Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Section 144 Imposed in Lucknow
Why in News?
Recently, the Uttar Pradesh government has imposed Section 144 Code Of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) in Lucknow till 17th May, 2024 in the wake of upcoming Lok Sabha elections and festivals.
Key Points
- The Lok Sabha election in Uttar Pradesh for the year 2024 will be conducted in seven phases, spanning from 19th April to 1st June.
- The election schedule, announced by the Election Commission of India (ECI), will commence from the sugarcane belt in the western region of the state and conclude in Purvanchal, often described as the rice bowl of UP.
- Vote counting is set to take place on 4th June, 2024.
Section 144 CrPC
- This law empowers the magistrate of any state or union territory in India to pass an order prohibiting the gathering of four or more people in a specified area.
- It is imposed in urgent cases of nuisance or apprehended danger of some event that has the potential to cause trouble or damage to human life or property.
- This order can be passed against a particular individual or general public.
- Features of Section 144:
- It places restrictions on handling or transporting any kind of weapon in the given jurisdiction.
- The maximum punishment for such an act is three years.
- According to the order under this section, there shall be no movement of public and all educational institutions shall also remain closed.
- Further, there will be a complete bar on holding any kind of public meeting or rallies during the period of operation of this order.
- It is deemed a punishable offence to obstruct law enforcement agencies from disbanding an unlawful assembly.
- It also empowers the authorities to block internet access in the region.
- The ultimate purpose of Section 144 is to maintain peace and order in the areas where trouble could erupt to disrupt the regular life.
- It places restrictions on handling or transporting any kind of weapon in the given jurisdiction.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Deepak Kumar New Home Secretary of Uttar Pradesh
Why in News?
Recently, the Election Commission has approved Senior IAS officer Deepak Kumar as the new Home Secretary of Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- Deepak Kumar, a 1990 batch IAS officer, is presently Additional Chief Secretary of Finance and Basic Education.
Chief Secretary of State
- Appointment:
- The Chief Secretary is ‘chosen’ by the Chief Minister.
- As the appointment of Chief Secretary is an executive action of the Chief Minister, it is taken in the name of the Governor of the State.
- Position:
- The post of Chief Secretary is the senior-most position in the civil services of the states and union territories of India.
- The position is a cadre post for the Indian Administrative Services.
- The Chief Secretary is the chief advisor to the Chief Minister in all matters of the cabinet.
- Tenure:
- The office of Chief Secretary has been excluded from the operation of the tenure system.
- There is no fixed tenure for this post.
Election Commission of India
- The Election Commission of India (ECI) is an autonomous constitutional authority responsible for administering Union and State election processes in India.
- It was established in accordance with the Constitution on 25th January 1950 (celebrated as National Voters' Day). The secretariat of the commission is in New Delhi.
- The body administers elections to the Lok Sabha, Rajya Sabha, and State Legislative Assemblies in India, and the offices of the President and Vice President in the country.
- It is not concerned with the elections to panchayats and municipalities in the states. For this, the Constitution of India provides for a separate State Election Commission.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh to Have 3,500 'Pink' Booths
Why in News?
Around 3,500 'pink' booths, to be managed exclusively by women government personnel, are expected to be set up in the state.
Key Points
- The Lok Sabha election 2024 in Madhya Pradesh for 29 seats, polling will take place in four phases on April 19, April 26, May 7 and May 13 and votes will be counted on June 4.
- According to Chief Electoral Officer (CEO) Anupam Rajan, 5.64 crores voters, including 2.90 crores males, 2.74 crores female and 1,228 third gender electors, are registered in the state.
- In addition, there are 118 overseas voters and 74,835 service electors (Army personnel posted at borders and other places), taking the number of total voters in Madhya Pradesh to more than 5.65 crore.
- In the 2023 assembly elections, the voter turnout was 77.82%.
Chief Electoral Officer (CEO)
- According to section 13A of the Representation of the People Act 1950, and section 20 of the Representation of the People Act, 1951, the Chief Electoral Officer of a State/ Union Territory is authorised to supervise the election work subject to the overall superintendence, direction and control of the Election Commission.
- The Election Commission of India designates an Officer of the Government as the Chief Electoral Officer in consultation with that State Government/Union Territory Administration.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Begusarai: World's Most Polluted Metropolitan
Why in News?
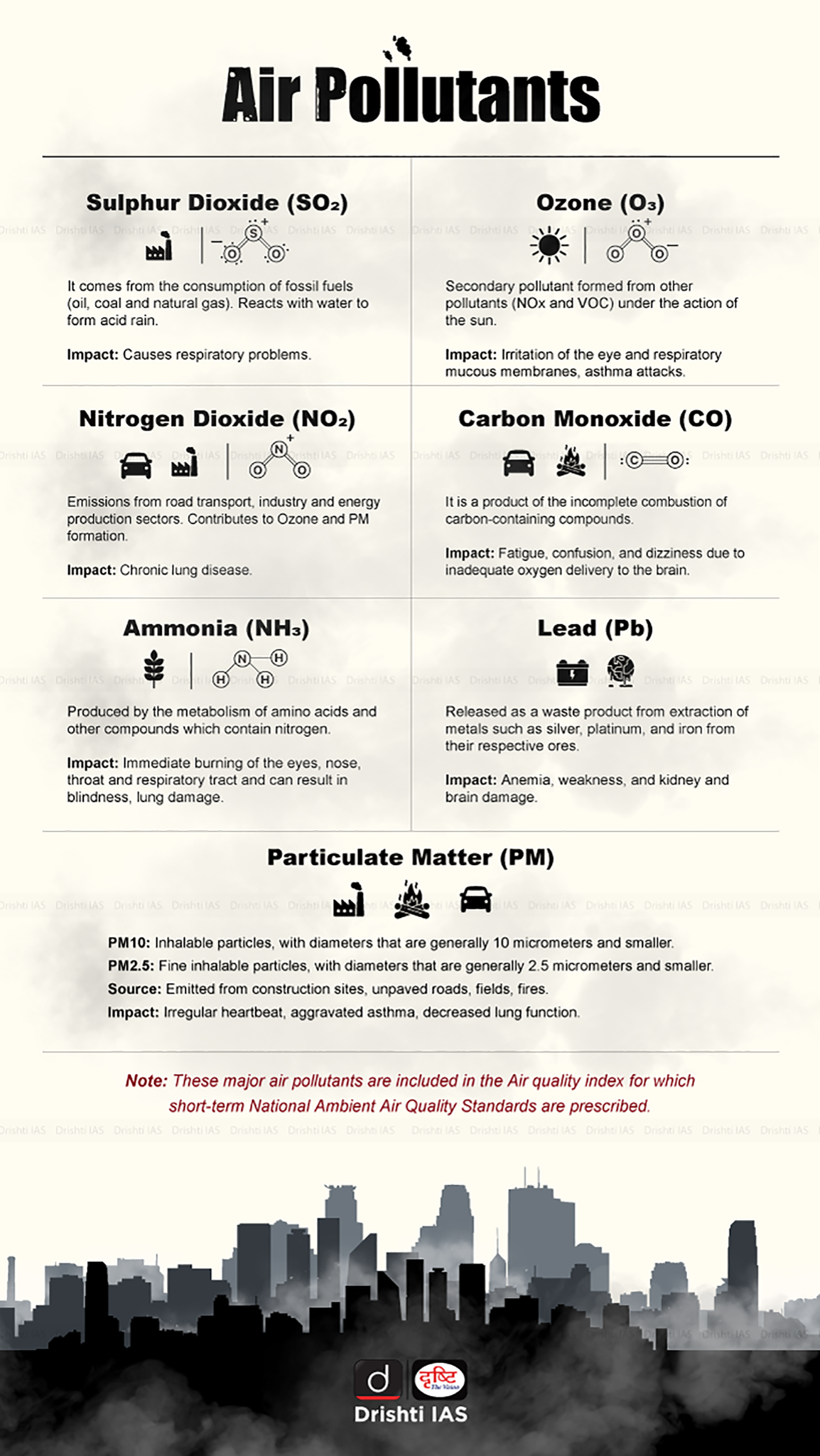
As per the World Air Quality Report 2023 released by the Swiss organization IQAir, Bihar's Begusarai has emerged as the world's most polluted metropolitan area.
Key Points
- The report underscores India's ranking as the third-highest in air pollution levels among 134 countries, following Bangladesh and Pakistan.
- This marks a shift from 2022 when India stood at eighth place globally in terms of air pollution.
- Begusarai, with an average PM2.5 concentration of 118.9 micrograms per cubic meter, has surpassed all other metropolitan areas.
- Delhi has once again been designated as the capital city with the poorest air quality. Its PM2.5 levels have also worsened from 89.1 to 92.7 micrograms per cubic meter in 2023.
- The capital has retained the title of the most polluted capital city for the fourth consecutive year since 2018.
- The report highlights that:
- Approximately 1.36 billion people are exposed to PM2.5 levels exceeding the World Health Organization (WHO) guideline of 5 micrograms per cubic meter.
- 1.33 billion individuals, equivalent to 96% of the Indian population, are grappling with PM2.5 levels surpassing the WHO standard by seven times.
- The data for this report was compiled from a comprehensive network of air quality monitoring stations and sensors worldwide, involving various institutions, organizations, and citizen scientists.
- The 2023 report has expanded its coverage to encompass 7,812 locations in 134 countries, compared to 7,323 locations in 131 countries in 2022.
- According to the report:
- Air pollution remains a critical global issue, contributing to approximately one in nine deaths worldwide.
- The WHO estimates that air pollution leads to seven million premature deaths annually, impacting individuals with various health conditions such as asthma, cancer, stroke, and lung disease.
- Exposure to high levels of PM2.5 pollution can also affect children's cognitive development, mental health, and exacerbate existing illnesses like diabetes.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Approval Accorded for Infrastructure Development in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Minority Affairs (MoMA) has allocated Rs. 101.27 Crore to Uttarakhand government for the development of Educational Infrastructure.
Key Points
- The Educational institutes would cater to 1,05,818 Lakh population out of which more than 25% belongs to the minority communities.
- Acknowledging the importance of inclusive and holistic infrastructure during the complete educational journey of students, MoMA has approved these projects for the Educational infrastructure development in colleges.
- These facilities signify the importance of higher education, thereby reverberating the contribution of higher education in development of analytical mindset, skill development, career advancement etc., leading to academic and professional growth of youth of the state.
Constitutional Provisions for Minority
- Article 29:
- It provides that any section of the citizens residing in any part of India having a distinct language, script or culture of its own, shall have the right to conserve the same.
- It grants protection to both religious minorities as well as linguistic minorities.
- However, the SC held that the scope of this article is not necessarily restricted to minorities only, as use of the word ‘section of citizens’ in the Article includes minorities as well as the majority.
- Article 30:
- All minorities shall have the right to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- The protection under Article 30 is confined only to minorities (religious or linguistic) and does not extend to any section of citizens (as under Article 29).
- Article 350-B:
- The 7th Constitutional (Amendment) Act 1956 inserted this article which provides for a Special Officer for Linguistic Minorities appointed by the President of India.
- It would be the duty of the Special Officer to investigate all matters relating to the safeguards provided for linguistic minorities under the Constitution.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
FSSAI Sets up Lab Network to Test Food for Pathogens
Why in News?
The Food Safety and Standards Authority of India (FSSAI) is working towards creating a network of 34 microbiology labs across the country that will be equipped to test food products for 10 pathogens, including E. coli, salmonella and listeria.
Key Points
- These labs will help test food for microbial contamination that can lead to spoilage of food and potential health risks.
- Data from the National Centre for Disease Control, which tracks the trajectory of several diseases every week, shows that acute diarrhoeal disease and food poisoning were the two most common outbreaks in the country.
- There were over 1,100 outbreaks of acute diarrhoeal disease across the country in the last four years and nearly 550 outbreaks of food poisoning.
- There are 79 state food testing laboratories in the country,none of them are currently equipped to test for pathogens as they require maintaining live reference samples, expensive reagents and a microbiologist.
E. coli
- Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, is a type of bacteria that can be found in the intestines of humans and animals.
- It is a rod-shaped bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family.
- Some kinds of E. coli can cause diarrhea, while others cause urinary tract infections, respiratory illness and pneumonia, and other illnesses.
- Pathogenic E. coli can be transmitted to humans through contaminated food, water, or contact with fecal matter from infected individuals or animals.
Salmonella
- It is a group of bacteria that can cause food-borne illnesses known as salmonellosis.
- Salmonella bacteria typically live in animal and human intestines and are shed through feces. Humans become infected most frequently through contaminated water or food.
- The symptoms of Salmonella include nausea, diarrhoea, fever, and abdominal cramps 12-72 hours after contracting the infection.
- WHO has identified Salmonella as one of four key global causes of diarrhoeal diseases.
Listeria
- This bacterium is naturally present in the environment and can be found in the intestines of certain animals, as well as in soil and water.
- It can cause symptoms similar to the flu, making it particularly dangerous for people over 65 and pregnant women.
- It can infect humans through the consumption of unpasteurized milk and dairy products, as well as certain pre-prepared fruits like sliced melons.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)



.jpg)






.png)
.png)



 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan