Haryana Switch to Hindi
Observers for Haryana Assembly Elections
Why in News?
According to the sources, The Election Commission of India would deploy over 400 observers for the Assembly elections in Haryana and Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Points
- The poll body deploys observers under Section 20B of the Representation of the People Act, 1951 and plenary powers of the Constitution.
- In a meeting, the Election Commissioner emphasised that the officials should observe the complete election ecosystem for free and fair polls and asserted that the role of observers becomes all the more critical in these elections.
- The observers were strictly directed to remain accessible to all parties, candidates and voters for timely redressal of their grievances.
Section 20B in The Representation of the People Act, 1951
- The Election Commission may nominate a Government officer as an Observer to monitor the conduct of elections in a constituency or group of constituencies and perform other functions entrusted by the Commission.
- The Observer shall have the power to direct the returning officer to stop the counting of votes or not to declare the result if in the observer's opinion booth capturing has taken place at a large number of polling stations or ballot papers are unlawfully taken, destroyed, lost, or tampered with to such an extent that the result of the poll cannot be ascertained.
- Then the Observer shall report the matter to the Election Commission.
Election Commission of India
- It is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India.
- It was established in accordance with the Constitution on 25th January 1950 (celebrated as National Voters' Day). The secretariat of the commission is in New Delhi.
- The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, and State Legislative Assemblies in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country.
- It is not concerned with the elections to panchayats and municipalities in the states. For this, the Constitution of India provides for a separate State Election Commission.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Recommendation for Bifurcation of SC Quota in Haryana
Why in News?
Recently, The Haryana State Commission for Scheduled Castes has recommended that one-half of the 20% quota reserved for the Scheduled Castes in government jobs will be set aside for candidates from deprived Scheduled Castes.
- It comprises 36 castes such as Balmikis, Dhanaks, Khatik and Mazhabi Sikhs.
Key Points
- The commission conducted a data analysis to ascertain the inadequacy of representation of Scheduled Castes (SCs) in public employment because of their backwardness.
- The commission's report to the council of ministers recommends that if suitable candidates from deprived Scheduled Castes are unavailable, candidates from other Scheduled Castes, including Chamars, Jatav, Mochi, Raigars, Ramdasias, and Ravidasisas, may be considered to fill vacant posts.
- It also suggests reserving half of the 20% Scheduled Caste quota for candidates from other Scheduled Castes.
- If candidates from these groups are unavailable, candidates from deprived Scheduled Castes may be considered.
- The report emphasizes that the order of seniority will be based on a common merit list without the need for separate points within the existing system.
- According to The Supreme Court, the state can sub-classify SCs based on factors such as inadequate representation of certain castes.
- However, it stipulated that the state must demonstrate that the inadequate representation of a caste or group is due to its backwardness, and must gather data on the inadequacy of representation in the state's services, as it is used as an indicator of backwardness.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Use of AI for School Education in Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
According to the officials, Chhattisgarh government’s education department is using Artificial Intelligence (AI) to improve school education and programmes like midday meals.
Key Points
- AI systems are being utilized to track student performance, oversee sanitation, monitor toilet cleanliness, and assess manpower status.
- Additionally, a geo-fenced attendance system will be implemented to ensure teacher presence in schools, enhancing accountability and student safety.
- AI-powered systems will be used in monitoring food by analysing vegetable freshness, rice texture, and oil content to objectively assess meal quality.
- The state government is collaborating with the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) Bhilai to develop software and mobile apps for monitoring schools and students.
- Vidya Samiksha Kendra is set up in Raipur to implement the AI system. It will be used for online monitoring and data analysis of various beneficiary-oriented schemes operated by the school education department.
- Information and facilities related to government schemes will be available to students, parents and teachers.
- A toll-free phone number will be issued to solve problems related to students, parents, and teachers.
Vidya Samiksha Kendras (VSKs)
- VSK is aimed at leveraging data and technology to bring a big leap in learning outcomes.
- This will cover data of more than 15 Lakh schools, 96 Lakh teachers and 26 Crore students and analyze them meaningfully using big data analysis, Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning in order to enhance the overall monitoring of the education system and thereby improving learning outcomes.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Performance Review of Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Minister for Finance and Corporate Affairs chaired a meeting to review performance of nine Regional Rural Banks (RRBs) in Udaipur.
Key Points
- RRBs of the states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Rajasthan were reviewed.
- The meeting focused on business performance, digital technology upgrades, MSME (Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises) cluster growth, and rural financial inclusion.
- The Union Minister directed:
- the State Level Bankers’ Committee (SLBC) to hold meetings with State Government, Sponsor Banks and RRBs to improve performance of MUDRA scheme and other financial inclusion schemes in Bundelkhand and aspirational districts.
- RRBs to generate awareness and provide credit under the PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana scheme in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- RRBs to identify potential trades under PM Vishwakarma scheme and increase their share in ground level agriculture credit disbursement to achieve the stated objectives of Priority Sector Lending.
Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- RRBs were established in 1975 under the provisions of the Ordinance promulgated on 26th September 1975 and Regional Rural Banks Act, 1976.
- These are financial institutions which ensure adequate credit for agriculture and other rural sectors.
- They combine the characteristics of a cooperative in terms of the familiarity of the rural problems and a commercial bank in terms of its professionalism and ability to mobilise financial resources.
- After the reforms in the 1990s, the government in 2005-06 initiated a consolidation program that resulted in the number of RRBs declining from 196 in 2005 to 43 in FY21, and 30 of the 43 RRBs reported net profits.
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana (PMMY)
- PMMY was launched by the Government of India in 2015.
- The PMMY provides collateral-free institutional loans up to Rs. 10 lakhs for small business enterprises.
- It is provided by Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) i.e. Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs).
PM Surya Ghar Muft Bijli Yojana
- The government introduced the Programme in 2014 to promote rooftop solar installation.
- The original target was 40 GW installed capacity (out of 100 GW by 2030) by 2022 but the goal was not met by 2022, the deadline was extended to 2026.
- Rooftop solar panels are photovoltaic panels installed on the roof of a building and connected to the main power supply unit.
- Its objective is to promote grid-connected solar rooftop systems on residential buildings.
- Key Initiatives under Rooftop Solar:
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
SLCR Project in Varanasi
Why in News?
Recently, The Green Strategic Partnership between the Governments of India and Denmark has facilitated major cooperation, resulting in the establishment of the Smart Laboratory on Clean Rivers (SLCR) in Varanasi.
Key Points
- It is a unique tripartite initiative between the Government of India (Department of Water Resources, River Development and Ganga Rejuvenation), the Indian Institute of Technology - Banaras Hindu University (IIT-BHU), and Government of Denmark, to bring excellence in small river rejuvenation and management.
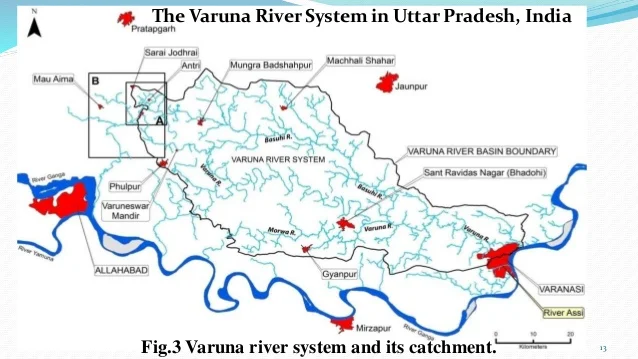
- The SLCR seeks to restore the Varuna River using sustainable methods.
- Its goals include establishing a collaborative platform for government agencies, academic institutions, and local communities to exchange knowledge and devise solutions for maintaining clean river water.
- The initiative includes a hybrid lab model at IIT-BHU and a living lab on the Varuna River to test and scale solutions in real-world environments.
- The Indo-Danish Joint Steering Committee (JSC) is the highest forum for SLCR which provides strategic guidance and reviews progress.
- The Project Review Committee (PRC), with members from National Mission on Clean Ganga (NMCG), Central Water Commission (CWC), Central Ground Water Board (CGWB), IIT-BHU and Denmark's Urban Sector Counsellor will oversee quality control at project level.
- Four projects to be taken up under the collaboration. These are:
- The First project involves creating a Decision Support System (DSS) for water management, designed to analyze basin water dynamics using hydrological models, scenario generation, forecasting, and data analytics.
- The second project focuses on the characterization of emerging pollutants and fingerprint analysis. It will use advanced analytical techniques, such as chromatography and mass spectrometry, to identify and quantify contaminants.
- The Hydrogeological Model of the Varuna Basin for Recharge Sites will be the fourth project. It aims to enhance base flow through Managed Aquifer Recharge (MAR).
Varuna River
- It is a Minor Tributary of the Ganga River. It rises from Phulpur town in the Prayagraj district.
- It flows into the Ganges river near Sarai Mohana village in the Varanasi district.
- The name 'Varanasi' district is derived from the names of Two rivers, Varuna and Assi rivers.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan