Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
New Nodal Agency to Probe Naxal Cases in Chhattisgarh
Why in News?
The Chhattisgarh government has announced that it will constitute State Investigation Agency (SIA) as a new nodal agency to probe cases of terrorism, naxalism and left extremism in the State.
Key Points
- This agency will act as the nodal agency of the state for coordination with the National Investigation Agency (NIA).
- For this, a total of 74 new posts including one Superintendent of Police have been created.
- In another major decision, the Cabinet also decided that it will provide farmers grants at the rate of ₹19,257 per acre under Krishak Unnati Yojana, based on the quantity of paddy procured in Kharif year 2023.
- Also started the restoration of pension scheme for those jailed under the Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA), 1971 during the Emergency period from 1975 to 1977.
- Those detained for less than One month will be given Rs 8,000 per month, the ones detained for one to five months will be given Rs 15,000 per month and people detained for five months and more will be given Rs 25,000 per month.
- The Cabinet also announced the formation of a Department of Good Governance and Convergence for “effective implementation of public welfare policies, to facilitate best possible use of available resources and to ensure quick resolution of public problems”.
National Investigation Agency (NIA)
- The NIA is a federal agency of the Indian government responsible for investigating and prosecuting crimes related to Terrorism, Insurgency, and other national security matters.
- Federal agencies in a country typically have jurisdiction over matters that affect the country as a whole, rather than just individual states or provinces.
- It was established in 2009 following the Mumbai terrorist attacks in 2008, under the National Investigation Agency (NIA) Act, 2008, operates under the Ministry of Home Affairs.
- The National Investigation Agency (Amendment) Act, 2019 was passed in July 2019, amending the NIA Act, 2008.
- The NIA has the power to take over investigations of terrorism-related cases from state police forces and other agencies. It also has the authority to investigate cases across state boundaries without obtaining prior permission from state governments.
Krishonnati Yojana
- The government of India introduced the green revolution Krishonnati Yojana in 2005 to boost the agriculture sector.
- Government through the scheme plans to develop the agriculture and allied sector in a holistic & scientific manner to increase the income of farmers.
- The scheme looks to enhance agricultural production, productivity and better returns on produce.
- It comprises of 11 schemes and mission under a single umbrella scheme:
- Mission for Integrated Development of Horticulture (MIDH)
- National Food Security Mission (NFSM)
- National Mission for Sustainable Agriculture (NMSA)
- Submission on Agriculture Extension (SMAE)
- Sub-Mission on Seeds and Planting Material (SMSP)
- Sub-Mission on Agricultural Mechanization (SMAM)
- Sub-Mission on Plant Protection and Plan Quarantine (SMPPQ)
- Integrated Scheme on Agriculture Census, Economics and Statistics (ISACES)
- Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Cooperation (ISAC)
- Integrated Scheme on Agricultural Marketing (ISAM)
- National e-Governance Plan in Agriculture (NeGP-A)
Maintenance of Internal Security Act, 1971
- The Maintenance of Internal Security Act (MISA) was a controversial law passed by the Indian parliament in 1971 giving very broad powers – indefinite preventive detention of individuals, search and seizure of property without warrants, and wiretapping – in the quelling of civil and political disorder in India, as well as countering foreign-inspired sabotage, terrorism, subterfuge and threats to national security.
- The law was amended several times during the subsequently declared national emergency (1975–1977) and used for quelling political dissent.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh Launches Air Ambulance
Why in News?
Recently, Madhya Pradesh government has inaugurated a new mixed-aircraft air ambulance service, known as the PM Shri Air Ambulance Service.
Key Points
- The PM Shri Air Ambulance Service, is intended to provide access to medical services for residents of the state, operating both a helicopter and a fixed-wing air ambulance.
- The service was inaugurated by the Chief Minister at the Ujjain Regional Industry Conclave.
- The service will offer better access to advanced medical care, particularly for those in rural or poorer areas, and significantly reduce transport times to healthcare facilities.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Madhya Pradesh to Boost Regional Connectivity with Two New Airports
Why in News?
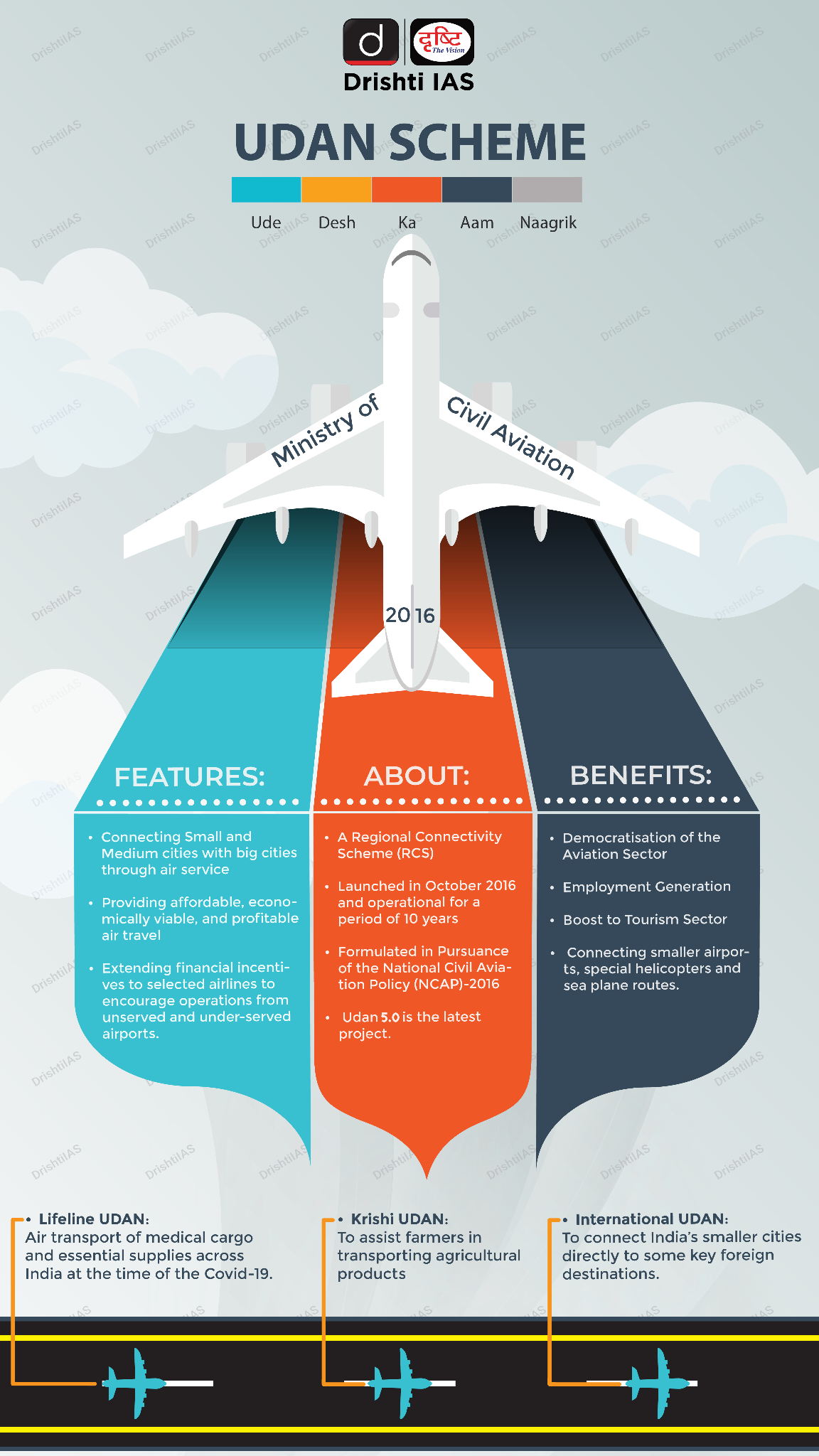
The Ministry of Civil Aviation (MoCA) has announced plans to develop Guna and Shivpuri airports in Madhya Pradesh under the UDAN (Ude Desh Ka Aam Nagrik) scheme.
Key Points
- This initiative aims to improve regional air connectivity and make air travel more accessible for residents in these areas.
- Guna Airport, owned by the state government, was identified for development under the UDAN 5.2 scheme. MoCA has allocated ₹45 crore for its development.
- Shivpuri Airport, located in the Shivpuri district and also owned by the state government, will be developed under UDAN 5.2. This airport is designated for operation with 9-seater aircraft.
- Spirit Air, a new startup airline, has placed bids for the Shivpuri-Bhopal route.
- The Airports Authority of India (AAI) will play a crucial role, providing Communication, Navigation, Surveillance (CNS)/Air Traffic Management (ATM), and Aeronautical Information Services (AIS). It will manage the operation and maintenance (O&M) of both the airports.
UDAN Scheme
- Ude Desh Ka Aam Naagrik (UDAN) was launched as a Regional Connectivity Scheme (RCS) under the Ministry of Civil Aviation in 2016.
- It was formulated based on the review of the National Civil Aviation Policy (NCAP)-2016 and it was planned to remain in force for a period of 10 years.
- Under this Scheme, Regional Connectivity Fund (RCF) was created, which funds the Viability Gap Funding (VGF) requirements of the scheme through a levy on certain domestic flights.
- VGF means a grant one-time or deferred, provided to support infrastructure projects that are economically justified but fall short of financial viability.
- Phases of the Scheme:
- Phase 1 was launched in 2017, with the objective of connecting underserved and unserved airports in the country.
- Phase 2 was launched in 2018, with the aim of expanding air connectivity to more remote and inaccessible parts of the country.
- Phase 3 was launched in November 2018, with the focus on enhancing air connectivity to hilly and remote regions of the country.
- Phase 4 of the UDAN scheme was launched in December 2019, with a focus on connecting islands and other remote areas of the country.
- Phase 5 of the UDAN scheme was launched in 2023, with the focus on increased air connectivity, reduced airfares, creating more jobs, boosting tourism, trade and economic development, and achieving last-mile connectivity.
- UDAN 5.2 focuses on achieving last-mile connectivity through small aircraft such as Category 1A (<9 seats) and Category 1(<20 seats).
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Workshop On 21st Livestock Census in Madhya Pradesh
Why in News?
Recently, the Department of Animal Husbandry and Dairying, Ministry of Fisheries, Animal Husbandry and Dairying organised a workshop on ‘Count of Pastoralists and their Livestock in 21st Livestock Census’ in Indore, Madhya Pradesh.
Key Points
- This workshop was organised to have better idea on the practice of Pastoralism, their habitats, routes in different areas etc. and to arrive at a common consensus on different issues like inclusive definition of Pastoralist, data to be collected and methodology to collect data.
- The department conducts livestock census across the country every 5 years since 1919. The 21st livestock census is due in 2024.
- The livestock census is the main source of data for proper planning and formulation of the Livestock Welfare Programme for bringing further improvement in this sector.
- It covers all domestic animals and head counts of these animals which includes various species of animals/poultry birds possessed by the households, household enterprises/non-household enterprises at that site Breed-wise with their age, sex.
Note
National Livestock Mission (NLM) scheme has been restructured for 2021-22 to 2025-26. The scheme focuses on entrepreneurship development and breeds improvement in poultry, sheep, goat and piggery, including feed and fodder development.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Tiger Safari Banned in Jim Corbett
Why in News?
Recently, the Supreme Court reprimanded the Uttarakhand government for its involvement in the felling of trees and unauthorised construction activities within the Jim Corbett National Park.
Key Points
- According to the Supreme Court a committee will look into whether tiger safaris can be permitted in buffer or fringe areas of national parks in the country.
- The apex court also directed the Centre to establish a committee tasked with proposing measures to alleviate the environmental damage caused and to seek reimbursement from those accountable.
- The Supreme Court pulled up the government over unprecedented felling of trees and environmental damage in the Tiger reserve. It has asked for a status report on illegal construction, felling of trees in Corbett within three months.
- Earlier in January, the Supreme Court had dismissed the National Tiger Conservation Authority's (NTCA) proposal to establish a tiger safari within national parks, emphasizing the need for an "animal-centric" approach over a "tourism-centric" one.
- The Court's stance underscores the importance of prioritizing the welfare and conservation of wildlife within national parks, reaffirming the principle of maintaining natural habitats for animals over tourist attractions.
Jim Corbett National Park
- It is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand. The Project Tiger was launched in 1973 in Corbett National Park (first National Park of India), which is part of Corbett Tiger Reserve.
- The national park was established in 1936 as Hailey National Park to protect the endangered Bengal tiger.
- It is named after Jim Corbett who played a key role in its establishment.
- The core area forms the Corbett National Park while the buffer contains reserve forests as well as the Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The entire area of the reserve is mountainous and falls in the Shivalik and Outer Himalaya geological provinces.
- Ramganga, Sonanadi, Mandal, Palain and Kosi are the major rivers flowing through the Reserve.
- Sprawling over 500 square kilometres, CTR is home to 230 tigers and has the world’s highest tiger density — at 14 tigers per hundred square kilometres.
National Tiger Conservation Authority's (NTCA)
- National Tiger Conservation Authority (NTCA) is a statutory body under the Ministry of Environment, Forests and Climate Change.
- It was established in 2005 following the recommendations of the Tiger Task Force.
- It was constituted under enabling provisions of the Wildlife (Protection) Act, 1972, as amended in 2006, for strengthening tiger conservation, as per powers and functions assigned to it.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan