Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Extreme Weather Events in J&K
Why in News?
The occurrence of cloudburst, flash flood, and landslide, in Ramban, Jammu & Kashmir caused deaths, damaged buildings, disrupted transport, and displaced many. This highlights the issue of increasing frequency of extreme weather events in the ecologically sensitive Himalayan region.
Key Points
Cloudburst
- A cloudburst is a localised extreme rainfall event, defined as 10 cm or more rainfall within an hour over an area of approximately 10 km².
- The phenomenon is common in hilly regions due to orographic lift—where warm air rises along mountain slopes, cools rapidly at higher altitudes, and releases accumulated moisture as sudden, intense rainfall.
- Cloudbursts are difficult to predict or monitor due to their localized and short-lived nature.
- It can trigger flash floods and landslides by overwhelming natural and artificial drainage.
- Cloudbursts in Himachal Pradesh (2024) and Uttarakhand (2021) caused fatal floods, landslides, and extensive damage to infrastructure.
Flash Floods
- A flash flood occurs when sudden, intense rainfall leads to rapid runoff into rivers, streams, and drainage systems, especially in rocky terrains that have low water absorption capacity.
- These floods are short-lived but violent, and can result in serious loss of life, unlike riverine floods that are slower but more damaging to property.
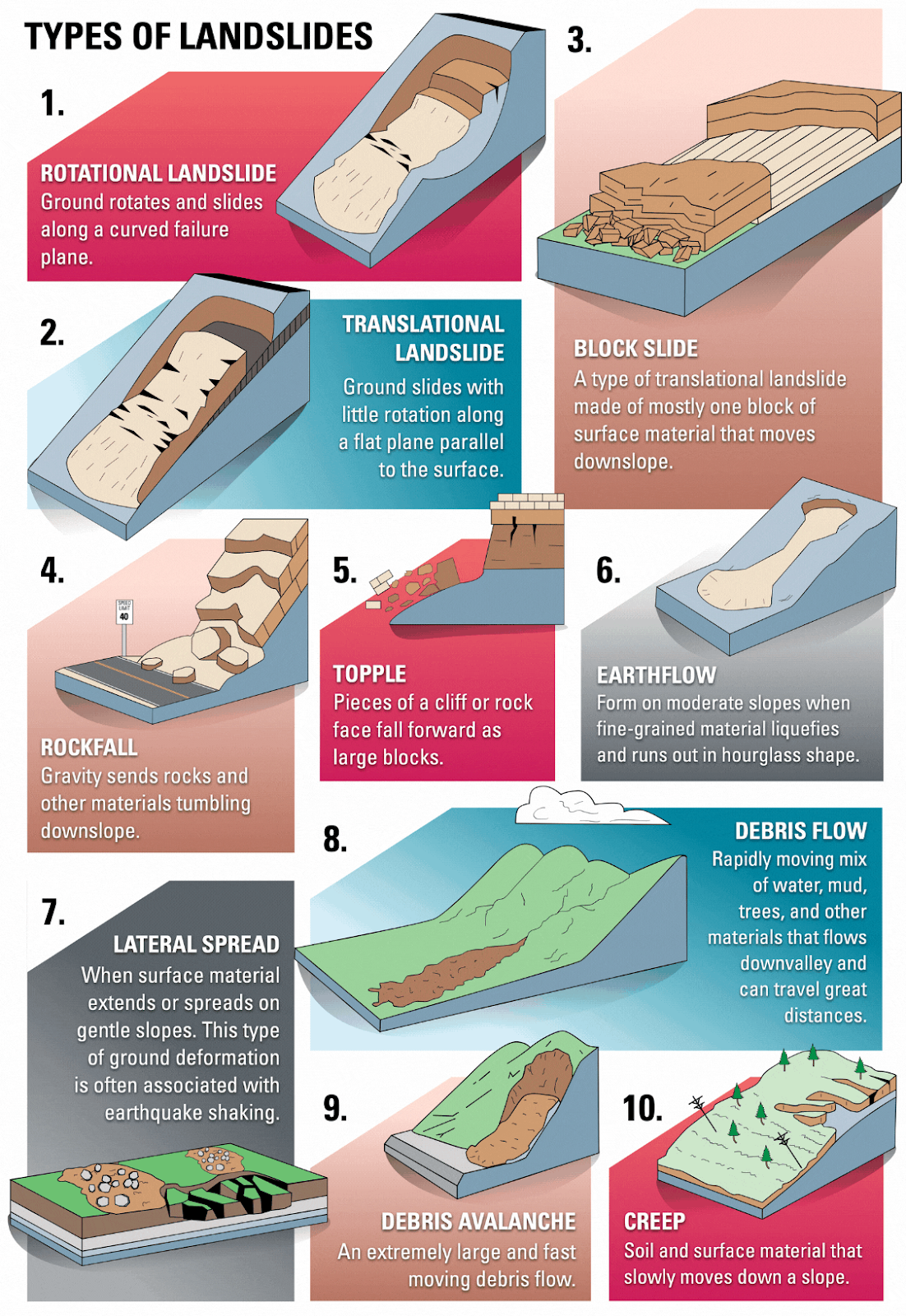
Landslide
- A landslide is the downward movement of soil, rocks, and debris due to gravity, often triggered by water infiltration.
- Excess rainfall reduces soil strength and friction, making it easier for slopes to fail.
- Landslides in hilly areas block roads, destroy homes, and even cause secondary flooding by displacing water bodies.
- The 2021 Chamoli landslide, triggered by heavy rain and a glacier burst, led to widespread flooding and fatalities.
Why Himalayan Regions Like Ramban Are Vulnerable?
- The Himalayas are young fold mountains, tectonically active and prone to erosion, making the region naturally unstable.
- Roads, buildings, and dams are often built without adequate slope stabilization or environmental assessments, increasing the risk of disaster.
- Loss of vegetation reduces soil cohesion, which increases the chances of landslides and slope failure.
- The frequency of extreme weather events such as cloudbursts is rising due to changing climate patterns, leading to intense and erratic rainfall.
- Local populations often lack the training and resources to respond quickly and effectively during such disasters.
Mitigation Measures
- Enhance satellite-based monitoring and real-time forecasting tools to track localised extreme weather events.
- Enforce eco-sensitive construction norms, especially in hilly and ecologically fragile districts like Ramban.
- Integrate climate vulnerability assessments into district-level disaster management plans and planning processes.
- Train local communities in evacuation protocols and first-response mechanisms to minimise casualties during extreme weather events.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan.png)




-min.jpg)