Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand Cabinet to Take Oath
Why in News?
Ten ministers are going to take the oath of office as part of Jharkhand's 12-member Cabinet. The swearing-in ceremony is set to take place at the Raj Bhavan in Ranchi.
Key Points
- The Council of Ministers in the states is constituted and functions in the same way as the Council of Ministers at the Centre (Article 163 and Article 164).
- Article 163 states that there is a council of ministers headed by the Chief Minister to aid and advise the Governor in the exercise of his functions, except some conditions for discretion.
- Discretionary Powers Include:
- Appointment of a Chief Minister when no party has a clear majority in the state legislative assembly
- In times of no-confidence motions
- In case of failure of constitutional machinery in the State (Article 356)
- Discretionary Powers Include:
- Under Article 164 of the Constitution, the Chief Minister is appointed by the Governor without any advice from anyone. But he appoints the individual Ministers only on the advice of the Chief Minister.
- The Article implies that the Governor cannot appoint an individual Minister according to his discretion. Therefore, the Governor can dismiss a Minister only on the advice of the Chief Minister.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Misuse of Surveillance Technology at Corbett National Park
Why in News?
According to a study published in the journal Environment and Planning F, forest rangers at Corbett Tiger Reserve deliberately used drones to monitor local women and deter them from gathering natural resources, even though they were legally entitled to access these resources.
Key Points
- Significance of the Study:
- The study revealed that surveillance technologies negatively affect the mental health of local women who depend on forests for daily activities.
- This study highlights the intersection of technology, conservation, and social equity, urging stakeholders to adopt more inclusive approaches.
- Issues Faced by Women:
- It was highlighted that while technologies like camera traps are common in wildlife monitoring, they can unintentionally invade privacy and alter human behavior.
- These findings underscore the need to ensure such tools do not harm local communities.
- Recommendations:
- In northern India, women’s identities are deeply tied to their daily forest activities, making it crucial to consider their perspectives in conservation efforts.
- Conservation strategies must strike a balance between wildlife monitoring and safeguarding the dignity, safety, and rights of local communities.
Corbett Tiger Reserve
- About:
- It is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand. The Project Tiger was launched in 1973 in Corbett National Park (first National Park of India), which is part of Corbett Tiger Reserve.
- The national park was established in 1936 as Hailey National Park to protect the endangered Bengal tiger.
- It is named after Jim Corbett who played a key role in its establishment.
- The core area forms the Corbett National Park while the buffer contains reserve forests as well as the Sonanadi Wildlife Sanctuary.
- The entire area of the reserve is mountainous and falls in the Shivalik and Outer Himalaya geological provinces.
- It is located in the Nainital district of Uttarakhand. The Project Tiger was launched in 1973 in Corbett National Park (first National Park of India), which is part of Corbett Tiger Reserve.
- Flora:
- Dense moist deciduous forests are found. According to the Botanical Survey of India, Corbett has 600 species of plants - trees, shrubs, ferns, grass, climbers, herbs, and bamboo. Sal, Khair, and Sissoo are the most visible trees found in Corbett.
- Fauna:
- Apart from tigers, Corbett also has leopards. Other mammals such as jungle cats, barking deer, spotted deer, sambar deer, sloth etc. are also found there.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Aravali Green Wall Project
Why in News?
At a United Nations climate event held as part of the United Nations Convention to Combat Desertification Data (UNCCD) CoP16, India highlighted its ambitious 'Aravali Green Wall' project, emphasizing the importance of adopting innovative approaches to restore degraded forest lands on a global scale.
Key Points
- About the Aravali Green Wall Project Presentation:
- Inspired by Africa's Great Green Wall initiative, the Aravali Green Wall project aims to-
- Restore over 1.1 million hectares of degraded landscapes by 2027.
- Focus on afforestation with native species, soil health improvement, and groundwater replenishment.
- Develop an "ecological wall" to mitigate urban heat islands and act as a carbon sink for NCR.
- Inspired by Africa's Great Green Wall initiative, the Aravali Green Wall project aims to-
- Significance of the Aravali Hills:
- The Aravali range acts as a natural barrier preventing the eastward spread of the Thar Desert.
- It serves as a "repository of unique flora and fauna" but is facing severe challenges, including land degradation and desertification, encroachment, mining, and urbanisation.
- Need for Restoration:
- Urgent action is required to address these threats and reverse the degradation.
- The restoration effort involves collaboration among Haryana, Delhi, Rajasthan, and Gujarat.
- Implementation Strategy:
- State governments will plant millions of native trees and shrubs and promote soil conservation.
- The first phase in Haryana will involve the revival of 66 water bodies in key districts, including Gurgaon, Faridabad, and Bhiwani.
- Haryana's plan covers the restoration of 35,000 hectares, with 18,000 hectares in Gurgaon alone.
- Global Appeal and Vision:
- Global partnerships involving governments, international organisations, and private entities are called to support the initiative with technical and financial resources.
- The project aims to serve as a "blueprint" for global efforts to restore degraded landscapes.
- Innovative Approaches:
- The project incorporates nature-based solutions, focusing on afforestation with indigenous species, Soil health and moisture rejuvenation, Community participation in conservation.
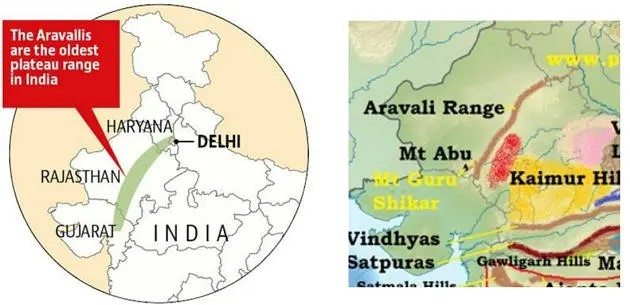
Aravali Mountain Range
- The Aravallis, is the oldest fold mountains on Earth. Geological studies indicate that it is three billion years old.
- It spans over 800 km from Gujarat to Delhi (through Rajasthan and Haryana).
- The highest peak in the Aravalli Range is Guru Peak on Mount Abu.
- Influences Climate:
- The Aravallis have an impact upon the climate of northwest India and beyond.
- During monsoons, the mountain range gently guides the monsoon clouds eastwards towards Shimla and Nainital, thus helping nurture the sub-Himalayan rivers and feeding the north Indian plains.
- During the winter months, it shields the fertile alluvial river valleys of the Indus and Ganga from the harsh cold westerly winds blowing in from Central Asia.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Groundwater Extraction in Haryana
Why in News?
The Stage of Groundwater Extraction (SoE) in Haryana has reached 135.74%, signifying that the rate of groundwater extraction exceeds the sustainable utilization limit.
Key Points
- Current State of Groundwater Extraction:
- Haryana
- Annual Groundwater Recharge: 9.55 billion cubic metres (bcm)
- Annual Extractable Groundwater: 8.69 bcm
- Total Groundwater Extraction (2023): 11.8 bcm
- SoE: 135.74%, indicating that extraction exceeds sustainable levels.
- Punjab
- Annual Groundwater Recharge: 18.84 bcm
- Annual Extractable Groundwater: 16.98 bcm
- Total Groundwater Extraction (2023): 27.8 bcm
- SoE: Exceeds sustainable levels, with extraction higher than what can be sustainably used.
- Rajasthan
- Annual Groundwater Recharge: 12.45 bcm
- Annual Extractable Groundwater: 11.25 bcm
- Total Groundwater Extraction (2023): 16.74 bcm
- SoE: 148.77%, indicating a significant over-extraction compared to recharge.
- Haryana
- Groundwater Depletion Concerns:
- Environmental Degradation: When groundwater levels drop, saltwater can intrude into coastal areas, contaminating freshwater resources.
- Groundwater Contamination: Human activities like agriculture, sewage, and industries can introduce pollutants like arsenic, fluoride, nitrate, and iron into groundwater.
- Land Subsidence: When groundwater is overused, the soil can collapse, compact, and drop, causing land subsidence.
- Policy Recommendations:
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) has urged states to reassess policies on providing free or subsidised electricity to farmers.
- Introduce water pricing mechanisms to encourage sustainable use.
- Implement crop rotation, diversification, and other measures to reduce dependency on groundwater.
- The Ministry of Jal Shakti (MoJS) has urged states to reassess policies on providing free or subsidised electricity to farmers.
- Jal Shakti Abhiyan (JSA) Efforts:
- Since 2019, the Jal Shakti Abhiyan has been a mission-driven program focusing on rainwater harvesting and water conservation.
- JSA 2024 is focused on 151 water-stressed districts across India.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Post Offices in Remote Areas of J&K
Why in News?
Recently, the Ministry of Communications informed that Jammu and Kashmir currently has 1,617 operational post offices which improved access to postal, financial, and insurance services in remote and underserved regions.
- 34 new post offices were established during the 2023-24 financial year.
Key Points
- Policy on New Post Offices:
- The establishment of new post offices is an ongoing process guided by identified needs and established norms.
- The government aims to provide essential postal services even in the most remote areas.
- Government’s Vision:
- The initiative reflects a strong commitment to enhancing infrastructure in geographically challenging and underserved regions.
- This effort underscores the focus on improving accessibility and ensuring equitable access to postal services.
India Post
- About:
- India Post is the trade name for the Department of Posts (DoP), a government-operated postal system in India under the Ministry of Communications.
- With 164,972 post offices (as of 2024) Post Offices, the DoP has the most widely distributed postal network in the world.
- Functions:
- Delivering mails, accepting deposits under Small Savings Schemes, providing life insurance cover under Postal Life Insurance (PLI) and Rural Postal Life Insurance (RPLI) and providing retail services like bill collection, sale of forms, etc.
- It also acts as an agent for the Government in discharging other services for citizens such as Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) wage disbursement and old age pension payments.
- Significance:
- India Post has been serving the people in an extraordinary way in the difficult situation which has emerged due to Covid-19, by bringing them medicines and financial assistance.
- The Postal Department has been playing a major role in the implementation of Government schemes, leveraging the immense strength of its vast network.
- Postal schemes are known for providing highly secured deposits, they provide a higher return of interest with low risk.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Progress of Swachh Bharat Mission-Grameen in Rajasthan
Why in News?
The Union Minister for Jal Shakti chaired a crucial review meeting to assess Rajasthan's progress and challenges in implementing the Swachh Bharat Mission-Grameen (SBM-G).
Key Points
- Swachh Bharat Mission Grameen (SBM-G) & Rajasthan:
- It was launched in 2014 by the Ministry of Jal Shakti to accelerate the efforts to achieve universal sanitation coverage and to put focus on sanitation.
- The mission was implemented as a nation-wide campaign/Janandolan which aimed at eliminating open defecation in rural areas.
- Rajasthan has demonstrated notable progress under the SBM-G initiative:
- Ranked 10th nationally for ODF (Open Defecation Free) Plus Model achievements.
- 98% of villages in the state have been declared ODF Plus.
- 85% of villages have successfully achieved ODF Plus Model status.
- It was launched in 2014 by the Ministry of Jal Shakti to accelerate the efforts to achieve universal sanitation coverage and to put focus on sanitation.
- Achievements:
- Faecal Sludge Management (FSM):
- Current Status: Only 114 blocks have completed FSM verification.
- No rural Faecal Sludge Treatment Plants (FSTPs) have been constructed yet.
- Recommendations: Utilize urban resources effectively.
- Finalize and implement a robust FSM policy.
- Current Status: Only 114 blocks have completed FSM verification.
- Solid Waste Management (SWM):
- Progress: 94% of villages are covered under SWM initiatives.
- Recommendations: Ensure the proper functioning of segregation sheds and vehicles while connecting compost markets to enhance sustainability.
- Plastic Waste Management Units (PWMUs):
- Only one operational PWMU exists in rural Rajasthan, needing significant scale-up.
- Grey Water Management (GWM):
- Progress: 98% of villages have GWM systems in place, with saturation in remaining villages expected soon.
- Focus Areas: Promote household soak pits for tap water connections under the Jal Jeevan Mission (JJM).
- Strengthen the role of self-help groups in driving sanitation initiatives.
- Faecal Sludge Management (FSM):
- Tourism and Cleanliness:
- Rajasthan was urged to combine its rich tourism heritage with cleanliness initiatives and adopt the Swachhta Green Leaf Rating program to demonstrate tradition and innovation can unite for sustainable sanitation.
Swachhata Green Leaf Rating (SGLR) Program
- It is a government initiative to promote hygiene and sanitation in the hospitality sector.
- The SGLR program aims to improve the quality of life and public health by:
- Ensuring world-class cleanliness and hygiene in hotels, resorts, and homestays
- Improving the reputation of tourist destinations
- Supporting local Gram Panchayats to achieve ODF Plus Model status




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan