Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Dumak Village will Get Road in 8 Months
Why in News?
The under-construction road connecting Dumak and other villages in Chamoli district along the Indo-China border in Uttarakhand, which has been delayed for 17 years, will be completed before the year ends.
Key Points
- According to the sources, few voters in Dumak have decided to boycott Lok Sabha polls after being fed up with constant delays on the road construction.
- Uttarakhand Rural Roads Development Agency (URRDA) CEO issued a statement saying that the pending work on the road will be completed in the next eight months.
- The Agency shall act for the sole purpose of implementation of the Pradhan Mantri Gram Sadak Yojana under the guidance and norms as fixed by the National Rural Road Development Agency.
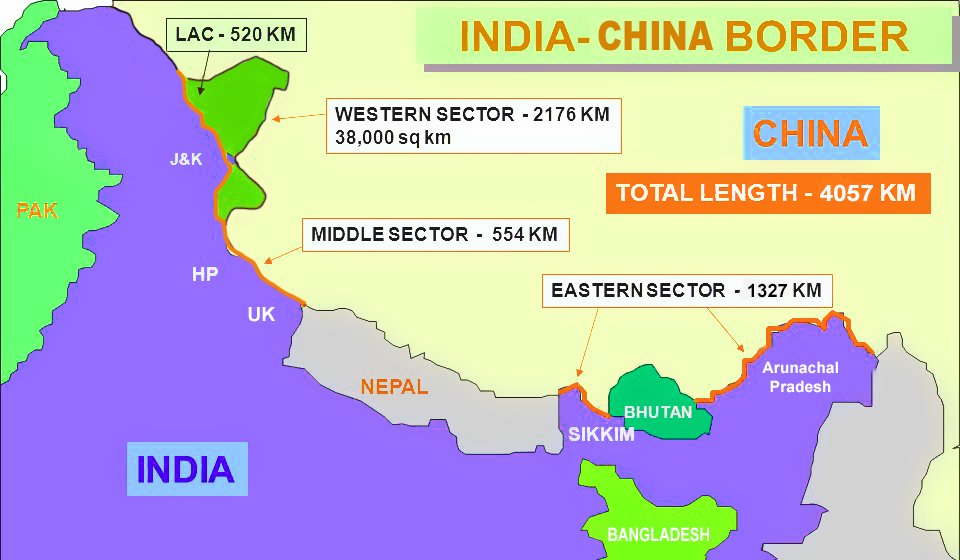
Indo-China Border
- The border between India and China is not clearly demarcated throughout and there is no mutually agreed Line of Actual Control (LAC) along certain stretches.
- LAC came into existence after the 1962 Indo China war.
- India-China border is divided into three sectors:
- Western Sector: Ladakh
- Middle Sector: Himachal Pradesh and Uttarakhand
- Eastern Sector: Arunachal Pradesh and Sikkim
Uttarakhand Switch to Hindi
Snowfall in Gangotri Dham
Why in News?
Recently, Gangotri Dham in Uttarakhand, the highest temple dedicated to Goddess Ganga, received fresh rain and snowfall.
- The India Meteorological Department (IMD), earlier, issued an alert for the districts of Chamba, Kangra, Kullu, Mandi, Shimla, Solan and some parts of Lahaul-Spiti.
Key Points
- The Gangotri Temple, where Goddess Ganga is worshipped, stands at a height of 20 feet and boasts of exquisite carvings on white granite.
- It is the origin of the River Ganges and is one of the four sites in the Char Dham pilgrimage of Uttarakhand.
- The other shrines included in the Char Dham pilgrimage are Badrinath, Kedarnath, and Yamunotri.
- The river is called Bhagirathi at the source and acquires the name Ganga (the Ganges) from Devprayag onwards where it meets the Alaknanda.
- The origin of the holy river is at Gomukh, set in the Gangotri Glacier, and is a 19 km trek from Gangotri.
India Meteorological Department
- IMD was established in 1875. It is the National Meteorological Service of the country and the principal government agency in all matters relating to meteorology and allied subjects.
- It works as an agency of the Ministry of Earth Sciences of the Government of India.
- It is headquartered in New Delhi.
- IMD is also one of the six Regional Specialized Meteorological Centres of the World Meteorological Organization.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand Government Takes Action to Improve Education System
Why in News?
Recently, the Jharkhand government laid the foundation stone of a degree college in Potka area of East Singhbhum district, paving the way for higher education in the region.
Key Points
- The college is set up with the objective of providing quality education to children of all sections and communities including tribals, indigenous people, farmers, labourers, SC/ST, and minorities.
- For the development and promotion of the rich tribal and regional languages of the state, teaching in these languages will start from the primary schools.
- Appointment of bell-based teachers of tribal languages including Santali, Mundari and Oraon will be done soon.
- The government’s priority is to start teaching Bengali and Oriya languages from primary schools in the state.
- The government reckons that only when the young generation gets a better education, will the condition and direction of the state change, with more people able to come out of poverty.
- The government is also helping students finance their education through the Guruji Credit Card Scheme.
- Under this scheme, education loans are being provided as per the need for a higher education degree.
- It is also giving 100% scholarships to the children of tribal and indigenous communities who want to study in educational institutions abroad.
- The scholarship amount has been increased by three times so that the children of farmers and labourers, and the children of every poor family in the state can get a better education.
- The state government is providing all the necessary facilities to ensure that the education of the students does not stop due to lack of funds.
- Work is being done to strengthen social, economic and educational systems in the state.
Guruji Student Credit Card Scheme
- This scheme was launched on 14th March, 2024 by the Jharkhand government.
- Under the Guruji Student Credit Card Scheme, students will get a maximum loan of Rs 15 lakh. A maximum of 30% of this amount will be available for non-institutional work (including living and food expenses).
- Students will have to pay a simple rate of interest of 4%. The rest of the interest will be paid by the state government in the form of interest subvention.
- Students will not need to give any kind of collateral security to take a loan. Students will be able to repay the loan amount in 15 years.
- The interest on the loan that the children will take will be calculated at the rate of simple interest. It will remain fixed for the entire tenure of the loan.
Jharkhand Switch to Hindi
Jharkhand Government Implements Schemes for Social Upliftment
Why in News?
Recently, the Jharkhand government launched schemes to benefit the people. It claims that Jharkhand is the first state in the country where the Sarvajan Pension Scheme has been implemented.
Key Points
- In the last four years, the government has worked to link all the eligible people who come under the purview of social security with the Sarvajan Pension Scheme.
- According to the state government, people were connected with schemes with the help of district headquarters and block-level officials who are working to reach each village and every house with a bundle of schemes.
- The government has also worked to promote important schemes like the Abu Awas Yojana off the ground.
- Under this, pucca houses will be given to 20 lakh eligible families in the state.
- To provide benefits to farmers, the Sindri urea factory was recently inaugurated in Dhanbad district.
- The government is working on providing irrigation water through pipelines to the fields all around the year.
- To promote employment, the Jharkhand government has enacted a law to ensure that 75% of the recruitment in private industrial institutions established within the state is fulfilled by local people.
- An Employment Generation Scheme has also been operated to provide employment to the unemployed youth in the state.
Sarvajan Pension Scheme
- It was launched by the Government of Jharkhand on 6th March 2024. Through this scheme, pensions will be provided to poor citizens above 60 years of age.
- This pension will be of ₹ 1000 which will be distributed in the bank account of the beneficiaries on the 5th of every month.
- All eligible widows, disabled, and old people within the state have been linked to the pension scheme.
- The government will now give the benefit of the pension scheme to women of all sections in the state from the age of 50 years.
- Men from the SC/ST community will also be covered under the pension scheme from the age of 50 years.
Rajasthan Switch to Hindi
Rajasthan Diwas 2024
Why in News?
Rajasthan Diwas is observed annually on 30th March to celebrate the foundation day of the state, marking the day it officially became a part of the federal entity.
Key Points
- It is the largest state in terms of area. Rajasthan has a long history that dates back to prehistoric times. Its culture was similar to the Indus Valley civilization, dating back to between 3,000 and 1,000 BC.
- The Chauhans became an imperial power by the 12th century, having dominated Rajput affairs since the 7th century. Following the Chauhans, the Mewar Guhilots ruled over the fate of the warring tribes.
- The present day Rajasthan came into being in following 7 phases:
- Matsya Union: The division of India was manifested by communal agitation on a great scale that overwhelmed the nation. Bharatpur and Alwar were also not secured from these riots.
- On 17th March 1948, the Indian Government took over the supervision of these states as the rulers failed to uphold peace. Neighbouring regions to these states were Karauli and Dholpur. On Government advice, all four states agreed to come together to form the Matsya Union.
- Rajasthan Union: On 25th March 1948, ten more states namely Kushalgarh, Banswara, Kota, Bundi, Jhalawar, Tonk, Shahpura, Pratapgarh, Dungarpur and Kishangarh of southern and South-eastern Rajputana joined together to structure another union that is named East Rajasthan.
- United States of Rajasthan: Subsequently, the Udaipur state (Mewar) also got united in the Rajasthan union on 18th April 1948. The name was then changed to United Rajasthan. Therefore 15 states of Rajasthan created their own association.
- Greater Rajasthan: On 30th March 1949, the four states viz. Jodhpur, Jaipur, Bikaner and Jaisalmer joined this integration and the region came to be known as Greater Rajasthan. The principalities of Neemra and Lawa also joined this. March 30th is now celebrated as Rajasthan day.
- United States of Greater Rajasthan: On 15th May 1949, the Matsya Union was amalgamated into Greater Rajasthan and thereafter the confederation was named the United state of Greater Rajasthan.
- United Rajasthan: The only state, Sirohi, had not joined the federation so far. Sirohi state joined the federation on 26th January 1950.
- Re-organized Rajasthan: Ajmer-Merwara region was for a long period of time under unswerving British rule and it was fused with Rajasthan on 1st November 1956 on the proposal of the statement of the State Reorganization Commission. Madhya Pradesh’s Bhanpura Tehsil and Gujarat’s Abu Tehsil were also merged with Rajasthan at that time.
- Matsya Union: The division of India was manifested by communal agitation on a great scale that overwhelmed the nation. Bharatpur and Alwar were also not secured from these riots.
Uttar Pradesh Switch to Hindi
Uttar Pradesh Aims to Increase Maize Production
Why in News?
The Uttar Pradesh government is targeting to increase the production of Maize to more than 3.2 million tonnes (mt) by 2027-28.
Key Points
- Currently, the state’s maize production across different cropping seasons (kharif, rabi, and zaid) is estimated at 2.12 mt across 830,000 hectares.
- The yield is at nearly 25.49 quintals (100 kg) per hectare, which is lower than the national average.
- The state plans to increase maize acreage by 200,000 hectares and boost production by an additional 1.1 mt.
- This will hike the state’s maize area and production to about 1.03 million hectares (MH) and 3.2 mt, respectively.
- The state will invest almost Rs 150 crore on various maize publicity programs and give incentives to food processing units.
- Maize crop has multifarious uses as food, poultry feed, and fuel (grain based ethanol).
- It is also used in pharmaceutical, cosmetic, textile, paper, and alcohol industries.
- Maize is the third most important cereal crop in India, after paddy and wheat, and accounts for nearly 10% of total food grain production.
- Globally, maize is referred to as the ‘queen of cereals’ owing to its high genetic yield potential among the cereal crops.
- Industry has estimated that India needs to ramp up maize production by 10 mt over the next four-five years to cater to the demand from the ethanol and poultry sectors.
- The demand for maize is rising due to growing health awareness. People prefer maize for its high nutritional value, macronutrients like starch, fiber, protein, fat, vitamin B complex, carotene and essential minerals like magnesium, zinc, phosphorus, and copper.
Maize
- Temperature: Between 21-27°C
- Rainfall: High rainfall.
- Soil Type: Old alluvial soil.
- Top Maize Producing States: Karnataka, Madhya Pradesh, Bihar, Tamil Nadu, Telangana, Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh.
- As per the FAO (Food and Agriculture Organisation) data, India was the fifth largest producer of Maize in 2020.
- It is used both as food and fodder.
- Use of modern inputs such as High-Yielding Variety seeds, fertilisers and irrigation have contributed to the increasing production of maize.
- Technology Mission on Maize is one of the government’s initiatives for maize.








%20MPPCS%202025%20Desktop%20E.jpg)
%20MPPCS%202025%20Mobile%20E%20(1).jpg)










.png)
.png)











 PCS Parikshan
PCS Parikshan