Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Re-Exploration of J&K's Lithium Reserve
Why in News?
Recently, the 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves in Jammu & Kashmir (J&K) are set for re-exploration after failed attempts to auction the reserve due to insufficient exploration data and industry reluctance.
- This move aims to boost India's domestic lithium production, which is critical for energy transitions and reducing dependence on imports.
Key Points
- Current Status of the Reserve:
- The Salal-Haimana block in the Reasi district of J&K holds an estimated 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves. It is India's largest lithium find, announced in February 2023.
- The Salal-Haimana block also contains titanium and bauxite, which may have additional extraction potential .
- However, the block is still at the G3 level of exploration, which involves preliminary prospecting and mapping
- The Salal-Haimana block in the Reasi district of J&K holds an estimated 5.9 million tonnes of lithium reserves. It is India's largest lithium find, announced in February 2023.
- Re-Exploration to G2 Level:
- The Ministry of Mines has directed the Geological Survey of India (GSI) to elevate the exploration to at least the G2 level.
- This involves more detailed surveys and geological studies, which provide better data on the commercial viability of the reserves. Achieving G2 means clearer reserve estimates and improved resource confidence.
- The Ministry of Mines has directed the Geological Survey of India (GSI) to elevate the exploration to at least the G2 level.
- G2 exploration is more detailed compared to G3. It includes drilling and trenching to estimate the size, grade, and shape of the mineral deposit. Further exploration to G1 (the final stage) is necessary for a more precise assessment before mining
- Lithium Ores and Extraction:
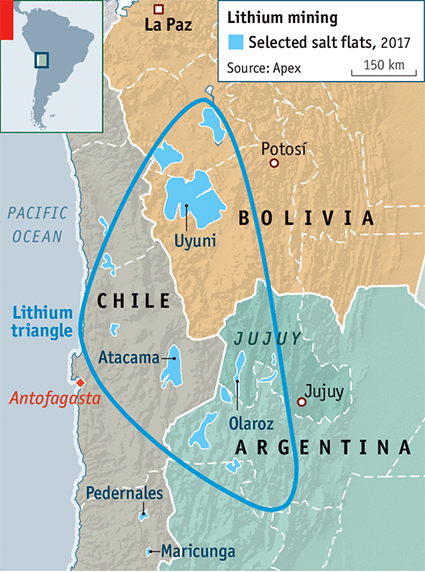
- Lithium is extracted primarily from spodumene (a lithium-bearing mineral found in pegmatites) or from brine pools where lithium salts are concentrated. In places like Chile and Argentina, lithium is mainly extracted from brines, while in Australia, it is mined from spodumene
- Challenges Faced in Auctioning:
- The first auction attempt in November 2023 failed due to a lack of sufficient bidders. The second attempt, which allowed for a single bidder, also saw no success. The key issue is inadequate exploration data, which makes potential bidders reluctant to commit.
- Experts caution that detailed exploration should not be rushed, as premature auctioning without solid resource estimates might deter future interest
- India’s Lithium Import Dependency:
- India currently imports all its lithium, with lithium-ion battery imports reaching USD 2.9 billion in 2023-24, primarily from China and Hong Kong. This underscores the importance of developing domestic lithium resources
- The discovery of lithium in J&K is seen as pivotal for reducing import dependence, particularly as India pushes for electric vehicle (EV) adoption
- Global Lithium Reserves and India's Efforts:
- Globally, 98 million tonnes of lithium resources exist, but only 26 million tonnes are considered reserves. Countries like Chile, Australia, and Argentina dominate the market. India has partnered with Argentina for lithium exploration and is exploring opportunities in Chile, Bolivia, and Australia
Properties of Lithium
- It is a chemical element with the symbol Li.
- It is a soft, silvery-white metal.
- Under standard conditions, it is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element.
- It is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in mineral oil.
- It is an alkali metal and a rare metal.
- The alkali metals consist of the chemical elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, caesium, and francium. Together with hydrogen they constitute group, which lies in the s-block of the periodic table.
- Rare Metals (RM) include Niobium (Nb), Tantalum (Ta), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Cesium (Cs) etc. and Rare Earths (RE) include Lanthanum (La) to Lutetium (Lu) besides Scandium (Sc) and Yttrium (Y).
- These metals are strategic in nature with wide application in the nuclear and other high tech industries such as electronics, telecommunication, information technology, space, defense etc.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Russell's Viper Snake
Why in News?
Recently, a man in Bihar shocked everyone by arriving at a hospital with the venomous snake (Russell's Viper) that had bitten him.
Key Points
- Russell's Viper:
- Russell’s Viper is one of India's most dangerous snakes. Its venom is hemotoxic, causing internal bleeding, muscle damage, and renal failure.
- Bites from this snake can be fatal if untreated, with symptoms including severe pain, swelling, and bleeding .
- Venom and Antivenom:
- Venom Composition: The venom of Russell’s Viper disrupts blood clotting, leading to internal bleeding.
- Antivenom Production: Venom is extracted from snakes, injected into animals (usually horses), which then produce antibodies. These antibodies are extracted to create antivenom
- Legal Protection under WPA, 1972:
- The Wildlife Protection Act (WPA), 1972 classifies Russell’s Viper as protected wildlife under schedule II.
- Handling, capturing, or harming these snakes without permission is illegal.
Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972
- The Wild Life (Protection) Act, 1972 provides a legal framework for the protection of various species of wild animals and plants, management of their habitats, regulation, and control of trade in wild animals, plants, and products made from them
- The act also lists schedules of plants and animals that are afforded varying degrees of protection and monitoring by the government.
- India's entry to the CITES (Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora) was made easier by the Wildlife Act, 1972.
- Earlier, Jammu and Kashmir was not covered by the Wildlife Protection Act of 1972. The Indian Wildlife Protection Act, 1972 now applies to J&K as a result of the reorganisation act.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
PM to Inaugurate Sports Facilities in Varanasi
Why in News?
Recently, Prime Minister Modi is set to inaugurate new sports facilities in Varanasi, enhancing opportunities for athletes.
Key Points
- PM Modi will inaugurate phases 2 and 3 of the National Center of Excellence at Dr. Sampurnanand Stadium, Varanasi.
- The upgrade cost Rs 325.65 crore, enhancing infrastructure for over 20 sports disciplines.
- The complex includes multi-level courts, swimming pools, athletic tracks, and spaces for indoor/outdoor sports, para-sports, and recovery zones.
- PM Modi will also launch development projects worth over Rs 1,000 crore
Varanasi
- Varanasi is in southeastern Uttar Pradesh state. It is located on the left bank of the Ganges (Ganga) River and is one of the seven sacred cities of Hinduism.
- It is one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world. Its early history is that of the first Aryan settlement in the middle Ganges valley.
- Varanasi was the capital of the kingdom of Kashi during the time of the Buddha (6th century BCE), who gave his first sermon nearby at Sarnath.
- The city remained a centre of religious, educational, and artistic activities as attested by the celebrated Chinese Buddhist pilgrim Xuanzang, who visited it in about 635 CE.
- Varanasi subsequently declined during three centuries of Muslim occupation, beginning in 1194.
- Varanasi became an independent kingdom in the 18th century, and under subsequent British rule it remained a commercial and religious centre.
- In 1910, the British made Varanasi a new Indian state, with Ramnagar (on the opposite bank) as headquarters but with no jurisdiction over the city of Varanasi.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Chhattisgarh Govt Announces DA Hike for State Employees
Why in News?
Recently, the Chhattisgarh government announced a 4% hike in Dearness Allowance (DA) for its employees ahead of Diwali.
Key Points
- DA Hike Details:
- The Chhattisgarh government increased DA by 4%, benefiting state employees and pensioners.
- This brings the total DA to 42% of the basic salary, aligning with the Seventh Pay Commission's recommendations.
- Dearness Allowance (DA):
- It is the cost-of-living adjustment to offset inflation, provided to government employees and pensioners. It is calculated as a percentage of the basic salary.
- Impact on Economy:
- Increased Consumer Spending: The hike boosts disposable income, especially around festive periods, spurring consumer demand.
- Inflation Control: DA helps employees manage inflation, but an increase in demand could potentially raise inflation if supply doesn’t keep pace.
- Fiscal Pressure: For the government, DA hikes increase expenditure, which may strain the fiscal budget but stimulate economic growth through consumption.
Pay Commission
- The Pay Commission is a body set up by the Central Government that reviews and recommends changes to the salary structure of employees.
- The composition of the Pay Commission comes under the Department of Expenditure (Ministry of Finance).
- Pay commissions are usually constituted every 10 years and the first pay commission was set up in 1946. Since Independence, a total of seven pay commissions have been formed.
- The latest pay commission was set up in 2014 and its recommendations came into effect in 2016. Currently, central government employees and pensioners get salaries based on the recommendations of the 7th pay commission.
- It is not mandatory for the government to accept the recommendations of the pay commission. The government may choose to accept or reject the recommendations.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan