Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Antar Drishti
Why in News?
On 7th April 2025, the National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Disabilities (Divyangjan), Dehradun, and the National Association for the Blind (NAB), New Delhi, jointly inaugurated ‘Antar Drishti’.
Key Points
- Objective and Features:
- ‘Antar Drishti’ is designed as a unique sensory dark room to simulate the daily experiences of persons with visual impairments.
- The facility enables sighted individuals to engage in activities in complete darkness, thereby promoting empathy and understanding of the challenges faced by persons with blindness or low vision.
- The initiative aims to foster inclusion by bridging the perceptual gap between the general public and the lived experiences of visually impaired individuals.
- Implementation of the ‘Enable Inclusion’ App:
- Through this partnership, NIEPVD will implement the ‘Enable Inclusion’ App developed by Amar Seva Sangam for early detection, intervention, and tracking of children with developmental disabilities.
- NIEPVD will integrate its specialization in visual disabilities to enhance the app’s accessibility and responsiveness for users with visual impairments.
- The app will provide personalized support through tele-counseling, rehabilitation planning, and early intervention, advancing DEPwD’s vision of accessible, inclusive, and tech-driven empowerment for persons with disabilities across India.
NIEPVD
- The National Institute for the Empowerment of Persons with Visual Impairment (NIEPVD), under Department of Empowerment of Persons with Disabilities (DEPwD), has been working since 1943 for the education, training, rehabilitation, and empowerment of the visually impaired.
- It established a Regional Centre in Chennai in 1988 for serving the Southern Region, and coordinates four CRCs at Sundernagar (H.P.), Gorakhpur (U.P.), and Jaipur (Rajasthan) to provide rehabilitation and skill development services for persons with disabilities.
Other Initiatives for Persons with Disability
- Rights of Persons with Disabilities Act, 2016:
- It aims to protect and promote the rights of persons with disabilities (PwDs).
- It aims to give effect to the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities (UNCRPD), which India ratified in 2007.
- A person with a benchmark disability is defined as someone with at least 40% of a specified disability.
- Unique Disability Identification Portal:
- The project is being implemented with a view of creating a National Database for persons with disabilities (PwDs), and to issue a Unique Disability Identity Card to each PwDs.
- DeenDayal Disabled Rehabilitation Scheme (DDRS):
- DDRS is a Central Sector Scheme of Government of India which has been implemented since 1999 for providing financial assistance to NGOs working for education and rehabilitation of persons with disabilities.
- National Fellowship for Students with Disabilities:
- It aims to increase opportunities for students with disabilities for pursuing higher education and grants 200 fellowships per year to students with disabilities.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Chintan Shivir 2025
Why in News?
The Union Minister of Social Justice and Empowerment launched the two-day Chintan Shivir 2025 in Dehradun, Uttarakhand to strengthen Centre-State partnerships for ensuring social justice for marginalized communities.
Key Points
- Key Focus Areas:
- The deliberations revolved around four core pillars—education, economic development, social protection, and accessibility.
- The Department showcased progress in schemes like Assistance to Disabled Persons (ADIP), scholarships for PwDs, skill development, and digital inclusion.
- States shared best practices such as mobile assessment camps, inclusive school infrastructure, and accessible transportation models.
- Discussions also covered Pre-Matric and Post-Matric Scholarships and PM-YASASVI, focusing on marginalised groups.
- States flagged issues in digital applications, verification systems, and outreach to rural and tribal communities.
- The Ministry urged adoption of proactive communication and grassroots-level mobilisation to improve scholarship implementation.
- Livelihood and Economic Inclusion:
- The Ministry assessed performance of PM-AJAY and SEED, with states showcasing successful models in asset creation, cluster development, and entrepreneurship.
- Discussions focused on modernising sanitation work, eliminating manual scavenging, and promoting dignity for sanitation workers—especially women—through technology and inter-agency coordination.
PM-YASASVI Scheme
- About: Launched by the Ministry of Social Justice and Empowerment, it provides financial aid for quality education to marginalized students.
- Eligibility: It is open to OBC, Economically Backward Classes (EBC), and DNT students with family income up to Rs 2.5 lakh per annum.
- Sub-Schemes: It is an umbrella scheme consisting of sub-schemes like:
- Pre-Matric Scholarship: Rs. 4,000 annual academic allowance to families with income below Rs. 2.5 lakh.
- Post-Matric Scholarship: Rs. 5,000 to Rs. 20,000 depending on the course category.
- College Education: Top college students get full financial support, including tuition, living expenses, and education materials.
- Hostels: Accommodation facility near government schools and institutions.
SEED
- The Scheme for Economic Empowerment of Denotified/Nomadic/SemiNomadic (SEED) communities was launched in February 2022 by the Ministry of Social Justice & Empowerment.
- It aims to provide free competitive exam coaching to these students, to provide health insurance to families, to uplift clusters of these communities through livelihood initiatives, and to provide financial assistance for housing.


Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Equine Influenza
Why in News?
After detecting equine influenza in horses and mules in two villages of Rudraprayag, the Uttarakhand government has begun taking steps to contain its spread ahead of the Char Dham Yatra.
Key Points
- Equine Influenza: Commonly known as "horse flu," is a fast-spreading respiratory illness affecting horses.
- The disease is primarily caused by two subtypes of the influenza A virus — H3N8 and H7N7.
- The virus spreads rapidly through direct contact with infected animals or contaminated environments.
- While equine influenza is rarely fatal, it can lead to serious complications, particularly in young foals, including secondary bacterial infections and prolonged respiratory issues.
- The disease is primarily caused by two subtypes of the influenza A virus — H3N8 and H7N7.
- Government Response and Action Plan:
- The Uttarakhand government has initiated containment measures to prevent the disease from spreading during the pilgrimage season.
- The State Animal Husbandry Minister chaired a review meeting to assess the situation and guide the response.
- The minister directed officials to prioritise the screening of all horses and mules before allowing their participation in the yatra.
- Horses and mules entering Uttarakhand from other states must carry a valid health certificate and a negative equine influenza test report.
- Char Dham Yatra Schedule 2025:
- The Char Dham Yatra is set to begin with the opening of Yamunotri and Gangotri Dhams on 30th April 2025.
- Kedarnath Dham will open on 2nd May followed by Badrinath Dham on 4th May.
Char Dham Yatra
- Yamunotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Yamuna.
- River Yamuna is the second-most sacred river in India after River Ganga.
- Gangotri Dham:
- Location: Uttarkashi district.
- Dedicated to: Goddess Ganga.
- Considered the most sacred of all Indian rivers.
- Kedarnath Dham:
- Location: Rudraprayag district.
- Dedicated to: Lord Shiva.
- Situated on the bank of the Mandakini River.
- One of the 12 Jyotirlingas (divine representations of Lord Shiva) in India.
- Badrinath Dham:
- Location: Chamoli district.
- Home to the sacred Badrinarayan Temple.
- Dedicated to: Lord Vishnu.
- One of the holy shrines for Vaishnavites.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Protected Archaeological Sites in Haryana
Why in News?
The Haryana government has declared two Harappan civilisation sites in Bhiwani district as protected monuments and archaeological sites.
Key Points
- About the Notification:
- The Haryana’s Principal Secretary for Heritage and Tourism issued a notification declaring the Mitathal site, covering 10 acres, as protected under the Haryana Ancient and Historical Monuments and Archaeological Sites and Remains Act, 1964.
- The Department will take steps to safeguard the site, including fencing and deploying a guard.
- Historical Significance of Mitathal:
- Excavations at Mitathal, conducted since 1968, have revealed evidence of a Copper-Bronze Age culture from the 3rd-2nd millennia BCE.
- The site was first identified in 1913 when a hoard of Samudra Gupta coins was found. Further discoveries included beads, copper implements, and proto-historic material between 1965 and 1968.
- Excavations at Mitathal demonstrate Harappan traditions in urban planning, architecture, and craftsmanship. The site yielded well-burnt pottery, geometric designs, and various antiquities including beads, bangles, and terracotta objects.
- Archaeological Importance of Tighrana:
- The Tighrana site offers insight into the evolution of human settlement after the Harappan period.
- Evidence suggests that the region was first inhabited by Chalcolithic agricultural communities around 2,400 BCE.
- The Sothians, as the early settlers were known, lived in small mud-brick houses with thatched roofs. They were engaged in agriculture and used wheel-made pottery with black-and-white designs.
- The remains from Tighrana show evidence of bead-making and jewellery production, with the discovery of beads and green carnelian bangles.
- Officials have confirmed that the ongoing discoveries provide valuable insights into pre-Siswal, pre-Harappan, and post-Harappan settlements in the area.
- The Tighrana site offers insight into the evolution of human settlement after the Harappan period.
Harappan Civilization
- The Harappan Civilization, also known as the Indus Valley Civilization (IVC), flourished around 2500 BCE along the Indus River .
- It was the largest of the four ancient urban civilizations alongside Egypt, Mesopotamia, and China.
- The IVC is classified as a Bronze-age civilization due to the discovery of numerous artefacts made from copper-based alloys.
- Daya Ram Sahni first excavated Harappa in 1921-22, and Rakhal Das Banerji began excavating Mohenjo-daro in 1922.
- Sir John Marshall, DG of ASI, was responsible for the excavations that led to the discovery of Harappa and Mohenjo-Daro sites of IVC.


Maharashtra Switch to Hindi
New Species of Land Snail in Maharashtra
Why in News?
A team of researchers from India and the UK has discovered a new species of land snail in Maharashtra’s Konkan region and named it Theobaldius konkanensis.
Key Points
- Research Publication and Team:
- Researchers published their findings in the Molluscan Research journal on 11th March 2025.
- The study titled "A new species of cyclophorid land snail from the coastal regions of Maharashtra".
- Endemic Status and Conservation Significance:
- The species is endemic to the northern Western Ghats, a largely unexplored biodiversity hotspot.
- Researchers emphasized the snail’s restricted distribution in Konkan, calling for urgent conservation efforts to preserve its ecological niche.
- Habitat and Behaviour:
- The snail prefers tropical evergreen and semi-evergreen forests.
- Live snails were found from June to September in leaf litter and on damp branches; only shells were observed in other seasons.
- The species is active both day and night, especially under shaded forest canopies.
- Distinctive Morphological Traits:
- The species has a thick, conoidally depressed, widely umbilicated shell with increasing whorls.
- It has a yellowish-brown shell with black striations and unique operculum features—triangular aperture notch, raised fold, and short spines.
- Its spire is more elevated compared to other Theobaldius species.
- Ecology and Reproductive Biology:
- Snails are most active in the monsoon and are important bioindicators sensitive to climate change.
- Most land snails are hermaphrodites; some have separate sexes.
- Reproduction involves courtship, dart-shooting, and both self- and cross-fertilisation.
- Eggs are laid in soil or under litter; they hatch in 2–4 weeks. Lifespan ranges from 2 to 7 years.


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
108 Kundiya Rudra Mahamrityunjaya Mahayagna
Why in discussion?
The Union Minister of Home Affairs and Minister of Cooperation participated in the Maha Purnahuti of 108 Kundiya Rudra Mahamrityunjay Maha Yagya and Sanatan Sammelan in Kotputli, Rajasthan .
Key Points
- About Maha Yagya:
- The main objective of the Mahayagna conducted by Baba Nastinath for a year was to connect every section of the society and spread religious awareness in the society.
- Spiritual and Life Philosophy Principles:
- The Minister praised the four foundational principles advocated by Baba Nastinath — truth, penance, detachment, and selfless service — urging that these be embraced as guiding values in life.
- These principles serve as vital steps toward inner purification, righteous living, and meaningful contribution to society.
- In addition to spiritual values, Baba Nastinath also stressed the importance of protecting nature and caring for animals and birds, reflecting a holistic approach to spiritual and ecological well-being.
- Importance of Nath the Sect:
- The Union Home highlighted the Nath sect’s vital role in strengthening Sanatan Dharma—from Mahaprabhu Adinath to the nine gurus and their successors.
- He noted that in the Nath tradition, the Dhuni is a key spiritual medium, symbolizing self-realization through the harmony of the five elements—earth, water, fire, sky, and air.
Nath Sect
- Nath Sampradaya is a major Hindu religious sect that emerged in the medieval period and in which a unique synthesis of Shaivism, Buddhism and Yoga traditions is seen.
- This sect is based on the practice of Hatha Yoga, which provides guidance towards the highest experience of the soul and physical control.
- The founder of this sect is believed to be Matsyendranath , a great Indian yogi and sage of the 9th century.
- Matsyendranath laid the foundation of the Nath sect and gave it an important place within the Shaiva tradition.
- Due to his contribution, the Nath sect gained widespread recognition and became an important religious tradition in India and Nepal.
- Additionally, Matsyendranath is also revered as a Mahasiddha in Tibetan Buddhism.
- Gorakhnath , a great 10th century master, was a disciple of Matsyendranath.
- Gorakhnath further developed the Nath sect and made it popular in different parts of India.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Child Mortality Rate in Uttar Pradesh
Why in News?
According to the latest Annual Health Report (2024-25) released by the Union Ministry of Health and Family Welfare , despite improvements in the past years, Uttar Pradesh is among the states with the highest Child Mortality Rate in India.
Key Points
- About Child Mortality Rate:
- According to the report, 43 out of every 1,000 children in Uttar Pradesh die before their fifth birthday.
- The current Infant Mortality Rate (IMR) is 38 per 1,000 live births, while the Neonatal Mortality Rate (NMR) is 28.
- According to UNICEF India Report 2020, about 46% of maternal deaths and 40% of neonatal deaths occur during delivery or within the first 24 hours after birth.
- The leading causes of newborn deaths include premature birth (35%), neonatal infections (33%), birth asphyxia (20%) and congenital malformations (9%).
- The annual report,stated that Uttar Pradesh and Karnataka witnessed the highest decline in under-five mortality rate,.
- Uttar Pradesh had set a target to reduce its maternal mortality rate (MMR) to 140 per lakh live births by the year 2020 under its Vision 2030 plan.
- However, the Sample Registration System (SRS) report 2018-20, published by the Registrar General of India in November 2022, showed that the MMR was 167 per lakh live births, which is higher than the national average of 97 per lakh live births.
- The Comptroller and Auditor General of India ( CAG) report said that there was improvement in indicators such as institutional deliveries, neonatal mortality rate, infant mortality rate, and under-5 mortality rate from NFHS 4 (2015-16) to NFHS 5 (2019-21).
- According to the report, 43 out of every 1,000 children in Uttar Pradesh die before their fifth birthday.
- Causes of Child Mortality:
- Septicemia is a major cause of death in newborns, It is a serious bloodstream infection that can lead to sepsis, a life-threatening condition, and organ damage.
- The state has a high rate of home deliveries, which is a major risk. The lack of trained midwives, poor hygiene, and the absence of medical professionals in home deliveries increase the risk of infection.
- Uttar Pradesh lacks access to health care in remote and under-served areas. Lack of health care, such as lack of prenatal and postnatal care, increases infant mortality.
- Although the government has introduced several initiatives like the Janani Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (JSSK) and Home-Based Newborn Care (HBNC) to safeguard maternal and child health, the benefits of these schemes are not uniformly reaching all families.
- As a result, the infant mortality rate remains high, particularly in remote and underserved regions.
- Malnutrition and climate change affect the health of children. This leads to an increase in infant mortality rate.
- Many families lack awareness about infections during delivery and baby care.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Anant Nagar Housing Scheme
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh Chief Minister launched Anant Nagar Housing Scheme of Lucknow Development Authority.
Key Points
- About the Scheme:
- The cost of this scheme is Rs 6500 crore which is proposed in 785 acres.
- Under this, one and a half lakh people will get residential facilities.
- 10 thousand flats will be constructed on 60 plots.
- Provision of housing for more than 25 thousand people has been made in 5 thousand buildings of EWS (Economically Weaker Section) and LIG (Low Income Group) category.
- 3 thousand houses will also be constructed here under the Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana.
- Apart from this, an education city will be developed in an area of 102 acres.
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Urban (PMAY-U)
- Launch:
- PMAY-U was launched on June 25, 2015 with the main objective of providing housing to the people of urban areas by the year 2022.
- Implementation:
- Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs.
- Features:
- It addresses the urban housing shortage among the urban poor (including slum dwellers) by ensuring proper housing for the eligible urban poor.
- Under PMAY(U), basic amenities like toilets, water supply, electricity and kitchen are provided in all houses.
- This scheme promotes women empowerment by providing ownership of houses in the name of the female member or in joint name.
- Priority is given to persons with disabilities, senior citizens, Scheduled Castes, Scheduled Tribes, Other Backward Classes, Minorities , Single Women, Transgender and weaker sections of the society.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan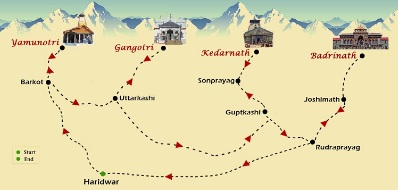
.png)


