Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana CM Approves 10 Projects Worth 56 crore
Why in News?
The Haryana government has decided to implement 10 projects worth Rs 56.4 crore under Rural Augmentation Water Supply programme in Sirsa, Hisar, Palwal, Mahendragarh, Jhajjar and Rewari districts.
Key Points
- The CM accorded administrative approval for these projects to be implemented by the public health engineering department.
- According to the officials, the water supply scheme includes:
- improvement of water supply at Niyana village, Hisar, for Rs 2.95 crore;
- augmentation of water supply scheme and strengthening of distribution system at Kurangawali, Sirsa, for Rs. 5.9 crore;
- canal-based water supply scheme in seven villages of Rewari for Rs 16.9 crore;
- providing independent water works at Neola block in Jhajjar for Rs. 6.2 crore.
- construction of boosting stations at Nangal Sirohi tehsil in Mahendergarh for Rs 2.7 crore.
Rural Augmentation Water Supply Programme
- Under this programme, the existing drinking water supply facilities are improved / strengthened in the villages by undertaking an array of activities which amongst other include Drilling additional tubewells, Augmentation of existing canal based schemes, Creating new canal based water works, Constructing boosting stations, Strengthening of existing distribution system.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Farmers’ ‘Delhi Chalo’ March
Why in News?
Recently, the Union home ministry has deployed at least 50 companies of central paramilitary forces in Haryana to deal with any law and order situation during farmers’ ‘Delhi Chalo’ agitation.
Key Points
- The Haryana police have asked farmers not to participate without permission in a planned march to the Capital.
- According to the official sources, the Haryana government had requested the Centre to deploy at least 64 companies of central paramilitary forces, including the Rapid Action Force (RAF).
- In 2020, the farmers protested against the three laws which after one year of their protest on Delhi borders were repealed in 2021.
- Delhi Chalo was announced in December 2023 demanding the following:
- A legal guarantee to Minimum Support Price (MSP) for all crops.
- Implementation of Swaminathan Commmission’s formula.
- Full debt waiver for farmers.
- Pension for farmers and labourers.
- Withdrawal of cases against farmers during the 2020-21 protest.
- Farmers protest 2.0 is being spearheaded by different unions. After the 2020 protest, farmers’ unions witnessed several factionalism.
- More than 200 farmers’ unions from across the country would participate in the ‘Delhi Chalo’ march.
- The steps taken to not allow farmers to enter Delhi:
- Section 144 has been imposed in Delhi.
- The Haryana government sealed its borders with Punjab.
- Barbed wire, cement barricades, nails on roads have been put.
- Massive security at all entry points to the national capital.
Minimum Support Price (MSP)
- It is the guaranteed amount paid to farmers when the government buys their produce.
- It is based on the recommendations of the Commission for Agricultural Costs and Prices (CACP), which considers various factors such as cost of production, demand and supply, market price trends, inter-crop price parity, etc.
Swaminathan Commission
- The Swaminathan Commission was established in 2004.
- Its report states that the government should raise the MSP to at least 50% more than the weighted average cost of production. It is also known as the C2+ 50% formula.
- It includes the imputed cost of capital and the rent on the land (called ‘C2’) to give farmers 50% returns.
Rapid Action Force (RAF)
- It is a specialised rapid reaction wing of the Central Reserve Police Force, established in October 1992 to deal with riot and crowd control situations.
- It is a zero-response force that can be deployed to crisis situations within a minimum time, instilling confidence, and security among the general public.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
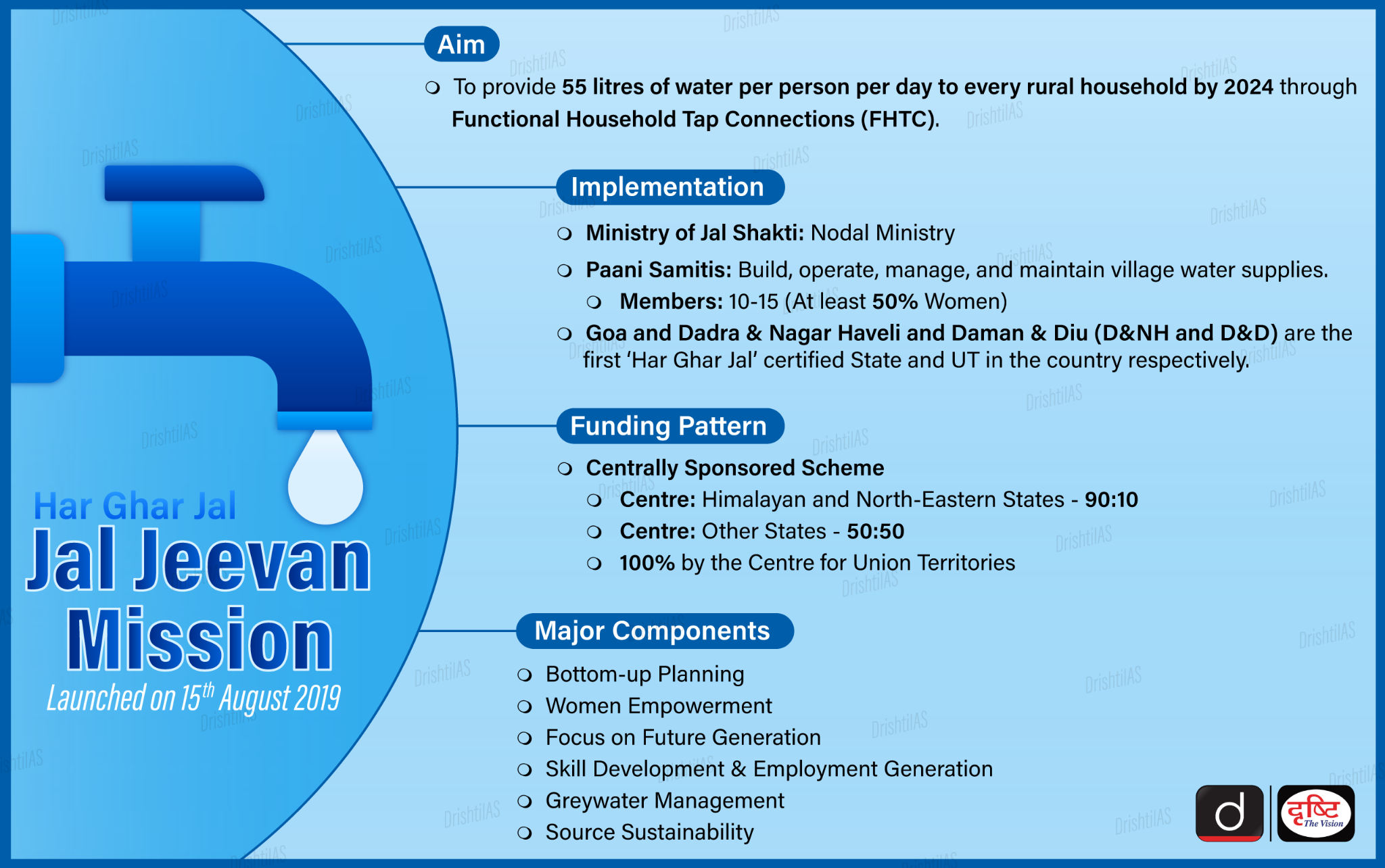
Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM)
Why in News?
In an aim to implement the Centre’s flagship Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM) in the State, the Rajasthan government has instructed water engineers to carry out quality testing by monitoring the situation at the grassroot level, to meet the targets set under the mission and ensure piped water supply to all villages.
Key Points
- The JJM envisages the supply of safe drinking water through tap connections to all rural households by the end of 2024, and has set a target to supply 55 liters of water per person, per day, to every household in villages where the people have been facing water scarcity.
- In Rajasthan, the action plans to achieve the targets under the mission are based on water availability, rainfall pattern, drought situation, groundwater level, water harvesting, water-borne diseases and the situation of water resources in each village.
- The State government has made arrangements for the training of the members of village-level committees to make them aware of the operation of schemes, water conservation, efficient use of drinking water, and bank account operations.
- The district and village action plans, presented and approved by the Gram Sabhas, have also played an important role in meeting the water needs of different areas.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Zero Tolerance Policy Against Corruption
Why in News?
According to Rajasthan Chief Minister Bhajanlal Sharma, the government is working on the policy of 'zero tolerance' against corruption.
Key Points
- The CM stated that negligence and corruption in works related to public interest will not be tolerated under any circumstances.
- The CM instructed the officers to ensure regular public hearing, prompt disposal of complaints, monitoring them and taking feedback.
- All district-level officers should hold public hearings for at least one hour regularly, so that the complainants do not have to come to the capital with their problems.
- The status of electricity and drinking water supply, medical facilities, progress of Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM), Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra, law and order and other issues were also reviewed.
Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra
- It is a nationwide campaign to raise awareness through outreach activities to achieve saturation of schemes of Government of India across the country covering all Gram Panchayats, Nagar Panchayats and Urban Local Bodies.
- The campaign is being taken up by adopting a whole of government approach with active involvement of various Ministries/Departments of Government of India, State Governments, Central Government Organisations and Institutions.
Bihar Switch to Hindi
Illegal Mining in Bihar
Why in News?
According to the sources, Enforcement Directorate (ED) has turned its attention towards the mining mafia in Bihar, where large syndicates are allegedly involved in illegal sand mining, causing environmental degradation and huge losses to the state exchequer.
Key Points
- In the past eight months alone, ED has established that illegal sand mining has caused revenue loss worth ₹400 crore to the Bihar government.
- The first case under ED’s scanner pertains to Janata Dal-United (JD-U) MLC, Radha Charan Sah, who was arrested by the agency in September 2023.
- The second case pertains to a company, Aditya Multicom Private Limited, and its directors Jag Narayan Singh and Satish Kumar Singh.
- Earlier, ED has investigated illegal sand or coal mining cases in West Bengal, Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh.
Sand Mining
- About:
- It is defined as the removal of primary natural sand and sand resources (mineral sands and aggregates) from the natural environment (terrestrial, riverine, coastal, or marine) for extracting valuable minerals, metals, crushed stone, sand and gravel for subsequent processing.
- This activity, driven by various factors, poses serious threats to ecosystems and communities.
- Initiatives to Prevent Sand Mining in India:
- Mines and Mineral Development and Regulation Act, 1957 (MMDR Act):
- Sand is classified as a “minor mineral”, under The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulations) Act, 1957 (MMDR Act) and administrative control over minor minerals vests with the State Governments.
- The Mines and Minerals (Development and Regulation) Amendment Act, 2023 was recently passed by the Parliament to amend the MMDR Act, 1957.
- 2006 Environment Impact Assessment (EIA):
- The Supreme Court of India mandated that approval is required for all sand mining collection activities, even in areas less than 5 hectares.
- Sustainable Sand Management Guidelines (SSMG) 2016:
- Issued by the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC), the main objectives of these guidelines include environmentally sustainable and socially responsible mining, conservation of the river equilibrium and its natural environment.
- Enforcement and Monitoring Guidelines for Sand Mining 2020:
- The guidelines provide a uniform protocol for monitoring sand mining across India.
- Mines and Mineral Development and Regulation Act, 1957 (MMDR Act):
Directorate of Enforcement (ED)
- ED is a multi-disciplinary organisation mandated with investigation of offences of money laundering and violations of foreign exchange laws.
- It functions under the Department of Revenue of the Ministry of Finance.
- As a premier financial investigation agency of the Government of India, the ED functions in strict compliance with the Constitution and Laws of India.
- The Directorate of Enforcement was established in the year 1956 with its Headquarters at New Delhi.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand CM Lays Foundation to Palamu Pipeline Project
Why in News?
Recently, Jharkhand Chief Minister laid the foundation stone of the ₹456.52 crore Palamu pipeline irrigation project, aiming to ensure irrigation water availability throughout the year.
Key Points
- According to the sources, the project aims to connect rivers in the area and small dams in different blocks of the drought-hit Palamu district through pipelines to ensure water availability across all seasons.
- The project would cover Chainpur and Medininagar, Satbarwa, Bishrampur, Chhatarpur, Hussainabad, Haidernagar, and Mohemadganj blocks of Palamu district.
- The major water bodies that would be connected to the project include Ranital Dam, Temrain Dam, Butanduba Dam, Malay Dam, Postia Dam, Panghatwa Dam, Kacharwatand Dam, Kundalwa Dam, Wahevadhwa Dam, Batre Dam, Dhankai Dam, Taali Dam, Sukhnadia Dam, and Karmakalan Dam.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Passes Escalator Bill And Lokayukta Amendment Bill, 2024
Why in News?
Recently, the Uttar Pradesh Legislative Assembly passed the Uttar Pradesh Lift and Escalator Bill, 2024 and Uttar Pradesh Lokayukta and Up-Lokayukta (Amendment) Bill, 2024.
Key Points
- After the Bill becomes a law, lifts and escalators cannot be installed without obtaining the approval of the Energy Department.
- A fine will be imposed on the owner or the institution concerned if they fail to get the repairs done and ignore the standards.
- A provision has been made in the Bill that registration will be mandatory for installing lifts and escalators in public.
- They will need to be renewed every five years, tested annually, and a fee of Rs 1,500 needs to be deposited for this.
- Under the Uttar Pradesh Lokayukta and Up-Lokayukta (Amendment) Bill, 2024, the tenure of the lokayukta and the up-lokayukta has been reduced from eight years to five years and the maximum age has been increased to 70 years.
- States like Maharashtra, Gujarat, West Bengal and Haryana have their own laws for installing lifts, but there was no such provision for it in Uttar Pradesh.
- Its implementation will not only curb accidents, but will also strengthen the system.
Lokayukta
- The Lokayukta is the Indian Parliamentary Ombudsman, executed into power, through and for, each of the State Governments of India.
- It is an anti-corruption authority. The object of the Lokayukta system in a state is to investigate grievances, allegations against public servants.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan