Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar’s Land Survey Sparks Mixed Reactions
Why in News?
Bihar's recent land survey aims to update century-old records, impacting ownership claims, especially among marginalized communities.
Key Points
- Historical Background
- Bihar’s last comprehensive land survey dates to the British period in 1910-1911, with partial attempts made in 1967 and 1980.
- The current survey, initiated in 2013, aims to cover all 45,000 revenue villages by 2025 .
- Scope and Process
- Over 10,000 personnel, including land surveyors, have been deployed to digitize over 150 million land records.
- This includes verifying the genealogy charts, critical for proving familial claims to land. Boundary measurement for each landholding is slated for early 2025.
- Challenges Encountered
- Verification of Ownership: Absence of clear partition deeds has led to disputes, with residents struggling to confirm family-owned land as informal, verbal agreements often dictate ownership.
- Document Translation: Historical documents, many written in Kaithi script, require translation and comprehension, creating delays. The government has introduced training to facilitate script translation .
- Technology Hurdles: Poor internet connectivity in rural areas hampers real-time updating and retrieval of records, leading to inconsistencies in uploaded data .
- Social Implications
- Gendered Disputes: A significant issue is the inclusion of women’s inheritance rights, leading to conflicts within families. Married women have faced pressure to relinquish their claims, challenging entrenched patriarchal norms .
- Community Tensions: Land claims have led to violence in some cases, with recent instances of Dalit homes being torched due to boundary disputes with upper-caste communities .
Haryana Switch to Hindi
High Court Mandates CCTV with Audio in Police Stations
Why in News?
The Madhya Pradesh High Court has mandated CCTV installations in all rooms of police stations.
Key Points
- Directive for CCTV Installations
- Justice G. S. Ahluwalia of the Madhya Pradesh High Court directed the state police to install CCTV cameras with audio in every room of police stations across the state within three months.
- The Director General of Police (DGP) must ensure there are no “black spots” (areas not covered by CCTV) in police stations. Failure to comply could lead to contempt of court charges.
- Data Related to Violence in Custody:
- According to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, between 2001 and 2018, only 26 policemen were convicted of custodial violence despite 1,727 such deaths being recorded in India.
- Only 4.3% of the 70 deaths in 2018 were attributed to injuries during custody due to physical assault by police.
- Apart from custodial deaths, more than 2,000 human rights violation cases were also recorded against the police between 2000 and 2018. And only 344 policemen were convicted in those cases.
- According to National Crime Records Bureau (NCRB) data, between 2001 and 2018, only 26 policemen were convicted of custodial violence despite 1,727 such deaths being recorded in India.
National Crime Record Bureau (NCRB)
- NCRB was set-up in 1986 under the Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) to function as a repository of information on crime and criminals so as to assist the investigators in linking crime to the perpetrators.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- It was set up based on the recommendations of the National Police Commission (1977-1981) and the MHA’s Taskforce (1985).
- It was constituted by merging the Directorate of Coordination and Police Computer (DCPC), Inter-State Criminals Data Branch of CBI, Central Finger Print Bureau of CBI and Statistical Branch of BPR&D.
- NCRB brings out the annual comprehensive statistics of crime across the country through ‘Crime in India’ report.
- Being published since 1953, the report serves as a crucial tool in understanding the law and order situation across the country.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
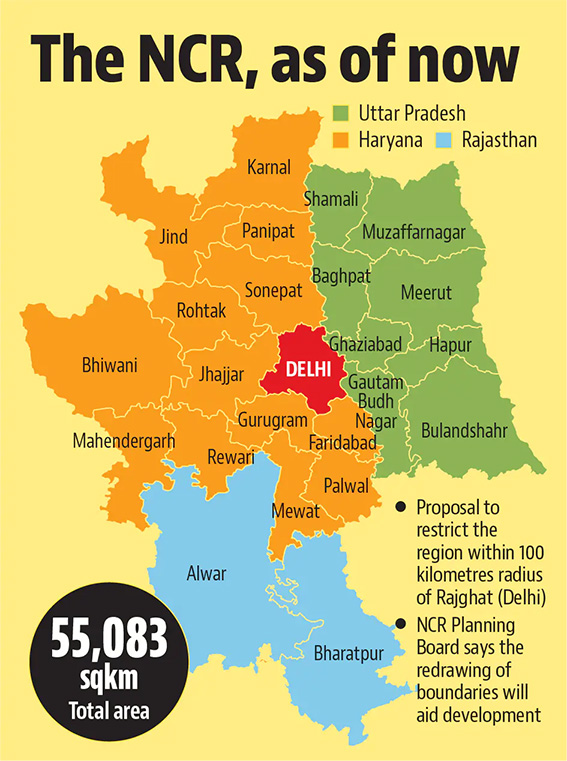
Severe Pollution Crisis in NCR
Why in News?
The National Capital Region (NCR) faces hazardous air quality levels, exacerbated by farm fires and other factors.
Key Points
- Air Quality Index (AQI):
- Panipat AQI reached 450, indicating “severe” pollution; other NCR areas also report rising levels.
- AQI is a tool for effective communication of air quality status to people in terms, which are easy to understand.
- AQI has been developed for eight pollutants viz. PM2.5, PM10, Ammonia, Lead, nitrogen oxides, sulfur dioxide, ozone, and carbon monoxide.
- Primary Causes:
- Stubble burning in nearby states like Haryana and Punjab contributes heavily, alongside vehicular emissions and industrial pollution.
- The high pollution levels pose significant health risks, especially for vulnerable groups, leading to calls for emergency measures.
| Air Quality Index (AQI) | Category |
| 0-50 | Good |
| 51-100 | Satisfactory |
| 101-200 | Moderate |
| 201- 300 | Poor |
| 301-400 | Very Poor |
| 401-500 | Severe |




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan