Haryana Switch to Hindi
National Highway Projects in Haryana
Why in News?
In a recent rally at Gurgaon ahead of the Haryana Assembly polls on 5th October, the Union Minister highlighted major infrastructure projects and compared Haryana’s upcoming national highways to the US by 2024.
Key Points
- Current and Upcoming Projects:
- The Ministry of Road Transport and Highways has completed or initiated projects worth Rs. 2 lakh crore in Haryana, including:
- Tenders for 9 foot-overbridges for Gurgaon and Rewari will be floated in October, and work on 4 new flyovers will commence within two months.
- Sonipat to Jind 352A National Highway:
- This highway will ease travel between Sonipat and Jind. The total length is 80 km, divided into two sections: Sonipat-Gohana and Gohana-Jind.
- Jind-Panipat State Highway:
- Haryana is spending Rs. 170 crore on this highway under the Central Road Fund scheme. It will benefit commuters traveling between Jind and Panipat.
- 152D National Highway:
- Completed, this highway shortens the travel time from Jind to Ambala and Chandigarh from 3-4 hours to 2 hours, improving connections to Delhi and Rajasthan as well.
- Rohtak-Jind and Narwana National Highway 352:
- This highway, now complete, eases travel from Jind to Rohtak, Delhi, and Punjab.
- Panipat-Dabwali National Highway:
- This upcoming project will connect Karnal, Jind, Panipat, Fatehabad, and Sirsa, simplifying travel from Jind to Sirsa.
- Jammu-Katra and Delhi National Highway:
- Currently under construction by NHAI, this highway will pass through Jind’s Pilukhra, enhancing connectivity between Jammu, Delhi, and Jind while reducing traffic in surrounding areas.
National Highways Authority of India (NHAI)
- It was set up under NHAI Act, 1988. It is under the administrative control of the Ministry of Road Transport and Highways.
- It has been entrusted with the National Highways Development Project, along with other minor projects for development, maintenance and management.
- National Highways Development Project (NHDP) is a project to upgrade, rehabilitate and widen major highways in India to a higher standard. The project was started in 1998.
- NHAI maintains the National Highways network to global standards and cost effective manner and promotes economic well being and quality of life of the people.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
36 Biradaris
Why in News?
Recently, as the Haryana Assembly elections approach, political parties frequently refer to the “36 biradaris” to signal their commitment to various caste groups.
Key Points
- Meaning of Biradari:
- Derived from the Persian word baradar, meaning "brotherhood" or "clan."
- In North India, biradari is often synonymous with caste, though terms like kaum or jaat may also be used.
- Origin of '36 Biradaris':
- The phrase "36 biradaris" is not literal; it generally refers to various caste groups.
- Historical sources, such as the Ajmer-Merwar Gazetteer and Lt. Col. James Todd’s writings, mention 36 dynasties or communities in medieval North India.
- Social Role:
- Biradaris are akin to extended families and play roles in marriages, caste disputes, and social identity.
- The concept promotes unity and social security, especially in Haryana, Punjab, and Rajasthan.
National Party
- About: As the name suggests, it has a nationwide presence as opposed to a regional party that is restricted to only a particular state or region.
- A certain stature is sometimes associated with being a national party, but this does not necessarily translate into having a lot of national political influence.
- Conditions for Declaring a Party ‘National’:
- As per the ECI’s Political Parties and Election Symbols, 2019 handbook, a political party would be considered a national party if:
- It is ‘recognised’ in four or more states
- If its candidates have secured at least 6% of total valid votes in at least 4 states (in latest Lok Sabha or Assembly elections) and the party has at least 4 MPs in the last LS polls
- If it has won at least 2% of the total seats in the LS from at least 3 states.
- As per the ECI’s Political Parties and Election Symbols, 2019 handbook, a political party would be considered a national party if:
State Party
- A party is recognised as a state party in a state if any of the following conditions is fulfilled:
- If it secures 6% of the valid votes polled in the state at a general election to the respective state legislative assembly (state LA) and also, it wins 2 seats in the same state LA.
- If it secures 6% of the total valid votes in the state at a general election to the LS; and also, it wins 1 seat in the LS from the same state.
- If it wins 3% of seats in the LA at a general election to the legislative assembly of the state concerned or 3 seats in the assembly (whichever is more).
- If it wins 1 seat in the LS for every 25 seats or any fraction thereof allotted to the state at a general election to the LS from the state concerned.
- If it secures 8% of the total valid votes polled in the state at a General Election to the LS from the state or to the State LA.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Crack Down on Food Adulteration
Why in News?
Recently, Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister issued new directives to combat food adulteration in the state.
Key Points
- Display of Proprietors' Names:
- All restaurants and eateries must prominently display the names and addresses of their operators, proprietors, managers, and other key staff.
- The move is aimed at ensuring transparency and accountability in food establishments.
- Amendment to Food Safety Act:
- Amendments to the Food Safety and Standards Act, 2006 will be made to enforce compliance with the new display rules.
- A state-wide verification campaign will be conducted, involving the Food Safety and Drug Administration, Police, and Local Administration.
- Mandatory CCTV Installation:
- All eateries, hotels, and dhabas must install CCTV cameras covering both dining areas and other sections of the establishment.
- Operators are responsible for securely storing CCTV footage and providing it to law enforcement upon request.
- Public Health and Hygiene:
- The directives are part of the state’s response to food adulteration cases where human waste and other contaminants were found in food.
- Strict hygiene practices will be enforced, including mandatory use of masks and gloves for all food preparation and serving staff.
FSSAI
- The Food Safety and Standards Act (FSSAI), established in 2006, serves as India's primary legislation for regulating food safety. It sets standards for food products and oversees their manufacture, storage, distribution, sale, and import. The Act aims to ensure the availability of safe and wholesome food for consumers.
- Key features of the FSSAI Act, 2006 :
- Unified Food Laws: It consolidates multiple food laws into one unified system, establishing clear standards for food safety and quality.
- Powers to State Governments: The Act allows state governments to frame rules and take measures to regulate food safety at the local level, such as conducting inspections, ensuring compliance, and initiating actions against violations.
- Food Safety Authority: The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) was created under this Act to set food standards, conduct food safety audits, and promote safe food practices.
- The Act empowers both central and state authorities to maintain strict vigilance on food safety and take action in case of non-compliance, such as the recent directives issued by Uttar Pradesh to address food adulteration concerns.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
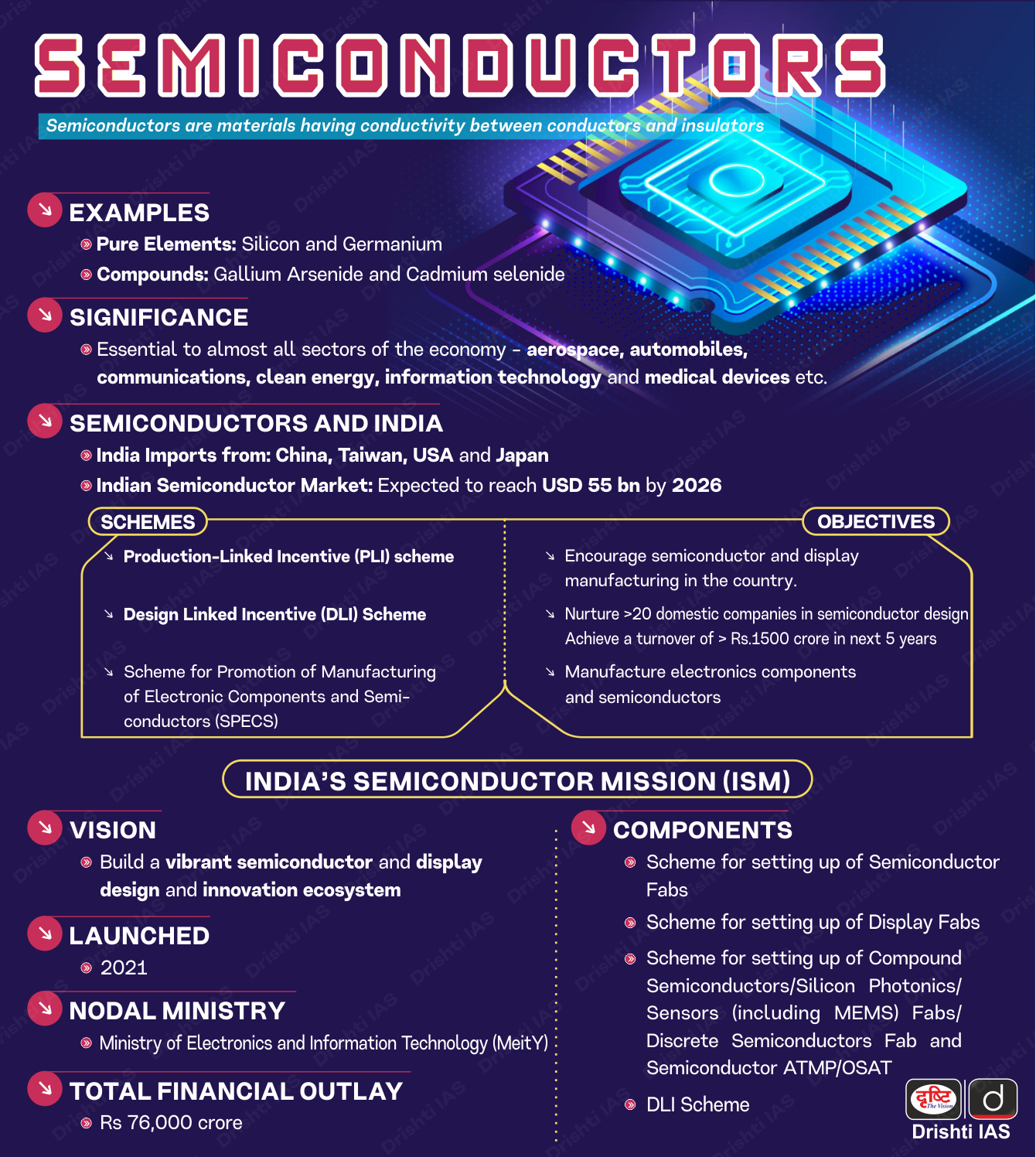
Semiconductor Facility in UP
Why in News?
Recently, it was announced that Uttar Pradesh is set to have its first semiconductor manufacturing unit, marking a significant development in India's tech sector and positioning the state as a critical player in the country's digital transformation.
Key Points
- India-US Semiconductor Partnership:
- The announcement follows a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) signed between India and the US to collaborate on chip manufacturing.
- The India-US partnership in semiconductor development will have a far-reaching impact on India’s technological advancements.
- Importance for Digital Transformation:
- Semiconductors are critical for India's digital transformation goals and will become increasingly visible in daily life.
- This development is part of a broader initiative to leverage technology for India's progress, extending its benefits to rural and interior areas.
- Cybersecurity Focus:
- The semiconductor industry is also seen as crucial for strengthening cybersecurity, given the shift in warfare from physical attacks to the cyber realm.
- Economic Impact:
- The establishment of this facility will contribute to macroeconomic growth, with India’s economy being described as resilient and on a strong growth trajectory.
- The Indo-US bilateral ties are now mutually beneficial, contributing to India’s ongoing economic development.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Voting Turnout in Jammu & Kashmir
Why in News?
Recently, Jammu & Kashmir recorded a 56.79% voter turnout in the second phase of its 2024 assembly elections.
- This election is the first since the abrogation of Article 370 in 2019 and marks the first assembly elections in a decade for the Union Territory.
Key Points
- Second Phase of Voting:
- Voting took place in 26 assembly seats across six districts (three in Jammu division, three in Kashmir Valley).
- A total of 56.79% voter turnout was recorded in this phase.
- 2.5 million voters were eligible to vote, including 1.20 lakh first-time voters aged 18-19.
- Key Districts & Constituencies:
- Kashmir Valley: 15 seats including Ganderbal, Srinagar, Budgam.
- Jammu Division: 11 seats including Reasi, Rajouri, Poonch.
- Highest Turnout: Reasi (71.81%) and Poonch (71.59%).
- Lowest Turnout: Srinagar (27.31%) and Habbakadal (11.1%).
- Polling Stations:
- A total of 3,502 polling stations were set up across the 26 constituencies.
- 100% webcasting was conducted at all polling stations for transparency.
- Phases of Election:
- First phase held on 18th September recorded a 61% turnout.
- The final phase of voting will be held on 1st October, 2024.
Kashmir Valley
- Geography and Climate:
- The Kashmir Valley is situated between the Himalayas and the Pir Panjal range, covering approximately 55,538 square kilometers. It experiences a temperate climate with distinct seasons.
- Cultural Diversity:
- The region is home to a diverse population, including Kashmiri Muslims, Hindus, Sikhs, and Buddhists, renowned for its rich cuisine, handicrafts like Pashmina shawls, and vibrant festivals.
- Protected Areas:
- The Kashmir Valley is home to several protected areas, including Gulmarg Biosphere Reserve and Hemis National Park, which are vital for conserving its unique flora and fauna, including critically endangered species like the Hangul deer.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan