Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Naini Lake
Why in News?
Naini Lake, a key attraction in Nainital, has reached a water level of 4.7 feet, its lowest in five years.
Key Points
- Concerns Over Drinking Water Scarcity:
- Experts warn that Naini Lake’s water level may drop below the "zero level," raising concerns about drinking water shortages before summer.
- The "zero level" does not indicate complete drying but refers to the lake’s water falling below its normal gauge level, determined based on historical data.
- Water Extraction and Declining Levels:
- Naini Lake, with a deepest point of 89 feet, has a gauge level of 12 feet.
- Uttarakhand Jal Sansthan extracts 10 million litres daily to supply drinking water to Nainital.
- Reduced snowfall and rainfall during winter, along with long-term maintenance issues, have contributed to the drop.
- Historical and Geographical Significance:
- Naini Lake is a natural kidney-shaped lake surrounded by seven hills in Nainital.
- English businessman P. Barron discovered it in the mid-19th century, leading to Nainital’s development as a British hill station.
- Rising Demand and Impact on the Lake:
- According to environmental scientists, in 2024 Naini Lake supplied 76% of the city's water.
- Population growth, increased tourism, and commercial activities have negatively impacted the lake.
- Human-Induced Degradation:
- A 2017 Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology report found that Naini Lake faces the most human-made disturbances among Kumaon lakes.
- Issues include unplanned construction, encroachments, and degradation of recharge zones.
- Concrete structures reduce rainwater infiltration, worsening water shortages in low-rainfall years.
- Dumping debris into Sukhatal Lake, a crucial recharge source, has caused it to shrink from its original two-hectare area.
- Encroachments and illegal constructions have reduced the lake's catchment area, with houses and hotels expanding near the lake.
- A 2017 Uttarakhand State Council for Science and Technology report found that Naini Lake faces the most human-made disturbances among Kumaon lakes.
- Pollution and Civic Issues:
- Discharge of untreated wastewater and improper solid waste disposal contribute to pollution.
- Inadequate sewer systems lead to sewage overflow into stormwater drains, which discharge into the lake.
- Changing Weather Patterns and Climate Impact:
- Climate change has altered weather patterns in Uttarakhand.
- A study by Climate Trends found that between 1970 and 2022, annual mean temperatures in the state increased by 1.5°C.
- Rising temperatures have affected rainfall and snowfall patterns.
- Annual rainfall declined from 2,400 mm in 2022 to 2,000 mm in 2024.
- Nainital received only 107 mm of rainfall from January to March 2025, lower than in previous years.
- While the region had four snowfall days in winter 2022, it had none in 2025.
- Naini Lake reached zero level only twice in the 1900s but has exceeded that mark over ten times since 2000.
- Need for Rejuvenation and Conservation Efforts:
- Several legal petitions have sought to protect the lake, with a Supreme Court ruling in 1993 banning commercial complexes in Nainital.
- However, unregulated construction, including homestays and building on wetlands, continues.
- In 2021, concerns were raised about the Sukhatal Lake revamp project, leading to a Public Interest Litigation(PIL) in the Uttarakhand High Court.
- The HC halted construction in November 2022, but work resumed in 2024 under a beautification plan.
- Several legal petitions have sought to protect the lake, with a Supreme Court ruling in 1993 banning commercial complexes in Nainital.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Himalayan Ibex
Why in News?
Authorities rescued a Himalayan Ibex with a gunshot injury and arrested four poachers in a remote area between Leh and Kargil districts in Ladakh.
Key Points
- Himalayan Ibex:
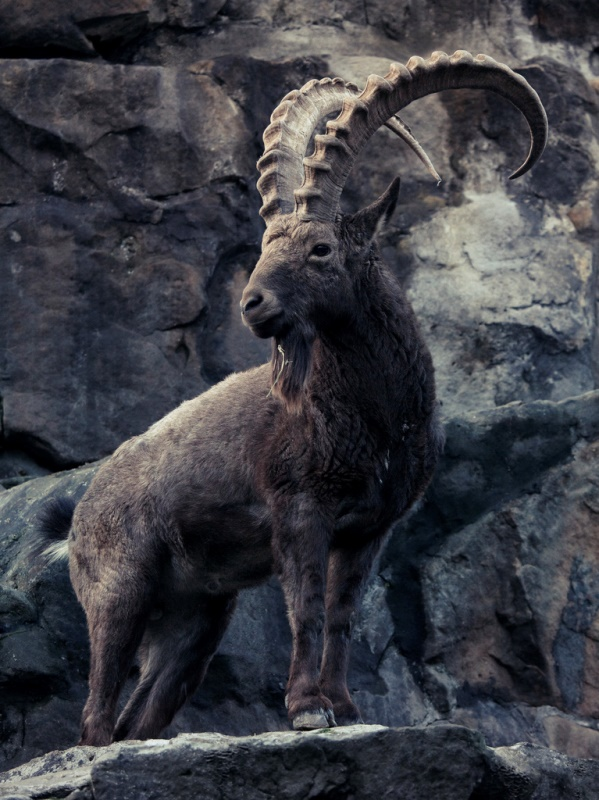

- Scientific Classification & Habitat:
- The Himalayan Ibex is a subspecies of the Siberian Ibex, scientifically named Capra sibirica hemalayanus.
- It is native to the Himalayan region, including India, Pakistan, Tibet, and Nepal.
- These ibexes inhabit high-altitude regions, typically found between 3,000 and 5,800 meters in the Trans-Himalayan region.
- In India, they are primarily found in Jammu and Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, and Uttarakhand.
- Physical Features:
- An adult ibex weighs around 90 kg and stands about 40 inches tall.
- Males are larger than females and possess massive curved horns with annual growth notches.
- Their coat ranges from light brown to reddish-brown, with a white belly and black-and-white leg markings.
- During winter, their thick woolly coat provides insulation, which they shed in early summer.
- They exhibit a darker dorsal stripe, with coat color varying from pale to dark brown.
- Behavior & Adaptations:
- Himalayan Ibexes are usually found in small herds, sometimes forming groups of up to 50 individuals.
- They are highly agile and can run at speeds of up to 50 km/h, enabling them to navigate rugged mountainous terrain.
- Conservation Status:
- According to the IUCN Red List, the Himalayan Ibex is classified as Near Threatened, facing threats from habitat loss, poaching, and climate change.
- Scientific Classification & Habitat:


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
LG Pays Obeisance at Vaishno Devi Shrine
Why in News?
Jammu and Kashmir Lieutenant Governor Manoj Sinha visited the cave shrine of Mata Vaishno Devi to offer prayers.
Key Points
- Vaishno Devi Temple:
- The temple is located at 5,200 feet in the Trikuta mountains, sees over one crore visitors annually, with a 12 km trek from Katra.
- Key Landmarks: Darshani Deodhi, Banganga, Chara Paduka, Indraprastha, Adhkuari, Garbha Joon, Himkoti, Haathi Matha, Sanji Chhat Bhavan, Sher ka Panja and Bhairon Mandir.
- According to officials from the Shri Mata Vaishno Devi Shrine Board, around one lakh pilgrims have visited the shrine since the start of Chaitra Navratri.
- Security Measures:
- Authorities have implemented tight security arrangements to manage the heavy influx of pilgrims.
- Artificial Intelligence (AI)-enabled CCTV cameras and drones have been deployed at the base camp, the bhawan, and along the pilgrimage route.


Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Free Bus Service for Women in J&K
Why in News?
Jammu and Kashmir Chief Minister launched the Zero-Ticket Travel Initiative, enabling free bus travel for women across Jammu and Kashmir.
- He flagged off the initiative at the Sher-i-Kashmir International Convention Centre (SKICC), taking a significant step toward gender-inclusive mobility.
Key Points
- Significance of the Initiative:
- This initiative allows women to travel free of cost on Smart City e-buses and J&K Road Transport Corporation (JKRTC) buses across the Union Territory.
- The CM also inaugurated zero-ticket travel for schoolgirls, highlighting the government's commitment to ensuring safe and convenient transport for young students.
- The Zero-Ticket Travel Initiative is part of a broader set of pro-women and pro-poor initiatives aimed at social and economic empowerment.
- Financial Sustainability of the Scheme:
- He also clarifies that transport operators would not suffer financial losses under this scheme.
- The government will compensate JKRTC and Smart City bus services from the state budget.
PM-eBus Sewa
- About:
- It aims to enhance urban transportation efficiency and promote Environmentally-Friendly Practices.
- Segment A: Augmenting City Bus Services (169 cities):
- This segment is dedicated to strengthening urban transportation by 10,000 e-buses under the PPP model.
- The initiative recognizes that efficient operations require the development or upgrading of depot infrastructure, alongside the creation of essential behind-the-meter power infrastructure like substations to accommodate the electric buses.
- Segment B: Green Urban Mobility Initiatives (181 cities):.
- This segment includes enhancing bus priority, improving infrastructure, establishing multimodal interchange facilities, implementing NCMC (National Common Mobility Card)-based Automated Fare Collection Systems, and building necessary charging infrastructure.
- By integrating these sustainable practices, the scheme aims to transform urban mobility landscapes.


Haryana Switch to Hindi
PM Awas Yojana in Jhajjar
Why in News?
Officials of Jhajjar district of Haryana are conducting a large-scale survey for Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana—Gramin (PMAY-G) 2.0 to identify needy families in rural areas and provide them with financial assistance for constructing new permanent houses.
Key Points
- Fulfilling the Dream of a Permanent Home:
- The PMAY-G initiative is designed to help needy families achieve a secure and dignified life through permanent housing.
- Officials have been instructed to speed up the survey process to include every eligible beneficiary and help fulfill the residential dreams of rural families.
- The last date to apply for PMAY-G 2.0 has been extended to 30th April 2025 to ensure that more eligible families benefit from the scheme.
- So far, 6,163 applications have been received from all seven blocks of the district.
- Villagers can also apply themselves through the "Awas Plus" mobile app to avail benefits.
- Financial Assistance Structure:
- Under the scheme, beneficiaries receive a total financial assistance of Rs 1.38 lakh for the construction of permanent houses.
- The amount is disbursed in three installments:
- First installment: Rs 45,000
- Second installment: Rs 60,000
- Third installment: Rs 33,000
Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)
- About: Launched in 2016, the PMAY-G aims to provide housing for the poorest segments of society.
- The selection of beneficiaries involves a thorough three-stage validation process, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensuring that aid reaches the most deserving individuals.
- Under PMAY-G Beneficiaries Receive:
- Financial Assistance: Rs 1.20 lakh in plain areas and Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly states, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Additional Support for Toilets: Rs 12,000 for constructing toilets through convergence with schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin (SBM-G) or Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) or any other dedicated source of funding.
- Employment Support: Mandatory provision of 90/95 person-days of unskilled wage employment for beneficiaries through Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) for house construction.
- Basic Amenities: Access to water, Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and electricity connections through convergence with relevant schemes.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
National Junior Girls Handball Championship
Why in News?
Uttar Pradesh won the 47th National Junior Girls Handball Championship .
Key Points
- About the Championship:
- Uttar Pradesh won the title of this championship for the first time .
- Uttar Pradesh defeated Himachal Pradesh in the final .
- This championship was organized from 26 to 30 March 2025 at K.D. Singh Babu Stadium in Lucknow .
- It was organised on the occasion of the 50th foundation day of Uttar Pradesh Handball Association.
- Handball:
- It is an indoor game , consisting of two teams and each team has seven players.
- Handball originated in Scandinavia and Germany in the late 19th century .
- Earlier it was an outdoor game and was known as ‘Field Handball’. Later, G. Wallstrom introduced indoor handball in Sweden in 1910.
- Between 1938 and 1966, separate world championships were held for both formats of handball, but from 1967 onwards the world championship was held only for indoor handball.
- Handball was included in the Olympics only once as an exhibition sport in Berlin in 1936, while it was officially included as an Olympic sport in Munich in 1972.
- Women's handball was included in the Olympics in 1976.


Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Crude Oil Discovery in Ballia
Why in News?
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) discovered huge reserves of crude oil at a depth of 3,000 metres in Sagarpali village of Ballia district located in the Ganga Basin of Uttar Pradesh .
Key Points
- About the Discovery:
- This will help India's energy security and also reduce the dependence on Arab countries. This reserve will provide India with the necessary fuel for many decades, which will strengthen the country's economy.
- This oil reserve is spread over an area of 300 km from Sagarpali in Ballia to Phaphamau in Prayagraj.
- The major crude oil producing states in India are Rajasthan (21.82%), Gujarat (13.53%), Assam (12.50%), Tamil Nadu (1.15%), Andhra Pradesh (0.87%) and Arunachal Pradesh (0.13%).
Oil and Natural Gas Corporation(ONGC)
- It is a Maharatna Public Sector Undertaking (PSU) of the Government of India.
- It was established in 1995 and is under the Ministry of Petroleum and Natural Gas .
- It is India's largest crude oil and natural gas company, contributing around 70% of Indian domestic production.
Ganges Basin
- The tributary of the Ganga called 'Bhagirathi' is fed by the Gangotri glacier and meets the Alaknanda at Devprayag in Uttarakhand.
- At Haridwar, the Ganga emerges from the mountains and comes towards the plains .
- The Ganga receives many tributaries from the Himalayas, some of the major rivers are Yamuna, Ghaghara, Gandak and Kosi.


Bihar Switch to Hindi
Xavier University
Why in News?
On 29 March 2025, the Chief Minister of Bihar inaugurated the Xavier University located on 36 acres in Patna, Bihar.
Key Points
- About Patna:
- It is the capital and largest city of Bihar .
- This ancient city is situated on the southern banks of the Ganga .
- Patna has been a centre of administration, education, tourism, historical heritage, religion, spirituality, and culture .
- Demographics (2011 census):
- Total Population : 58,38,465 (Male – 30,78,512, Female – 27,59,953)
- Population growth rate (2001–2011): 23.73%
- Density: 1,800 km2
- Literacy rate : 70.68% (Male – 78.48%, Female – 61.96%) Official language: Hindi .
- Other spoken languages: English , Urdu , Bengali , Oriya .
- Local dialect: Magahi , Bhojpuri , Maithili .
- History:
- The old name of Patna was Pataliputra or Patalipattana, which is found in history before 600 BC .
- Chandragupta Maurya made his capital here in the 4th century AD.
- Ajatashatru laid the foundation of Pataliputra, which later developed as Patna .
- In Greek history it was called Patalibothra.
- Great rulers like Emperor Ashoka , Chandragupta Maurya , and Samudragupta ruled from this city.
- In 1703 AD, Prince Azim-e-Shan was made the governor of Patna and he gave it a modern look and named it Azimabad, but among the general public it remained popular by the name Patna .
- Major places of interest:
- Bihar Museum
- Patna Planetarium
- Japanese Peace Pagoda
- Sanjay Gandhi Botanical Garden
- Lauria Nandangarh
- Golghar
- potter
- Ajanta Gandhi Museum
- Jalan Museum


Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Gangaur Festival
Why in News?
In Rajasthan, Gangaur Festival is celebrated every year on the Tritiya Tithi of Shukla Paksha of Chaitra month. This time Gangaur Festival was celebrated on 31 March 2025.
Key Points
- About the Festival:
- Gangaur is a major festival celebrated in different forms in Rajasthan, celebrated every year in the month of Chaitra (first month of Hindu calendar).
- "Gan" refers to Lord Shiva and "Gauri" or "Gaur" refers to Goddess Parvati.
- This festival is mainly celebrated by women, in which they worship Goddess Gauri and Lord Shiva to attain a happy married life, unbroken good fortune and the happiness of children.
- This festival reflects Rajasthani culture and the devotion of women towards their husbands.
- Gangaur is a major festival celebrated in different forms in Rajasthan, celebrated every year in the month of Chaitra (first month of Hindu calendar).
- Gangaur Dance:
- This is a famous folk dance of Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh , in which girls hold each other's hands and move around in a circular circle, praying to Goddess Gauri for the long life of their husbands.
- The songs of this dance glorify and praise Shiva-Parvati, Brahma-Savitri and Vishnu-Lakshmi.
Hindu Solar Calendar (Shaka Samvat)
- The zero year of Shaka Samvat is 78 AD.
- It was started by the Shaka rulers to mark their victory over the Kushans .
- It is a solar calendar, with its date system based on the time it takes the Earth to complete one revolution around the Sun, a seasonal year of approximately 365 1/4 days.
- It was adopted as the official calendar by the Government of India in 1957 .
- It has 365 days every year.










%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan