Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Ecotourism in J&K
Why in News?
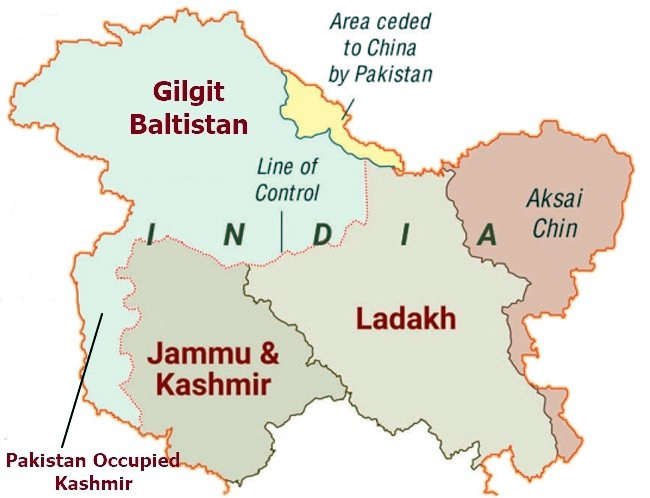
The Jammu and Kashmir government announced new rules for Bangus, a remote tourist spot near the Line of Control (LoC) in north Kashmir, to promote it as an ecotourism destination.
Key Points
- Uncontrolled Construction in Popular Tourist Spots:
- The decision to develop Bangus as an ecotourism destination follows unchecked and unplanned construction in Pahalgam, Gulmarg, and Sonamarg.
- Authorities have observed rapid concrete expansion in these traditional tourist hubs, affecting the ecological balance.
- Focus on Sustainable Development:
- The concerned department aims to prevent large-scale hotel and building constructions to maintain the region’s ecological balance.
- The approach prioritizes sustainable tourism while preserving the natural landscape.
- Basic Amenities for Visitors:
- The government plans to create recreational spaces, rain shelters, public conveniences, signages, lighting, and waste disposal facilities.
- These developments aim to enhance visitor experience while minimizing environmental impact.
- Work on basic facilities will begin after the Deputy Commissioner of Kupwara, in consultation with the Forest Department, identifies suitable land parcels.
- Necessary permissions and clearances will be obtained through the Parivesh Portal for forest clearance before proceeding with construction.
- The government plans to create recreational spaces, rain shelters, public conveniences, signages, lighting, and waste disposal facilities.
- Geographic and Strategic Importance:
- Bangus is located in Kupwara district near the Line of Control (LoC), approximately 100 km from Srinagar.
- It consists of two bowl-shaped valleys at an altitude of 10,000 feet.
- The region, once an infiltration route for militants, is now being promoted as a secure tourist destination.
- Promoting Local Livelihoods:
- The J&K Tourism Department is registering paying guest houses to support local shepherds, nomads, and residents.
- This initiative seeks to preserve and promote the local culture, traditions, and cuisine while offering tourists an immersive experience.
Line of Control
- The Line of Control (LoC) emerged from the 1948 ceasefire line negotiated by the United Nations (UN) after the Kashmir War.
- It was designated as the LoC in 1972, following the Shimla Agreement between the two countries.
- LoC is demarcated up to the Siachen Glacier (Point NJ9842)- the world's highest battlefield.
- LoC is delineated on a map signed by the Director General of Military Operations (DGMO) of both armies and has the international sanctity of a legal agreement.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Business Rules for J&K
Why in News?
The Jammu and Kashmir Chief Minister announced that the government had framed the Business Rules for the Union Territory (UT) administration and sent them to J&K Lieutenant Governor for the Centre’s final approval.
Key Points
- Purpose and Significance:
- The Business Rules aim to prevent confusion regarding institutional dignity and respect.
- The CM emphasized the need to uphold the institution’s honor, expressing disappointment over the loss of J&K’s statehood.
- Key Provisions of the Revised Business Rules:
- The revised rules outline the roles and authority of the Chief Minister, Cabinet, Ministers, and Administrative Secretaries.
- They specify that matters related to law and order, public order, and All India Services remain under the Lieutenant Governor’s jurisdiction.
- The amendments define the procedures for resolving disagreements between the Lieutenant Governor and the Council of Ministers or an individual Minister.
- Context and Implementation:
- The J&K government took over four months to draft these rules as mandated by the J&K Reorganisation Act, 2019.
- J&K became a Union Territory in 2019 following the abrogation of Article 370.
- The UT conducted its first Assembly elections in 2024.
Jammu and Kashmir Reorganisation Act, 2019
- It divided Jammu and Kashmir into 2 Union Territories of Jammu and Kashmir and Ladakh.
- It repealed Article 370, which had granted Jammu and Kashmir a unique status.
- Leh and Kargil districts were included in the Union Territory of Ladakh, while the remaining areas became part of Jammu and Kashmir.
- Five Lok Sabha seats were retained by Jammu and Kashmir, and one was transferred to Ladakh.
- Legislature: The seats in the Legislative Assembly will be reserved for tribal and scheduled caste people to keep the proportion intact of their population in the Union Territory of Jammu and Kashmir.
- The Lt. Governors can nominate two women members for the Assembly to represent women if women are not sufficiently represented to justify equality between men and women.
- The elected Legislative Assembly will be for 5 years, and the Lt. The Governor will summon the Assembly once every six months.
- The Legislative Assembly has the right to pass a law for any given part of the Union Territory of J&K related to any of the matters listed in the Indian Constitutions State's List except for the "Police" and "Public Order."
- Any matter specified in the Concurrent List will be applied to Indian Union Territories. Furthermore, Parliament will have the decision-making power to create laws for Jammu Kashmir and its Union Territory.


West Bengal Switch to Hindi
Implementation of NEP in West Bengal
Why in News?
A Supreme Court lawyer petitioned the top court to direct the Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and West Bengal governments to implement the National Education Policy (NEP).
- The plea comes amid a heated debate led by Tamil Nadu Chief Minister M.K. Stalin, who has accused the Centre of imposing Hindi on the State.
Key Points
- Argument for NEP Implementation:
- The plea urged Tamil Nadu, Kerala, and West Bengal to sign a memorandum of understanding with the Centre to implement the NEP.
- It was argued that these States must act to protect children’s fundamental right to education.
- Clarification on Hindi in NEP:
- The NEP mentions ‘Hindi’ only once and does not mandate its imposition.
- The policy does not compel State governments to teach Hindi to children.
- Constitutional and Legal Considerations:
- The plea argued that both the Centre and the States have a stake in education, as it falls under the Concurrent List of the Constitution.
- The petition acknowledged that the Supreme Court cannot directly compel a State to adopt a policy or sign an MoU.
- However, the court can intervene if the matter affects fundamental rights.
National Education Policy 2020
- About:
- The National Education Policy 2020 seeks to tackle the evolving development needs of India.
- It calls for a comprehensive overhaul of the education system, including its regulations and management, to establish a modern system that aligns with 21st-century educational goals, including Sustainable Development Goal 4 (SDG4), while respecting India's cultural heritage and values.
- It replaces the thirty-four year old National Policy on Education, 1986, modified in 1992 (NPE 1986/92).
- The National Education Policy 2020 seeks to tackle the evolving development needs of India.
- Salient Features:
- Universal Access: NEP 2020 focuses on universal access to school education, including pre-school to secondary levels.
- Early Childhood Education: The 10+2 structure will shift to a 5+3+3+4 system, bringing 3-6-year-olds under school curriculum, with a focus on Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE).
- Multilingualism: Mother tongue or regional language will be the medium of instruction till Grade 5, with options for Sanskrit and other languages.
- Indian Sign Language (ISL) will be standardized.
- Inclusive Education: Special emphasis on Socially and Economically Disadvantaged Groups (SEDGs), support for children with disabilities, and establishment of "Bal Bhavans."
- Elimination of Barriers: The policy promotes a seamless education system with no rigid distinctions between arts and sciences, curricular and extracurricular activities, and vocational and academic streams.
- GER Enhancement: Aim to increase Gross Enrolment Ratio from 26.3% to 50% by 2035, adding 3.5 crore new seats.
- Research Focus: Creation of National Research Foundation to boost research culture and capacity.
- Language Preservation: Support for Indian languages, including an Institute of Translation and Interpretation (IITI) and strengthening language departments.
- Internationalization: Facilitation of international collaborations and entry of top-ranked foreign universities.
- Funding: Joint efforts to increase public investment in education to 6% of GDP.
- PARAKH Assessment Center: The establishment of PARAKH (Performance Assessment, Review, and Analysis of Knowledge for Holistic Development) as a national assessment center signifies a significant step towards competency-based and holistic assessment in education.
- Gender Inclusion Fund: The policy introduces a Gender Inclusion Fund, emphasizing the importance of gender equality in education and supporting initiatives to empower disadvantaged groups.
- Special Education Zones: Special Education Zones are envisioned to address the specific needs of disadvantaged regions and groups, furthering the policy's commitment to equitable access to quality education for all.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
Seminar on Health Challenges and Healthy Lifestyle
Why in News?
Union Minister for Labour & Employment attended a seminar on "Health Challenges and Healthy Lifestyle" organized by Arogya Bharti in collaboration with ESIC Medical College & Hospital, Faridabad, Haryana.
Key Points
- Emphasis on Preventive Healthcare:
- The Union Minister underscored the importance of preventive and promotive healthcare in fostering a healthy and fit India.
- He highlighted India’s rich healthcare heritage by citing ancient medical pioneers like Charak, Sushruta, and Lord Dhanwantari.
- Role of Traditional Practices:
- He stressed the significance of meditation, yoga, and fasting as essential components of preventive healthcare.
- He commended Arogya Bharti for organizing wellness camps nationwide to promote holistic well-being.
- Inauguration of Advanced Medical Facilities:
- During his visit, the Union Minister inaugurated three cutting-edge medical facilities to enhance diagnostic and treatment capabilities:
- Digital Mammography Services
- A high-resolution, digital detector-based mammography machine designed for early detection and evaluation of breast cancer.
- 1000 mA Digital Radiography Fluoroscopy (DRF) System
- A modern diagnostic system that improves X-ray radiography and fluoroscopic-guided interventions for insured workers and their families.
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS) Application
- An advanced technology supporting oncology research, RNA sequencing, and pathogen identification, paving the way for precision medicine.
- Digital Mammography Services
- Unveiling of Lord Dhanwantari’s Statue:
- As a tribute to India’s ancient medical wisdom, the minister unveiled a statue of Lord Dhanwantari, the god of Ayurveda, at ESIC Medical College & Hospital.
- During his visit, the Union Minister inaugurated three cutting-edge medical facilities to enhance diagnostic and treatment capabilities:


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Bihar Budget 2025-26
Why in News?
On 3rd March 2025, the Bihar Finance Minister presented a Rs 3.17 lakh crore budget in the state assembly, prioritizing education and women's empowerment.
Key Points
- Key provisions of the budget:
- The total revenue expenditure in the financial year 2025-26 is estimated at Rs 2 lakh 52 thousand crore, which is 79.52% of the total expenditure.
- The highest provision of Rs 60,964 crore has been made on education.
- A provision of Rs 20 thousand crore was made for health and Rs 17 thousand crore for roads.
- Rs 17831 crore has been made for the Home Department, Rs 16043 crore for Rural Development, Rs 13484 crore for the Energy Department and more than Rs 13 thousand crore for the Social Welfare Department, SC, ST, Minority, Backward, Extremely Backward.
- Focus on women empowerment:
- Construction of pink toilets .
- Mahila Haats will be opened in Patna .
- Pink bus service will start (all drivers and conductors will be women).
- Hostels will be built for working women .
- Appointment of women tourist guides .
- Financial assistance for purchasing e-rickshaw.
- Increase in the number of women police personnel.
- Construction of 'Kanya Vivah Mandap' for the marriage of poor girls .
- Education and social welfare:
- The rate of scholarship will be doubled.
- Incentive amount will be increased for SC/ST and backward classes.
- Health and medical facilities
- Construction of a cancer hospital in Begusarai .
- 108 new urban medical centers will open in Bihar .
- Provision of a special care centre for cancer patients .
- Infrastructure and Transportation
- Construction of Purnia Airport will start soon.
- 8 new airports including Rajgir, Sultanganj, Raxaul, Madhubani will be built.
- 33% reservation for women in Bihar State Road Transport Corporation.
- Environment and Clean Energy
- Investment of Rs 1 crore for improving air quality.
- Solar plants will be installed along the canal banks at a cost of Rs 25 crore.
- Agriculture and Rural Development
- Market committees will be empowered.
- Stalls for selling vegetables will be opened at block level.
- Formation of vegetable production committee in all blocks.
- Migrant Biharis and tourism
- Help centres in various cities for migrant Biharis.
- Government assistance for home-stay facility for Chhath Puja .
- Industry and Trade
- Promotion to companies setting up compressed biogas plants.
- New incentive policy for pharmaceutical manufacturing companies.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana Rural
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Bihar transferred assistance amount of Rs 1,200 crore as the first installment for three lakh families under Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin .
Key Points
- The beneficiaries will be given another 80 thousand rupees in the form of second and third installments in the next hundred days.
- Apart from this, Rs 22,050 will be provided as unskilled labour for 90 days through MNREGA and Rs 12,000 will be provided for toilet construction under Lohia Swachh Bihar Abhiyan .
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana – Gramin (PMAY-G)
- Launch: To achieve the objective of “Housing for All” by the year 2022 , the erstwhile rural housing scheme Indira Awas Yojana (IAY) was restructured into Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G) as a Centrally Sponsored Scheme from 1 April 2016 .
- Ministry Involved: Ministry of Rural Development.
- Status: States/UTs have sanctioned 2.85 crore houses to the beneficiaries and 2.22 crore houses have been completed till March 2023.
- Objective: To provide pucca houses with basic amenities to all the rural families who are homeless or living in kutcha or dilapidated houses by the end of March 2022.
- To provide assistance to rural people living below the poverty line (BPL) in the form of full grants for construction of housing units and upgradation of existing unusable kutcha houses.
- Beneficiaries: Scheduled Castes / Scheduled Tribes , freed bonded labourers and persons belonging to non-SC/ST categories, widows or next of kin of defence personnel killed in war, ex-servicemen and retired members of paramilitary forces, persons with disabilities and minorities .
- Selection of Beneficiaries: Three-step verification such as through Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha and Geo-tagging.
- Cost Sharing: The Centre and the States share expenditure in the ratio of 60:40 in case of plain areas and 90:10 in case of North-Eastern States, two Himalayan States and the Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir .
- In case of other Union Territories including Union Territory of Ladakh, the Centre bears 100% of the cost.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India’s First Lithium Grade Refinery
Why in News?
Lohum Company launched India's first lithium grade refinery in Greater Noida, Uttar Pradesh.
Key Points
- Production capacity and efficiency:
- This refinery will produce 1,000 metric tonnes of battery-grade lithium annually. Its capacity will increase to 20 thousand tonnes in the year 2029.
- The black mass generated from e-waste will be recycled and lithium will be emitted from it.
- Additionally, the company is expanding its capabilities in the production of Cathode Active Material (CAM) , an essential component for large-scale lithium-ion battery production.
- The company is currently refining more than 90% of lithium in India.
- According to the company, its technical efficiency is competitive with that of China and more economical than US/European facilities.
- Lithium refining:
- Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in electric vehicles (EVs), smartphones, laptops, and other electronic devices.
- The demand for electric vehicles and battery storage is going to increase rapidly in India in the coming years, which will also increase the need for lithium .
- A large portion of India's lithium supply comes from China , which poses a strategic and economic challenge for India.
- This expansion of Lohum will play an important role in freeing India from this dependence.
Lithium
- Introduction:
- About:
- It is a chemical element whose symbol is (Li) .
- It is a soft and silver-white metal .
- It is the lightest metal and the lightest solid element under standard conditions .
- It is highly reactive and flammable , so must be stored as mineral oil.
- It is alkaline and a rare metal .
- Alkali metals include the chemical elements lithium, sodium, potassium, rubidium, cesium and francium. Together with hydrogen, they form group-1 which is located in the s-block of the Periodic Table.
- Rare Metals (RM) include Niobium (Nb), Tantalum (Ta), Lithium (Li), Beryllium (Be), Cesium (Cs) etc. and Rare Earths (RE) include Scandium (Sc) and Yttrium (Y) besides Lanthanum (La) to Lutetium (Lu).
- Due to their strategic importance, these metals are used in nuclear and other high-tech industries like electronics, telecommunication, information technology, space, defence etc.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UNESCO Recognition for Cities
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government will apply for UNESCO recognition for five cities as intangible heritage and creative cities to preserve the state's cultural heritage and gain global recognition.
Key Points
- Selected Cultural Cities (Elements):
- Perfume of kannauj
- Holi of Braj
- Ganga Aarti in Varanasi
- Glass Art of Firozabad
- Black Pottery of Azamgarh (Nizamabad)
- Further Attempt:
- The State government is also making efforts to include the folk art and folk literature of Bundelkhand in the intangible cultural heritage of humanity.
- Research will be conducted on the Deg-Bhapka method , historical importance, socio-economic impact and traditional processes for Kannauj perfume.
- The historical, spiritual and ritualistic significance of the Ganga Aarti of Varanasi will be studied.
- Holi of Braj, especially Lathmar Holi will be given prominence.
- Documents will be prepared by conducting research on Alha singing and Rai dance of Bundelkhand , black pottery of Azamgarh and glass industry of Firozabad.
- Historical context and UNESCO recognition:
- In the year 2017, due to the efforts of the central and state governments, Kumbh was for the first time recognized by UNESCO as an intangible cultural heritage of humanity.
- Effects and potential benefits:
- By getting global recognition , these cultural heritages will get promotion at international level.
- Tourism will be boosted , which will benefit the local economy.
- Local artisans, artists and traditional industries will get protection , which will strengthen their livelihood.
- Preservation of culture and heritage will be promoted, so that these traditions remain safe for generations to come.
UNESCO
- The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO) is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) . This organization strives to establish peace through international cooperation in the field of education, science and culture.
- UNESCO's programmes contribute to the achievement of the Sustainable Development Goals defined in Agenda 2030 , adopted by the United Nations General Assembly in 2015.
- It has 193 member countries and 11 associate members. India joined UNESCO in 1946 .
- The United States and Israel formally left UNESCO in 2019.
- Its headquarters is in Paris (France).






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan