Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Admissions of Poor Children on Priority in New Academic Session
Why in News?
The Rajasthan government has taken up the admissions of children from underprivileged sections in private schools under the Right to Education (RTE) Act 2009 on priority for the next academic session.
Key Points
- According to the sources, over 3.08 lakh children had applied for admissions to 31,857 private schools in the State.
- 25% of the seats in the private schools would be filled up with the students belonging to weaker sections of society.
- The Directorate of Elementary Education has made a provision for RTE admissions to the pre-primary classes and Class 1 in the schools, while fixing the age limit for the two categories.
- The children from three to four years of age are admitted to pre-primary classes and those between six and seven years are eligible to get admission to Class 1.
- A large number of private schools in the State have expressed concerns about the admission of students to the pre-primary classes, as the category was added in 2023-24 without any clear guidelines for payment of fees by the government for three years until a student is promoted to Class 1.
Right to Education (RTE) Act, 2009
- The Right to Education Act (RTE), 2009 provided free and compulsory education to children in 2009 and enforced it as a fundamental right under Article 21-A.
- The RTE Act, 2009 aims to provide primary education to all children aged 6 to 14 years.
- Section 12(1)(c) mandates that non-minority private unaided schools should reserve at least 25% of seats in entry-level grades for children from economically weaker and disadvantaged backgrounds.
- It also makes provisions for a non-admitted child to be admitted to an age appropriate class.
- It also states about sharing of financial and other responsibilities between the Central and State Governments.
- Education in the Indian constitution is a concurrent issue and both centre and states can legislate on the issue.
- It lays down the norms and standards related to: Pupil Teacher Ratios (PTRs), Buildings and infrastructure, School-working days, Teacher-working hours.
- It also provides for prohibition of deployment of teachers for non-educational work, other than decennial census, elections to local authority, state legislatures and parliament, and disaster relief.
- It provides for the appointment of teachers with the requisite entry and academic qualifications.
- It prohibits
- Physical punishment and mental harassment.
- Screening procedures for admission of children.
- Capitation fee.
- Private tuition by teachers.
- Running of schools without recognition.
- It focuses on making the child free of fear, trauma and anxiety through a system of child friendly and child centered learning.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Semal Trees
Why in News?
Semal trees are disappearing from south Rajasthan, launching a cascade of adverse consequences for forests and people in the area.
Key Points
- Large quantities of semal are cut in southern Rajasthan, in places like Bhil and Garasia, and sold in Udaipur.
- The cutting violates many laws, from the Rajasthan Forest Act, 1953 to the Forest (Conservation) Act 1980.
- Semal is an integral species that holds the forest ecosystem together. The rock bees nestle on its branches because the tree’s spikes keep its predator, the sloth bears, away.
- Members of tribal communities consume the tree’s reddish root for food during the monsoons. Larvae of the moth Bucculatrix crateracma feed on its leaves.
- The golden-crowned sparrow weaves the lining of its nests with white cotton from its seeds.
- The Dysdercus bugs, the Indian crested porcupine, Hanuman langurs, and some other species feast on the nectar in its flowers.
- The Garasia tribe in the area also believe they are descended from semal trees. The Kathodi tribe use its wood to craft musical instruments while those of the Bhil use it to make utensils.
Semal trees
- Also known as the silk cotton tree and Bombax Ceiba, the Semal tree is a large, fast-growing tree native to India.
- It is known for its distinctive, spiky red flowers and its fluffy seed pods, which contain a cotton-like substance that was once used for stuffing pillows and mattresses.
- The tree is prized for its ornamental value and is often grown in parks and gardens.
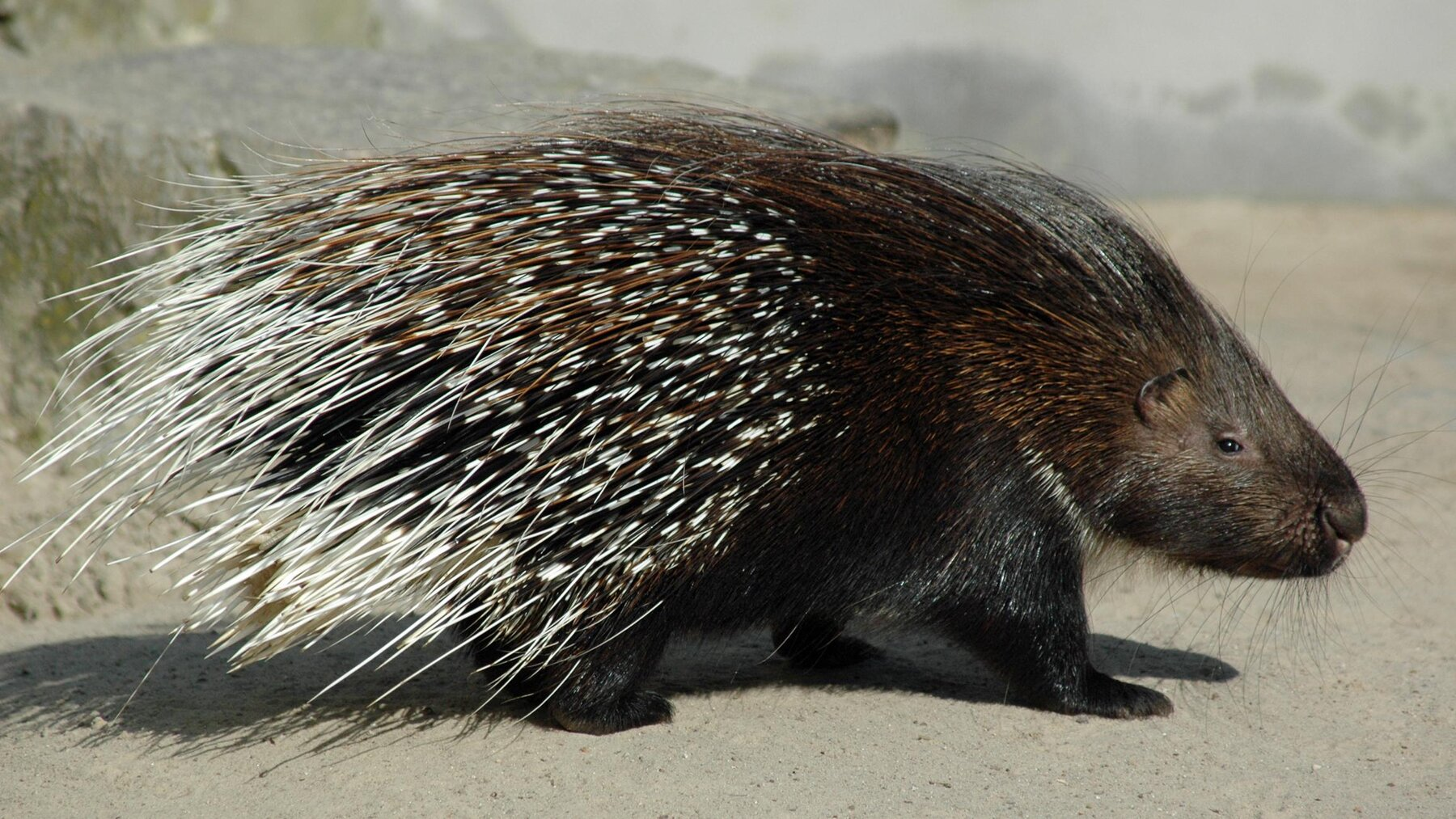
Indian Crested Porcupine
- Scientific Name: Hystrix indica
- Geographical Range: It is found throughout southeast and central Asia and in parts of the Middle East, including such countries as India, Nepal, Bhutan, Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Pakistan, Israel, Iran, and Saudi Arabia.
- Behaviour:
- Nocturnal creatures that spend around 7 hours foraging every night.
- Live in natural caves or excavated burrows.
- Predators include large cats, wolves, hyenas, and humans.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern (LC)
- Wildlife Protection Act 1972: Schedule IV
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Shambhu River
Why in News?
The Shambhu river at Kunwari village in Bageshwar district of Uttarakhand has once more created a man-made lake, covering an area of around 2 square kilometers, causing concern among the locals about an imminent disaster.
Key Points
- This revival of the significant lake is reminiscent of previous events in 2022 and 2023 when comparable formations caused by landslides obstructing the river's course led to prompt administrative actions to prevent potential flooding downstream.
- The Shambhu river originates from Bageshwar and joins the Pindar river in Chamoli district.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Pine Needle Power Projects Prove to be Inadequate
Why in News?
Bio-energy projects set up by the Uttarakhand Renewable Energy Development Agency (UREDA), to use the vast quantities of flammable pine needles for generating electricity have been “unsuccessful”, with officials saying appropriate technology does not yet exist to use them.
Key Points
- State authorities have frequently attempted to mitigate the risk of worsening annual forest fires caused by a combination of factors such as climate change-induced droughts and increasing stores of organic material like pine needles and agricultural waste.
- The Uttarakhand government was criticized by the Supreme Court following petitions related to the forest fires caused by the accumulation of dry pine due to low rainfall in April and May 2024.
- In 2021, the State government announced a scheme to establish power projects utilizing pine needles as fuel to produce electricity.
- The initial proposal included creating several units ranging from 10kW to 250 kW in three phases (totalling about 150 MW).
- Despite anticipating the establishment of 58 units, only six 250 kW units (with a total capacity of 750 kW) have been installed so far.
- In 2023, the Uttarakhand government said it was unable to meet its renewable power purchase due to the shortfall in power generated from pine needle projects.
- The abundance of pine needles in Uttarakhand offers a valuable resource.
- Official records indicate that approximately 16.36% of the State's forest area, which is around 3,99,329 hectares, is occupied by Chir Pine (Pinus Roxburghii) forests.
- Each year, it is estimated that over 15 lakh tonnes of pine needles are produced.
- If even 40% of this estimated amount, along with other agricultural waste, could be utilized, it would greatly assist the State in meeting its energy needs while also creating employment opportunities and supporting livelihoods.
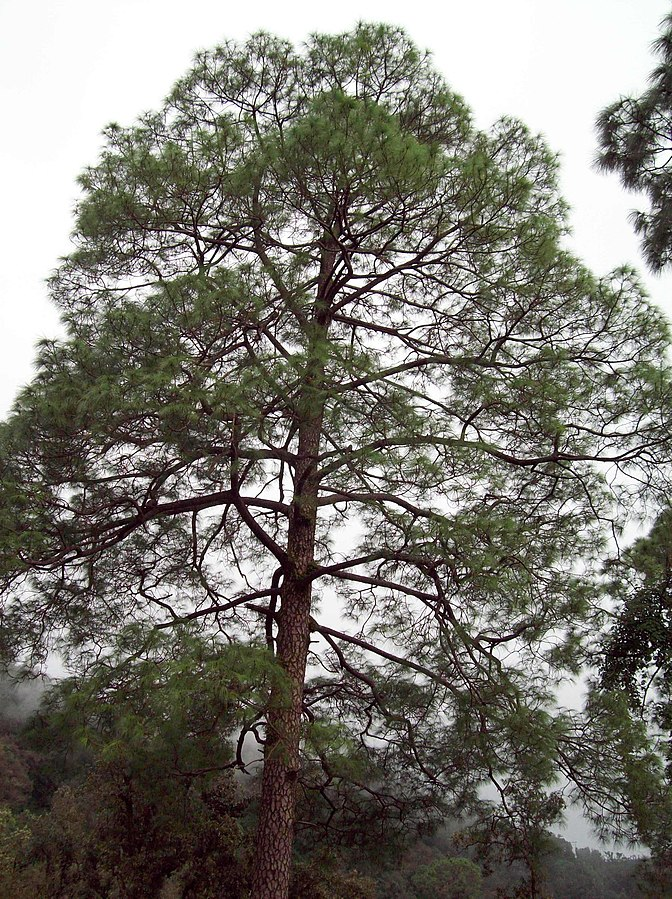
Chir Pine (Pinus Roxburghii)
- Pinus Roxburghi, commonly known as chir pine, is a species of pine tree native to the Himalayan region. It is an important timber species and is widely used for commercial purposes.
- It is native to the Indian subcontinent, particularly in countries like India, Nepal, Bhutan, and parts of Pakistan.
- It is an evergreen coniferous tree that can grow up to 30-50 meters in height.
- The bark of Pinus Roxburghii is thick and scaly, with a reddish-brown color.
- The leaves are needle-like, arranged in bundles of three, and can grow up to 20-30 cm long.
- The tree produces oval-shaped cones that contain seeds.
- Conservation Status:
- IUCN Status: Least Concern (LC)
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
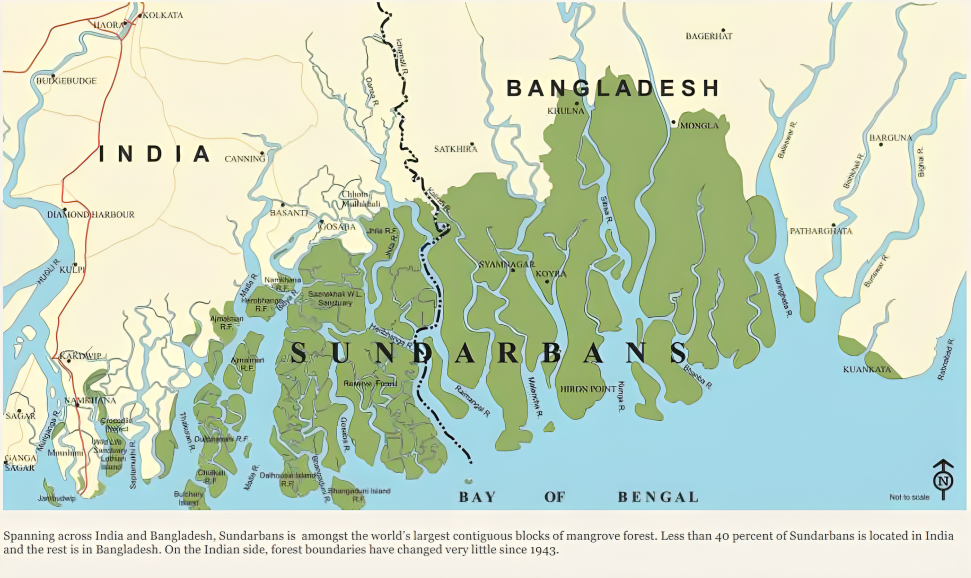
Air Pollution Threatening the Mangrove Ecosystem: Study by IIT Kanpur
Why in News?
The study authored jointly by leading scientists from the Bose Institute, Kolkata, and the Indian Institute of Technology (IIT), Kanpur states that air pollution poses a significant threat to the Sundarbans.
Key Points
- The study is titled “Acidity and oxidative potential of atmospheric aerosols over a remote mangrove ecosystem during the advection of anthropogenic plumes”.
- The study found that huge amounts of pollutants, mainly enriched with black carbon or soot particles, arriving from not only Kolkata metropolis but the entire Indo-Gangetic Plain region, are significantly deteriorating Sundarbans’ air quality, thus affecting its ecosystem.
- The authors of the study have suggested 10-point recommendations to stop Sundarbans’s air quality and overall ecosystem degradation.
- The recommendations include solar energy promotion, wind energy utilisation, electric transportation, subsidised LPG, regulated tourism, banning diesel generators, banning of toxic shipments, closing down of pollutant factories, regulation of brick kilns and land use and strengthening of coastal regulations.
Sundarbans
- The Sundarbans hosts the largest mangrove forests in the world, lying on the delta of the Ganges, Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers on the Bay of Bengal.
- The mangrove ecosystem is a specialised environment between the land and the sea in the tropical and subtropical regions.
Mangroves
- Mangroves are the plant communities occurring in inter-tidal zones along the coasts of tropical and subtropical countries.
- Mangrove forests perform multiple ecological functions such as production of woody trees, provision of habitat, food and spawning grounds for fin-fish and shellfish, provision of habitat for birds and other valuable fauna; protection of coastlines and accretion of sediment to form new land.
- Among the states and Union Territories, West Bengal has the highest percentage of area under total Mangrove cover followed by Gujarat and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
- The India State of Forest Report gives the data about mangroves and their conditions in the country.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Singhbhum Recorded the Highest Voter Turnout
Why in News?
In the first round of polling in Jharkhand, Singhbhum recorded the highest voter turnout at 63.14%.
Key Points
- Singhbhum was followed by Khunti with 62.82%, Lohardaga with 62.60%, and Palamu with 59.99%.
- In Rengdahatu, Murmura, Tensara, and Siamba, polling booths were established alongside an intensive anti-Maoist operation and the setup of CRPF camps.
- The effectiveness of anti-Maoists campaigns is evident as numerous villages have local polling booths for the first time in two decades, leading to high voter turnouts.
- Despite improvement in the situation, West Singhbhum remains one of the worst left-wing extremism-affected districts of the country. It had also witnessed 46 Maoist-related incidents resulting in 22 deaths in 2023.
- Maoism is a form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung. It is a doctrine to capture State power through a combination of armed insurgency, mass mobilization and strategic alliances.
Left Wing Extremism (LWE)
- Also known as left-wing extremism or radical left-wing movements, refers to political ideologies and groups that advocate for significant societal and political change through revolutionary means.
- LWE groups may target government institutions, law enforcement agencies, or private property to further their agenda.
- The LWE movement in India originated in a 1967 uprising in Naxalbari, West Bengal.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan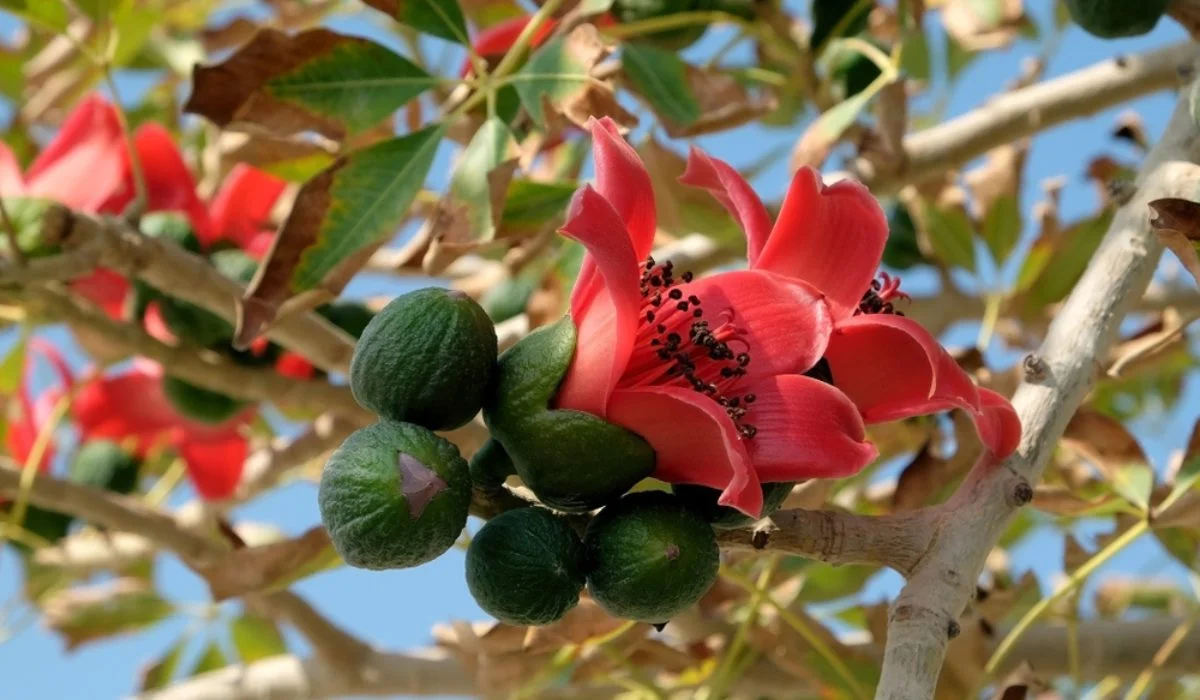





-min.jpg)