Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Food Irradiation
Why in News?
The government of India plans to use radiation processing (Food Irradiation) to extend the shelf life of a 100,000 tonne onion buffer stock in 2024, aiming to prevent shortages and price hikes.
- India, a major onion exporter, is facing a 16% decline in onion output for the 2023-24 season, bringing production down to an estimated 25.47 million tonnes.
Key Points
- Food irradiation is the process of exposing food and food products to ionising radiation, such as gamma rays, electron beams, or X-rays.
- In India, irradiated food is regulated in accordance with the Atomic Energy (Control of Irradiation of Food) Rules, 1996.
- Significance:
- It is used in food processing to help ensure food safety.
- Seasonal overstocking and long transport times lead to food waste.
- India's hot, humid climate is a breeding ground for spoilage-causing insects and microbes.
- Seafood, meat, and poultry can harbour harmful bacteria and parasites that make people sick.
Onion Production in India
- India is the second-largest (after China) onion-growing country in the world, famous for its pungent onions available year-round.
- Major Onion Producing States:
- Maharashtra, Karnataka, Orissa, Uttar Pradesh, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Tamil Nadu are the major onion-producing states.
- Maharashtra ranks first in Onion production with a share of 42.53% followed by Madhya Pradesh with a share of 15.16% in 2021-22 (3rd Advance Estimate).
- Export Destination: Major export destinations of Indian onion include Bangladesh, Malaysia, the United Arab Emirates, Sri Lanka and Nepal.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
India to Import Wheat After 6 years
Why in News?
India, the world's second-largest wheat producer, plans to begin wheat imports after a six-year gap to replenish depleted reserves and control rising prices, driven by three consecutive years of disappointing crops.
Key Points
- India's wheat production has declined in the last 3 years due to unfavourable weather conditions, leading to a sharp drop in wheat output.
- The government estimates this year's wheat crop to be 6.25% lower than the previous year's (2023) record production of 112 million metric tons.
- The government's target for wheat procurement the year 2024 was 30-32 million metric tons, but it has managed to buy only 26.2 million tons so far.
- Domestic wheat prices have stayed above the government's minimum support price (MSP) of 2,275 rupees per 100 kg and have been on the rise recently.
- So, the government decided to remove the 40% import duty on wheat to allow private traders and flour millers to import wheat, primarily from Russia.
Wheat
- This is the second most important cereal crop in India after rice and main food crop, in the north and north-western part of the country.
- Wheat is a rabi crop that requires a cool growing season and bright sunshine at the time of ripening.
- Success of the Green Revolution contributed to the growth of Rabi crops, especially wheat.
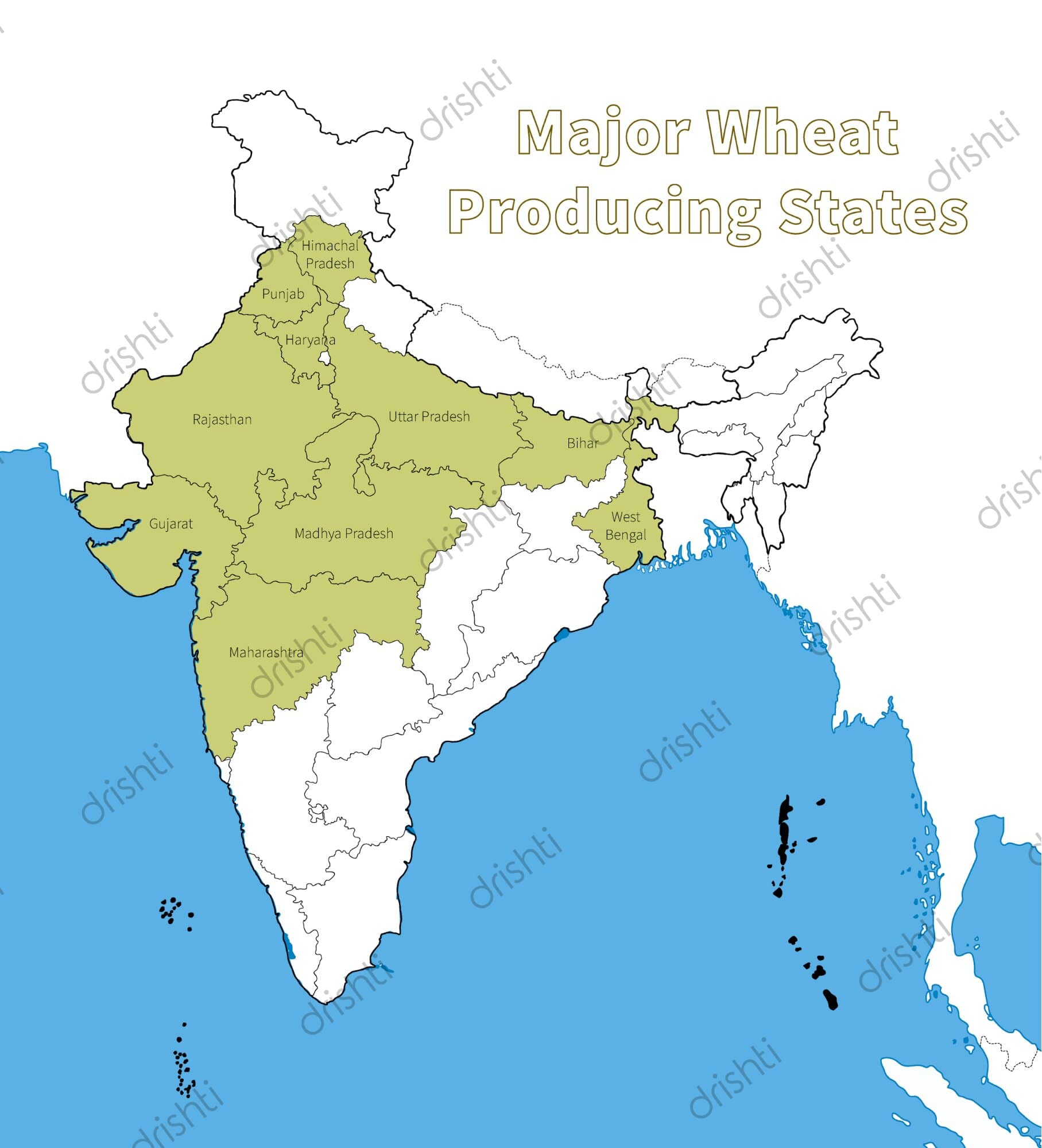
- Top 3 Wheat Producers in World (2021): China, India and Russia.
- Top 3 Wheat Producers in India (in 2021-22): Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Punjab
- Government Initiatives:
- Macro Management Mode of Agriculture, National Food Security Mission and Rashtriya Krishi Vikas Yojana etc.






%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan