Haryana Switch to Hindi
Rise in Plastic Waste Generation
Why in News?
According to the Haryana State Pollution Control Board's annual report, there is an increase in plastic waste production in 2023 to 1,79,406.5 tonnes, marking a 38% surge from 2022’s 1,29,866.7 tonnes. About 14% of this waste was disposed of in landfills.
Key Points
- The report has highlighted a rise in plastic consumption in the state, possibly leading to more plastic waste.
- This development is concerning as it presents major hurdles for waste management and can have lasting environmental consequences.
- Experts suggest that the solution to this problem involves cutting down on plastic usage and encouraging the adoption of eco-friendly alternatives.
- Burning plastic waste in landfills poses a significant environmental issue as it can lead to toxic Particulate Matter (PM) and gaseous emissions due to poorly managed sites where fires can commonly occur.
- Therefore, it is advised to minimize the disposal of plastics in landfills as a preventive measure.
- The Urban Local Body (ULB) department has devised a strategy for managing plastic waste, which has been submitted to the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB).
- All municipal corporations have been instructed to establish Material Recovery Facilities (MRFs) as necessary and to handle their plastic waste in accordance with the Solid Waste Management Rules, 2016, and Plastic Waste Management Rules, 2016.
Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB)
- CPCB is a statutory organisation which was constituted in September, 1974 under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974.
- It was entrusted with the powers and functions under the Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981.
- It serves as a field formation and also provides technical services to the Ministry of Environment and Forests and Climate Change of the provisions of the Environment (Protection) Act, 1986.
Haryana State Pollution Control Board
- It was formed as a statutory organisation by Government of Haryana in the year 1974 to preserve the wholesomeness of water and prevent water pollution after Government of India legislation of Water Act, 1974.
Particulate Matter (PM)
- Particulate matter, or PM, refers to a complex mixture of extremely small particles and liquid droplets suspended in the air. These particles come in a wide range of sizes and can be made up of hundreds of different compounds.
- PM10 (coarse particles) - Particles with a diameter of 10 micrometres or less.
- PM2.5 (fine particles) - Particles with a diameter of 2.5 micrometres or less.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
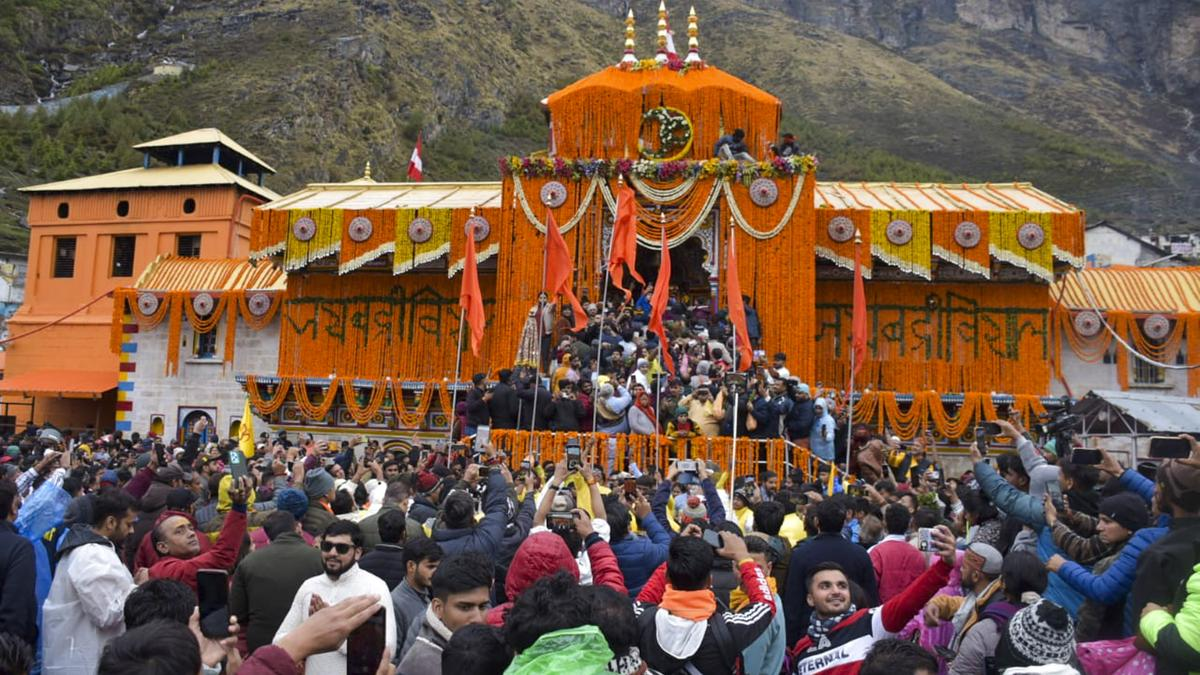
Badrinath Temple in Uttarakhand Opens for Devotees
Why in News?
The doors of the Badrinath temple in the Garhwal Himalayas in Uttarakhand opened for devotees on 12th May 2024 after remaining closed during the winter season.
Key points
- The Chardham Yatra to Badrinath, Kedarnath, Yamunotri, and Gangotri began with the opening of the shrine.
- Following six months of closure, the doors of the Badrinath temple were unlocked while vedic mantras were chanted, rituals were performed, and drums were played.
- The doors of the Kedarnath, Yamyunotri and the Gangotri temples opened for devotees on the occasion of Akshaya Tritiya.
Badrinath Temple
- The temple is also one of the 108 Divya Desams dedicated to Vishnu holy shrines for Vaishnavas who is worshipped as Badrinath.
- It is situated along the banks of Alaknanda river, in Chamoli district of Uttarakhand.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Government to Spend Money on Roads Along China Border
Why in News?
According to the sources, The government is likely to spend over Rs. 2 crore on each kilometre of road to be constructed along the China border in Uttarakhand and Sikkim under the Vibrant Village Programme (VVP).
Key Points
- The Union Ministry of Home Affairs (MHA) has sanctioned 113 roads under the VVP in Arunachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand and Sikkim, to improve connectivity in areas along the China border.
- While 105 roads have been sanctioned in Arunachal Pradesh, five roads in Uttarakhand and three roads in Sikkim have also been approved.
- According to the MHA’s sanction letter, 43.96 km of roads are to be built at a cost of Rs. 119 crore at Pithoragarh district in Uttarakhand.
- Each kilometre of road is expected to cost Rs. 2.7 crore. Once constructed, the “asset” will have to be maintained by the State government.
- In Sikkim, around 18.73 km of roads and 350 metres of steel bridges have been sanctioned under the VVP at the Chungthang and Mangan block in north Sikkim at a cost of Rs. 96 crore.
- Each kilometre of road construction will cost Rs. 2.4 crore.
Vibrant Villages Programme
- It is a Centrally sponsored scheme, announced in the Union Budget 2022-23 (to 2025-26) for development of villages on the northern border, thus improving the quality of life of people living in identified border villages.
- It will cover the border areas of Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim and Ladakh.
- It will cover 2,963 villages with 663 of them to be covered in the first phase.
- Vibrant Village Action Plans will be created by the district administration with the help of Gram Panchayats.
- There will not be overlap with the Border Area Development Programme.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Uttarakhand High Court Asks Government for Relocation
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand High Court has directed the Uttarakhand State Government to locate a new site for moving its operations out of Nainital within a month, stating that this move is in the best interest of the public.
Key Points
- The court also directed the Registrar General to create a portal to take suggestions from advocates and the general public on the issue.
- On the state government's earlier proposal for shifting the High Court to Gaulapar in Haldwani, the high court observed that the land earmarked for the purpose had 75% forest cover and construction in the area would lead to deforestation.
- The high court also made a few recommendations for the kind of land required for its relocation and facilities, including proper accommodation for judges, judicial officers, staff and court rooms.
- The high court's decision to shift its premises has drawn a lot of resistance by the bar association.
Bar Council of India
- About:
- The Bar Council of India is a statutory body created by Parliament under the Advocates Act, 1961 to regulate and represent the Indian bar.
- Regulatory Functions:
- Prescribing standards of professional conduct and etiquette for advocates.
- Establishing procedures for disciplinary actions.
- Setting standards for legal education in India and recognizing qualifying law degrees.
- Other Responsibilities:
- Protecting the rights, privileges, and interests of advocates.
- Organising legal aid for the underprivileged.
- Conducting elections for Bar Council members.
- To deal with and dispose of any matter which may be referred to it by a State Bar Council.
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
SAIL-Bhilai to Set Up Chhattisgarh's First Floating Solar Plant
Why in News?
Bhilai Steel Plant (BSP), the Chhattisgarh-based arm of the state-run Steel Authority of India Limited (SAIL), will install the state's first 15-megawatt (MW) floating solar project in its Maroda-1 reservoir to improve its carbon footprint.
- The steel major is undertaking various projects to reduce carbon emissions, conserve energy, and promote renewable energy.
Key Points
- The project is being implemented through NTPC-SAIL Power Supply Company Limited (NSPCL), a 50:50 joint venture company of National Thermal Power Corporation (NTPC) and SAIL. The solar plant will be set up in Durg district.
- The Maroda reservoir is spread across 2.1 square kilometers with a water storage capacity of 19 cubic milimetres (MM3).
- The water stored in the Maroda-I reservoir not only feeds the plant but also the township.
- Total green power generation estimated from this plant is likely to be about 34.26 million units annually.
- The project is expected to reduce the CO2 emission of BSP by 28,330 tonnes annually.
Carbon Footprint
- According to the World Health Organization (WHO), a carbon footprint is a measure of the impact people’s activities have on the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) produced through the burning of fossil fuels and is expressed as a weight of CO2 emissions produced in tonnes.
- It is usually measured as tons of CO2 emitted per year, a number that can be supplemented by tons of CO2-equivalent gases, including methane, nitrous oxide, and other greenhouse gases.
- It can be a broad measure or be applied to the actions of an individual, a family, an event, an organization, or even an entire nation.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh to Implement CAA as Centre Approves
Why in News?
According to the Madhya Pradesh Chief Minister, the Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA), 2019 will be implemented in the state as and when the Centre signals.
Key Points
- The CM, also said that the policies of both the Central and Madhya Pradesh governments align completely. He emphasized their full readiness to implement the CAA as soon as directed by the Centre.
- The Phase 4 voting for eight seats in Madhya Pradesh Lok Sabha Election 2024 will take place on 13th May 2024.
- Madhya Pradesh will see voting for Dewas, Ujjain, Mandsour, Ratlam, Dhar, Indore, Khargone, Khandwa.
Citizenship Amendment Act (CAA), 2019
- The CAA provides citizenship on the basis of religion to six undocumented non-Muslim communities (Hindus, Sikhs, Buddhists, Jains, Parsis and Christians) from Pakistan, Afghanistan and Bangladesh who entered India on or before 31st December, 2014.
- It exempts the members of the six communities from any criminal case under the Foreigners Act, 1946 and the Passport Act, 1920.
- The two Acts specify punishment for entering the country illegally and staying here on expired visas and permits.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan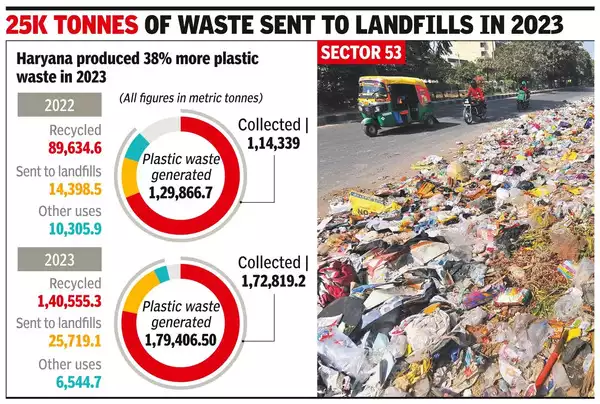





-min.jpg)