Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
CRPF’s New Operations Base in Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
The Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF) has established a new operations base in the Maoist corridor in Chhattisgarh’s south Bastar region, strengthening its presence in core Left Wing Extremism-affected areas of the State.
Key Points
- About Forward Operating Base (FOB):
- The 196th and 205th Commando Battalion for Resolute Action (CoBRA), along with other paramilitary units, assisted in establishing the base.
- The FOB is in a remote, hilly region that houses Maoist training camps, weapons, ammunition dumps, and ration units.
- It lies within the stronghold of the Maoists from the south and west Bastar divisions.
- Security Challenges and Resistance:
- The area serves as the operations centre of the first battalion of armed Maoist cadres.
- The CRPF demolished a tall red-colored memorial erected by Maoists in memory of their fallen cadres using a heavy earth-moving machine.
- Government Strategy and Expansion:
- This base is the 13th in a series of new FOBs being created as part of the Union government’s goal to eliminate Left-Wing Extremism by March 2026.
- More FOBs are planned before the Maoists' annual Tactical Counter-Offensive Campaign (TCOC) begins.
- The TCOC is a summer offensive by Naxals, leveraging improved visibility in dry forests to launch attacks on security forces.
- Anti-Naxal Operations in Chhattisgarh:
- Over the past three to four years, the CRPF has established more than 40 FOBs in Chhattisgarh.
- The most intense anti-Naxal operations are concentrated in southern Bastar, bordering Odisha and Telangana.
Central Reserve Police Force (CRPF)
- The CRPF was initially established as the Crown Representatives Police in 1939 in response to political turmoil and unrest within the princely states.
- The force was renamed the Central Reserve Police Force in 1949.
- Sardar Vallabh Bhai Patel, the then Home Minister, envisioned a multifaceted role for the CRPF, aligning its functions with the evolving needs of a newly independent nation.
- COBRA:
- It is a special operation unit of the Central Reserve Police Force of India proficient in guerrilla tactics and jungle warfare. Originally established to counter the Naxalite movement.
- CoBRA is deployed to address insurgent groups engaging in asymmetrical warfare.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Oncology Conclave 2025
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Health Minister inaugurated the second AIIMS Oncology Conclave 2025 at the National Cancer Institute (NCI) of AIIMS, Jhajjar, in Haryana.
Key Points
- Jhajjar Institute:
- The Jhajjar institute is among India's largest public-funded healthcare projects.
- It focuses on advancing cancer care and enhancing research capabilities.
- Oncology Conclave:
- The two-day conclave gathered top oncology experts from Institutes of National Importance (INIs) across India.
- Discussions centered on advancements in cancer care, treatment methodologies, and ongoing research initiatives.
- The event highlighted collaborative efforts in preventing and managing breast cancers, as well as head and neck cancers.
- Innovation and Research at the Institute:
- The centre collaborates with start-ups, engages Ph.D. students, and involves scientists in research.
- The research aims to create real-world applications benefiting both the market and society.
Cancer
- It is a complex and broad term used to describe a group of diseases characterised by the uncontrolled growth and spread of abnormal cells in the body.
- These abnormal cells, known as cancer cells, have the ability to invade and destroy healthy tissues and organs.
- In a healthy body, cells grow, divide, and die in a regulated manner, allowing for the normal functioning of tissues and organs.
- However, in the case of cancer, certain genetic mutations or abnormalities disrupt this normal cell cycle, causing cells to divide and grow uncontrollably.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Tremor in Bihar
Why in News?
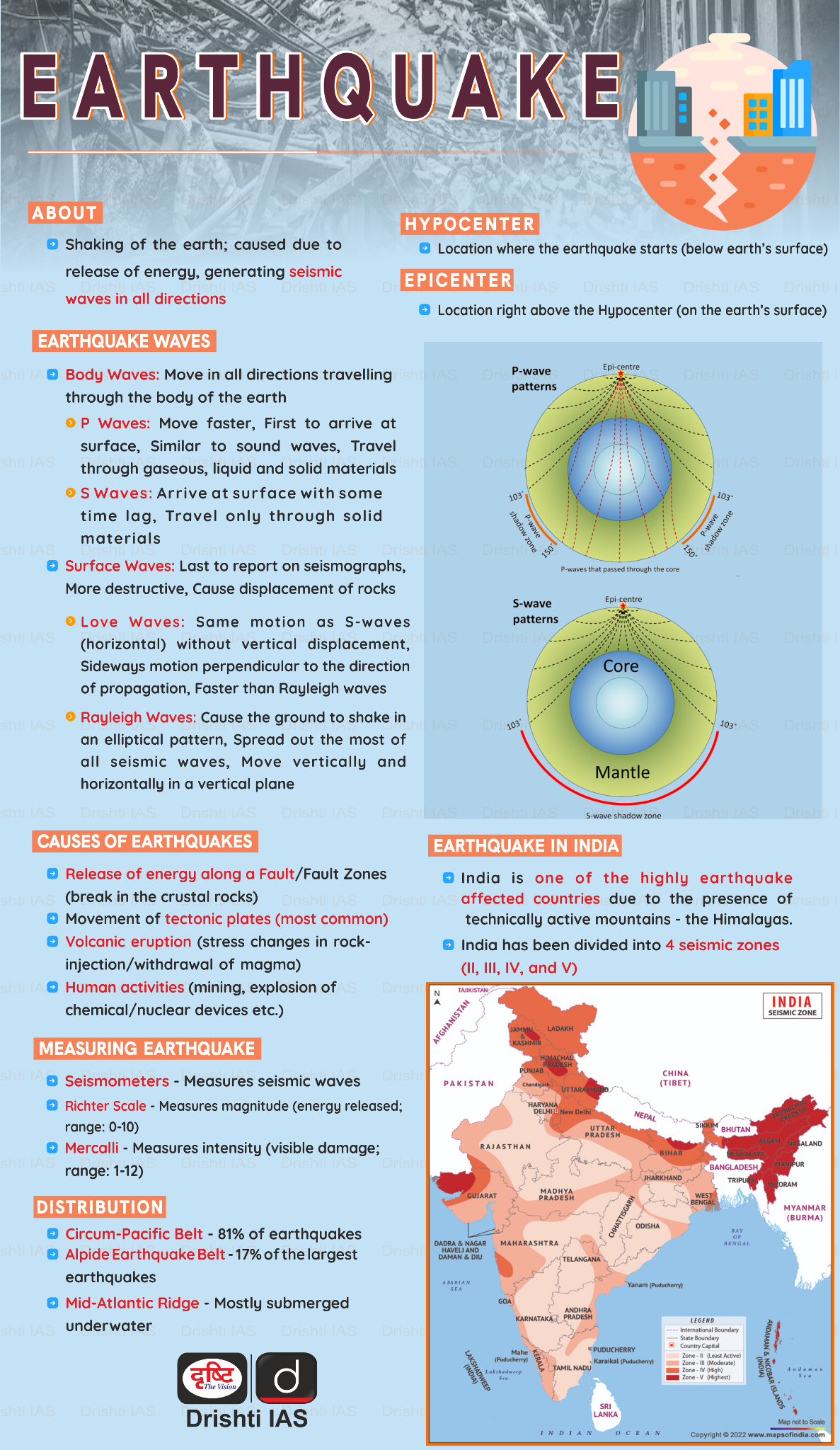
According to the National Center for Seismology, a 4.0-magnitude earthquake struck Siwan, Bihar, on 17th February 2025.
Key Points
- National Centre for Seismology (NCS):
- This is the agency responsible for monitoring and reporting the seismic activity in India and its neighbourhood.
- It operates a network of seismological observatories across the country, and provides real-time data and information on earthquakes and tsunamis.
- It also maintains a website and a mobile app, called BhooKamp, to provide earthquake alerts and updates to the public.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh GCC Policy 2025
Why in News?
Madhya Pradesh has introduced the country’s first dedicated Global Capability Centre (GCC) policy, aiming to establish the state as a leading hub for global innovation and collaboration.
Key Points
- Madhya Pradesh GCC Policy 2025:
- The Madhya Pradesh GCC Policy 2025 integrates incentives for capital expenditure, payroll, upskilling, and research and development.
- A dedicated nodal agency, the Madhya Pradesh State Electronics Development Corporation Limited (MPSeDC), will oversee policy implementation.
- Target Sectors and Strategic Focus:
- The policy targets key sectors, including IT, finance, engineering, human resources, and emerging technologies.
- Special emphasis is placed on artificial intelligence (AI) and cybersecurity to drive digital transformation.
- Decentralizing Business Hubs:
- This is India’s first dedicated framework for fostering GCC growth in tier-2 cities.
- The initiative aims to shift business hubs beyond traditional metro cities, promoting regional economic development.
- The policy seeks to attract over 50 GCCs, generating more than 37,000 direct jobs.
- It aims to position Madhya Pradesh as a center of excellence for IT/ITeS, advanced analytics, R&D, and digital transformation.
- Foreign Investments and Industrial Ecosystem:
- The policy facilitates foreign investments and infrastructure development across multiple industries.
- The policy was unveiled ahead of the biennial Global Investors' Summit in Bhopal.
- Infrastructure:
- Madhya Pradesh houses over five Special Economic Zones (SEZs), 15+ IT parks, and 150+ Electronics System Design and Manufacturing (ESDM) units.
- Key IT hubs include Indore, Bhopal, and Jabalpur, with upcoming projects like Knowledge City and Electronics Manufacturing Cluster 2.0.
- Ranked 4th in the Ease of Doing Business Rankings (2023), Madhya Pradesh ensures streamlined regulatory processes and investor-friendly policies.
- Policy Implementation and Governance:
- The MPSeDC serves as the nodal agency for policy execution.
- A dedicated Policy Implementation Unit (PIU) will manage project approvals, incentive allocation, and compliance monitoring.
- By fostering innovation and attracting global tech centers, Madhya Pradesh contributes to India’s vision of a USD 110 billion GCC market by 2030.
Global Capability Centers (GCCs)
- About:
- Global Capability Centers (GCCs), also known as Global In-House Centers (GICs), are strategic outposts established by multinational corporations (MNCs) in countries around the world.
- Operating as internal entities within the global corporate framework, these centres offer specialised capabilities including IT services, research and development, customer support, and various other business functions.
- Examples of GCCs:
- General Electric (GE) has a large GCC in Bangalore, focused on R&D and engineering for its aviation and healthcare businesses.
- Nestle has established a GCC in Lausanne, Switzerland, dedicated to product development and innovation for its food and beverage brands.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Ammonia Gas Leak in Kota
Why in News?
Ammonia gas leaked from a Chambal Fertilisers and Chemicals Limited (CFCL) plant near Gadepan village in Kota district of Rajasthan. This leak caused students of a government school to fall sick, with the children complaining of nausea and fainting after inhaling the gas’s sharp, suffocating odor.
Key Points
- Impact of the Gas Leak:
- The gas leak affected students who went to the school grounds to fetch water, with some complaining of breathlessness and abdominal pain.
- The school and the CFCL factory share boundaries, likely contributing to the exposure.
- School staff immediately transported the students to the hospital in their own vehicles as their condition worsened.
- Precautionary Measures:
- As a precautionary measure, the school was closed, and children were sent home after the incident, which caused panic in the village.
- Lok Sabha Speaker and local officials visited the hospital to check on the affected students.
Ammonia Gas (NH3)
- About:
- It is a compound of Nitrogen and Hydrogen.
- It is a colorless gas with a pungent, penetrating odor.
- Ammonia is highly reactive and a soluble alkaline gas.
- Mode of Production:
- Natural:
- Produced in soil through bacterial processes.
- Generated during the decomposition of organic matter, including plants, animals, and animal waste.
- Bacteria in the intestines also produce ammonia, and a small amount is generated by lightning strikes.
- Commercial:
- Produced through steam reforming of natural gas and coal gasification.
- Natural:
- Uses:
- Used to produce nitrogen compounds like urea, the most commonly used source of nitrogen in fertilizers.
- Applied directly to soil for crops, lawns, and plants.
- Utilized in various cleaning products.
- Forms compounds like ammonium nitrate, ammonium sulfate, and various ammonium phosphates.
- Used in the manufacture of explosives.
- Used in refrigeration and cooling systems.
- Impact:
- Plants:
- Causes direct toxic damage to leaves.
- Alters plant susceptibility to frost, drought, and pathogens, including insect pests and invasive species.
- Health Risks:
- Long-term exposure to low concentrations or short-term exposure to high concentrations can cause adverse health effects from inhalation.
- Symptoms may include burning sensations in the nose, throat, and respiratory tract irritation.
- Plants:
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Kashi Tamil Sangamam
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister inaugurated the third edition of the Kashi Tamil Sangamam in Varanasi. The unique event highlights India’s cultural foundations and emphasizes the emotional and creative bond shared between Kashi and Tamil Nadu.
Key Points
- Inspiration and Vision:
- The Sangamam is inspired by the vision of ‘Ek Bharat, Shrestha Bharat (One India, Excellent India)’.
- Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister highlighted that the event is part of a grand spiritual and cultural initiative aimed at advancing this vision.
- The event is integrated with the grand Maha Kumbh 2025 celebrations, elevating the centuries-old tradition and strengthening the vision of uniting India through the Kashi Tamil Sangamam.
- Significance of Kashi, Kumbh, and Ayodhya:
- This edition holds special significance as the first to be held after the construction of the Ram Temple in Ayodhya.
- Delegates will have the opportunity to immerse themselves in the divinity of Kashi, Kumbh, and Ayodhya.
- The CM emphasized Kashi’s historical significance as a centre of India’s cultural heritage and spirituality and praised the legacy of Tamil literature.
- The event reconnects participants with this invaluable heritage.
- Theme of '4S':
- This year’s Sangamam is centered around the theme of ‘4S’, uniting India’s Saint tradition, Scientists, Social reformers, and Students.
- The theme draws inspiration from Maharishi Agastya, believed to be the sage who bridged north and south India.
- The Kashi Tamil Sangamam has become an effective platform for dialogue between the people of north and south India.
- Music, Heritage, and Devotion:
- The Union Education Minister stated that the celebration weaves together music, heritage, and devotion on the banks of the Ganga.
- He emphasized that development and heritage must go hand in hand.
- Union Government Initiatives:
- Initiatives such as the establishment of the National Digital Repository of the Indian Knowledge System to digitize ancient texts and use Artificial Intelligence (AI) for research were highlighted.
- The Bharatiya Bhasha Pustaka Yojana, which will translate textbooks into 22 Indian languages, creating a "digital Maha Kumbh" for students.
Kashi Tamil Sangamam Significance
- The ancient connection between Kashi (Uttar Pradesh) and Tamil Nadu dates back to the 15th century when King Parakrama Pandya, ruler of the region around Madurai, traveled to Kashi to bring back the lingam for his temple.
- While returning, he stopped to rest under a tree — but when he tried to continue his journey, the cow carrying the lingam refused to move.
- Parakrama Pandya understood this to be the Lord’s wish, and installed the lingam there, a place that came to be known as Sivakasi, Tamil Nadu.
- For devotees who could not visit Kashi, the Pandyas had built the Kasi Viswanathar Temple in what is today Tenkasi in southwestern Tamil Nadu, close to the state’s border with Kerala.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan
 (1).jpg)
 (1).jpg)

.jpg)


