Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Study in Chhattisgarh Analysed PM-JAY Implementation
Why in News?
Recently, a study by researchers from the state health resource centre in Chhattisgarh anaylsed the Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (PMJAY).
- PMJAY aimed to reduce out-of-pocket health expenses, particularly during hospital stays.
Key Points
- The study revealed that patients utilizing the scheme faced high out-of-pocket costs, notably in private hospitals, largely due to the common occurrence of dual billing.
- The study was conducted in 2022 by researchers of the State Health Resource Centre in Chhattisgarh, by interviewing 768 individuals who had used PMJAY for hospitalisation in the month preceding the interview. PMJAY has empanelled 1,006 public and 546 private hospitals in the state.
- Private hospitals were found to be charging patients even though they are not supposed to under PMJAY or Ayushman Bharat.
- They would then claim reimbursement from the government for the same treatment, engaging in dual billing, which is considered fraudulent.
- The utilization of private hospitals was identified as the primary factor leading to severe financial burden under PMJAY.
- About 30% of stays in private hospitals resulted in catastrophic health expenses, exceeding 10% of a household's total yearly non-medical spending.
- The research revealed that marginalized groups like scheduled tribes and women heavily relied on public hospitals, despite the accessibility of private healthcare through PMJAY.
- It pointed out that seeking treatment in public hospitals helped individuals avoid high out-of-pocket expenses, as public services were considerably more cost-effective for patients compared to private healthcare, regardless of being covered under publicly funded insurance schemes.
- In India, private healthcare providers lack effective price and quality regulation, leading to the adoption of dual billing by private hospitals, which prioritize profits over patient care.
- The study highlighted the government's failure to enforce a crucial condition in its agreements with hospitals, which prohibits additional charges to patients.
Ayushman Bharat-PMJAY
- About:
- PM-JAY is the world’s largest health insurance scheme fully financed by the government.
- Launched in February 2018, it offers a sum insured of Rs.5 lakh per family for secondary care and tertiary care.
- Health Benefit Packages covers surgery, medical and day care treatments, cost of medicines and diagnostics.
- Beneficiaries:
- It is an entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- The National Health Authority (NHA) has provided flexibility to States/UTs to use non- Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) beneficiary family databases with similar socio-economic profiles for tagging against the leftover (unauthenticated) SECC families.
- It is an entitlement-based scheme that targets the beneficiaries as identified by latest Socio-Economic Caste Census (SECC) data.
- Funding:
- The funding for the scheme is shared – 60:40 for all states and UTs with their own legislature, 90:10 in Northeast states and Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal and Uttarakhand and 100% Central funding for UTs without legislature.
- Nodal Agency:
- The NHA has been constituted as an autonomous entity under the Society Registration Act, 1860 for effective implementation of PM-JAY in alliance with state governments.
- The State Health Agency (SHA) is the apex body of the State Government responsible for the implementation of AB PM-JAY in the State.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Capacity Building Programme
Why in News?
Recently, a two weeks program on Capacity Building Programme on Project and Risk Management for Public Works for the officers from Republic of Tanzania commenced at the National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG), Mussoorie.
Key Points
- NCGG is committed to action research, studies, and capacity building at both the national and international levels.
- It's efforts align with the Indian philosophy of 'Vasudhaiva Kutumbakam’ i.e., “The world is one Family” and emphasizes strengthening bilateral ties and fostering cooperation with other countries.
- The capacity building program focuses on providing a rich cross country experience and a platform for policy dialogue, while sharing best practices focusing on project and risk management in various sectors.
- This will result in the officers gaining valuable insights into the manner in which projects are planned and executed and institutions are being transformed and people are getting closer to the government.
- The core objectives of the two-week training program is to equip officers with essential skills in Project and Risk Management for Public Works, while showcasing several projects and works in several important sectors relevant to the participants.
- The program incorporates immersive field visits, with officers slated to visit key project sites such as Dakpathar Hydropower and Irrigation Dam, NHAI in Uttarakhand, Dwarka Expressway in New Delhi, Indira Paryavaran Bhawan, World Trade Centre NBCC in New Delhi, and the Delhi Metro Rail Corporation, culminating with a visit to the iconic Taj Mahal.
The National Centre for Good Governance (NCGG)
- It was set up in 2014 by the Government of India as an apex–level autonomous institution under the Ministry of Personnel, Public Grievances and Pensions.
- The Centre traces its origin to the National Institute of Administrative Research (NIAR), which was set up in 1995 by the Lal Bahadur Shastri National Academy of Administration (LBSNAA), the Government of India's topmost training institute for civil services.
- NIAR was subsequently rechristened and subsumed into NCGG.
- NCGG deals with a gamut of governance issues from local, state to national levels, across all sectors.
- The Centre is mandated to work in the areas of governance, policy reforms, capacity building and training of civil servants and technocrats of India and other developing countries. It also works as a think tank.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Abbott Mountain’s of Uttarakhand
Why in News?
Abbott Mountain can be found in the beautiful Himalayan ranges of Uttarakhand, in the town of Lohaghat in the Champawat district.
Key Points
- Abbott Mountain holds historical significance, named after British surgeon Dr. James Abbott, who served as the Commissioner of Kumaon during the British Raj era. His contributions to the development of the region are commemorated through this majestic peak.
- Apart from its natural beauty, Abbott Mountain also serves as a paradise for adventure enthusiasts.
- The region is home to a diverse array of flora and fauna, including rare Himalayan species such as musk deer, Himalayan black bear, and a variety of bird species.
Indian Himalayan Region
- The IHR covers ten states and four hill districts of India, viz. Jammu & Kashmir, Uttarakhand, Himachal Pradesh, Sikkim, Arunachal Pradesh, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Nagaland, Tripura, among the states and the hill districts of Dima Hasao, Karbi Anglong in Assam and Darjeeling, Kalimpong in West Bengal.
- The uncontrolled demand-driven economic growth has led to haphazard urbanization, environmental degradation and increased risks and vulnerabilities, seriously compromising the unique values of Himalayan ecosystems.
- In addition to a focus on economic growth, the roadmap for sustainable development of the Indian Himalayas needs to be in sync with the relevant Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs).
- Therefore the development in the Himalayas must be fully embedded in the environmental, socio-cultural and sacred tenets of the region.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
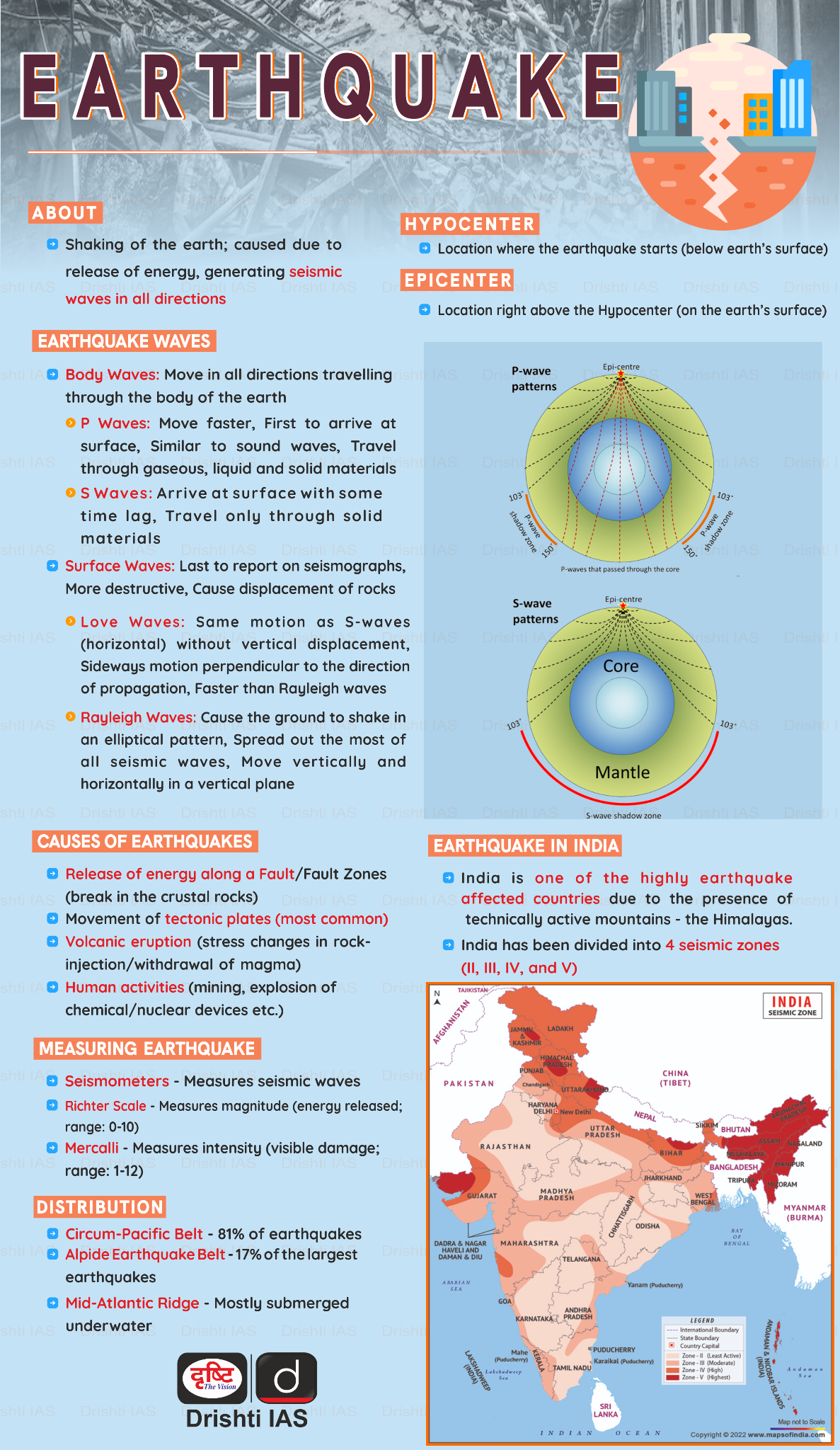
Earthquake in Uttarkashi
Why in News?
According to the National Centre for Seismology (NCS) data, an earthquake of 2.6 magnitude on the Richter scale hit Uttarkashi district of Uttarakhand.
Key Points
- The epicentre of the earthquake was located at Latitude 31.00 and Longitude 79.31, at a depth of 5 kilometres.
- National Center for Seismology (under the Ministry of Earth Sciences) is the nodal agency of the Government of India for monitoring of earthquake activity in the country.
- Currently, India has only 115 earthquake observatories.
- The most important aspect of the Earthquake Observatory is to be able to accurately predict the time of the earthquake.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
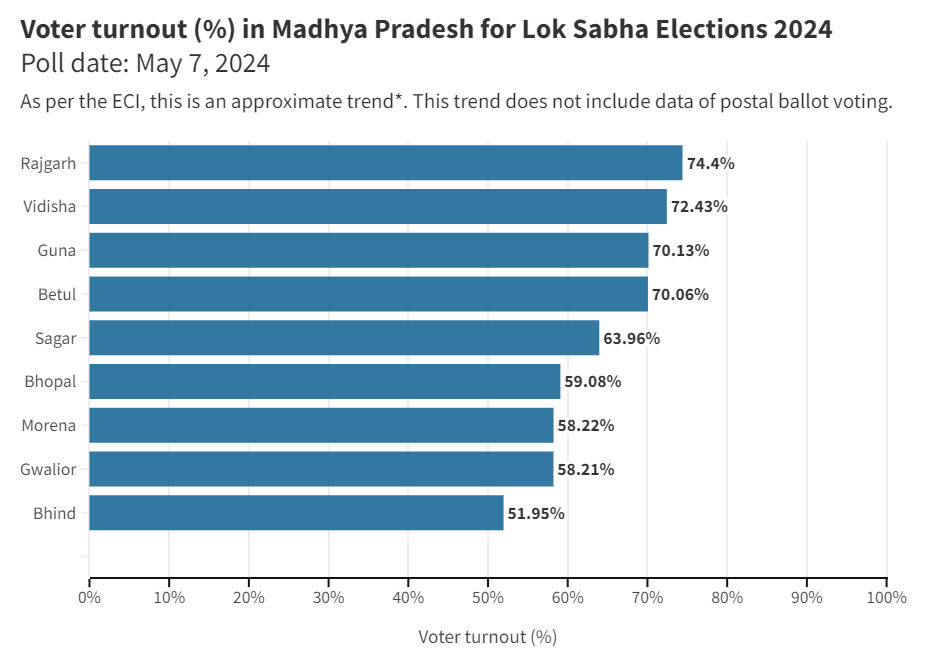
Polling for Nine Seats in Madhya Pradesh
Why in News?
The nine seats in Madhya Pradesh- Morena, Bhind, Gwalior, Guna, Rajgarh, Sagar, Vidisha, Bhopal and Betul that voted in the third phase of the Lok Sabha election recorded an approximate turnout of 66.5%.
Key Points
- According to data shared by State’s Chief Electoral Officer, Rajgarh reported the highest turnout with 76.19% electors voting, while Bhind in the Chambal division recorded the lowest polling in the State at 55.44%.
- So far, 21 seats in Madhya Pradesh have gone to polls in the first three phases, while the remaining eight seats will vote in the fourth phase on 13th May 2024.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
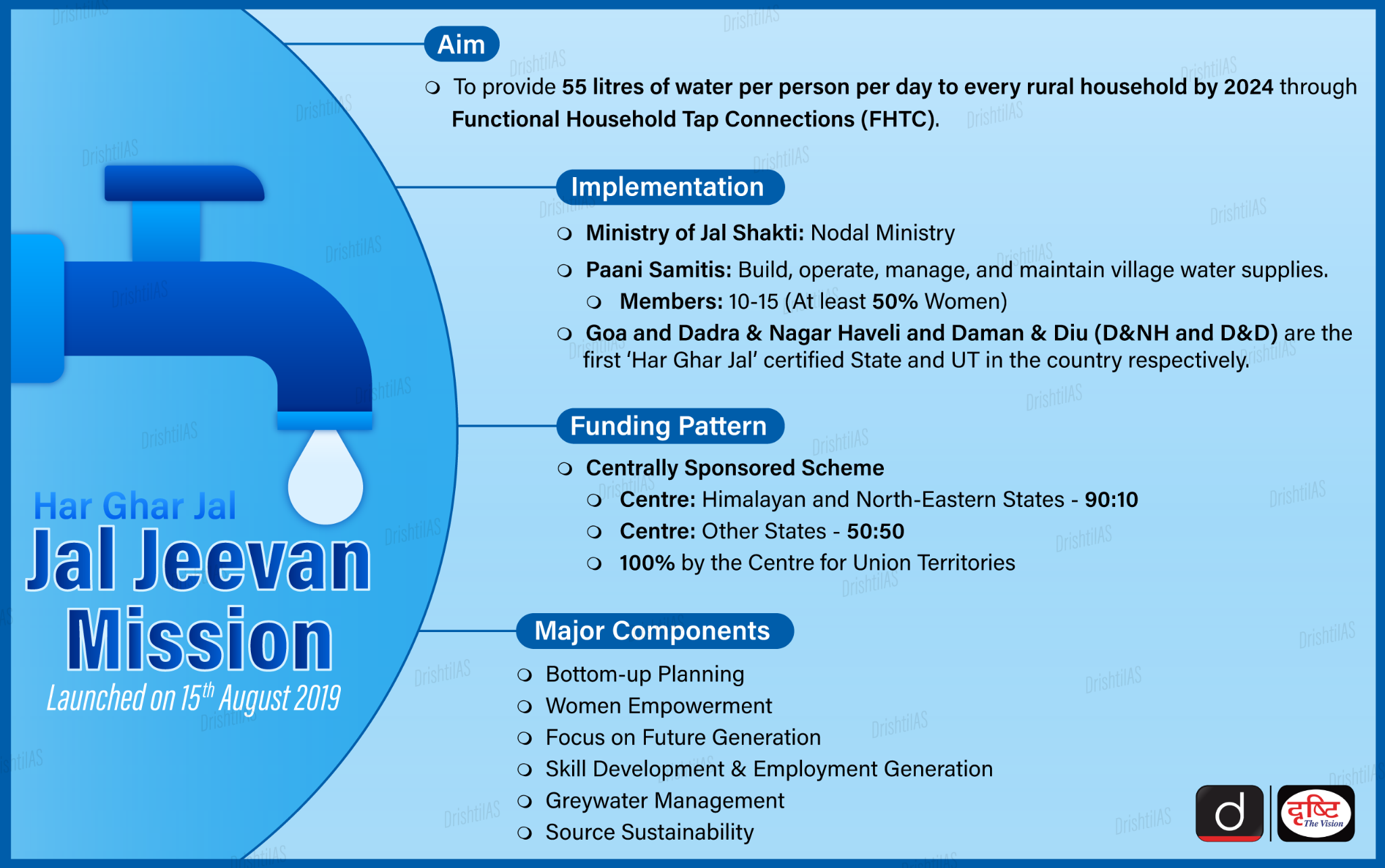
Jal Jeevan Mission Scam in Rajasthan
Why in News?
Recently, the Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI) has registered an First Information Report (FIR) in the centrally-funded Jal Jeevan Mission scheme scam case in Rajasthan.
Key Points
- According to the officials, Jaipur-based contractors used fake completion certificates purportedly issued by Indian Railway Construction International Limited (IRCON) to get tenders from the Public Health Engineering Department of the state.
- The CBI action came after the conclusion of an eight-month-long preliminary enquiry registered in August 2023.
Central Bureau of Investigation (CBI)
- It is the premier investigating police agency in India.
- It provides assistance to the Central Vigilance Commission and Lokpal.
- It functions under the superintendence of the Deptt. of Personnel, Ministry of Personnel, Pension & Public Grievances, Government of India - which falls under the prime minister’s office.
- However, for investigations of offences under the Prevention of Corruption Act, 1988 its superintendence vests with the Central Vigilance Commission.
- It is also the nodal police agency in India which coordinates investigations on behalf of Interpol Member countries.
- Its conviction rate is as high as 65 to 70% and it is comparable to the best investigation agencies in the world.
First Information Report (FIR)
- It is a written document prepared by the police when they receive information about the commission of a cognizable offence.
- It is a report of information that reaches the police first in point of time and that is why it is called the First Information Report.
- It is generally a complaint lodged with the police by the victim of a cognizable offence or by someone on his/her behalf. Anyone can report the commission of a cognizable offence either orally or in writing.
- The term FIR is not defined in the Indian Penal Code (IPC), Code of Criminal Procedure (CrPC), 1973, or in any other law.
- However, in police regulations or rules, information recorded under Section 154 of CrPC is known as First Information Report (FIR).
- There are three important elements of an FIR:
- The information must relate to the commission of a cognizable offence,
- It should be given in writing or orally to the head of the police station,
- It must be written down and signed by the informant, and its key points should be recorded in a daily diary.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan



-min.jpg)