Rajasthan
RPSC Exam Syllabus – Mains
- 29 Jan 2025
- 16 min read
The Mains Examination of the Rajasthan State and Subordinate Services Combined Competitive Examination or RPSC- RAS is designed to comprehensively assess candidates' knowledge, analytical abilities, and understanding of diverse subjects relevant to the state, nation, and global affairs.
The syllabus emphasizes a balance of theoretical understanding and practical application across varied domains, fostering a holistic evaluation of aspirants' competencies.
Scheme and Syllabus of Examination:
|
The detailed syllabus for the Mains Examination is provided below for the reference.
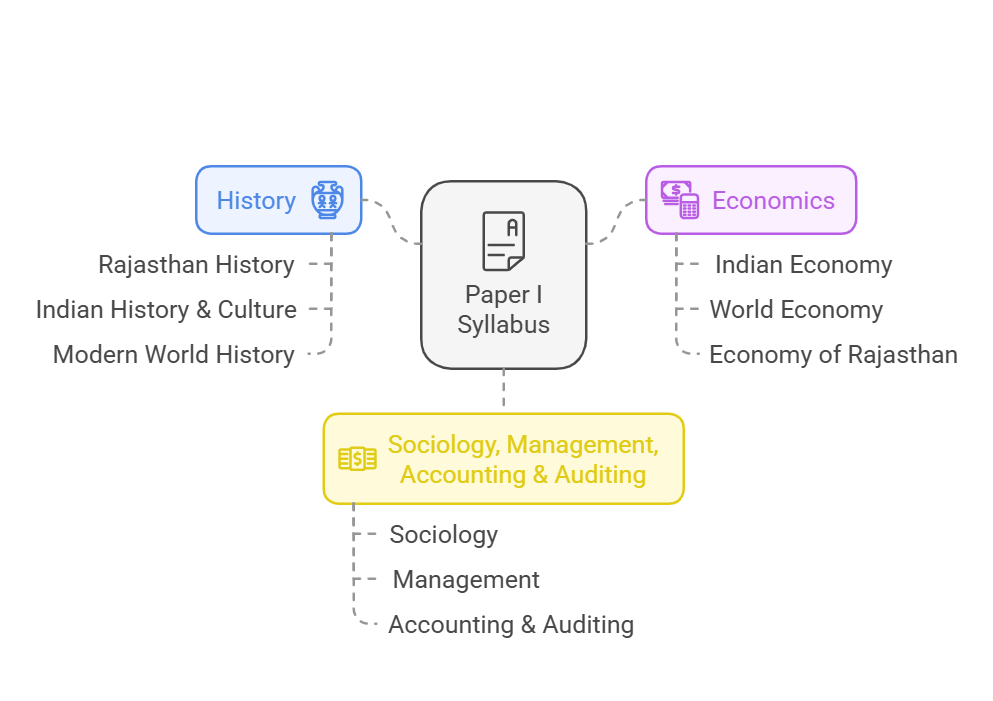
Paper I: General Studies - I
|
Unit I - History |
|
|
Part A - History, Art, Culture, Literature, Tradition and Heritage of Rajasthan |
|
|
Part B - Indian History & Culture |
|
|
Part C - History of the Modern World (up to 1950 AD) |
|
|
Unit II - Economics |
|
|
Part A - Indian Economy |
|
|
Part B - World Economy |
|
|
Part C - Economy of Rajasthan |
|
|
Unit III - Sociology, Management, Accounting & Auditing |
|
|
Part A - Sociology |
|
|
Part B - Management |
|
|
Part C - Accounting & Auditing |
|
Paper II: General Studies - II
|
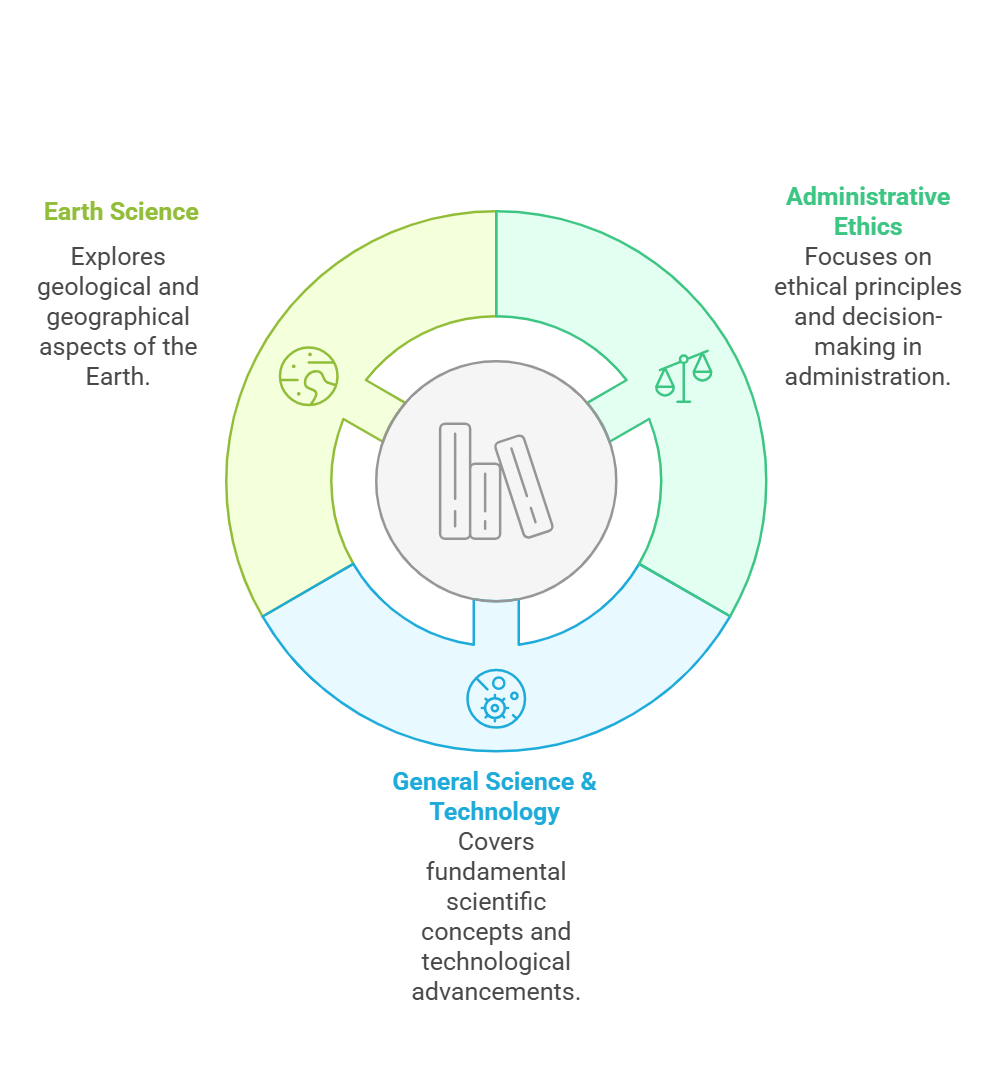
Unit I - Administrative Ethics |
|
|
Ethics and Human Values |
|
|
Ethical Concepts |
|
|
Ethics in Relationships |
|
|
Specific Ethical Teachings |
|
|
Moral Thinkers and Philosophers |
|
|
Administrative Challenges |
|
|
Practical Applications |
|
|
Unit II - General Science & Technology |
|
|
Chemistry in Everyday Life |
|
|
Physics in Everyday Life |
|
|
Biology in Everyday Life |
|
|
Computer Science & IT |
|
|
Scientific Developments |
|
|
Space & Defence Technology |
|
|
Unit III - Earth Science (Geography & Geology) |
|
|
Part A - World |
|
|
Part B - India |
|
|
Part C - Rajasthan |
|
Paper III: General Studies - III
|
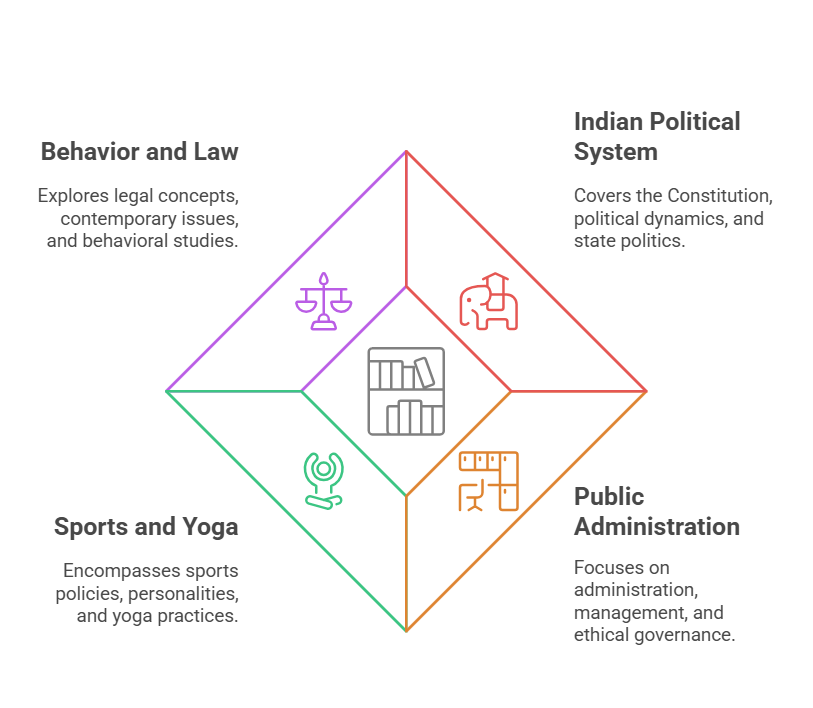
Unit I - Indian Political System, World Politics and Current Affairs |
|
|
Constitution of India |
|
|
Ideological Contents |
|
|
Institutional Framework - I |
|
|
Institutional Framework - II |
|
|
Institutional Framework - III |
|
|
Political Dynamics |
|
|
State Politics of Rajasthan |
|
|
Emerging World Order |
|
|
Foreign Policy of India |
|
|
Geo-political and Strategic Issues |
|
|
Current Affairs |
|
|
Unit II - Concepts, Issues and Dynamics of Public Administration and Management |
|
|
Administration and Management |
|
|
Key Concepts |
|
|
Principles of Organization |
|
|
Functions of Management |
|
|
Attitude and Values of Civil Services |
|
|
Control over Administration |
|
|
Administrative Setup of Rajasthan |
|
|
District Administration |
|
|
Development Administration |
|
|
Key Commissions/Acts in Rajasthan |
|
|
Unit III - Sports and Yoga, Behavior and Law |
|
|
Part A - Sports and Yoga |
|
|
Part B - Behavior |
|
|
Part C - Law |
|
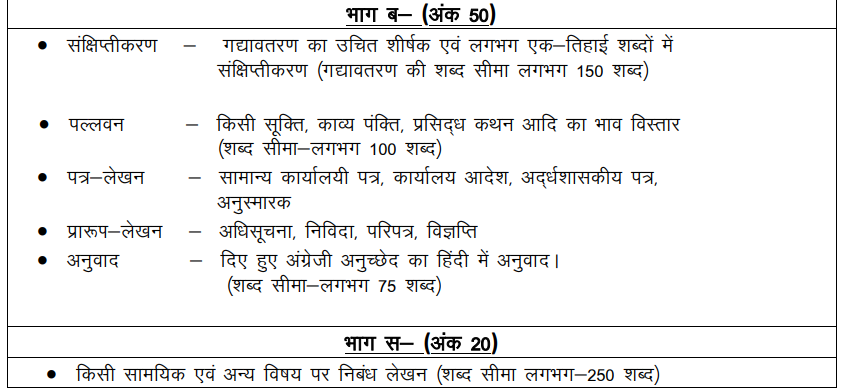
Paper IV: General Hindi and General English
|
General English (Total Marks: 80) |
Details |
|
Part A - Grammar & Usage (20 Marks) |
|
|
Part B - Comprehension, Translation & Precis Writing (30 Marks) |
|
|
Part C - Composition & Letter Writing (30 Marks) |
|

.jpg)
.jpg)