Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Man Files FIR Against Political Leader
Why in News?
A Bihar resident has filed a case against a political party leader, accusing him of causing financial loss.
Key Points
- The complainant, reportedly a milk vendor, approached the local court, alleging that a political rally led by a political leader disrupted his business operations.
- The complainant, however, has asserted his right to seek compensation for the inconvenience caused by the rally.
- The incident underscores the growing trend of citizens seeking legal redress for grievances stemming from political events, reflecting a larger debate on balancing political expression with public convenience.
- A resident of Sonupur village is seeking the trial of the political leader under various sections of the Bharatiya Nyaya Sanhita (BNS), 2023, including Section 152, which deals with sedition.
- Section 152 of the BNS criminalises any act of exciting secession, armed rebellion, and subversive activities.
- It also criminalises acts encouraging feelings of separatism or endangering the sovereignty, unity, and integrity of India.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Cabinet Approves Key Projects at Maha Kumbh
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh Cabinet, led by Chief Minister Yogi Adityanath, held a significant meeting on 22nd January, 2025, at the Maha Kumbh Mela site in Prayagraj.
- The State government reiterated its focus on creating a safe, prosperous, and well-connected Uttar Pradesh, blending economic development with cultural pride.
Key Points
Key Highlights of the Meeting:
- Major Decisions and Announcements:
- The Cabinet approved a revamp of the State’s aerospace and defence policies.
- New incentives were introduced to attract substantial investments in these sectors, aligning with Uttar Pradesh’s vision for economic growth and industrial development.
- Two significant expressway projects received in-principle approval:
- Vindhya Expressway: A 320-kilometre-long project connecting Prayagraj, Mirzapur, Varanasi, Chandauli, and Sonbhadra.
- Vindhya-Purvanchal Link Expressway: A 100-kilometre-long expressway aimed at further improving regional connectivity.
- Significance:
- The Vindhya Expressway will link Prayagraj and Sonbhadra, starting from the Ganga Expressway and ending at National Highway (NH 39).
- The expressway will strengthen Uttar Pradesh’s infrastructure and improve access to neighboring States like Jharkhand, Madhya Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh.
- These projects are expected to boost social and economic development, particularly in the Vindhya and Purvanchal regions, while complementing the State’s existing network of expressways.
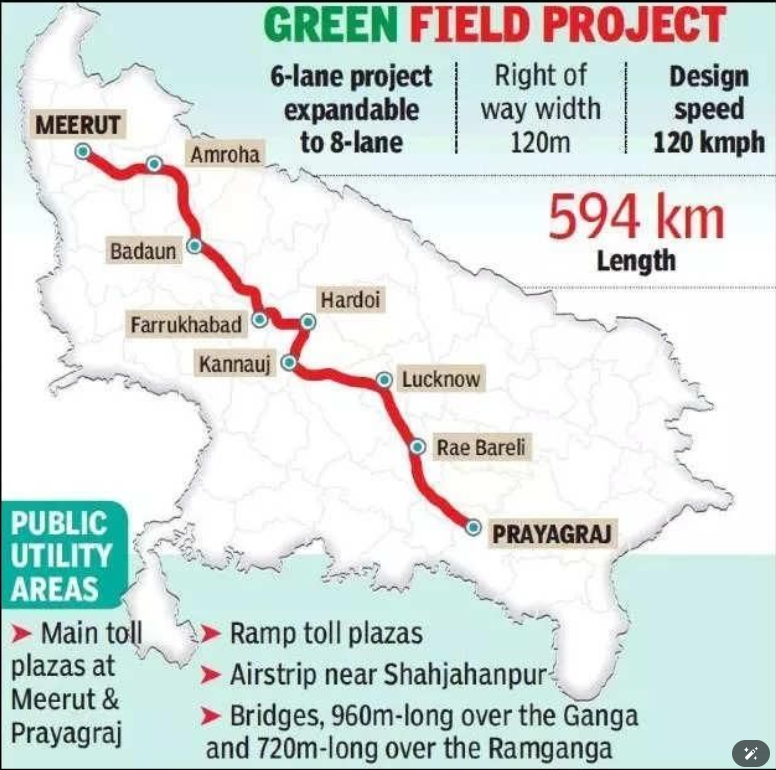
Ganga Expressway
- This expressway, connecting the state from east to west, will traverse 518 villages across 12 districts, significantly reducing travel time between Meerut and Prayagraj.
- It is designed to accommodate six lanes initially, expandable to eight lanes, boasting a maximum speed of 120 kilometers per hour.
- Another important feature includes two long bridges spanning the Ganga and Ramganga rivers, allowing even big planes to land. A 3.50-kilometer airstrip near Jalalabad tehsil in Shahjahanpur adds to the project’s versatility.
- To enhance public convenience, nine public amenities complexes are planned along the expressway, with main toll plazas at Meerut and Prayagraj, and ramp toll plazas at 15 locations.
- The Ganga Expressway is not merely a transportation link but a testament to Uttar Pradesh’s commitment to modernising its connectivity landscape.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Punjab & Haryana HC Issues Notice on Anti-Begging Laws
Why in News?
The Punjab and Haryana High Court has issued notices to the governments of Haryana and Punjab regarding a Public Interest Litigation (PIL) petition that challenges the constitutionality of certain provisions in 50-year-old state laws that criminalise begging.
Key Points
- About the Petition:
- The petition contends that anti-begging laws in Punjab and Haryana are discriminatory and infringe upon the rights to equality, life, and personal liberty guaranteed by the Constitution of India.
- The PIL argues that the State has a social contract to ensure its citizens are able to live a dignified life and that the State “cannot be allowed” to treat begging as an offence.
- The petition further takes issue with the way the act of begging has been defined in these laws, arguing that they violated Articles 14, 19, and 21 of the Constitution of India.
- Definition of Begging:
- The definition classifies any act of soliciting or receiving alms in public places as begging, including by singing, dancing, fortune-telling, performing tricks, or selling articles.
- The only difference between these vocations and others is that these vocations have “no price tag” as that’s been left to the audience to pay.
- The law also defines begging as asking for alms on private property, especially if it involves showing wounds, deformities, or injuries.
- The definition of begging in the Haryana Prevention of Beggary Act, 1971, which has been challenged, is based on the Bombay Prevention of Begging Act, 1959.
- It is a definition that is used by the Union government, to identify people engaged in begging, for welfare and rehabilitation schemes.
- Legal Implications:
- The outcome of this case could have significant implications for the treatment of marginalized communities and the legal framework surrounding poverty and homelessness in India.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
UGC Halts PhD Admissions in Three Rajasthan Universities
Why in News?
The University Grants Commission (UGC) has prohibited three universities in Rajasthan from enrolling new Ph.D. students. This action follows investigations into allegations of issuing fake and backdated degrees.
Key Points
- Universities Affected: The institutions barred from enrolling new Ph.D. scholars are OPJS University, Churu, Sunrise University, Alwar and Singhania University, Jhunjhunu.
- Allegations: A Standing Committee appointed by UGC has found that the three Universities did not follow the provisions of the UGC PhD Regulations and the academic norms for awarding of PhD degrees.
- UGC's Action: The Standing Committee has recommended that the UGC may debar these Universities from enrolling PhD students for the next five years.
- Implications: This incidence raises concerns about the quality and credibility of higher education institutions in Rajasthan.
- It underscores the need for stringent oversight to maintain academic standards and protect students' interests.
University Grants Commission (UGC)
- UGC came into existence on 28th December, 1953 and became a statutory Organisation of the Government of India under the University Grants Commission Act, 1956 for the coordination, determination and maintenance of standards of teaching, examination and research in university education.
- The UGC operates under the Ministry of Education, the Central Government appoints a Chairman, a Vice-Chairman, and ten other members to the UGC.
- The Chairman is chosen from people who are not officers of the Central Government or any State Government.
- Apart from providing grants to eligible universities and colleges, the Commission also advises the Central and State Governments on the measures that are necessary for the development of Higher Education.
- It functions from New Delhi as well as its six Regional offices located in Bangalore, Bhopal, Guwahati, Hyderabad, Kolkata and Pune.
- It also regulates the recognition of fake universities, autonomous colleges, deemed to be universities and distance education institutions.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Mount Abu Records Lowest Temperature at 2.4°C
Why in News?
Mount Abu, Rajasthan's only hill station, recorded a temperature of 2.4 degrees Celsius, marking the state's lowest temperature.
Note: The highest peak in the Aravalli Range is Guru Shikhar, located on Mount Abu.
Key Points
- Other Regions: In the plains, Sangaria of Hanumangarh recorded a minimum of 5.8°C followed by 6.8°C in Lunkaransar, 7.3°C each in Sirohi and Fatehpur.
- According to the Indian Meteorological Department (IMD), Pilani recorded 7.6°C followed by 7.8°C in Churu, 8.2°C each in Sikar and Sriganganagar and 8.8°C in Nagaur.
- Weather Conditions: The cold conditions have affected various parts of Rajasthan, with temperatures significantly lower than usual for this time of year.
- Impact: The unusual cold has prompted discussions about its effects on daily life, agriculture, and tourism in the region.
India Meteorological Department (IMD)
- About:
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It works as an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- Roles and Responsibilities:
- To take meteorological observations and to provide current and forecast meteorological information for optimum operation of weather-sensitive activities like agriculture, irrigation, shipping, aviation, offshore oil explorations, etc.
- To warn against severe weather phenomena like tropical cyclones, norwesters, dust storms, heavy rains and snow, cold and heat waves, etc., which cause destruction of life and property.
- To provide meteorological statistics required for agriculture, water resource management, industries, oil exploration and other nation-building activities.
- To conduct and promote research in meteorology and allied disciplines.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan