Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Chinar Boat Race
Why in News?
Recently, the famous Chinar boat race 2024 was organised in Jammu and Kashmir’s Dal Lake by the Indian Army.
Key Points
- About the Race:
- The Indian Army, in collaboration with White Globe NGO and the Lake Conservation and Management Authority (LCMA), successfully organised the Chinar Boat Race 2024.
- A total of 60 boats competed enthusiastically, reflecting the vibrant cultural traditions of Kashmir.
- Winners and Awards:
- First Prize: Cash prize of Rs 10,000 and a trophy.
- Second Prize: Rs 7,500.
- Third Prize: Rs 5,000.
- Consolation Prizes: Distributed to the top 20 participants to recognise their efforts.
- Purpose and Message:
- The event celebrated the rich culture and tradition of Kashmir.
- It highlighted the importance of protecting Kashmir’s water bodies, especially Dal Lake.
- Fostered a sense of community through traditional sports, promoting ecological health.
- Army's Role in J&K:
- The Indian Army continues to organise sports and cultural events to strengthen ties with the local population.
- These efforts enable the Army to serve the community effectively during natural disasters like earthquakes and floods.
- Such events inspire local youth to pursue honourable professions, including joining the Army.
- The Indian Army continues to organise sports and cultural events to strengthen ties with the local population.
Dal Lake
- It is a lake in Srinagar, the capital of the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir (J&K).
- It is one of the world's largest natural lakes and the second largest lake in J&K.
- It is integral to tourism and recreation in Kashmir and is named the “Jewel in the crown of Kashmir” or “Srinagar’s Jewel”.
- It is also an important source for commercial operations in fishing and water plant harvesting.
- It covers an area of 18 square kilometres and is part of a natural wetland including its floating gardens.
- The floating gardens, known as “Raad” in Kashmiri, blossom with lotus flowers during July and August.
Chinar Tree
- About:
- The Chinar, also known as the Oriental plane, is a large, deciduous tree that is native to the Western Himalayas and is a symbol of Kashmir.
- It is an important part of Kashmiri culture and tradition. There is a Chinar tree in almost every village in Kashmir, and the oldest Chinar in Kashmir is over 600 years old.
- Appearance:
- The Chinar tree has maple-like leaves that are deep green in the summer and change to red, amber, and yellow in the fall. It has a spreading crown and flaking bark.
- Uses:
- The leaves and bark of Chinar are used for medicinal purposes.
- The wood, also known as lacewood, is used to make fine furniture.
- Twigs and roots are used to make fabric dye.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Public Durbar in Kathua
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister of Personnel, Public Grievances, Pensions conducted a "Public Durbar" in block Marheen, district Kathua of Jammu and Kashmir.
- It is part of his outreach initiative, in which he directly engaged with the public to address their issues and concerns.
Key Points
- Outcomes of the Public Durbar:
- Several issues raised by individual citizens and delegations were resolved on the spot.
- Instructions for immediate action in several other cases were issued.
- This marked the third Public Durbar held in different parts of Kathua district in recent months, showcasing sustained public engagement.
- Several issues raised by individual citizens and delegations were resolved on the spot.
- Commitment to Public Service:
- It was emphasized that elected leaders must address genuine public needs while reassuring citizens that their concerns are valued and heard.
- Such events bridge the gap between the public and administration, fulfilling the government's promise to serve citizens effectively.
- Focus of the Government:
- Serving common citizens.
- Reducing public inconvenience.
- Delivering services at citizens’ doorsteps to enhance their ease of living.
- Rising above narrow considerations of politics, caste, creed, and region.
- Guided by the motto of Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas, Public Durbars are used as a platform to connect with citizens, ensuring their issues are addressed comprehensively.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Hemant Soren to Take Oath as Jharkhand CM
Why in News?
Jharkhand Mukti Morcha (JMM) leader Hemant Soren will take oath as the new Chief Minister of Jharkhand on 28th November 2024.
Key Points
- Governor's Decision:
- The Governor accepted Hemant Soren’s resignation and appointed him as the nominated Chief Minister, asking him to continue until the new government is formed.
- Governor's Role (Now LG)
- Under Article 164, the Governor plays a key role in inviting the leader of the majority party or coalition to form the government.
- The governor ensures the formation of a government that enjoys majority support in the legislature.
- Oath of Office
- As per Article 164(3), the Governor of a state must administer the oaths of office and secrecy to a Minister before they take office.
- The oath signifies allegiance to the Constitution and the discharge of duties in accordance with the law.
Appointment of Chief Minister
- Article 164 of the Constitution envisages that the Chief Minister shall be appointed by the governor.
- A leader of the party that has got the majority share of votes in the assembly elections, is appointed as the Chief Minister of the state.
- The Governor is the nominal executive authority, but real executive authority rests with the Chief Minister.
- However, the discretionary powers enjoyed by the governor reduces to some extent the power, authority, influence, prestige and role of the Chief Minister in the state administration.
- A person who is not a member of the state legislature can be appointed as Chief Minister for six months, within which time, he should be elected to the state legislature, failing which he ceases to be the Chief Minister.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
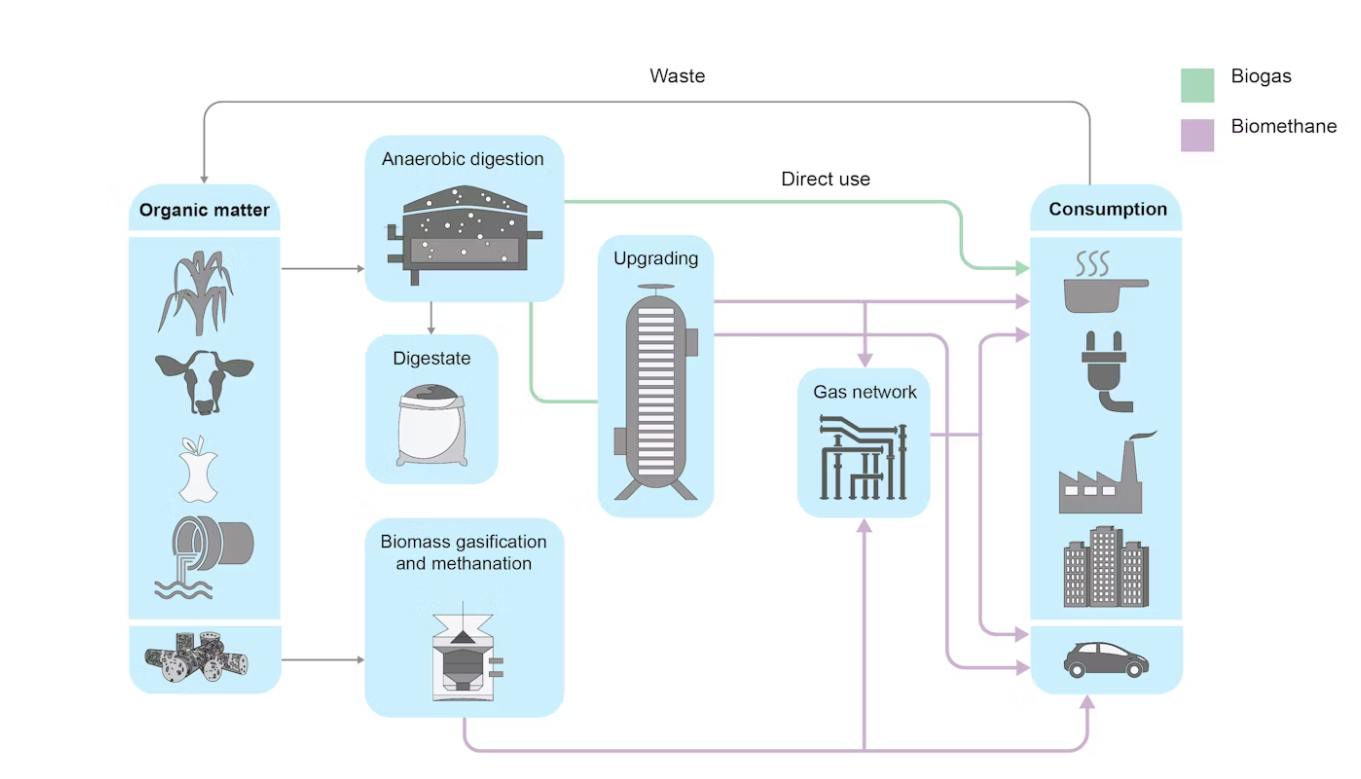
Compressed Biogas Plant in Gwalior
Why in News?
Recently, India's first modern and self-sufficient gaushala with a state-of-the-art Compressed Biogas (CBG) plant was launched in Gwalior, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- Location and Management:
- The CBG plant is located at Adarsh Gaushala, the largest cowshed in Gwalior, managed by the Gwalior Municipal Corporation. It houses over 10,000 cattle.
- Unique Achievement:
- Madhya Pradesh’s first CBG plant producing biogas from cattle dung and organic waste like vegetable and fruit waste collected from local mandis and homes.
- Technology and Output:
- Produces 2-3 tons of Bio-CNG daily from 100 tons of cattle dung.
- Generates 10-15 tons of dry bio-manure daily, supporting organic farming.
- Incorporates windrow composting for additional organic waste processing.
- Windrow composting is a method of composting organic waste that involves stacking the waste into long, narrow piles called windrows and regularly turning them.
- It is considered to be a cost-effective method of composting, but it can also produce the most emissions.
- Environmental Benefits:
- Converts cow dung and organic waste into Bio-CNG and organic manure, reducing carbon emissions significantly.
- Provides a cleaner, eco-friendly alternative to fossil fuels, contributing to climate change mitigation.
- Transforms underutilized resources like cow dung into valuable energy and fertilizer, promoting circular economy practices.
- Economic and Social Impact:
- Creates jobs for locals, boosting the economy while promoting green energy skills.
- Provides affordable bio-manure to farmers in nearby districts, encouraging organic farming practices.
- Model for Sustainable Development:
- As India’s first self-reliant gaushala, the Laltipara plant serves as a pioneering model for other regions to adopt.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Good Governance Conference in Raipur
Why in News?
Recently, At the 2-day Conference on Good Governance in Raipur, the Union Minister of State (Independent Charge) for Science and Technology emphasized that the governance reforms initiated under Prime Minister prioritize "ease of living" and transparency.
Key Points
- Event Details:
- Organized jointly by the Department of Administrative Reforms & Grievance Redressal (DARPG) and the Government of Chhattisgarh.
- Brought together policymakers, bureaucrats, and experts to discuss public service delivery reforms.
- Decentralizing Governance Discussions:
- The significance of moving governance discussions beyond central halls of power was emphasized.
- Conferences held across states ensure solutions tailored to regional needs and foster collaboration between the Centre and States.
- Similar events have been conducted in J&K, Arunachal Pradesh, Goa, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Tamil Nadu, and others, reflecting nationwide outreach.
- Landmark Governance Reforms:
- Over 2,000 obsolete rules have been removed to reduce bureaucratic red tape.
- Simplified administrative procedures by scrapping the requirement for attested documents, reinforcing trust in citizens.
- Introduced face-recognition technology for pensioners, eliminating the need for physical verification.
- Expanded digitization of pension and family entitlement systems for timely disbursal.
- Eliminated interviews for Group B and C posts, reducing bias and corruption in recruitment processes.
- Impact of the Reforms:
- Governance reforms aim to reduce delays, combat corruption, and simplify administrative processes for citizens.
- Leveraged technology to enhance efficiency, especially benefiting senior citizens and rural populations.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Core Cold Wave Zone
Why in News?
The National Programme on Climate Change and Human Health (NPCCHH), under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has a public advisory on cold wave conditions for Rajasthan and 16 other states and Union Territories.
Key Points
- Cold Wave Season and Core Cold Wave Zone:
- A cold wave is a rapid fall in temperature within 24 hours to a level requiring substantially increased protection to agriculture, industry, commerce, and social activities.
- The cold wave season spans from November to March, with December and January experiencing the most extreme cold events.
- Affected Regions:
- Telangana, Punjab, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Jammu and Kashmir, Ladakh, Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Bihar, Jharkhand, West Bengal, and Odisha.
- Vulnerable Groups:
- The advisory identifies the following populations as particularly at risk:
- Homeless individuals
- Elderly people
- Economically disadvantaged individuals
- Pregnant and lactating women
- Children
- Outdoor workers and farmers
- Managers of night shelters
- The advisory identifies the following populations as particularly at risk:
- Definition of a Cold Wave:
- According to Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) Standards:
- For plains, a cold wave occurs when the minimum temperature is ≤10°C.
- For hilly regions, it is defined as a minimum temperature of ≤0°C.
- According to Indian Meteorological Department (IMD) Standards:
- Potential Health Issues:
- Hypothermia is caused by prolonged exposure to very low temperatures.
- Frostbite is damage to skin and tissues due to freezing temperatures.
- Non-freezing Cold Injuries are conditions like Immersion Foot, resulting from prolonged exposure to cold and wet conditions.
- In severe cases, cold exposure can lead to fatalities if precautions are not taken.
India Meteorological Department
- IMD was established in 1875.
- It is an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is the principal agency responsible for meteorological observations, weather forecasting and seismology.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan