Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Implementing the Street Vendors Act 2014
Why in News?
A decade has passed since the Street Vendors (Protection of Livelihood and Regulation of Street Vending) Act, 2014 came into effect on 1st May 2014, marking a significant milestone after nearly four decades of legal jurisprudence and the tireless efforts of street vendor movements across India.
Key Points
- The Act was enacted in order to legalise the vending rights of street vendors (SVs).
- It aimed to protect and regulate street vending in cities, with State-level rules and schemes, and execution by Urban Local Bodies (ULBs) through by-laws, planning, and regulation.
- The Act clearly delineates the roles and responsibilities of both vendors and various levels of government.
- It commits to accommodating all ‘existing’ vendors in vending zones and issuing vending certificates (VCs).
- The Act establishes a participatory governance structure through Town Vending Committees (TVCs).
- It mandates that street vendor representatives must constitute 40% of TVC members, with a sub-representation of 33% of women SVs.
- These committees are tasked with ensuring the inclusion of all existing vendors in vending zones.
- Additionally, the Act outlines mechanisms for addressing grievances and disputes, proposing the establishment of a Grievance Redressal Committee chaired by a civil judge or judicial magistrate.
- It provides that the States/ULBs conduct a survey to identify SVs at least once every five years.
Government’s Initiatives for Street Vendors
- SVANidhi Scheme:
- SVANidhi Scheme was launched to benefit over 50 lakh street vendors who had been vending in urban areas including those from surrounding peri-urban/rural areas.
- It also aims to promote digital transactions through cash-back incentives up to an amount of Rs. 1,200 per annum.
- National Association of Street Vendors of India:
- NASVI is an organization working for the protection of the livelihood rights of thousands of street vendors across the country.
- The main objective was to bring together the street vendor organizations in India so as to collectively struggle for macro-level changes.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Green Lynx Spider
Why in News?
Recently, Green Lynx Spider was discovered in Tal Chhapar, Rajasthan. The spider species has been named Peucetia chhaparajnirvin.
Key Points
- The spider was found in Tal Chhapar Wildlife Sanctuary in Churu district during fieldwork by Nirmala Kumari.
- The specimens have been deposited in the entomology lab at the University of Rajasthan, Jaipur.
- The species was identified and described in the Spider Research Lab at JD Patil Sangludkar Mahavidyalaya, Daryapur, in the Amravati district.
- This spider is found on the green leaves of the Vachellia nilotica (babul) tree. Their green hue aids in blending within surroundings and ambushing prey, while their long legs allow them to move quickly.
- This spider is nocturnal and feeds on small insects. The climatic conditions in the sanctuary area are extreme, with very hot summers and very cool winters.
- They are significant insect predators in low shrubs and herbaceous plants, being crucial for controlling plant-damaging insects and forest ecosystem pests.
- The spiders prey on various types of moths and their young, such as bollworm moth, leafworm moth, and looper moth.
The Tal Chhapar Sanctuary
- It is situated on the border of the Great Indian Thar Desert.
- Tal Chhapar is a distinctive shelter of the most graceful Antelope seen in India, “the Blackbuck”.
- It was given the status of a sanctuary in 1966.
- Tal Chhapar was a hunting reserve of the erstwhile royal family of Bikaner.
- The “Tal” word is a Rajasthani word meaning plane land.
- This Sanctuary has nearly flat territory and a combined thin low-lying region. It has open and wide grasslands with spread Acacia and Prosopis plants that offer it a look of a characteristic Savanna.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
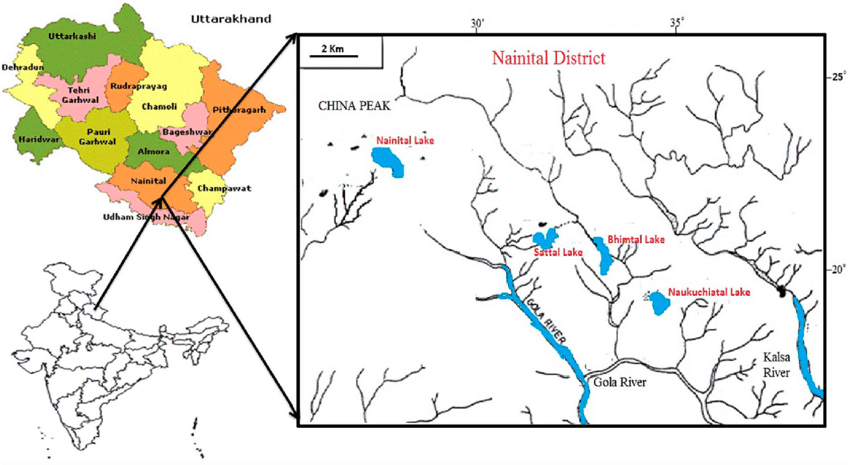
Bhimtal Lake
Why in News?
In response to a severe forest fire close to Nainital district headquarters the state government deployed the Army's MI 17 helicopters to fetch water from Bhimtal Lake and spray it over the affected forests.
Key Points
- Bhimtal Lake is the largest lake in the Nainital district, in the state of Uttarakhand. It is the largest lake in the Kumaon region, known as the "lake district of India".
- It is named after the second Pandava called Bhima of the famous epic Mahabharata.
- It is a natural lake and its origin is attributed to several faults that occurred due to the shifting of the Earth's crust.
- The lake was built during British time in 1883 and has a masonry dam built on it.
- The lake has rich flora and fauna around it and thick forests of pine and oak cover the hill slopes around the lake.
- It is home to a number of migratory birds in the winter months.
- Famous species found in the area include bulbul, wall creeper, Emerald Dove, Black Eagle, and Tawny fish owl.
- The lake has an island at its centre developed as a tourist attraction with an aquarium.
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Nakshatra Sabha
Why in News?
The Uttarakhand Tourism Development Board has joined hands with Starscapes, a leading astro-tourism company, to introduce Nakshatra Sabha, a new initiative to provide a comprehensive Astro Tourism experience to people.
Key Points
- The campaign will offer a range of activities, including stargazing, special solar observations, astrophotography contests, camping under the stars, and more.
- The initiative aims to bring together astronomy enthusiasts, adventurers, and travellers to marvel at the wonders of the cosmos.
- Uttarakhand is well-positioned to attract Astro Tourists worldwide with its abundant forest cover, nature-based tourism, convenient access to major cities, and well-established hospitality sector, including homestays.
- George Everest in Mussoorie is set to host Nakshatra Sabha from early June until mid-2025, presenting a range of engaging events at different spots throughout Uttarakhand.
- These events will explore potential night sky sites in districts such as Uttarkashi, Pithoragarh, Nainital, and Chamoli, along with seminars and webinars led by experts in the field.
- By creating a community of advocates committed to conserving dark skies in Uttarakhand, the Nakshatra Sabha campaign aims to promote professional training, skill development, and support local economies while advocating for the preservation of night skies.
- It plans to establish a policy for preserving dark skies across the region in 2025.
Uttarakhand Tourism Development Board (UTDB)
- It is a government body responsible for promoting tourism in the state of Uttarakhand.
- It was established in 1976 and is headquartered in Dehradun.
- The UTDB works to develop and promote tourism infrastructure, attract investment, and market Uttarakhand as a tourist destination.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
NGT Issues Notice to Thermal Power Plant in Jharkhand
Why in News?
The National Green Tribunal (NGT) has requested a reply from the concerned authorities, which includes the administrative chief of National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPC) North Karanpura super thermal power plant in Jharkhand's Chatra district, concerning the significant fire that consumed a unit in April 2024.
Key Points
- The NGT addressed a case where it had taken notice about a fire at a material yard in unit 3 of a power plant.
- The plant, a coal-based 660X3 MW unit of NTPC, the country's largest power producer, was under scrutiny.
- NGT considered the case a significant matter concerning environmental regulation compliance.
- The tribunal roped in various authorities like the plant's administrative head, member secretaries of Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) and Jharkhand State Pollution Control Board (JSPCB), as well as Chatra's deputy commissioner for the issue.
- The tribunal directed for specific parties like the plant's administrative head and the deputy commissioner to be served notices to respond to the matter.
National Green Tribunal (NGT)
- It is a specialised body set up under the National Green Tribunal Act (2010) for effective and expeditious disposal of cases relating to environmental protection and conservation of forests and other natural resources.
- With the establishment of the NGT, India became the third country in the world to set up a specialised environmental tribunal, only after Australia and New Zealand, and the first developing country to do so.
- NGT is mandated to make disposal of applications or appeals finally within 6 months of filing the same.
- The NGT has five places of sittings, New Delhi is the Principal place of sitting and Bhopal, Pune, Kolkata and Chennai are the other four.
National Thermal Power Corporation Limited (NTPC)
- NTPC is India’s largest power utility with an installed capacity of 68,961.68 MW plans to become a 130 GW company by 2032.
- Established in 1975, NTPC aims to be the world’s largest and best power major.
- NTPC has comprehensive Rehabilitation & Resettlement and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) policies well integrated with its core business of setting up power projects and generating electricity.
- The company is committed to generating reliable power at competitive prices in a sustainable manner by optimising the use of multiple energy sources with innovative eco-friendly technologies thereby NTPC is contributing to the economic development of the nation and upliftment of the society.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)









 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan