Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
PM Inaugurates Projects in Rajasthan
Why in News?
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated and laid the foundation stone for 24 projects worth over Rs 46,300 crore in Rajasthan.
- Projects span sectors like energy, roads, railways, and water resources.
Key Points
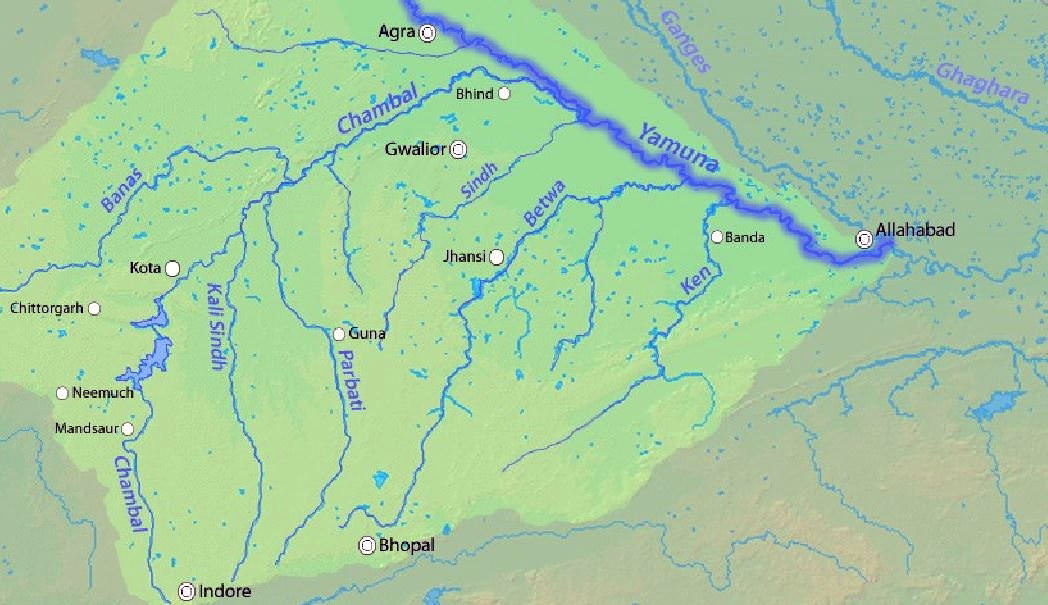
- Parvati-Kalisindh-Chambal Project:
- It is an inter-state river linking initiative designed to divert surplus water from the Parbati, Newaj, and Kalisindh rivers to the Chambal River in Madhya Pradesh to the Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP) in Rajasthan.
- This integration aims to address issues like water sharing, cost-benefit distribution, and water exchange between the concerned states.
- The project aims to provide irrigation and drinking water to 21 districts in Rajasthan.
- Expected to boost development in both Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Rivers Involved in the Project:
- Chambal River:
- Origin: Singar Chouri Peak, Vindhya Mountains, Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
- Major Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati.
- Parvati River:
- Origin: Vindhya Range, Sehore District, Madhya Pradesh.
- Significant Tributaries: None.
- Kali Sindh River:
- Origin: Bagli, Dewas District, Madhya Pradesh.
- Major Tributaries: Parwan, Newaj, Ahu.
- Chambal River:
- Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP):
- The state government approved and expanded the ERCP to address water issues.
- The Eastern Rajasthan Canal Project (ERCP), an ambitious drinking and irrigation water project, was announced by the state government in the state budget 2017-18 as a permanent solution to the problem of drinking and irrigation water in 13 districts of eastern Rajasthan.
- The districts included Jhalawar, Baran, Kota Bundi, Sawai Madhopur, Ajmer, Tok, Jaipur, Dausa, Karauli, Alwar, Bharatpur and Dholpur.
- ERCP aims to harvest surplus water available during rainy season in rivers in Southern Rajasthan such as Chambal and its tributaries, including Kunnu, Parvati, Kalisindh, and use this water in south-eastern districts of the state, where there is scarcity of water for drinking and irrigation.
- ERCP is planned to meet drinking and industrial water needs of the southern and south eastern Rajasthan, for humans and livestock till the year 2051.
Chambal River
- About:
- It originates at the Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains (Indore, Madhya Pradesh). From there, it flows in the North direction in Madhya Pradesh for a length of about 346 km and then follows a north-easterly direction for a length of 225 km through Rajasthan.
- It enters UP and flows for about 32 km before joining the Yamuna River in Etawah District.
- It is a rainfed river and its basin is bounded by the Vindhyan mountain ranges and the Aravallis. The Chambal and its tributaries drain the Malwa region of northwestern Madhya Pradesh.
- The Hadauti plateau in Rajasthan occurs in the upper catchment of the Chambal River to the southeast of the Mewar Plains.
- It originates at the Singar Chouri peak in the northern slopes of the Vindhya mountains (Indore, Madhya Pradesh). From there, it flows in the North direction in Madhya Pradesh for a length of about 346 km and then follows a north-easterly direction for a length of 225 km through Rajasthan.
- Tributaries: Banas, Kali Sindh, Sipra, Parbati, etc.
- Main Power Projects/ Dam: Gandhi Sagar Dam, Rana Pratap Sagar Dam, Jawahar Sagar Dam, and Kota Barrage.
- The National Chambal Sanctuary is located along river Chambal on the tri-junction of Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh and Uttar Pradesh. It is known for critically endangered gharial, the red-crowned roof turtle, and the endangered Ganges river dolphin.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan CM’s Welfare Initiatives at Kisan Sammelan
Why in News?
Recently, The Chief Minister of Rajasthan transferred Rs 700 crore as the second installment of the Kisan Samman Nidhi to the bank accounts of over 70 lakh farmers and credited Rs 200 crore to 3.25 lakh cattle breeders as assistance of Rs 5 per litre of milk.
Key Points
- Direct Benefit Transfers to Farmers:
- Under the Direct Benefit Transfers Rs 29 crore transferred to 15,983 farmers for drip and sprinkler irrigation equipment.
- Rs 96 crore disbursed to 14,200 farmers for activities like fencing, laying pipelines, farm pond construction, organic manure, and agricultural equipment.
- Rs 80 crore allocated for the installation of 8,000 solar pumps.
- Under the Direct Benefit Transfers Rs 29 crore transferred to 15,983 farmers for drip and sprinkler irrigation equipment.
- Recognition of Progressive Farmers:
- The Chief Minister honoured 10 innovative farmers under the Centrally sponsored ATMA Yojana.
- Investment in Agriculture:
- 2,500 MoUs signed for Rs 58,000 crore investment in agriculture during the Rising Rajasthan Global Investment Summit held in Jaipur.
- Key Decisions for Farmer Welfare:
- Distribution of short-term crop loans worth Rs 20,000 crore to 30 lakh farmers.
- Issuance of eight lakh soil health cards.
- Installation of 26,000 solar plants.
- Allotment of land for food parks at 31 locations.
- Procurement of wheat, moong, groundnut, and mustard at minimum support prices (MSP).
- Launch of New Schemes:
- Introduced a livestock insurance scheme.
- Announced a camel conservation and development mission.
- Initiated the installation of cow dung log machines in 100 gaushalas.
- Launched 1,000 new milk collection centres and installed 200 new bulk milk coolers.
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- About:
- It was launched on 24th February, 2019 to supplement financial needs of land holding farmers.
- Financial Benefits:
- Financial benefit of Rs 6000/- per year in three equal installments, every four months is transferred into the bank accounts of farmers’ families across the country through Direct Benefit Transfer (DBT) mode.
- Scope of the Scheme:
- The scheme was initially meant for Small and Marginal Farmers (SMFs) having landholding upto 2 hectares but scope of the scheme was extended to cover all landholding farmers.
- Funding and Implementation:
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- Objectives:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
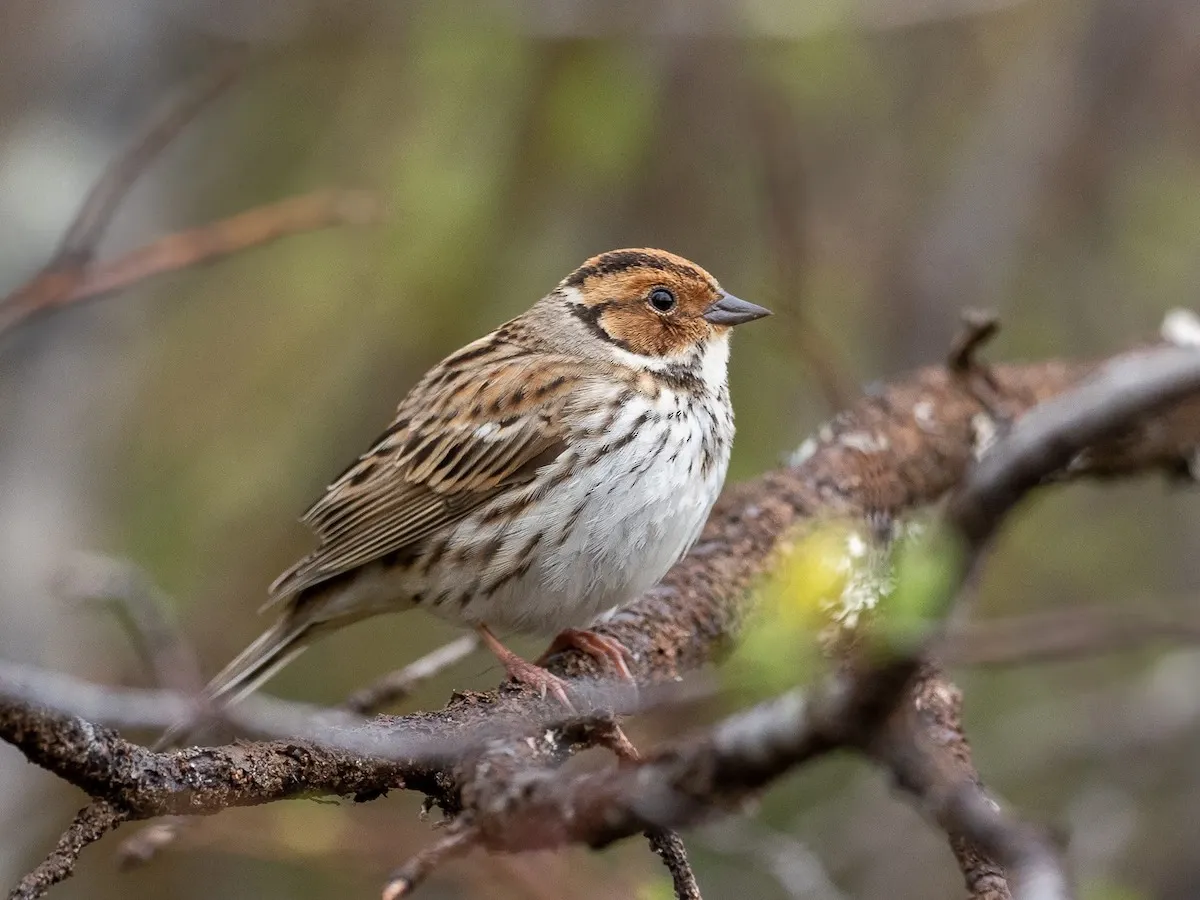
Little Bunting Bird
Why in News?
Recently, birdwatchers spotted a little bunting in Mount Abu, marking its first recorded appearance in Rajasthan.
Key Points
- Little Bunting Description and Habitat:
- About:
- Little bunting is a small passerine bird belonging to the bunting and sparrow family.
- Its breeding range spans the taiga of far northeast Europe and northern Asia.
- The bird migrates to southern China and northeast India during winter and typically inhabits agricultural areas, feeding on grains.
- Features:
- This is a small bunting, measuring only 12–14 cm (4.7–5.5 inch) in length.
- It has white underparts with dark streaking on the breast and sides.
- With its chestnut face and white malar stripe, it resembles a small female reed bunting, but has black crown stripes, a white eye-ring, and a fine dark border to the rear of its chestnut cheeks.
- IUCN Red List: Least Concern
- About:
- Possible Role of Climate Change:
- Experts suggest climate change might have pushed the bird to Rajasthan, as it tends to avoid extremely cold conditions.
- Sightings in Northern India:
- Little buntings have recently been spotted in regions like Gurugram, Chandigarh, and northern Punjab.
- These birds are typically seen in the subtropics of northern India, southern China, and northern Southeast Asia.
- Significance for Conservation:
- The sighting emphasizes the importance of preserving forest areas and wetlands to support such migratory species.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan