Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Landslide in Dharchula
Why in News?
Recently, A severe landslide has completely blocked the road to Dharchula in Pithoragarh district of Uttarakhand.
- Due to heavy rain, six highways and 96 roads are closed in Uttarakhand. Landslides have blocked 47 rural roads.
Key Points
- Heavy rainfall causes landslides and accidents, posing a significant challenge for Uttarakhand every monsoon.
- In 2023, nearly 100 people died and many went missing from June to September.
- The CM Pushkar Dhami called for a safety audit of all transformers during the monsoon and urged for rapid development of industrial institutions in the state to boost power generation.
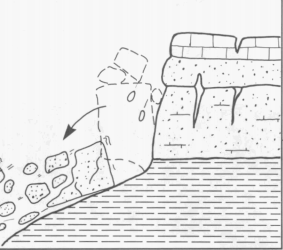
Landslide
- A landslide is defined as the movement of a mass of rock, debris, or earth down a slope.
- They are a type of mass wasting, which denotes any downward movement of soil and rock under the direct influence of gravity.
- The term landslide encompasses five modes of slope movement: falls, topples, slides, spreads, and flows.
- Causes:
- Slope movement occurs when forces acting downward (mainly due to gravity) exceed the strength of the earth materials that compose the slope.
- Landslides are caused due to three major factors: geology, morphology, and human activity.
- Geology refers to characteristics of the material. The earth or rock might be weak or fractured, or different layers may have different strengths and stiffness.
- Morphology refers to the structure of the land. For example, slopes that lose their vegetation to fire or drought are more vulnerable to landslides.
- Vegetation holds soil in place, and without the root systems of trees, bushes, and other plants, the land is more likely to slide away.
- Human activity which includes agriculture and construction increases the risk of a landslide.
- Landslide-Prone Areas:
- The entire Himalayan tract, hills/mountains in sub-Himalayan terrains of North-east India, Western Ghats, the Nilgiris in Tamil Nadu Konkan areas are landslide-prone.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan