Bihar Switch to Hindi
Kharif Crops Destroyed in Bihar
Why in News?
According to the sources, Farmers in northern Bihar are facing severe crop damage due to unexpected late-season floods that have submerged thousands of acres of standing crops, including paddy and vegetables.
Key Points
- Floodwaters have spread across hundreds of villages in districts like Madhepura, Supaul, Saharsa, Madhubani, and Bhagalpur, submerging vast stretches of farmland.
- The rising water levels in the Kosi and Ganga rivers, as well as the Burhi Gandak and Gandak rivers, have caused significant flooding and crop damage.
- The floods have displaced many people, forcing them to live in isolated villages cut off from nearby markets and offices.
- Also caused a shortage of both green and dry fodder for animals, further exacerbating the hardship faced by affected communities.
- Despite the widespread destruction there is a lack of response from Bihar Disaster Management Department.
- Flooding is not a new phenomenon in Bihar, affecting thousands of people annually, particularly in the Ganga, Kosi, Gandak, Bagmati, and Mahananda river basins.
- Bihar is the most flood-prone state in India, with around 6.88 million hectares of the state's total area of 9.41 million hectares classified as vulnerable to flooding.
Flood
- It is an overflowing of water onto land that is normally dry. Floods can happen during heavy rains, when ocean waves come on shore, when snow melts quickly, or when dams or levees break.
- Damaging flooding may happen with only a few inches of water, or it may cover a house to the rooftop. Floods can occur within minutes or over a long period, and may last days, weeks, or longer. Floods are the most common and widespread of all weather-related natural disasters.
- Flash floods are the most dangerous kind of floods, because they combine the destructive power of a flood with incredible speed.
- Flash floods occur when heavy rainfall exceeds the ability of the ground to absorb it.
- They also occur when water fills normally dry creeks or streams or enough water accumulates for streams to overtop their banks, causing rapid rises of water in a short amount of time.
- They can happen within minutes of the causative rainfall, limiting the time available to warn and protect the public.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Japanese Encephalitis Outbreak in Madhya Pradesh
Why in News?
According to the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare (MoHFW), eight people have died after Japanese Encephalitis (JE) infection in Madhya Pradesh since 2019.
Key Points
- Due to the rise in JE cases in Madhya Pradesh the situation is being closely observed as it poses a direct risk to public well-being.
- Earlier in 2024, Japanese Encephalitis was identified in 29 districts of Madhya Pradesh.
Japanese Encephalitis
- About:
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection that can cause inflammation in the brain.
- It is caused by a flavivirus that belongs to the same genus as dengue, yellow fever and West Nile viruses.
- Japanese encephalitis virus (JEV) is also a major cause of Acute Encephalitis Syndrome (AES) in India.
- Japanese Encephalitis (JE) is a viral infection that can cause inflammation in the brain.
- Transmission:
- The disease is transmitted to humans through bites from infected mosquitoes of the Culex species.
- These mosquitoes breed mainly in rice fields and large water bodies rich in aquatic vegetation.
- Treatment:
- There is no antiviral treatment for patients with JE.
- Treatment, available, is supportive to relieve symptoms and stabilise the patient.
- There is no antiviral treatment for patients with JE.
- Prevention:
- Safe and effective JE vaccines are available to prevent the disease.
- JE vaccination is also included under the Universal Immunisation Program of the Government of India.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Suggestions for Rajasthan Investor Summit, 2024
Why in News?
According to the sources, Trade associations and industry chambers have provided recommendations for the Rising Rajasthan, an investor summit scheduled to be held in Jaipur from 9th to 11th December 2024.
Key Points
- The summit was formally announced on 1st August 2024 and the state government had received a memorandum of understanding (MoU) committing investments worth more than Rs 5.40 trillion.
- The business sector in the state believes that the regular occurrence of such incidents could potentially draw attention, effort, and funds away from the industries department's other responsibilities, as organising these events involves extensive year-round planning and preparation.
- The All Rajasthan Trade and Industry Association (ARTIA) is committed to ensuring the success of this event.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Ranthambore Tiger Reserve
Why in News?
Recently, The forest department imposed a penalty of Rs 1 lakh each on 14 SUV owners who illegally entered Ranthambore Tiger Reserve (RTR) during an adventure rally.
Key Points
- The fine was imposed in accordance with Section 27/51 of the Wildlife Act of, 1972.
- About:
- Ranthambore Tiger Reserve lies in the eastern part of Rajasthan state in Karauli and Sawai Madhopur districts, at the junction of the Aravali and Vindhya hill ranges.
- It comprises the Ranthambore National Park as well as Sawai Mansingh and Kailadevi Sanctuaries.
- The Ranthambore fort, from which the forests derive their name, is said to have a rich history of over 1000 years. It is strategically located atop a 700 feet tall hill within the park and is believed to have been built in 944 AD by a Chauhan ruler.
- This isolated area with tigers in it represents the north-western limit of the Bengal tiger’s distribution range and is an outstanding example of Project Tiger’s efforts for conservation in the country.
- Features:
- The reserve consists of highly fragmented forest patches, ravines, river streams and agricultural land.
- It is connected to Kuno-Palpur Landscape in Madhya Pradesh, through parts of Kailadevi Wildlife Sanctuary, the ravine habitats of Chambal and the forest patches of Sheopur.
- Tributaries of River Chambal provide easy passage for tigers to move towards the Kuno National Park.
- Vegetation and Wildlife:
- The vegetation includes grasslands on plateaus and dense forests along the seasonal streams.
- The forest type is mainly tropical dry deciduous with ‘dhak’ (Butea monosperma), a species of tree capable of withstanding long periods of drought, being the commonest.
- This tree is also called 'Flame of forest' and is one of the many flowering plants that add colour to the dry summers here.
- The park is rich in wildlife with tigers at the apex of the food chain in mammals.
- Other animals found here are leopards, striped hyenas, common or hanuman langurs, rhesus macaques, jackals, jungle cats, caracals, blackbuck, Blacknaped hare and chinkara, etc.
- The vegetation includes grasslands on plateaus and dense forests along the seasonal streams.
- Other Protected Areas in Rajasthan:
- Sariska National Park, Alwar
- Desert National Park, Jaisalmer
- Keoladeo National Park, Bharatpur
- Sajjangarh wildlife sanctuary, Udaipur
- National Chambal Sanctuary (on tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh)
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Van Mahotsav Programme
Why in News?
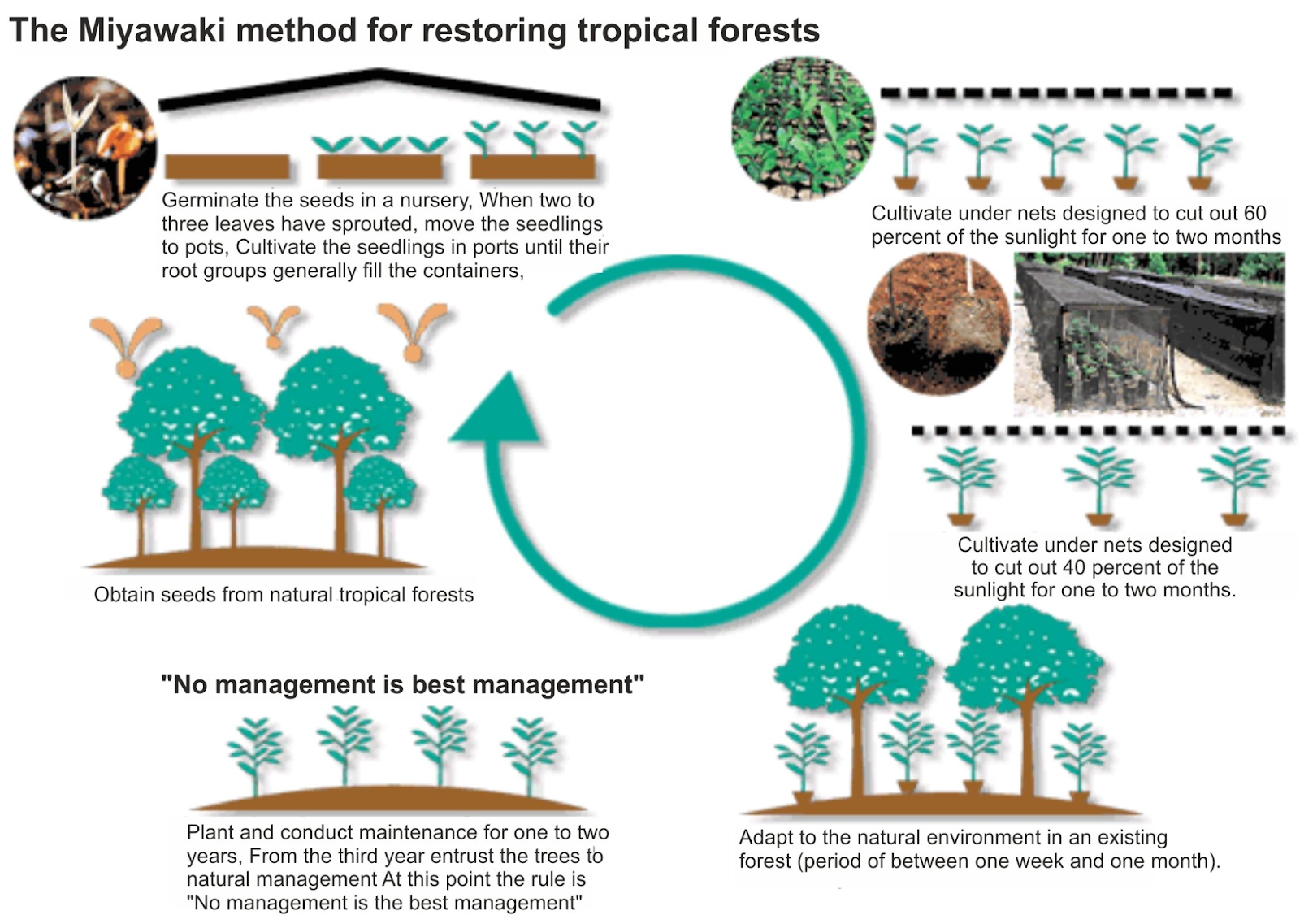
Recently, The Chhattisgarh Forest Department organised a Van Mahotsav programme in the Manendragarh-Chirmiri-Bharatpur (MCB) district by planting saplings using the Miyawaki method.
Key Points
- Around 6,000 seedlings were planted at five distinct locations. The primary aim behind adopting the Miyawaki technique is to mitigate urban heat islands and pollution.
- Miyawaki method:
- It was named after Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, this method involves planting two to four different types of indigenous trees within every square metre.
- The methodology was developed in the 1970s, with the basic objective to densify green cover within a small parcel of land.
- In this method, the trees become self-sustaining and they grow to their full length within three years.
- The plants used in the Miyawaki method are mostly self-sustaining and don’t require regular maintenance like manuring and watering.
- Significance:
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
- Some of the common indigenous plants that are used for these forests include Anjan, Amala, Bel, Arjun and Gunj.
- These forests encourage new biodiversity and an ecosystem which in turn increases the fertility of the soil.
- The dense green cover of indigenous trees plays a key role in absorbing the dust particles of the area where the garden has been set up. The plants also help in regulating surface temperature.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Agitators Quota in Government Jobs
Why in News?
Recently, The Uttarakhand agitators and their dependents met the Uttarakhand Chief Minister and expressed gratitude for the passage of the bill providing 10% reservation in government jobs.
Key Points
- According to the Chief Minister the state government recognizes the agitators' struggle and sacrifices and gives top priority to their welfare.
- Along with increasing the pension of the statehood agitators, the government has also decided to give pension to their dependents after their death.
Uttarakhand Movement
- The Uttarakhand movement led to the formation of Uttarakhand as a separate state from the undivided state of Uttar Pradesh.
- The demand to make Uttarakhand a state was first raised at a special session of the Indian National Congress in 1938.
- The movement gained traction and by 1994, the demand for a separate state eventually took the form of a mass movement that resulted in the formation of India's 27th state on 9th November 2000.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan