Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Maharashtra Reduces Women’s Welfare Aid
Why in News?
The Maharashtra government has reduced stipends for around eight lakh beneficiaries of the Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana as they also receive benefits under the Namo Shetkari Mahasanman Nidhi (NSMN) scheme.
Key Points
- Reduction in Monthly Assistance:
- Under the revised structure, affected women will now receive Rs 500 per month instead of Rs 1,500 under the Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana.
- The reduction applies to those already receiving Rs 1,000 monthly under the NSMN scheme.
- As per the scheme’s guidelines, the total government aid per woman cannot exceed Rs 1,500.
- Mukhya Mantri Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana:
- About:
- Majhi Ladki Bahin Yojana, launched in 2024, is a flagship welfare programme aimed at supporting women financially across Maharashtra.
- Benefits:
- The original Rs 1,500 monthly payout was designed to empower women economically and enhance their social security.
- Beneficiaries receive three free LPG cylinders each year.
- Poor girls from Other Backward Classes (OBC) and Economically Weaker Sections (EWS) are eligible for fee waivers during college admissions.
- Eligibility:
- The scheme covers women aged 21 to 65 including married, widowed, divorced, abandoned, and destitute women.
- About:
- Namo Shetkari Mahasanman Nidhi (NSMN) Scheme:
- About:
- Introduced in 2023 by the Maharashtra government, it aims to provide additional financial support to small and marginal farmers.
- It complements the Central government’s Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN) scheme.
- Eligibility:
- Farmers must be registered under PM-KISAN.
- Must meet Maharashtra’s criteria for small or marginal farmers.
- Benefits:
- Provides Rs 6,000 annually in three equal installments of Rs 2,000.
- This is over and above the Rs 6,000 received under PM-KISAN, totaling Rs 12,000 annually.
- About:
Pradhan Mantri Kisan Samman Nidhi (PM-KISAN)
- Under the scheme, the Centre transfers an amount of Rs 6,000 per year, in three equal installments, directly into the bank accounts of all landholding farmers irrespective of the size of their land holdings.
- It was launched in February 2019.
- It is a Central Sector Scheme with 100% funding from the Government of India.
- It is being implemented by the Ministry of Agriculture and Farmers Welfare.
- The entire responsibility of identification of beneficiary farmer families rests with the State / UT Governments.
- Objective:
- To supplement the financial needs of the Small and Marginal Farmers in procuring various inputs to ensure proper crop health and appropriate yields, commensurate with the anticipated farm income at the end of each crop cycle.
- To protect them from falling in the clutches of moneylenders for meeting such expenses and ensure their continuance in the farming activities.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
Exercise DUSTLIK-VI
Why in News?
India and Uzbekistan began the 6th edition of Joint Military Exercise DUSTLIK-VI at Aundh, Pune. The exercise will take place from 16 to 28 April 2025.
- The previous edition took place in Termez District, Uzbekistan, in April 2024.
Key Points
- Exercise Theme and Focus:
- The core theme is Joint Multi-Domain Sub-Conventional Operations in a Semi-Urban Scenario.
- The focus is on responding to terrorist actions involving the capture of a defined territory.
- A Joint Operations Centre will be established at the battalion level for continuous coordination.
- Participation and Representation:
- The Indian contingent includes 60 personnel from a battalion of the JAT Regiment and the Indian Air Force (IAF).
- The Uzbekistan Army is representing the Uzbek side.
- Strategic Objectives:
- The joint drill will promote interoperability, tactical cooperation, and mutual learning in sub-conventional warfare.
- It aims to enhance defence cooperation and deepen bilateral military relations between India and Uzbekistan.
- The exercise fosters camaraderie and trust between both armies through shared training and strategic alignment.
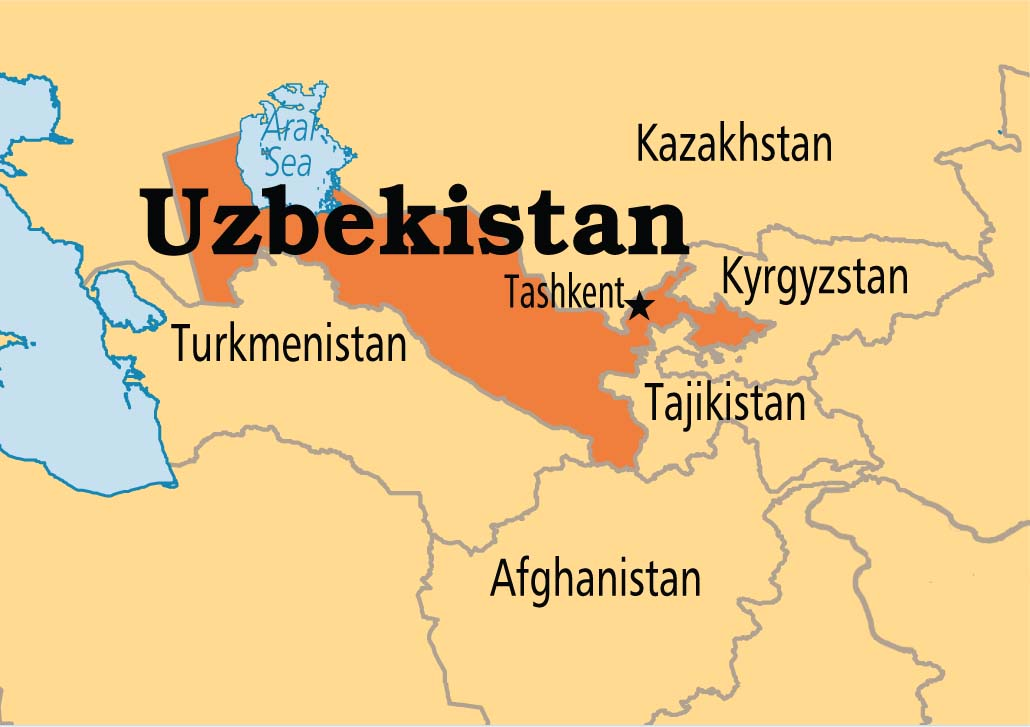
Uzbekistan
- About:
- Landlocked country in Central Asia, situated between the Syr Darya (northeast) and Amu Darya (southwest) rivers.
- Lies in the Northern and Eastern hemispheres.
- One of only two doubly landlocked countries in the world (the other is Liechtenstein).
- Neighbouring Countries:
- Kazakhstan (north and northwest)
- Kyrgyzstan (northeast)
- Tajikistan (southeast)
- Afghanistan (south)
- Turkmenistan (southwest)
- Topographical Features:
- Around 80% of the land is sandy desert, mostly the Kyzyl Kum Desert.
- Lowlands dominate the west; foothills and mountains (Tian Shan range) rise in the northeast and southeast.
- The highest peak is Adelunga Toghi (4,301 m) in the northeast.
- Fergana Valley is the most fertile and agriculturally productive region.
- Rivers and Lakes:
- Major rivers: Amu Darya and Syr Darya.
- The Aral Sea, shared with Kazakhstan, is a major environmental disaster due to water mismanagement.
- Important lakes: Lake Aydarkul and Lake Sarykamish.
- Major rivers: Amu Darya and Syr Darya.
- Vegetation and Climate:
- Dominated by desert scrub in arid zones.
- Fertile valleys, especially Fergana, support intensive agriculture.
- Natural Resources:
- Rich in natural gas, oil, coal, and minerals like gold, uranium, and copper.
- Holds the 4th largest gold reserves globally.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Paediatric Education Network Portal
Why in News?
Jammu and Kashmir Lieutenant Governor Manoj Sinha launched the Paediatric Education Network’s free online portal, developed by leading paediatricians and academicians.
Key Points
- About the Initiative:
- It aims to strengthen paediatric education and improve access to quality learning tools for practitioners and learners across the medical community.
- Lieutenant Governor acknowledged the platform’s goal to enhance paediatric healthcare education and empower medical professionals, students, and institutions with reliable, updated resources.
- Platform Features:
- The Paediatric Education Network serves as a comprehensive, user-friendly hub for child health knowledge.
- It offers a range of materials, including:
- Lectures
- Clinical guidelines
- Case studies
- Interactive modules
- Expert insights
- Accessibility


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Silkyara Tunnel in Uttarakhand
Why in News?
On April 16, 2025, Uttarakhand completed excavation of the 4.53-km Silkyara Tunnel, which will be named after local deity Baba Baukhnag.
Key Points
- Inauguration of Temple:
- The Chief Minister of the state inaugurated the Baba Baukhnag temple at the mouth of the Silkyara Tunnel.
- He called the tunnel breakthrough a symbol of advanced engineering, faith, and dedication.
- The construction of the tunnel was tendered to Hyderabad-headquartered Navayuga Engineering Company by the National Highways and Infrastructure Development Corporation Ltd (NHIDCL), a fully owned company of the Ministry of Road Transport & Highways, Government of India.
- Char Dham Connectivity and Strategic Importance:
- The double-lane tunnel, part of the Char Dham all-weather road project, is a major infrastructure project.
- With an estimated cost of Rs 1,384 crore, the tunnel will cut the distance between Gangotri and Yamunotri by 25 km, improving regional connectivity.
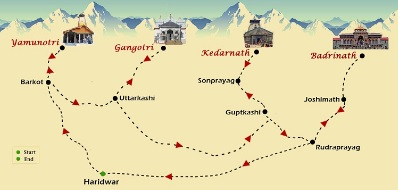
Char Dham Yatra
- The Char-Dham yatra in Uttarakhand consists of visiting four temples, Badrinath, Kedarnath, Gangotri, and Yamunotri.
- Yamunotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Yamuna.
- River Yamuna is the second-most sacred river in India after River Ganga.
- Gangotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Ganga.
- Considered the most sacred of all Indian rivers.
- Kedarnath Dham:
- Location: Rudraprayag district.
- Dedicated to: Lord Shiva.
- Situated on the bank of the Mandakini River.
- One of the 12 Jyotirlingas (divine representations of Lord Shiva) in India.
- Badrinath Dham:
- Location: Chamoli district.
- Home to the sacred Badrinarayan Temple.
- Dedicated to: Lord Vishnu.
- One of the holy shrines for Vaishnavites.
- Yamunotri Dham:


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Kathak Dancer Kumudini Lakhia Passed Away
Why in News?
On 12th April 2025, Kathak artist and choreographer Kumudini Lakhia passed away at the age of 95 due to age-related illness at her residence in Ahmedabad.
Key Points
- About Kumudini Lakhia :
- Kumudini Lakhia , also known as "Kumiben" , was among the artists who . blended modern expressions, techniques, and themes with the classical essence of the traditional dance form.
- She was born on 17 May 1930 in Ahmedabad (Gujarat) in a music-loving family.
- She received her initial training in Kathak dance from Pandit Sundar Prasad of the Jaipur Gharana .
- She also took training from the great dancer Pandit Shambhu Maharaj of the Lucknow Gharana.
- During her training she also got the opportunity to work with Pandit Birju Maharaj, which further enriched her dance vision.
- She exhibited her art not only in India but also in countries like Europe and the United States .
- Establishment of Kadamba
- In 1964 she founded the "Kadamba Dance and Music Center" in Ahmedabad . Through this center she trained a new generation of Kathak dancers.
- Awards and Honors
- Sangeet Natak Akademi Award (1982): Honour given by India's National Academy for contribution to classical dance .
- Padma Shri (1987): Fourth highest civilian award given by the Government of India .
- Padma Bhushan (2010): Third highest civilian award .
- Kalidas Samman (2002): A prestigious cultural award given by the Madhya Pradesh government .
- Padma Vibhushan (2025): India's second highest civilian award .
Kathak
- Introduction:
- The word Kathak is derived from the word Katha which literally means to tell a story. This dance is mainly performed in Northern India.
- It was primarily a temple or village performance in which dancers narrated stories from ancient texts.
- It is one of the classical dances of India .
- Development :
- Kathak dance developed as a distinct form with the spread of the Bhakti movement in the fifteenth and sixteenth centuries .
- The legends of Radha-Krishna were first enacted in folk dramas called 'Rasa Leela', which later incorporated folk dance with the original gestures of the Kathak storytellers.
- Kathak was performed in courts for the Mughal emperors and their nobles, where it acquired its present characteristics and developed into a distinct style.
- It developed into a major art form under the patronage of Wajid Ali Shah, the last Nawab of Awadh.
- Dance Style:
- Usually a single narrator or dancer pauses for a period of time to recite the verses, which are then demonstrated through physical movements.
- There is a greater focus on leg movements; body movements are skillfully controlled by dancers wearing 'ankle-bells' and performed with straight legs.
- 'Tatkar' kathak basically involves the movement of the feet.
- Kathak is the only form of classical dance that is related to Hindustani or North Indian music.
- Some of the prominent dancers include Birju Maharaj, Sitara Devi.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Food Industry Upgradation Scheme
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh has secured first place in the country in the implementation of Pradhan Mantri Micro Food Processing Enterprises Upgradation Scheme (PMFME).
Key Points
- About the issue:
- The average loan approval time in Uttar Pradesh is 101 days , while in Bihar it is 110 days and in Telangana it is 190 days .
- Uttar Pradesh has recorded a growth of 14 % in loan disbursement .
- Uttar Pradesh has spent Rs 250 crore more than 2024.
- At the same time, an additional amount of Rs 300 crore has been provided for Uttar Pradesh with an increase of 56 % in the budget for the year 2025-26 .
Pradhan Mantri Micro Food Processing Enterprises Upgradation Scheme (PMFME)
- About:
- Launched in 2020 under the Atmanirbhar Abhiyaan , it aims to enhance the competitiveness of existing individual micro enterprises in the unorganised sector of the food processing industry and promote formalisation of the sector and provide support to Farmer Producer Organisations , Self Help Groups and Producer Cooperatives.
- The scheme adopts One District One Product (ODOP) approach to leverage the benefits of scale with respect to procurement of inputs, common services and marketing of products .
- The PMFME Scheme is currently being implemented in 35 States and Union Territories
- It was implemented for a period of five years (2020-21 to 2024-25).
- Nodal Ministry:
- Ministry of Food Processing Industries (MoFPI).


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centre
Why in News?
Vultures raised by Madhya Pradesh Forest Department at Vulture Conservation and Breeding Centre, Kerwa Bhopal were released for the first time in their natural habitat 'Halali Dam forest area' .
Key Points
- Release of the Vultures:
- All the vultures have been fitted with solar powered GPS-GSM trackers (Ornitrack-25).
- So that their movement patterns and housing use can be monitored.
- Vulture Conservation Breeding Centre was started in the year 2014 in collaboration with Van Vihar and Bombay Natural History Society for the conservation of vultures in Madhya Pradesh.
- All the vultures have been fitted with solar powered GPS-GSM trackers (Ornitrack-25).
- About the Vultures Species in India:
- It is one of the 22 species of large scavenger birds that live predominantly in the tropics and subtropics.
- They act an important function as nature’s garbage collectors and help to keep the environment clean of waste.
- They also play a valuable role in keeping wildlife diseases in check.
- India is home to 9 species of Vulture namely the Oriental white-backed, Long-billed, Slender-billed, Himalayan, Red-headed, Egyptian, Bearded, Cinereous, and the Eurasian Griffon.
- Most of these 9 species are at risk of extinction.
- Bearded, Long Billed and Oriental White Backed are protected under Schedule I of the Wildlife Protection Act, 1972. The rest are protected under 'Schedule IV'.
- Dangers:
- Toxins like Diclofenac which is used as a medicine for animals.
- Loss of natural habitats due to anthropogenic activities.
- Food shortages and contaminated food.
- Current from power lines.
Bombay Natural History Society (BNHS)
- BNHS is an all-India wildlife research organisation, promoting nature conservation since the year 1883.
- The objective of BNHS is to conserve nature, mainly biodiversity, through action based on research, education and public awareness.
- BNHS also organises and conducts nature trails and camps for the general public.


Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Ammonia Gas Leak
Why in News?
An ammonia gas leak at an ice factory in Ratlam, Madhya Pradesh, raised concerns among residents.
Key Points
- About Ammonia:
- Ammonia (NH₃) is a colourless gas with a pungent odor that is widely used in industry and occurs naturally in the environment and the human body .
- It is produced by the Haber-Bosch process (N₂ + 3H₂ → 2NH₃) at high temperature and pressure in the presence of a catalyst .
- Its concentrated form is corrosive and can cause burns or explosions at high temperatures . It is stored as a compressed liquid .
- It is highly soluble in water and forms ammonium hydroxide on contact with water .
- It has 9 times higher energy density than Li-ion batteries and 3 times higher than compressed hydrogen , making it a promising carbon-free energy carrier .
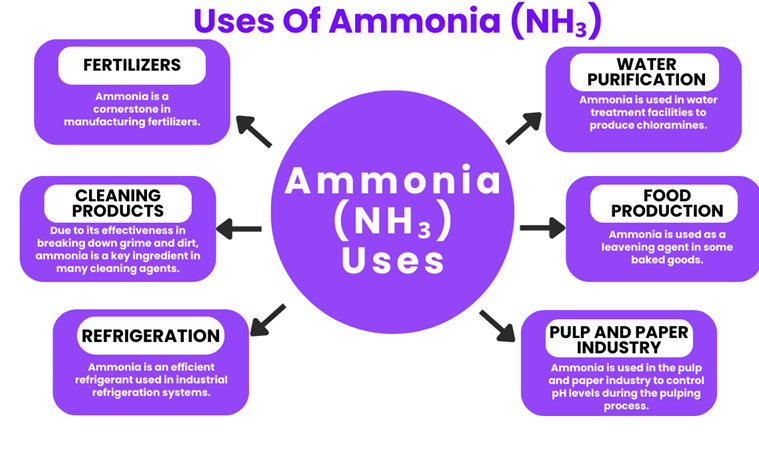
- Major Applications:


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Constitution Park in Kota
Why in News?
Lok Sabha Speaker Om Birla inspected the site earmarked for the proposed Constitution Park in Kota, Rajasthan .
Key Points
- About Constitution Park:
- This park, to be developed over 12,000 square meters, will offer Kota city a renewed cultural and intellectual identity.
- The entrance of the park will display the preamble of the Indian Constitution – “Justice, Equality and Fraternity” .
- A grand statue of Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar made of gunmetal will be installed in the centre .
- The historical events of the making of the Constitution will be depicted on a 20 feet high wall .
- Civil rights will be depicted through crafts and sculpture in the Fundamental Rights Path .
- Information about the personalities who contributed to the making of the Constitution will be made available through digital means in the park .
- This park, to be developed over 12,000 square meters, will offer Kota city a renewed cultural and intellectual identity.
- Objective:
- To convey the basic spirit of the Constitution ' justice, liberty, equality and fraternity ' to the general public.
- To create an inspiring hub for students, researchers, citizens and tourists .
The Indian Constitution
- The Constitution of India is the longest written constitution of any sovereign country in the world.
- The Constitution of India was handwritten in calligraphy font by Prem Bihari Narayan Raizada and each page was embellished by the artists of Shantiniketan under the guidance of Nandalal Bose .
- It took 2 years, 11 months and 18 days to create the Constitution.
- The basic structure of the Indian Constitution is based on the Government of India Act, 1935.
- The Constitution of India declares India a sovereign, socialist, secular and democratic republic which assures justice, equality and liberty to its citizens and seeks to promote fraternity .
- The Constitution of India was made by the Constituent Assembly. The Constituent Assembly of India formed a total of 13 committees to deal with various tasks related to the making of the Constitution.
- The Constitution of India was drafted by a seven-member committee headed by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar , who is considered the Father of the Indian Constitution .
- The Constitution of India was inspired by several other constitutions, such as the US Constitution, the UK Constitution, the Irish Constitution, the French Constitution, the Canadian Constitution, the Australian Constitution and the Japanese Constitution.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan