Bihar Switch to Hindi
Credit Outreach Programme in Bihar
Why in News?
Recently, the Union Finance and Corporate Affairs Minister distributed Rs 1,121 crore in loans to 50,294 beneficiaries during the Credit Outreach Programme in Bihar's Madhubani district.
Key Points
- Highlight of the Credit Outreach Programme:
- Drone Didi Scheme:
- The Union Finance Minister highlighted the crucial role women will play in achieving a developed India by 2047.
- She urges women to participate in government schemes for financial empowerment.
- For instance, she mentioned the Drone Didi initiative aimed at empowering Self-Help Groups (SHGs) and creating "Lakhpatididis," SHG members with annual household incomes exceeding Rs 1 lakh.
- The Union Finance Minister highlighted the crucial role women will play in achieving a developed India by 2047.
- Loan Sanctioning Initiatives:
- Loan sanction letters were distributed under programs like Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana, Prime Minister's Employment Generation Programme, Kisan Credit Card (Crop and Animal Husbandry & Fisheries), Stand Up India, PM-SVANidhi, and PM Vishwakarma.
- Infrastructure and CSR (corporate social responsibility) Initiatives:
- National Bank for Agriculture and Rural Development (NABARD) approved Rs 155.84 crore, and Small Industries Development Bank of India (SIDBI) sanctioned Rs 75.52 lakh for rural road projects.
- Various banks contributed through CSR activities to improve infrastructure in schools, particularly those for girls.
- Engagements in Madhubani:
- The minister visited the Mithila Chitrakala Sansthan, interacting with artisans specializing in Mithila paintings and terracotta art.
- Copies of the Constitution in Maithili and Sanskrit, recently released on Samvidhan Divas, were distributed to the attendees.
- The Minister toured around 25 stalls showcasing local products and handicrafts financed by banks.
- Ayushman Bharat Cards Distribution:
- Senior citizens aged 70 and above received Ayushman Bharat Pradhan Mantri Jan Arogya Yojana (AB PM-JAY) cards during the programme.
- Drone Didi Scheme:
Drone Didi Initiative
- It was launched by the PM on 30th November 2023 after his interaction with women beneficiaries of the Viksit Bharat Sankalp Yatra.
- It aims to provide drones to 15,000 women Self Help Groups (SHGs) in the next two years to be rented out to farmers for agricultural purposes.
- The Centre will provide each SHG identified a subsidy up to 80% towards the cost of a drone or a maximum of Rs 8 lakh. It is expected to generate an additional income of about Rs 1 lakh per head for them.
Pradhan Mantri Mudra Yojana
- About:
- PMMY was launched by the Government of India in 2015.
- The PMMY provides collateral-free institutional loans up to Rs. 10 lakhs for small business enterprises.
- Funding Provision:
- It is provided by Member Lending Institutions (MLIs) i.e. Scheduled Commercial Banks (SCBs), Regional Rural Banks (RRBs), Non-Banking Financial Companies (NBFCs) and Micro Finance Institutions (MFIs).
- Types:
- The loan can be used for income-generating activities in the manufacturing, trading, services sector, and agriculture.
- There are three loan products under PMMY:
- Shishu (loans up to Rs. 50,000)
- Kishore (loans between Rs. 50,000 and Rs. 5 lakh)
- Tarun (loans between Rs. 5 lakh and Rs. 10 lakh).
Prime Minister's Employment Generation Programme
- The Government of India approved the introduction of a credit linked subsidy programme called Prime Minister's Employment Generation Programme (PMEGP) in 2008 for generation of employment opportunities through establishment of micro enterprises in rural as well as urban areas.
- It allows entrepreneurs to set up factories or units.
- It is a central sector scheme administered by the Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME).
- The implementing Agency at the National Level is Khadi and Village Industries Commission (KVIC) - a statutory organization under the administrative control of the Ministry of MSME.
Kisan Credit Cards
- About:
- The scheme was introduced in 1998 for providing adequate and timely credit support from the banking system, under a single window with flexible and simplified procedure to the farmers for their cultivation and other needs like purchase of agriculture inputs such as seeds, fertilizers, pesticides etc. and to draw cash for their production needs.
- The scheme was further extended for the investment credit requirement of farmers viz. allied and non-farm activities in the year 2004.
- In the Budget-2018-19, government announced the extension of the facility of KCC to fisheries and animal husbandry farmers to help them to meet their working capital needs.
- Implementing Agencies:
- Commercial Banks
- Regional Rural Banks (RRBs)
- Small Finance Banks
- Cooperatives
Stand-Up India Scheme
- About:
- Stand up India Scheme was launched by the Ministry of Finance in April 2016 to promote entrepreneurship at grassroot level focusing on economic empowerment and job creation.
- This scheme has been extended up to the year 2025.
- Purpose:
- Promote entrepreneurship amongst women, Scheduled Caste (SC) and Scheduled Tribe (ST) category.
- Provide loans for greenfield enterprises in manufacturing, services or the trading sector and activities allied to agriculture.
- Facilitate bank loans between Rs.10 lakh and Rs.100 lakh to at least one SC/ST borrower and at least one-woman borrower per bank branch of Scheduled Commercial Banks.
PM-SVANidhi
- It is a Central Sector Scheme i.e., fully funded by Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs with the following objectives:
- To facilitate working capital loan;
- To incentivize regular repayment; and
- To reward digital transactions
- Introduction of 3rd term loan of up to Rs 50,000 in addition to 1st & 2nd loans of Rs 10,000 and Rs 20,000 respectively.
- The loans would be without collateral.
PM Vishwakarma Yojana
- Objective: Uplift traditional artisans and craftspeople by enhancing the quality and market accessibility of their products and integrate them in both domestic and global value chains.
- Features:
- Budgetary allocation for scheme – Rs 13,000 crore for 5 financial years (2023-24 to 2027-28).
- Provides recognition to beneficiaries through a PM Vishwakarma Certificate and an ID Card.
- Stipend of Rs 500 for skill training per day and Rs 15,000 grant for the purchase of modern tools.
- Category: Central Sector Scheme
- Nodal Ministry: Ministry of Micro, Small and Medium Enterprises (MoMSME)
Chhattisgarh Switch to Hindi
Centre Approves Proposal to Provide Houses Under PMGAY
Why in News?
The Chhattisgarh government announced that the Centre has approved its proposal to provide 15,000 houses under the Pradhan Mantri Gramin Awas Yojana. These houses will be allocated to surrendered Naxalites and individuals affected by Naxal violence as part of the welfare initiative.
- It is emphasized that the scheme aims to include families excluded from the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011 and Awas Plus 2018 lists.
Key Points
- Pradhan Mantri Awas Yojana-Gramin (PMAY-G)
- About:
- Launched in 2016, the PMAY-G aims to provide housing for the poorest segments of society.
- The selection of beneficiaries involves a thorough three-stage validation process, including the Socio-Economic Caste Census 2011, Gram Sabha approvals, and geo-tagging, ensuring that aid reaches the most deserving individuals.
- About:
- Under PMAY-G Beneficiaries Receive:
- Financial Assistance: Rs 1.20 lakh in plain areas and Rs 1.30 lakh in hilly states, including northeastern states and union territories.
- Additional Support for Toilets: Rs 12,000 for constructing toilets through convergence with schemes like Swachh Bharat Mission – Gramin (SBM-G) or Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme (MGNREGS) or any other dedicated source of funding.
- Employment Support: Mandatory provision of 90/95 person-days of unskilled wage employment for beneficiaries through Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Act (MGNREGA) for house construction.
- Basic Amenities: Access to water, Liquefied petroleum gas (LPG), and electricity connections through convergence with relevant schemes.
Naxalism
- It originated as rebellion against local landlords who bashed a peasant over a land dispute.
- The rebellion was initiated in 1967, with an objective of rightful redistribution of the land to working peasants under the leadership of Kanu Sanyal and Jagan Santhal.
- Started in West Bengal, the movement has spread across Eastern India; in less developed areas of states such as Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Andhra Pradesh.
- It is considered that Naxals support Maoist political sentiments and ideology.
- Maoism is a form of communism developed by Mao Tse Tung.
- It is a doctrine to capture State power through a combination of armed insurgency, mass mobilization and strategic alliances.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Progress of PMGSY in Jammu & Kashmir
Why in News?
Under the centrally sponsored Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY) nearly 3,500 projects, including 217 bridges, have been completed over the past two decades in Jammu and Kashmir.
Key Points
- Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY):
- PMGSY was launched on 25th December, 2000.
- However, the PMGSY was introduced in J&K in 2001-02 to provide all-weather connectivity to rural habitations with populations above 250, based on the 2001 Census.
- Objective: To provide connectivity, by way of an all-weather road to unconnected habitations.
- Eligibility: Unconnected habitations of designated population size (500+ in plain areas and 250+ in North-Eastern States, Himalayan States, Deserts and Tribal Areas as per 2001 census) in the core network for uplifting the socio-economic condition of the rural population.
- PMGSY was launched on 25th December, 2000.
- Progress and Achievements of PMGSY in J&K:
- A total of 3,742 projects, including 305 bridges, with a road length of 20,801 km, have been approved since its inception.
- As of now, 3,429 projects, including 217 bridges, have been completed, connecting 2,129 out of the targeted 2,140 habitations, with an expenditure of Rs 12,650 crore.
- Recent developments of PMGSY in J&K:
- Over the last five years, PMGSY in J&K has received focused attention, significantly improving rural connectivity, especially in remote and hilly areas, aligning with the "Sabka Saath, Sabka Vikas" vision.
- The uncompromising quality standards for road and bridge construction to ensure durable and safe infrastructure for the region was emphasized.
- The need for daily monitoring to address challenges and meet project timelines effectively was highlighted.
Phases of Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana (PMGSY)
- PMGSY - Phase I
- PMGSY - Phase I was launched in December, 2000 as a 100 % centrally sponsored scheme.
- Under the scheme, 1,35,436 habitations were targeted for providing road connectivity and 3.68 lakh km. for upgradation of existing rural roads in order to ensure full farm to market connectivity.
- PMGSY - Phase II
- The Government subsequently launched PMGSY-II in 2013 for upgradation of 50,000 Kms of existing rural road network to improve its overall efficiency.
- While the ongoing PMGSY - I continued, under PMGSY phase II, the roads already built for village connectivity were to be upgraded to enhance rural infrastructure.
- The cost was shared between the centre and the states/UTs.
- PMGSY - Phase III
- Phase III was approved by the Cabinet during July 2019.
- It gives priorities to facilities like:
- Gramin Agricultural Markets (GrAMs)
- GrAMs are retail agricultural markets in close proximity to the farm gate that promote and service a more efficient transaction of the farmers’ produce.
- Higher Secondary Schools and
- Hospitals.
- Gramin Agricultural Markets (GrAMs)
- Under the PMGSY-III Scheme, it is proposed to consolidate 1,25,000 Km road length in the States. The duration of the scheme is 2019-20 to 2024-25.
Madhya Pradesh Switch to Hindi
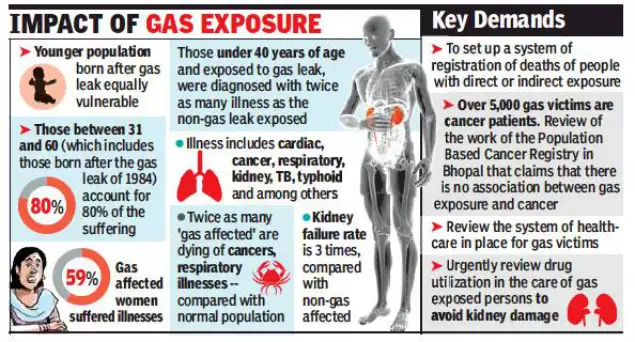
40 Years of Bhopal Gas Tragedy
Why in News?
Four decades after the Bhopal gas tragedy, government authorities have failed to safely dispose of hundreds of tonnes of toxic waste still present on the premises of Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL), despite multiple court orders and warnings.
Key Points
- Historical Context and Disposal Challenges:
- The Bhopal gas tragedy was one of the worst industrial accidents in history that occurred on the night of 2-3 December 1984 at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant in Bhopal, MP.
- It exposed people and animals to the highly toxic gas methyl isocyanate (MIC), causing immediate and long-term health effects and deaths.
- Toxic waste generated during pesticide production between 1969 and 1984 was dumped on-site, with hazardous practices and regulatory negligence worsening contamination.
- In 2005, the Madhya Pradesh Pollution Control Board collected waste, with a portion incinerated and 337 MT stored in a shed.
- In 2015, the Central Pollution Control Board incinerated 10 MT on a trial basis and recommended further disposal, which has not occurred.
- The Bhopal gas tragedy was one of the worst industrial accidents in history that occurred on the night of 2-3 December 1984 at the Union Carbide India Limited (UCIL) pesticide plant in Bhopal, MP.
- Government Funding and Toxic Waste Disposal:
- The Union government released Rs 126 crore to the Madhya Pradesh government for disposing of 337 MT of toxic waste stored on the Union Carbide premises since 2005.
- A 2010 study revealed the site also contains 11 lakh tonnes of contaminated soil, one tonne of mercury, and nearly 150 tonnes of underground dumps, with no disposal plans for this waste yet.
- The report noted that the 2005 collection of waste was incomplete, recommending excavation of buried toxic waste for remediation.
- The disposal of the 337 MT of waste has yet to begin due to administrative hurdles.
- Groundwater Contamination:
- Studies have found groundwater in residential areas near the factory contaminated with heavy metals and toxic substances, raising cancer and health risks. Experts warn of further contamination during rainy seasons.
- The government has sealed hand pumps and tube wells and expanded the distribution of safe drinking water to 42 localities near the factory. However, residents continue to use contaminated water for non-drinking purposes.
- Despite these measures, groundwater contamination continues to spread, creating new victims 40 years after the gas tragedy.
- Health impacts include severe diseases caused by prolonged exposure to toxic substances.
- Studies have found groundwater in residential areas near the factory contaminated with heavy metals and toxic substances, raising cancer and health risks. Experts warn of further contamination during rainy seasons.
- Judicial and Regulatory Oversight:
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) criticized the government’s inaction, emphasizing the leachate’s role in contaminating water bodies.
- It ordered waste disposal within six months in March 2022, but the directive remains unimplemented.
- Following complaints of groundwater contamination, the Supreme Court directed the state to enhance access to safe water and address contamination.
- The National Green Tribunal (NGT) criticized the government’s inaction, emphasizing the leachate’s role in contaminating water bodies.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
ASI Response on Sambhal Mosque
Why in News?
Recently, the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) has requested the civil court in Sambhal for control and management of the Mughal-era Shahi Jama Masjid in Sambhal, citing its status as a protected heritage site. The request follows the court’s approval of a survey of the mosque.
Key Points
- Controversy Around the Sambhal Mosque:
- On 19th January, 2018, an First Information Report (FIR) was filed against the mosque's management committee for installing steel railings on the mosque's steps without obtaining proper authorization.
- The ASI stated that the Shahi Jama Masjid which was notified as a protected monument in 1920, under the Ancient Monuments Preservation Act 1904, falls under its jurisdiction.
- The ASI argued that the mosque’s management committee made unauthorised structural modifications, which are unlawful and should be restricted.
- Access and Regulation:
- The ASI maintained that public access to the mosque is permissible, but only if it adheres to ASI regulations.
- The ASI has sought full control and management of the mosque, emphasizing its responsibility for maintaining the monument and regulating any changes to its structure.
- Violence During Court-Ordered Survey:
- Violence erupted in Sambhal on 24th November 2024, during a court-ordered survey of the Shahi Jama Masjid.
- Four people were killed, and several others sustained injuries during the clashes.
- Judicial Commission:
- A three-member judicial commission was formed on 28th November 2024, to investigate the violence.
- The commission will determine whether the violence was spontaneous or part of a premeditated conspiracy.
- The inquiry will analyze the events leading to the violence and recommend measures to prevent such incidents in the future.
- It is required to submit its findings within two months, with any extension subject to government approval.
- Survey and Temple Petition:
- The court-ordered survey was linked to a petition claiming that the Jama Masjid in Sambhal was originally a Hari Har temple located in mohalla Kot Purvi and was converted into a mosque in 1529.
- Historical Context:
- The Jama Masjid in Sambhal is one of three mosques constructed during Babur’s reign (1526–1530). The others include the mosque at Panipat and the now-demolished Babri Masjid.
- Historian Howard Crane described the mosque’s architectural features in his work, The Patronage of Babur and the Origins of Mughal Architecture.
- Crane noted a Persian inscription stating that Babur ordered the mosque’s construction in December 1526 through his subedar, Jahangir Quli Khan.
Ancient Monuments Preservation Act, 1904
- About:
- The Act was passed in 1904, during the tenure of Lord Curzon in British India.
- It aimed at preserving ancient monuments and objects of historical, archaeological, and artistic significance.
- Key Provisions:
- It empowered the Archaeological Survey of India (ASI) to protect and restore ancient Indian monuments.
- Regulated the movement and trade of antiquities to prevent illegal trafficking.
- Provided for control over archaeological excavations in specified areas.
- Facilitated the acquisition of ancient monuments for preservation in certain cases.
- Significance:
- Played a foundational role in protecting India’s historical and cultural heritage under a structured legal framework.
- Enhanced the responsibilities of the ASI in monument conservation.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
UP Declares Maha Kumbh Area a New District
Why in News?
Recently, the Uttar Pradesh government has declared the Maha Kumbh area in Prayagraj as a new district.
- It was made to streamline the management and administration of the upcoming Kumbh Mela scheduled for January 2025.
Key Points
- The notification was issued under Section 2 (th) of the Uttar Pradesh Prayagraj Mela Authority, Prayagraj Act, 2017.
- It officially declares the Mahakumbh Mela District for organizing the Mahakumbh 2025.
- The Mela Adhikari was made the administrative authority of the new district.
- Powers and Responsibilities of Mela Adhikari:
- The Mela Adhikari, Kumbh Mela, Prayagraj, will hold powers of the Executive Magistrate, District Magistrate, and Additional District Magistrate under Section-14 (1) and relevant sections of the Indian Civil Defense Code, 2023.
- The Mela Adhikari will also possess all the powers of the District Magistrate and Collector under the Uttar Pradesh Revenue Code, 2006 (amended in 2016), for handling all cases.
- The Mela Adhikari has the authority to appoint an Additional Collector for the district.
Maha Kumbh
- Kumbh Mela comes under United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organisation (UNESCO)’s Representative List of Intangible Cultural Heritage of Humanity.
- It is the largest peaceful congregation of pilgrims on earth, during which participants bathe or take a dip in a sacred river.
- It takes place on the banks of the Godavari river in Nashik, the Shipra river in Ujjain, the Ganges in Haridwar, and the confluence of the Ganges, Yamuna, and the mythical Saraswati river in Prayagraj. The confluence is referred to as the ‘Sangam‘.
- As it is held in four different cities in India, it involves different social and cultural activities, making this a culturally diverse festival.
- The over month-long fair is marked by the construction of a massive tented township, complete with cottages, huts, platforms, civic facilities, administrative and security measures.
- It is organised immaculately by the government, the local authorities and the police.
- The mela is especially renowned for the presence of an extraordinary array of religious ascetics enticed from remote hideaways in forests, mountains and caves.

.gif)

.png)





 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan