Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Tata Power's Massive Investment in Rajasthan
Why in News?
Recently, Tata Power announced a significant investment to support Rajasthan's transformation into a power surplus state with reliable, clean, and affordable energy.
Key Points
- Investment Commitment:
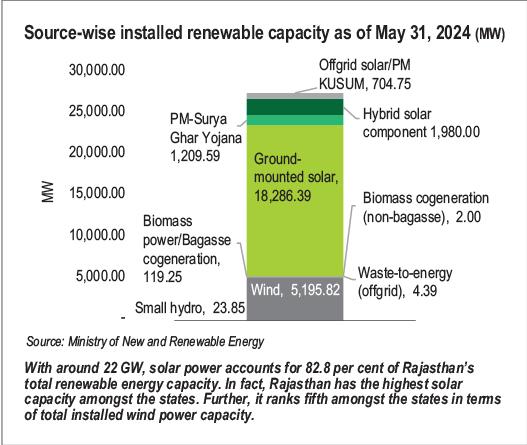
Tata Power will invest Rs.1.2 trillion ($14.3 billion) over the next 10 years in Rajasthan's power sector.- Rs.75,000 crore will be allocated to renewable energy projects.
- Rs.20,000 crore will be invested in modernizing transmission and distribution to reduce energy losses and improve power quality.
- Rs.10,000 crore will explore opportunities to develop nuclear power plants.
- Rs.1,000 crore will be invested in setting up 1 lakh EV charging points across the state.
- The plan includes rooftop solar power for 10 lakh households under the PM Surya Ghar Yojana.
- The investment is expected to generate over 28,000 direct jobs in Rajasthan.
PM Surya Ghar Yojana
- About: It is a central scheme to promote the adoption of solar rooftop systems by providing substantial financial subsidies and ensuring ease of installation.
- Objective: It aims to provide free electricity to one crore households in India, who opt to install roof top solar electricity units.
- Implementation Agencies: The scheme will be executed at two levels.
- National Level: Managed by the National Programme Implementation Agency (NPIA).
- State Level: Managed by State Implementation Agencies (SIAs), which are the Distribution Utilities (DISCOMs) or Power/Energy Departments of the respective states or UTs.
- Role of DISCOMs: As SIAs, DISCOMs are responsible for facilitating various measures to promote rooftop solar adoption, including ensuring the availability of net metres, and conducting timely inspections and commissioning of installations.
Jammu & Kashmir Switch to Hindi
Nalin Prabhat Appointed as J&K DGP
Why in News?
Recently, senior IPS officer Nalin Prabhat was appointed as the new Director General of Police (DGP) for Jammu & Kashmir.
Key Points
- New Appointment:
- Prabhat is a three-time Police Gallantry Medal winner.
- Prior to his current role, he was the NSG chief and held top positions in the CRPF in J&K, including Special DG and IG (Operations).
- He headed Greyhounds, an elite anti-Naxal unit in Andhra Pradesh.
The Greyhounds
- It is an elite anti-Maoist force raised in 1989 by IPS officer K.S. Vyas to combat the growing Maoist threat in Andhra Pradesh.
- The members are well-trained in guerilla and jungle warfare.
National Security Guard (NSG)
- The NSG is a counter-terrorism unit that formally came into existence in 1986 by an act of Parliament- ‘National Security Guard Act, 1986’.
- The idea behind raising such force came in the aftermath of Operation Blue Star (an Indian military action carried out to remove militant religious leader from the Golden Temple, Amritsar) in 1984, Akshardham Temple attack and the assassination of former PM Indira Gandhi, for ‘combating terrorist activities with a view to protect states against internal disturbances.’
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
'Khaki Mein Sthitpragya' Released
Why in News?
Recently, the Chief Minister of Uttarakhand released the book Khaki Mein Sthitpragya written by former DGP of Uttarakhand, Anil Raturi.
Key Points
- Book Release:
- The book Khaki Mein Sthitpragya was released by CM Pushkar Singh Dhami at the IRDT auditorium in Dehradun.
- The book is based on Anil Raturi's memoirs and experiences during his service as an IPS officer.
- The book presents challenges, experiences, and memories from Raturi's three-and-a-half decades in service.
- It aims to guide new police officers in dealing with challenges through patience, strong willpower, and dedication
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Negligence in Gang Chart Approval
Why in News?
Recently, the Uttar Pradesh government informed the Allahabad High Court about transferring the District Magistrate of Amroha for negligence in approving gang charts without proper justification violating the Uttar Pradesh Gangster and Anti-Social Activities (Prevention) Rules, 2021.
Key Points
- Case Background:
- The matter arose from a writ petition filed to quash an FIR lodged against him under Section 3(1) of the UP Gangsters and Anti-Social Activities (Prevention) Act, 1986.
- The petitioner contended that neither the Superintendent of Police (SP) nor the DM of Amroha recorded satisfaction while approving the gang chart.
- A Gang chart is a document that contains details about an accused's criminal history and other relevant information in cases related to the Uttar Pradesh Gangsters and Anti-Social Activities (Prevention) Act, 1986.
- High Court’s Observations:
- A bench comprising Justice Vivek Kumar Birla and Justice Arun Kumar Singh Deshwal noted that the SP-Amroha and DM-Amroha did not record satisfaction while preparing the gang chart, as required by Rule 16(2) of the 2021 Rules.
- The Allahabad High Court noted that the DM’s actions were contrary to both the 2021 Rules and the guidelines set by the HC in the Sanni Mishra vs State of UP case.
- The court labeled this as “sheer negligence,” noting similar cases from Amroha where officials did not properly prepare gang charts according to the rules.
- Court’s Final Decision:
- The court refrained from issuing direct action against the officers and left the decision to the state government.
The Uttar Pradesh Gangsters and Anti-Social Activities (Prevention) Act, 1986
- Purpose: To prevent gang-related and anti-social activities.
- Scope: Targets individuals involved in organized crime, violent offenses, or habitual criminals.
- Provisions:
- Defines “gang” and “gangster” in legal terms.
- Allows authorities to take preventive action, including detaining suspects.
- Allows the attachment of properties obtained through criminal activities.
- The act empowers district magistrates and police to approve gang charts (a formal record of an individual’s gang-related activities).
UP Gangster and Anti-Social Activities (Prevention) Rules, 2021
- Purpose: Provides detailed guidelines for implementing the UP Gangsters Act.
- Key Provisions:
- Recording Satisfaction: The competent authority, usually the District Magistrate, must record satisfaction while forwarding and approving gang charts.
- Joint Meetings: Mandates joint meetings between the Superintendent of Police and the District Magistrate before approving a gang chart.
- Due Process: Specifies procedural guidelines to ensure the preparation of gang charts is thorough and based on concrete evidence.
Haryana Switch to Hindi
Haryana's Electoral History
Why in News?
Haryana, a small yet politically significant state, has a history of frequent political defections, and its electoral landscape is influenced by key families and caste dynamics.
Key Points
- Birth of Haryana (1966):
- Haryana was carved out of undivided Punjab on November 1, 1966.
- Bhagwat Dayal Sharma, a former Labour Minister of Punjab, was appointed the first CM.
- Initially, Haryana had 54 seats, increased to 81 in 1967, and 90 by 1977.
- Aaya Ram, Gaya Ram Phenomenon (1967):
- Origin of Expression: Gaya Lal, an Independent MLA, switched parties multiple times in a single day.
- Impact: The term "Aaya Ram, Gaya Ram" became a popular descriptor for political turncoats in India.
- Political Dominance of Key Leaders:
- Bansi Lal (1968-1975): A Jat leader from Bhiwani, Bansi Lal held power until the Emergency.
- Devi Lal (1977): Led Janata Party to victory post-Emergency; ousted by Bhajan Lal in 1979.
- Bhajan Lal's Influence (1980-1982): Aligned with Indira Gandhi’s Congress, stayed in power despite frequent party shifts.
- Lok Dal Dominance: Devi Lal's Lok Dal, in alliance with BJP, gained a majority in 1987.
- V P Singh Era: Devi Lal supported V P Singh’s anti-corruption campaign, becoming Deputy PM, with son Om Prakash Chautala taking over Haryana.
- Chautala's Multiple Terms: Om Prakash Chautala served as CM multiple times between 1989 and 1991.
- Hooda's Era (2005-2014): Bhupinder Singh Hooda from Congress led the government, focusing on the Rohtak region.
- BJP's Rise (2014): BJP won 47 seats, making Manohar Lal Khattar the first non-Jat CM of Haryana.
- Current Political Landscape (2024):
- Rural-Urban Divide:
- Urban Regions: Gurugram, Faridabad, Panipat have more industry and non-farming sectors.
- Rural Belt: Central and southern areas like Rewari, Jind, Bhiwani, dominated by farming, with significant Jat population.
- Rural-Urban Divide:
- Jat Belt Concerns:
- Farmers' Protests: Resentment against farm laws, later repealed.
- Agniveer Scheme: Concerns about job security for soldiers.
- Wrestlers’ Protest: Anger over sexual harassment allegations against a BJP leader.
- Unemployment: Youth dissatisfied with job opportunities.
- Urban Regions: Focus on infrastructure, employment, and governance.
- Caste Dynamics:
- OBC Influence: Both BJP and Congress are courting OBC voters; Congress proposes a caste census and enhanced reservation limits.
- Jat-Dalit Coalition: Congress is attempting to bridge historical divides between Jats and Dalits for electoral gains.




%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)






.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan