Haryana Switch to Hindi
Diamond League
Why in News?
Recently, Neeraj Chopra finished second in the 2024 Diamond League Final, narrowly missing the top spot by just 1 centimeter.
Key Points
- Neeraj Chopra threw 87.86 meters, finishing 2nd behind Grenada's Anderson Peters, who threw 87.87 meters.
- Chopra’s best throw came on his third attempt, while Peters’ winning throw was achieved in his first attempt.
- This was Chopra’s second consecutive runner-up finish in the Diamond League Final, after winning the trophy in 2022.
- He maintained a consistent top-two finish streak throughout the season.
Diamond League
- The Diamond League is an annual series of outdoor track and field meetings organized by World Athletics, established in 2010.
- It features 32 Diamond Discipline events, with each meeting hosting several of these events.
- The 32 disciplines of the Diamond League are as follows: •
- Men: 100m, 200m, 400m, 800m, 1500m/Mile, 3000m/5000m, 3000m SC(Steeplechase), 110m Hurdles, 400m Hurdles, High Jump, Pole Vault, Long Jump, Triple Jump, Shot Put, Discus Throw, Javelin Throw;
- Women: 100m, 200m, 400m, 800m, 1500m/Mile, 3000m/5000m, 3000m SC(Steeplechase), 100m Hurdles, 400m Hurdles, High Jump, Pole Vault, Long Jump, Triple Jump, Shot Put, Discus Throw, Javelin Throw.
- The 32 disciplines of the Diamond League are as follows: •
- Some events losing Diamond Discipline status are moved to the World Athletics Continental Tour, the second tier of track and field competitions.
- The 2024 Diamond League concluded with its finals in Brussels, Belgium, on 13th and 14th September.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana Assembly Dissolved
Why in News?
Recently, the Haryana Assembly was dissolved ahead of polls to prevent a potential constitutional issue of mandatorily convening a session within 6 months.
Key Points
- The Haryana Assembly was dissolved by the Governor under Article 174(2)(b) of the Constitution on the recommendation of the Chief Minister and the council of ministers.
- Article 174 of the Constitution authorizes the Governor to summon, dissolve and prorogue the state legislative assembly.
- Article 174(2)(b) of the Constitution gives powers to the Governor to dissolve the Assembly on the aid and advice of the cabinet. However, the Governor can apply his mind when the advice comes from a Chief Minister whose majority could be in doubt.
- Article 174 of the Constitution authorizes the Governor to summon, dissolve and prorogue the state legislative assembly.
- The dissolution aimed to prevent the requirement to convene a session within six months of the last assembly meeting, which occurred on 13th March, 2024, with a session due by 12th September, 2024.
- Article 174(1): The Governor shall from time to time summon the House or each House of the Legislature of the State to meet at such time and place as he thinks fit, but six months shall not intervene between its last sitting in one session and the date appointed for its first sitting in the next session.
Governor
- Article 153 says that there shall be a Governor for each State. One person can be appointed as Governor for two or more States.
- A Governor is appointed by the President and is a nominee of the Central Government.
- It is stated that the Governor has a dual role.
- He is the constitutional head of the state, bound by the advice of his Council of Ministers (CoM).
- He functions as a vital link between the Union Government and the State Government.
- Articles 157 and 158 specify eligibility requirements for the post of governor.
- Governor has the power to grant pardons, reprieves, etc. (Article 161).
- There is a CoM with the CM at the head to aid and advise the Governor in the exercise of his functions, except some conditions for discretion. (Article 163)
- The Governor appoints the Chief Minister and other Ministers (Article 164).
- Governor assents, withholds assent, or reserves the bill for the consideration of the President passed by the Legislative Assembly (Article 200).
- Governors may promulgate the Ordinances under certain circumstances (Article 213).
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Cyber Tehsil
Why in News?
Cyber Tehsil is a digital governance initiative implemented by the Revenue Department, Government of Madhya Pradesh to streamline and modernize land-related administrative processes.
Key Points
- Statewide Expansion: Launched as a pilot on 1st June 2022, now implemented across all 55 districts.
- Purpose: Digitizes land registration and mutation processes, reducing manual intervention and improving transparency.
- Paperless System: Land mutation is fully automated and online, starting automatically after property registration.
- Quick Resolution: Entire process completed within 15 days, ensuring fast and efficient service.
- Automatic Case Generation: Mutation cases are automatically registered via the Inspector General of Registration and Stamps (IGRS) portal, cutting down manual delays.
- Digital Delivery: Updated land records are sent directly via email or WhatsApp.
- Court Case Reduction: Resolves 2 lakh of 14 lakh mutation cases without requiring court appearances, easing the judicial burden.
Inspector General of Registration and Stamps (IGRS)
- IGRS is a key official in charge of managing and overseeing the registration of documents and the stamping process in a state.
- The IGRS supervises the registration of various legal documents such as property deeds, marriage certificates, and other important documents.
- Ensures that the registration process adheres to legal requirements and standards set by the state.
- Manages the collection of stamp duty, which is a tax imposed on certain documents.
- Ensures compliance with stamp duty regulations and takes action against violations.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Diamond Mining in Panna
Why in News?
Recently, Panna district in Madhya Pradesh, a well-known diamond mining hub, announced an auction of rough diamonds.
Key Points
- Panna’s Diamond Industry:
- Panna has been a diamond mining center for centuries.
- The district’s diamond deposits have dwindled due to over-mining, making large discoveries rare.
- Mining serves as an alternative income source for the largely tribal population, with modest daily earnings of Rs. 250-300.
- Legal Issues: Most of the remaining diamond deposits are located in protected forest areas, restricting mining activities. The government is exploring legal solutions to expand operations.
- Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957: MMDR Act, 1957 governs mineral exploration and extraction in India. It grants the central government the authority to control mineral resources.
- When one finds a diamond, notify the local authorities, such as the District Collector or relevant mining department, about the diamond.
- Comply with regulations under the Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957, and the rules set by the Directorate General of Mines Safety (DGMS).
- When one finds a diamond, notify the local authorities, such as the District Collector or relevant mining department, about the diamond.
- Mineral Concession Rules, 1960: These rules provide the detailed procedures for obtaining mining leases and licenses.
- Diamonds found on government land or within licensed mining areas, rights may belong to the government or the mining leaseholder, subject to the Mineral Concession Rules, 1960.
- Distinction: Despite land ownership, the extraction of minerals requires separate permits from the government, and ownership of minerals may differ from land ownership.
- Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Act, 1957: MMDR Act, 1957 governs mineral exploration and extraction in India. It grants the central government the authority to control mineral resources.
Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) (MMDR) Act, 1957
- Regulation of Mineral Resources:
- The Act governs the exploration, extraction, and regulation of mineral resources in India, providing the central government with authority to control and manage these activities.
- Licensing and Lease:
- It establishes the framework for granting licenses and leases for mineral exploration and mining, including procedures for obtaining mining rights.
- Control and Compliance:
- The Act mandates adherence to prescribed standards and regulations for mineral extraction, ensuring environmental protection and proper management of resources.
- Central Government Authority:
- The central government has the power to issue directives and enforce regulations related to the development and regulation of mineral resources, including the collection of mineral royalties and fees.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Mukhyamantri School Jatan Yojana
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Chhattisgarh has highlighted concerns about irregularities in the implementation of the School Jatan Yojana by the previous government.
Key Points
- Mukhyamantri School Jatan Yojana: Chief Minister's School Care Scheme is an initiative by the Government of Chhattisgarh aimed at improving the infrastructure and facilities of government schools in the state.
- The Yojana focuses on constructing new classrooms, renovating existing facilities, and improving essential amenities like libraries and restrooms.
- The Yojana aims to enhance the learning environment by providing better seating arrangements and upgraded facilities, which can lead to increased student enrollment and satisfaction among students and teachers.
- Challenges:
- Substandard Work: Allegations of poor construction quality and financial mismanagement have emerged.
- Oversight Deficiencies: Concerns about inadequate oversight and accountability in the scheme’s implementation process.
- Impact on Schools:
- Irregularities may compromise the quality of infrastructure improvements intended for schools.
- Issues with the scheme could negatively affect the learning environment and overall satisfaction of students and teachers.
- Way Forward:
- Investigation: The state government is investigating the allegations and assessing the scheme’s implementation.
- Reforms: Potential reforms and corrective measures may be introduced to address identified issues and enhance the scheme’s effectiveness.
- Strengthened Accountability: Implementing improved oversight mechanisms to ensure better accountability and prevent future irregularities.
- Enhanced Monitoring: Increasing monitoring efforts to ensure the quality and proper execution of infrastructure projects under the scheme.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
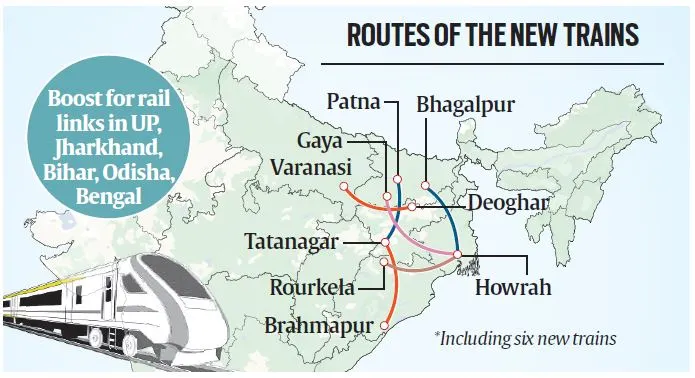
Bihar Gets Four More Vande Bharat Trains
Why in News?
Recently, four new Vande Bharat Express trains were inaugurated for Bihar, enhancing the state’s rail connectivity.
Key Points
- Routes:
- Tatanagar-Patna
- Bhagalpur-Howrah
- Gaya-Howrah
- Deoghar-Varanasi (passing through Bihar)
Vande Bharat Trains
- Features:
- Speed: Vande Bharat trains are designed to be high-speed trains with advanced technology, offering faster travel times compared to conventional trains.
- Comfort: They provide modern amenities including comfortable seating, better cleanliness, and enhanced safety features.
- Efficiency: These trains are known for their energy efficiency and reduced travel time.
- Technological Advancements:
- State-of-the-Art Design: Vande Bharat trains incorporate the latest rail technology and design improvements.
- Passenger Experience: The trains are equipped with facilities aimed at enhancing the overall passenger experience, including improved onboard services and amenities.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan