Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana’s Stubble Burning Crisis
Why in News?
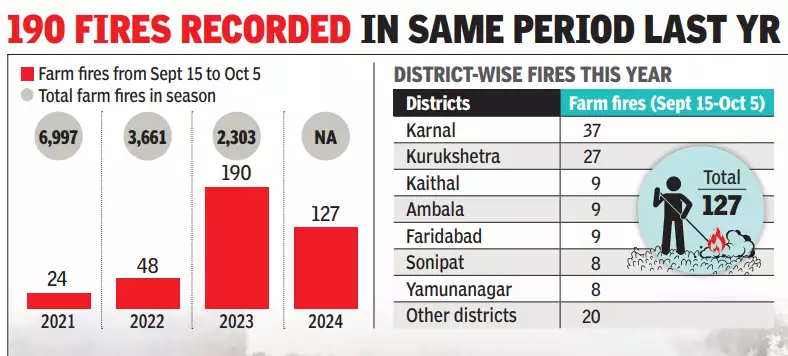
Recently, a report highlights that 84% of Haryana's stubble burning cases are concentrated in just seven districts, exacerbating air pollution and environmental concerns.
Key Points
- Stubble Burning:
- 84% of Haryana’s stubble burning incidents come from seven districts.
- The highest contributors are Fatehabad, Kaithal, Karnal, Jind, Kurukshetra, Ambala, and Yamunanagar.
- These seven districts account for 1,343 of the total 1,595 farm fire incidents recorded in the current season.
- Environmental Impact:
- Stubble burning is a significant contributor to air pollution in Haryana and the Delhi-NCR region.
- The smoke from these fires exacerbates health issues and worsens the already deteriorating air quality during the winter months.
- Government Efforts:
- The Haryana government has introduced various initiatives to discourage stubble burning, including promoting alternatives like crop residue management equipment.
- Fines and incentives have been implemented to motivate farmers to adopt eco-friendly methods of disposing of crop stubble.
- Challenges Faced by Farmers:
- Many farmers continue to burn stubble due to the high costs associated with alternative methods and the limited availability of machinery.
- The short window between harvesting and sowing the next crop puts pressure on farmers, leading them to opt for the quickest solution, i.e., burning the stubble.
- Policy and Enforcement:
- Enforcement of anti-burning laws remains a challenge, despite penalties being in place for violators.
- The government has encouraged the use of Happy Seeder machines, but their adoption has been slow.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Saras Aajeevika Mela 2024
Why in News?
- Recently, the Saras Aajeevika Mela 2024 began in Gurugram, showcasing rural products and promoting women empowerment through self-help groups (SHGs) from across India.
Key Points
- Saras Aajeevika Mela:
- Its aim is to provide a platform for rural artisans and SHG women to showcase and sell their products, including handicrafts, handlooms, organic products, and traditional foods.
- The fair is organized by the National Institute of Rural Development and Panchayati Raj.
- The mela acts as a marketing channel where rural producers can connect directly with urban consumers, helping them increase their income and expand market reach.
- The event significantly contributes to women empowerment by providing opportunities to rural women entrepreneurs to exhibit their craftsmanship on a larger scale.
- Initiatives like the Saras Mela are aligned with the government’s broader objectives of strengthening rural economies and promoting vocal for local under the vision of Atmanirbhar Bharat.
- The initiative is part of the Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission (DAY-NRLM).
Deendayal Antyodaya Yojana-National Rural Livelihood Mission
- About:
- It is a Centrally Sponsored Programme, launched by the Ministry of Rural Development in 2011.
- It aims to eliminate rural poverty through the promotion of multiple livelihoods and improved access to financial services for the rural poor households across the country.
- Functioning:
- It involves working with community institutions through community professionals in the spirit of self-help which is a unique proposition of DAY-NRLM.
- It impacts livelihoods by
- Mobilizing rural households into SHGs.
- Organizing one-woman member from each rural poor household into SHGs
- Providing training and capacity building to SHG members
- Providing access to financial resources from their own institutions and banks.
- Sub Programs:
- Mahila Kisan Shashaktikaran Pariyojana (MKSP): It aims to promote agro-ecological practices that increase women farmers’ income and reduce their input costs and risks.
- Start-Up Village Entrepreneurship Programme (SVEP): It aims to support entrepreneurs in rural areas to set up local enterprises.
- Aajeevika Grameen Express Yojana (AGEY): It was launched in August 2017, to provide safe, affordable and community monitored rural transport services to connect remote rural villages.
- Deendayal Upadhyaya Grameen Kaushalya Yojana (DDUGKY): It aims at building placement-linked skills of the rural youth and placing them in relatively higher wage employment sectors of the economy.
- Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs): DAY-NRLM, in partnership with 31 Banks and State Governments, is supporting Rural Self Employment Institutes (RSETIs) for skilling rural youth to take up gainful self-employment.


.png)




.jpg)







.png)


.jpg)

 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan