Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Naxal’s Encounter in Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
Recently, six naxalites were killed in an encounter with security personnel in Chhattisgarh’s Narayanpur district.
- The operation targeted Naxalites in forests near Kutul-Farasbeda and Kodtameta villages.
Key Points
- Those naxalites belonged to the People’s Liberation Guerrilla Army (PLGA).
- PLGA serves as the armed wing of the Communist Party of India (Maoist), a banned political organisation in India.
- The group seeks to overthrow the government through a prolonged people's war.
- This marks the second major success of the “Maad Bachao Abhiyan” (anti-Naxalite operation) by Narayanpur police within a week.
- The operation has contributed to reducing violence and fear in the Abhujmaad region, which had been affected by Naxal violence for 40 years.
- The operation involved personnel from the state police’s District Reserve Guard, Special Task Force (STF), Indo-Tibetan Border Police, and Border Security Force.
- Women commandos also played a crucial role in the operation.
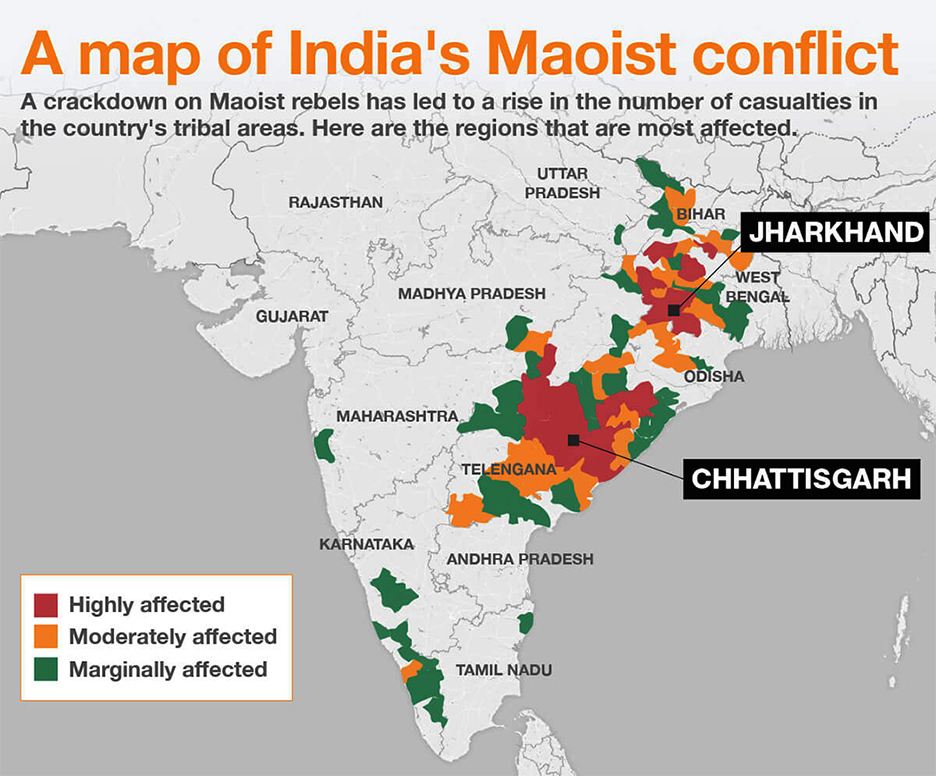
Red Corridor
- The Red Corridor is the region in the central, eastern and southern parts of India that experience severe Naxalism–Maoist insurgency.
- The States of Chhattisgarh, Jharkhand, Odisha, Bihar, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Telangana, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh and Kerala are considered Left Wing Extremism (LWE) affected.
Border Security Force (BSF)
- The BSF is meant to secure India’s borders with its neighbouring nations and is empowered to arrest, search and seize under a number of laws, such as the Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC) of 1973, the Passports Act 1967, the Passport (Entry into India) Act 1920, and the Narcotic Drugs and Psychotropic Substances Act (NDPS), 1985 etc.
Indo-Tibetan Border Police (ITBP)
- The ITBP is a specialised mountain force of India, which was established in 1962, soon after the India-China war which was initially meant for deployment along the India-China border.
- ITBP was initially raised under the Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) Act, 1949. However, in 1992, parliament enacted the ITBP Act and the rules were framed in 1994.


Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Mob Lynching
Why in News?
Recently, two cattle transporters were found dead, and a third was severely injured after being allegedly attacked by a mob in Raipur, Chhattisgarh.
- The victims were transporting cattle from Mahasamund to Raipur.
Key Points
- Mob lynching is a term used to describe the acts of targeted violence by a large group of people.
- The violence is tantamount to offenses against human body or property or both public as well as private.
- The mob believes that they are punishing the victim for doing something wrong (not necessarily illegal) and they take the law in their own hands to punish the purported accused without following any rules of law.
- Related Issues:
- Mob lynching is a violation of human dignity, Article 21 of the Constitution, and a gross infringement of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights.
- Such incidents violate the Right to Equality and Prohibition of discrimination, which are enshrined in Articles 14 and 15 of the Constitution of India.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
NEET Leak Controversy
Why in News?
The National Eligibility and Entrance Test (NEET) Undergraduate exam paper leak has escalated, leading to protests demanding a re-test and a Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) probe.
- The Economic Offences Unit (EOU) disclosed that NEET aspirants paid up to ₹30 lakh for leaked exam papers in Bihar.
Key Points
- The Supreme Court is hearing several petitions related to NEET, though it has not stayed counseling for admissions based on the results.
- This unfolding scandal highlights deep-rooted issues in the examination system and underscores the urgent need for reform and accountability.
- The National Eligibility Entrance Test (NEET), formerly the All-India Pre-Medical Test (AIPMT), is the qualifying test for MBBS and BDS programmes in Indian medical and dental colleges.
- It was introduced in 2013 by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) and is now conducted by the National Testing Agency (NTA).
- NTA was established as a Society registered under the Indian Societies Registration Act, 1860.
- It is an autonomous and self-sustained testing organisation to conduct entrance examinations for admission/fellowship in higher educational institutions.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Nalanda University
Why in News?
The Prime Minister of India will inaugurate the new campus of Nalanda University at Rajgir, Bihar.
Key Points
- The University is conceived as a joint collaboration between India and East Asia Summit (EAS) countries.
- The Campus is a ‘Net Zero’ Green Campus. It is self-sustainable with a solar plant, domestic and drinking water treatment plant, water recycling plant for reusing wastewater, 100 acres of water bodies, and many other environment friendly facilities.
- The original Nalanda University, established around 1600 years ago, is considered to be amongst the first residential universities of the world.
- The ruins of Nalanda Univesity was declared as a UN Heritage Site.
- East Asia Summit:
- The EAS was established in 2005 as an Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN)-led initiative.
- The EAS is the only leader-led forum in the Indo-Pacific that brings together all key partners to discuss political, security and economic issues of strategic importance.
- The EAS operates on the principles of openness, inclusiveness, respect for international law, ASEAN centrality, and ASEAN’s role as the driving force.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Accelerates Thermal Power Projects
Why in News
The Uttar Pradesh government is accelerating the Ghatampur and Obra C thermal power projects to address the state’s growing energy demand.
Key Points
- The combined capital expenditure (capex) for these projects exceeds Rs 32,000 crore.
- The Ghatampur project (1,980 MW) is estimated to cost Rs 19,006 crore and is being developed by Neyveli Uttar Pradesh Power (NUPPL).
- All three units of the Ghatampur project are expected to be commissioned in 2024-25, with the state receiving 75% of the production of electricity.
- The Obra C thermal power plant (1,320 MW) had a cost overrun due to changes in prices and exchange rates.
- The state will meet 70% of the augmented cost of Obra through borrowings, while the remaining 30% will be provided through share capital.
Capital Expenditure
- It is incurred with the purpose of increasing assets of a durable nature or of reducing recurring liabilities.
- Example: The expenditure incurred for constructing new schools or new hospitals. All these are classified as capital expenditure as they lead to creation of new assets.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan