemical feedstocks for fuels, fertilizers, explosives, and other industrial applications.
- The Ministry of Coal is fully committed to promoting coal gasification projects, recognizing their potential to transform coal into various high-value chemical products.
- The first phase involves creating a Technical Feasibility Report through borehole drilling and core testing. The next phase will focus on coal gasification at a pilot scale.
- The successful execution of this pilot project is expected to create transformative opportunities for India's energy sector, highlighting the sustainable and efficient use of the country's coal resources.
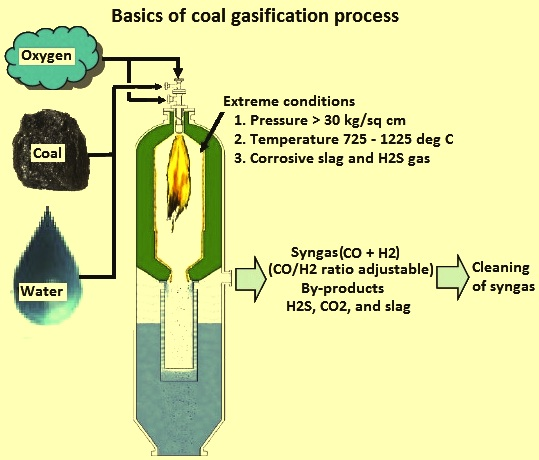
Coal Gasification
- Process: Coal gasification is a process in which coal is partially oxidised with air, oxygen, steam or carbon dioxide to form a fuel gas.
- This gas is then used instead of piped natural gas, methane and others for deriving energy.
- In-situ gasification of coal – or Underground Coal Gasification (UCG) – is the technique of converting coal into gas while it is still in the seam and then extracting it through wells.
- Production of Syngas: It produces Syngas which is a mixture consisting primarily of methane (CH4), carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), carbon dioxide (CO2) and water vapour (H2O).
- Syngas can be used to produce a wide range of fertilizers, fuels, solvent and synthetic materials.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan